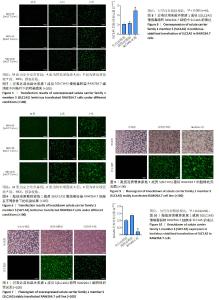
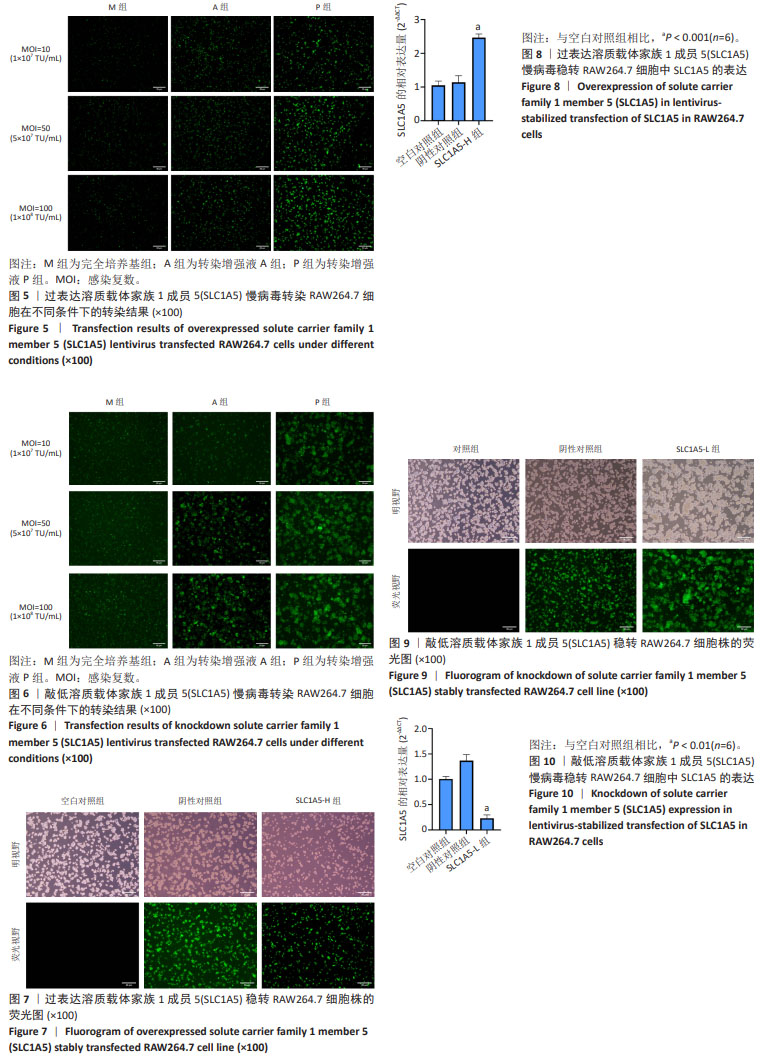
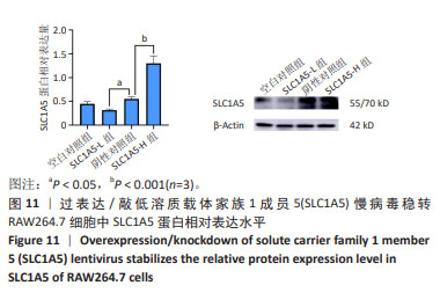
[1] CÉSAR-RAZQUIN A, SNIJDER B, FRAPPIER-BRINTON T, et al. A Call for Systematic Research on Solute Carriers. Cell. 2015;162(3):478-487.
[2] WANG W, ZOU W. Amino Acids and Their Transporters in T Cell Immunity and Cancer Therapy. Mol Cell. 2020;80(3):384-395.
[3] 宋晓翰,王江,柳红.先导化合物结构优化策略(八)——药物转运体及其相关药物设计策略[J].药学学报,2021,56(2):432-444.
[4] RON-HAREL N, GHERGUROVICH JM, NOTARANGELO G, et al. T Cell Activation Depends on Extracellular Alanine. Cell Rep. 2019;28(12): 3011-3021.e4.
[5] KISHTON RJ, SUKUMAR M, RESTIFO NP. Arginine Arms T Cells to Thrive and Survive. Cell Metab. 2016;24(5):647-648.
