Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 1466-1474.doi: 10.12307/2025.027
Previous Articles Next Articles
Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke
Wang Mi1, 2, Ma Shujie3, Liu Yang1, Qi Rui1
- 1Department of Rehabilitation, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China; 2Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; 3Second Rehabilitation Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 200431, China
-
Received:2023-11-25Accepted:2024-02-07Online:2025-03-08Published:2024-06-28 -
Contact:Qi Rui, MD, Chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China -
About author:Wang Mi, Master candidate, Department of Rehabilitation, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China; Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China. Ma Shujie, MD, Second Rehabilitation Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai 200431, China. Wang Mi and Ma Shujie contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81603713 (to MSJ); Baoshan District Medical Key Specialized Project, No. BSZK-2023-BZ12, BSZK-2023-BP08 (to MSJ); Baoshan District Science and Technology Innovation Project, No. 20-E-43 (to MSJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
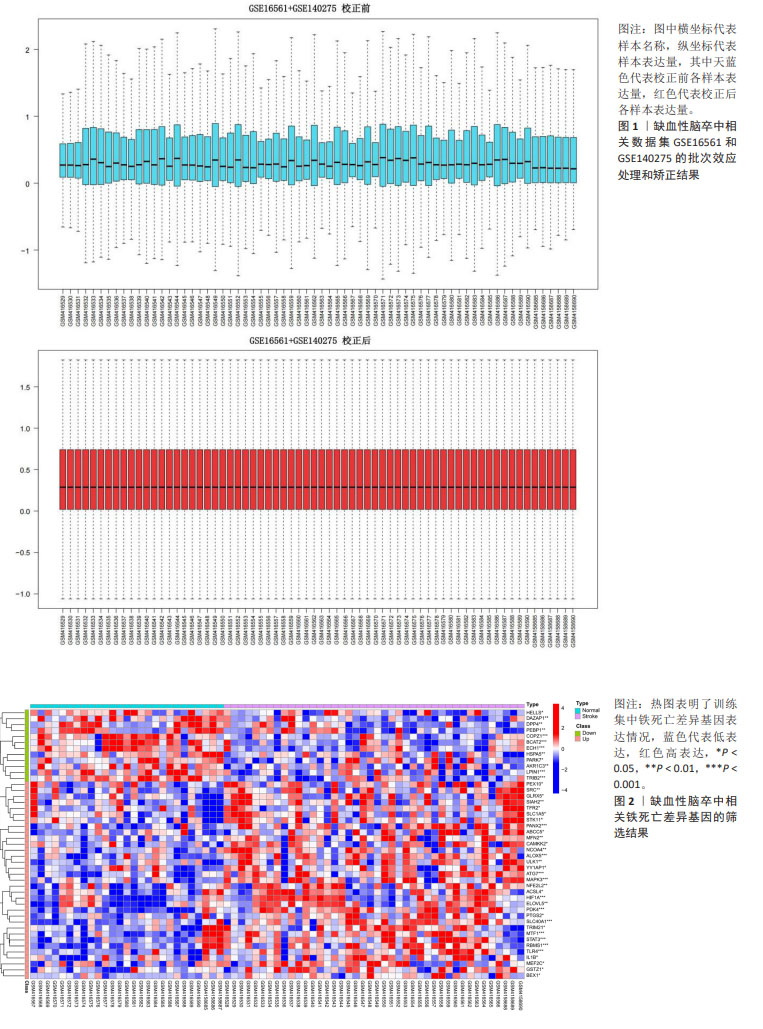
2.1 生物信息学分析结果 2.1.1 确定铁死亡相关差异基因 将GSE16561数据集与GSE140275数据集进行批次效应处理与校正后,获取了校正后的数据集,见图1。在FerrDb数据库下载铁死亡相关数据集,其中标志物数据集包含11个基因,激动剂数据集包含280个基因,抑制剂数据集包含297个基因,取交集后共获取378个已验证的人类铁死亡相关基因。将获取的378铁死亡基因映射到校正后的数据集中,获得101个铁死亡相关基因。随后通过t检验对数据集中正常组与组之间的铁死亡相关基因进行差异分析,确定45个铁死亡相关差异基因,其中33个为上调基因,12个为下调基因,并对45个铁死亡相关差异基因进行热图展示,见图2。"
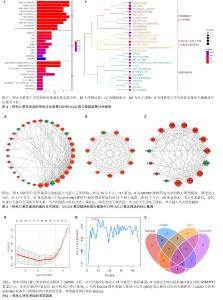
2.1.2 铁死亡差异基因的功能富集分析结果 GO富集分析显示,铁死亡差异基因的生物过程主要集中在小分子代谢、细胞对外界刺激化学应激及氧化应激的反应和自噬等;在细胞成分方面,铁死亡差异基因与过氧物酶体、线粒体和自噬体等密切相关;分子功能注释表明铁死亡差异基因显著富集在DNA结合转录因子结合、氧化还原酶活性和抗氧化活性等,见图3A。根据KEGG信号通路分析显示,差异基因主要在脂质与动脉粥样硬化、自噬、铁死亡、脂肪细胞因子信号通路等通路中富集表达,聚类树展示了富集信号通路聚类的三个类型,分别为脂肪细胞因子花生四烯酸、c型EGFR-巨细胞病毒和酒精性肠病,其中在第一类型下主要包括自噬、铁死亡、线粒体代谢及活性氧等相关信号通路,这与实验的差异基因密切相关,见图3B。 2.1.3 PPI网络的构建 通过Cytoscape软件将由STRING数据库构建的铁死亡差异基因PPI网络进行可视化与优化,该网络包括34个节点,111条边,见图4A;通过MCODE插件筛选出PPI网络中2个功能模块,选择聚类值> 5作为核心聚类模块,见图4B;cytoHubba插件中通过MCC算法选取前15个基因作为核心靶点,见图4C。 2.1.4 特征基因NFE2L2的鉴定结果 对铁死亡差异基因进行LASSO回归分析后,确定18个标记基因,见图5A;通过SVM-RFE机器学习分析,确定10个标记基因,见图5B。然后将MCODE插件获得的功能模块基因、MCC算法选取的核心靶点基因与两种机器学习算法筛选的标记基因进行交集,最终获得特征基因NFE2L2,见图5C。"
