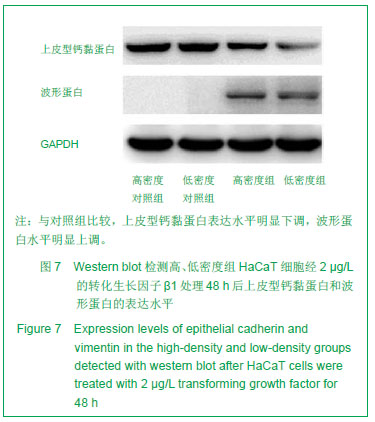
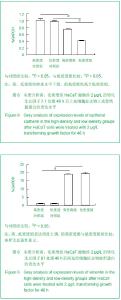
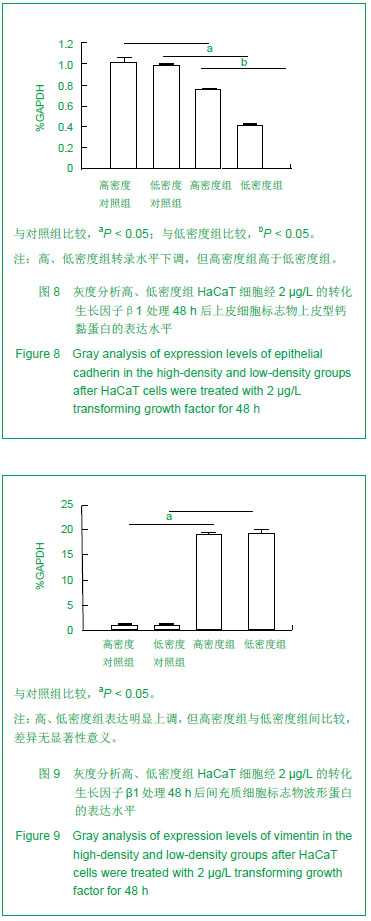
| [1]Coulombe PA. Wound epithelialization: accelerating the pace of discovery. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;121(2):219-230. [2]田鸣,青春,牛轶雯,等. 糖尿病大鼠表皮角质形成细胞生物学变化的机制研究 [J]. 创伤外科杂志,2007,9(4):306-310.[3]Siegel PM, Massagué J. Cytostatic and apoptotic actions of TGF-beta in homeostasis and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003; 3(11):807-821.[4]Nakamura M, Tokura Y, Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the skin. J Dermatol Sci.2011;61(1):7-13.[5]Wang T, Zhang L, Shi C, et al. TGF-β-induced miR-21 negatively regulates the antiproliferative activity but has no effect on EMT of TGF-β in HaCaT cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(2):366-376.[6]Scheel C, Eaton EN, Li SH, et al. Paracrine and autocrine signals induce and maintain mesenchymal and stem cell states in the breast. Cell. 2011;145(6):926-940. [7]Räsänen K, Vaheri A. TGF-beta1 causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HaCaT derivatives, but induces expression of COX-2 and migration only in benign, not in malignant keratinocytes. J Dermatol Sci. 2010;58(2): 97-104.[8]Lorincz MT. Optimized neuronal differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells: role of cell density. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;330:55-69.[9]Lu H, Guo L, Wozniak MJ, et al. Effect of cell density on adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;381(3):322-327. [10]Takagi M, Umetsu Y, Fujiwara M, et al. High inoculation cell density could accelerate the differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to chondrocyte cells. J Biosci Bioeng. 2007;103(1):98-100. [11]Hui TY, Cheung KM, Cheung WL, et al. In vitro chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in collagen microspheres: influence of cell seeding density and collagen concentration. Biomaterials. 2008;29(22):3201-3212. [12]Nelson CM, Khauv D, Bissell MJ, et al. Change in cell shape is required for matrix metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 2008;105(1):25-33.[13]Terai K, Call MK, Liu H, et al. Crosstalk between TGF-beta and MAPK signaling during corneal wound healing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(11):8208-8215. [14]Terao M, Ishikawa A, Nakahara S, et al. Enhanced epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like phenotype in N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V transgenic mouse skin promotes wound healing. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(32): 28303-28311.[15]Chaffer CL, Thompson EW, Williams ED. Mesenchymal to epithelial transition in development and disease. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;185(1-3):7-19.[16]Massagué J, Seoane J, Wotton D. Smad transcription factors. Genes Dev. 2005;19(23):2783-2810.[17]Lou C, Zhang F, Yang M, et al. SOX4 mediates TGF-β-induced expression of mesenchymal markers during mammary cell epithelial to mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53238. [18]Moustakas A, Pardali K, Gaal A, et al. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling in regulation of cell growth and differentiation. Immunol Lett. 2002;82(1-2):85-91. [19]Samarakoon R, Higgins PJ. Integration of non-SMAD and SMAD signaling in TGF-beta1-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Thromb Haemost. 2008;100(6):976-983. [20]Thiery JP, Sleeman JP. Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(2):131-142. [21]Venkov C, Plieth D, Ni T, et al. Transcriptional networks in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 2011;6(9): e25354.[22]Sleeman JP, Thiery JP. SnapShot: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell. 2011;145(1):162.e1. [23]Yang X, Wang J, Guo SL, et al. miR-21 promotes keratinocyte migration and re-epithelialization during wound healing. Int J Biol Sci. 2011;7(5):685-690. [24]Sarrió D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Hardisson D, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype. Cancer Res. 2008;68(4):989-997. [25]Jenndahl LE, Isakson P, Baeckström D. c-erbB2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells is suppressed by cell-cell contact and initiated prior to E-cadherin downregulation Int J Oncol. 2005;27(2):439-448.[26]Acloque H, Adams MS, Fishwick K, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: the importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(6):1438-1449. [27]Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, et al. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(2): 76-83. [28]Bachelder RE, Yoon SO, Franci C, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is an endogenous inhibitor of Snail transcription: implications for the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 2005;168(1):29-33. [29]Papkoff J, Aikawa M. WNT-1 and HGF regulate GSK3 beta activity and beta-catenin signaling in mammary epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;247(3):851-858. [30]Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, et al. Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(10): 931-940. |