[6] LUO Y, LI W, LING Z, et al. ASCT2 overexpression is associated with poor survival of OSCC patients and ASCT2 knockdown inhibited growth of glutamine-addicted OSCC cells. Cancer Med. 2020;9(10): 3489-3499.
[7] ZHANG Z, LIU R, SHUAI Y, et al. ASCT2 (SLC1A5)-dependent glutamine uptake is involved in the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2020;122(1):82-93.
[8] LI S, PEI L, ZHOU Q, et al. SLC1A5 regulates cell proliferation and self-renewal through β-catenin pathway mediated by redox signaling in arsenic-treated uroepithelial cells. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023;262: 115204.
[9] CONGER KO, CHIDLEY C, OZGURSES ME, et al. ASCT2 is the primary serine transporter in cancer cells. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023: 2023.10.09.561530.
[10] SIMCOX J, LAMMING DW. The central moTOR of metabolism. Dev Cell. 2022;57(6):691-706.
[11] VAN DEN BOSCH MHJ, VAN LENT PLEM, VAN DER KRAAN PM. Identifying effector molecules, cells, and cytokines of innate immunity in OA. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):532-543.
[12] SUN Z, LIU Q, LV Z, et al. Targeting macrophagic SHP2 for ameliorating osteoarthritis via TLR signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(7): 3073-3084.
[13] NICKLIN P, BERGMAN P, ZHANG B, et al. Bidirectional transport of amino acids regulates mTOR and autophagy. Cell. 2009;136(3):521-534.
[14] ZHU L, YANG T, LI L, et al. TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disease. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4696.
[15] ABU-REMAILEH M, WYANT GA, KIM C, et al. Lysosomal metabolomics reveals V-ATPase- and mTOR-dependent regulation of amino acid efflux from lysosomes. Science. 2017;358(6364):807-813.
[16] NALDINI L, BLÖMER U, GALLAY P, et al. In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector. Science. 1996;272(5259):263-267.
[17] 房恩岳,张丽萍,马雪征,等.慢病毒载体系统及其安全性研究进展[J].病毒学报,2023,39(4):1181-1192.
[18] LING ZN, JIANG YF, RU JN, et al. Amino acid metabolism in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):345.
[19] LI S, ZHOU Q, LIU W, et al. Targeting SLC1A5 blocks cell proliferation through inhibition of mTORC1 in arsenite-treated human uroepithelial cells. Toxicol Lett. 2021;345:1-11.
[20] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578.
[21] PHAM TM, ERICHSEN JL, KOWAL JM, et al. Elevation of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels Following Intra-Articular Fractures-A Systematic Review. Cells. 2021;10(4):902.
[22] MOBASHERI A, RAYMAN MP, GUALILLO O, et al. The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(5): 302-311.
[23] TAKAYAMA K, KAWAKAMI Y, KOBAYASHI M, et al. Local intra-articular injection of rapamycin delays articular cartilage degeneration in a murine model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(6):482.
[24] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257.
[25] WILLENBORG S, SANIN DE, JAIS A, et al. Mitochondrial metabolism coordinates stage-specific repair processes in macrophages during wound healing. Cell Metab. 2021;33(12):2398-2414.e9.
[26] DAGHESTANI HN, PIEPER CF, KRAUS VB. Soluble macrophage biomarkers indicate inflammatory phenotypes in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(4):956-965.
[27] KRAUS VB, MCDANIEL G, HUEBNER JL, et al. Direct in vivo evidence of activated macrophages in human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(9):1613-1621.
[28] GRIFFIN TM, SCANZELLO CR. Innate inflammation and synovial macrophages in osteoarthritis pathophysiology. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):57-63.
[29] ZHANG H, LIN C, ZENG C, et al. Synovial macrophage M1 polarisation exacerbates experimental osteoarthritis partially through R-spondin-2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(10):1524-1534.
[30] PALMIERI EM, MENGA A, MARTÍN-PÉREZ R, et al. Pharmacologic or Genetic Targeting of Glutamine Synthetase Skews Macrophages toward an M1-like Phenotype and Inhibits Tumor Metastasis. Cell Rep. 2017;20(7):1654-1666. |