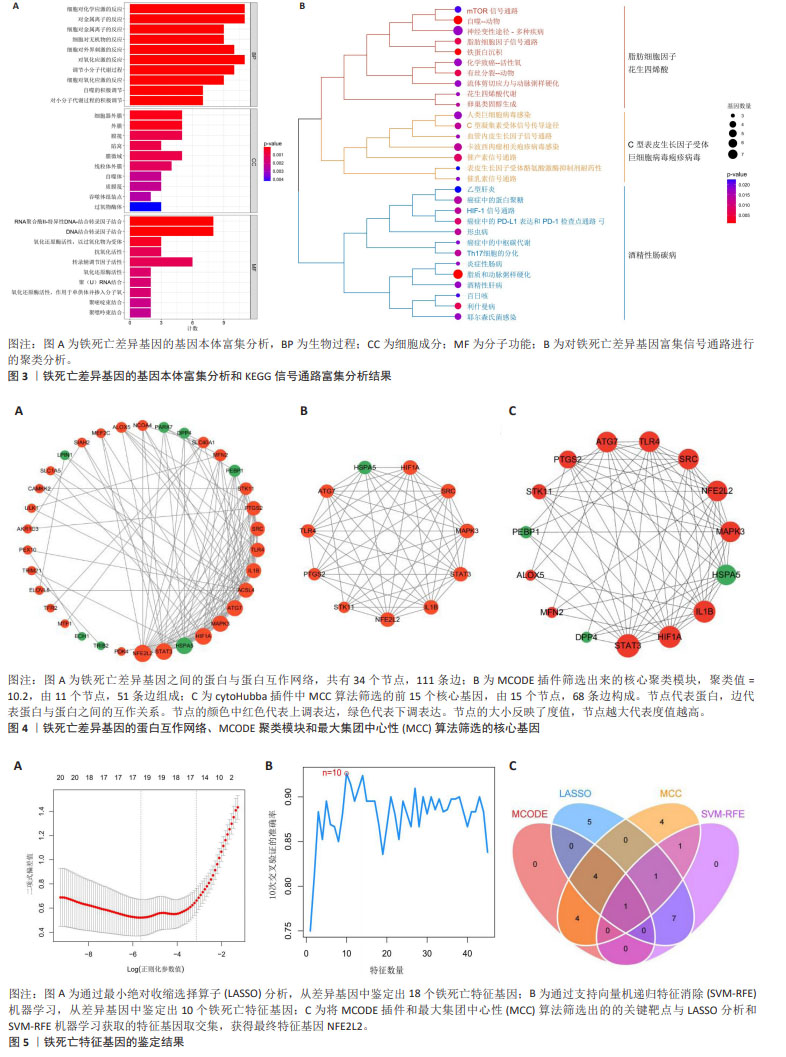
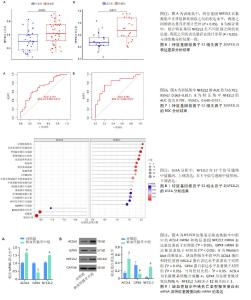
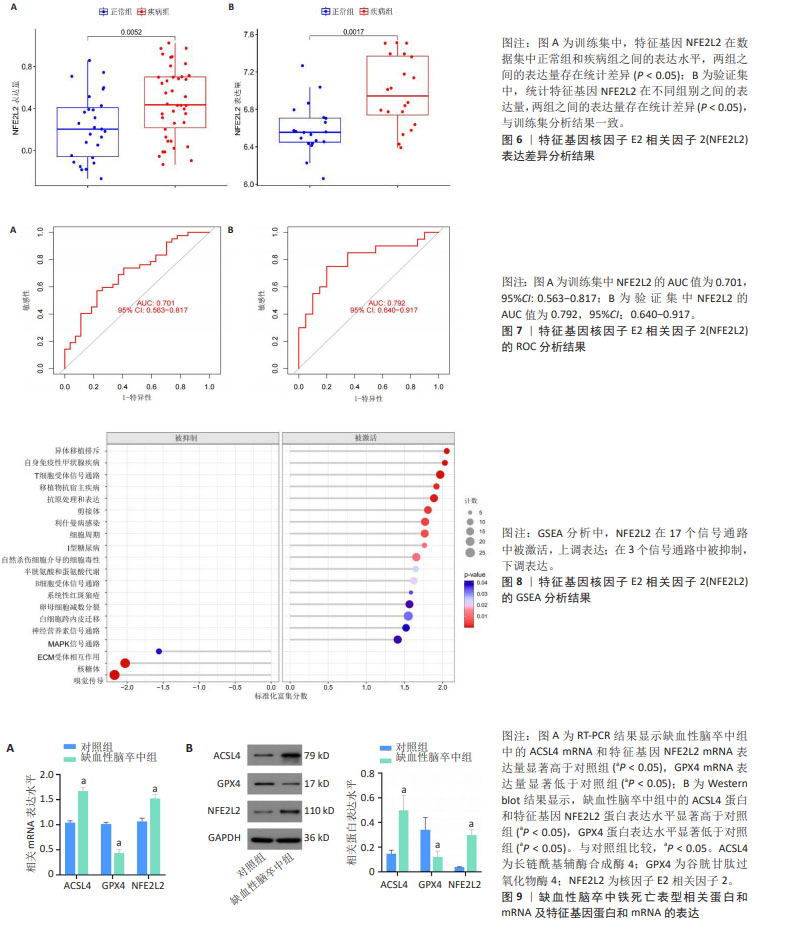
2.1.5 特征基因NFE2L2的验证结果 训练集中,疾病组与正常组相比,特征基因NFE2L2的表达水平明显增高(P < 0.05),见图6A,表3,验证集中NFE2L2的表达水平与训练集一致,见图6B,表3,结果表明了特征基因对缺血性脑卒中发生的潜在影响。 随后,通过R包“glmnet”评估特征基因对缺血性脑卒中诊断的准确性与特异性,训练集中NFE2L2的ROC曲线中AUC值为0.701,逻辑回归模型的AUC值95% CI:0.563?0.817,见图7A。同时,通过验证集中NFE2L2的ROC曲线分析与逻辑回归模型构建,其结果与验证集相符,见图7B,表明了特征基因NFE2L2对缺血性脑卒中的发生发展具有良好的诊断价值。 2.1.6 特征基因的基因富集分析结果 GSEA分析结果显示,特征基因共富集了20个主要信号通路,主要富集在免疫、炎症反应、氨基酸代谢及神经因子调控方面,其中在Ecm受体相互作用、核糖体和嗅觉传导中表达下调,在其他信号通路中均为上调,如T细胞与B细胞受体信号通路、系统性红斑狼疮、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢和神经营养因子信号通路,见图8。 2.2 细胞实验验证缺血性脑卒中铁死亡的发生和特征基因的表达 实验通过检测细胞模型中ACSL4与GPX4的表达,验证缺血性脑卒中由脂质过氧化诱导的铁死亡的发生。随后检测NFE2L2的表达量,验证筛选特征基因的准确性与可靠性。通过Western blot和RT-PCR实验结果表明,缺血性脑卒中组中的ACSL4蛋白与mRNA表达量显著高于对照组,GPX4蛋白与mRNA表达水平较对照组明显降低,这从很大程度上表明了缺血性脑卒中铁死亡的发生;NFE2L2蛋白与mRNA表达水平与对照组相比升高,差异具有显著性意义,表明实验筛选缺血性脑卒中铁死亡特征基因的准确性和诊断价值,见图9。"
| [1] ANDRABI SS, PARVEZ S, TABASSUM H. Ischemic stroke and mitochondria: mechanisms and targets. Protoplasma. 2020;257(2):335-343. [2] TUO QZ, ZHANG ST, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(1):259-305. [3] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018; 392(10159):1789-1858. [4] GBD 2019 STROKE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(10):795-820. [5] REN J X, LI C, YAN XL, et al. Crosstalk between oxidative stress and ferroptosis/oxytosis in ischemic stroke: possible targets and molecular mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6643382. [6] WEILAND A, WANG Y, WU W, et al. Ferroptosis and its role in diverse brain diseases. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(7):4880-4893. [7] WEI Z, XIE Y, WEI M, et al. New insights in ferroptosis: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1020918. [8] ZHANG Y, LU X, TAI B, et al. Ferroptosis and its multifaceted roles in cerebral stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15: 615372. [9] TUO QZ, LEI P, JACKMAN KA, et al. Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(11):1520-1530. [10] LIU J, GUO ZN, YAN XL, et al. Crosstalk between autophagy and ferroptosis and its putative role in ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:577403. [11] FABRIS F, PALMER D, DE MAGALHÃES JP, et al. Comparing enrichment analysis and machine learning for identifying gene properties that discriminate between gene classes. Brief Bioinform. 2020;21(3): 803-814. [12] AUSLANDER N, GUSSOW AB, KOONIN EV. Incorporating machine learning into established bioinformatics frameworks. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):2903. [13] MANN M, KUMAR C, ZENG WF, et al. Artificial intelligence for proteomics and biomarker discovery. Cell Syst. 2021;12(8): 759-770. [14] PENG C, AI Q, ZHAO F, et al. Quercetin attenuates cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023; 963:176264. [15] LIVAK KJ, SCHMITTGEN TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4): 402-408. [16] ZHAO Y, ZHANG X, CHEN X, et al. Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke:From mechanisms to treatment (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2022;49(2):15. [17] TUO QZ, ZHANG ST, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med Res Rev. 2022;42(1):259-305. [18] YAO MY, LIU T, ZHANG L, et al. Role of ferroptosis in neurological diseases. Neurosci Lett. 2021;747:135614. [19] LI Y, LI M, FENG S, et al. Ferroptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(3): 611-618. [20] LAN B, GE JW, CHENG SW, et al. Extract of Naotaifang, a compound Chinese herbal medicine, protects neuron ferroptosis induced by acute cerebral ischemia in rats. J Integr Med. 2020;18(4):344-350. [21] GUO H, ZHU L, TANG P, et al. Carthamin yellow improves cerebral ischemia‑reperfusion injury by attenuating inflammation and ferroptosis in rats. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(4):52. [22] 于瑜,王钟兴.基于生物信息学途径筛选缺血性脑卒中关键基因及药物预测[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2021,42(1): 42-50. [23] 周嫱,柏娜,刘生刚,等.基于生物信息学和机器学习方法探索缺血性脑卒中关键风险基因[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2022,48(9):525-532. [24] GUO Y, ZHOU P, QIAO L, et al. Maternal protein deficiency impairs peroxisome biogenesis and leads to oxidative stress and ferroptosis in liver of fetal growth restriction offspring. J Nutr Biochem. 2023; 121:109432. [25] CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Organelle-specific regulation of ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(10):2843-2856. [26] SHE R, LIU D, LIAO J, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunctions induce PANoptosis and ferroptosis in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: from pathology to therapeutic potential. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;17: 1191629. [27] ZHENG D, LIU J, PIAO H, et al. ROS-triggered endothelial cell death mechanisms: focus on pyroptosis, parthanatos, and ferroptosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1039241. [28] YANG K, ZENG L, YUAN X, et al. The mechanism of ferroptosis regulating oxidative stress in ischemic stroke and the regulation mechanism of natural pharmacological active components. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;154:113611. [29] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125. [30] ROJO DE LA VEGA M, CHAPMAN E, ZHANG DD. NRF2 and the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer cell. 2018;34(1):21-43. [31] CONRAD M, KAGAN VE, BAYIR H, et al. Regulation of lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in diverse species. Genes Dev. 2018;32(9-10):602-619. [32] NISHIZAWA H, YAMANAKA M, IGARASHI K. Ferroptosis: regulation by competition between NRF2 and BACH1 and propagation of the death signal. FEBS J. 2023;290(7): 1688-1704. [33] BERSUKER K, HENDRICKS JM, LI Z, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575(7784):688-692. [34] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021; 22(4):266-282. [35] LIU Z, LV X, SONG E, et al. Fostered Nrf2 expression antagonizes iron overload and glutathione depletion to promote resistance of neuron-like cells to ferroptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;407:115241. [36] DENG X, CHU W, ZHANG H, et al. Nrf2 and ferroptosis: a new research direction for ischemic stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023;43(8):3885-3896. [37] SONG X, LONG D. Nrf2 and ferroptosis: a new research direction for neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:267. [38] CUI Y, ZHANG Y, ZHAO X, et al. ACSL4 exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting ferroptosis-induced brain injury and neuroinflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;93:312-321. [39] FAN GB, LI Y, XU GS, et al. Propofol inhibits ferroptotic cell death through the Nrf2/Gpx4 signaling pathway in the mouse model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(3):956-966. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [3] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [5] | Zhao Nannan, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Zhu Bochao, Ding Huimin, Xu Zhenhua. Changes in ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons of vascular dementia model rats treated with Tongmai Kaiqiao Pill [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1401-1407. |
| [6] | Zhang Mingyang, Yang Xinling. Verbascoside inhibits Erastin-induced ferroptosis of dopaminergic nerve cell line MN9D cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1408-1413. |
| [7] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [8] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [9] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [10] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [11] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [12] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [13] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [14] | Yang Bo, Pan Xinfang, Chang Liuhui, Ni Yong. Correlation of echocardiographic parameters with disability at 3 months after acute ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7544-7551. |
| [15] | Jiang Qiyu, Zeng Huiyan. A novel analysis and prediction method for potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine based on artificial intelligence and omics data-driven approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7552-7561. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||