Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 590-598.doi: 10.12307/2025.125
Previous Articles Next Articles
Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in treatment of neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury: effects of nuclear transcription factor kappa B signaling pathway
Xu Zhenhua1, Li Yanjie2, Qin Hewei2, Liu Haoyuan2, Zhu Bochao1, Wang Yupu1
- 1School of Rehabilitation, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, Henan Province Hospital of TCM, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-25Accepted:2024-02-18Online:2025-01-28Published:2024-06-04 -
Contact:Li Yanjie, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation, Henan Province Hospital of TCM, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Xu Zhenhua, Master candidate, School of Rehabilitation, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Top Talents Training Special Project, No. 2022ZYBJ15 (to LYJ); 2023 Henan Province Traditional Chinese Medicine “Double First Class” Creation Scientific Research Special Project, No. HSRP-DFCTCM-2023-3-26 (to LYJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Zhenhua, Li Yanjie, Qin Hewei, Liu Haoyuan, Zhu Bochao, Wang Yupu. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in treatment of neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury: effects of nuclear transcription factor kappa B signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 590-598.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
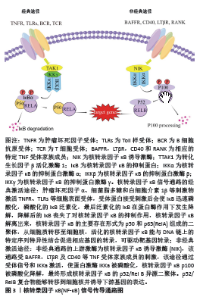
2.1 核转录因子κB信号通路与脊髓损伤神经炎症的关系 核转录因子κB信号通路由受体和受体近端信号衔接蛋白、核转录因子κB抑制蛋白(inhibitor of NF-κB,IκB)、IκB激酶复合物和核转录因子κB二聚体构成,其家族成员主要包括p65(RelA),RelB,c-Rel,核转录因子κB1(p50及其前体p105)、核转录因子κB2(p52及其前体p100)共5种蛋白质二聚体组成。所有的核转录因子κB亚基都包含一个保守的Rel同源域,主要负责同源和异二聚化以及DNA结合。在p65、c-Rel和RelB中存在相同的转录激活区域——TAD,该区域可以经核转位启动靶基因转录,正向调节基因的表达,p50和p52则不存在转录激活区域,其主要作用可能为抑制转录[7]。激活核转录因子κB信号通路有经典途径和非经典途径两种方式,如图3所示。由RelA和p50形成的核转录因子κB1主要在经典途径被激活,主要负责靶基因的转录;而RelB和p52主要在非经典核转录因子κB信号通路中形成异二聚体核转录因子κB2,负责多层免疫细胞的发育[8]。核转录因子κB通常与其抑制剂α(NF-κB inhibitorα,IκBα)结合并稳定的存在于细胞质中,主要作用为阻止核转录因子κB进入细胞核[9],当细胞受到各种内外刺激后可激活IκB激酶,将IκB蛋白磷酸化、泛素化,从而降解IκB蛋白并释放核转录因子κB二聚体[7]。核转录因子κB二聚体在细胞核内与目的基因结合,经转录、翻译后驱动炎症反应、免疫反应、分化和凋亡等相关靶基因的转录,产生并释放如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素2及干扰素γ等炎性细胞因子[8,10]。同时,释放的细胞因子也可以反过来激活核转录因子κB,进一步介导组织炎症。除此以外,在中枢神经系统损伤中,核转录因子κB的激活可导致分子重编程以刺激轴索发生,主要机制为通过调节突触基因的表达促进轴突的生长,发挥神经保护作用[11]。因此,抑制核转录因子κB信号通路或降低该通路激活程度可能有助于减轻脊髓损伤神经炎症的症状和促进神经的修复和再生。"
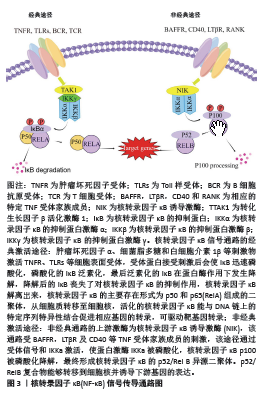

2.2 脊髓损伤后神经炎性反应中的细胞变化 脊髓损伤的过程中常伴有炎性细胞在脊髓组织中的聚集浸润、黏附分子的高表达、炎症因子的生成与释放等过程,核转录因子κB信号通路经此激活可诱导炎症的级联反应,加重脊髓损伤[12]。参与炎症的多种细胞均能激活核转录因子κB信号通路,如中性粒细胞、小胶质细胞、星形胶质细胞和巨噬细胞等[13],该通路激活后释放的白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子等炎症因子能影响组织修复[14]。因此,通过抑制核转录因子κB信号通路减少促炎细胞因子的释放可以阻碍继发性损伤的炎症反应、继而促进受损脊髓组织的修复。 1986年,核转录因子κB首次被SEN和BALTIMORE教授[15]发现和命名,研究中发现一种蛋白能够与κ增强子中的一个序列结合,并仅在B细胞中出现,又因其具有组织特异性和谱系中的阶段特异性,取名为核转录因子κB;1900年,SHAKHOV等[16]通过实验探讨了炎症反应期间巨噬细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α基因的激活问题,确定了核转录因子κB参与了巨噬细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α基因的转录与激活;1998年,BETHEA等[17]通过研究发现核转录因子κB激活最早发生在损伤后0.5 h,并持续至少72 h,首次证明了核转录因子κB在脊髓损伤后被激活,并且在受损脊髓内的巨噬细胞/小胶质细胞、内皮细胞和神经元中均可检测到活化的核转录因子κB,这些细胞中活化的核转录因子κB的表达可能在中枢神经系统炎症反应中起关键作用,说明阻断这种级联反应可能是治疗脊髓损伤的有效方法;2000年,KIM等[18]发现中性粒细胞产生的活性氧能够激活核转录因子κB,从而导致腺泡细胞炎症因子的上调,在中性粒细胞与核转录因子κB信号通路之间建立了联系;2005年,BRAMBILLA等[19]为了探究星形胶质细胞核转录因子κB对中枢神经系统病理生理学的贡献,生成了一种转基因(TG)小鼠系,证实了选择性抑制星形胶质细胞中核转录因子κB信号传导在脊髓损伤后产生保护作用;PAN等[20]发现鞘内注射核转录因子κB抑制剂吡咯烷二硫代氨基甲酸酯能够有效防止慢性收缩性损伤诱导的机械性异常性疼痛和热痛觉过敏,通过研究核转录因子κB抑制剂对大鼠小胶质细胞的活化程度和伤害感受行为的保护作用证实了转录因子κB信号通路与小胶质细胞的关系。CHEN等[21]研究发现戊丙酸能够调节小胶质细胞从M1向M2的表型转变,通过抑制小胶质细胞的活化降低脊髓损伤诱导的炎症因子,核转录因子κB p65的乙酰化状态增强后自身的转录活性会有所降低;JIANG等[22]最新研究发现中药单体枸杞多糖能够显著抑制脊髓损伤后的转录因子κB和细胞焦亡,通过改善验证微环境促进神经的修复和运动功能的恢复。核转录因子κB信号通路与炎症细胞开始联系的关键节点发展记录表 见表1。 2.2.1 核转录因子κB信号通路与中性粒细胞 中性粒细胞是脊髓损伤后第一类聚集到损伤部分的细胞,脊髓损伤以后,外周中性粒细胞会迅速变形、迁移并聚集在损伤部位,活化的中性粒细胞可以释放多种炎症因子或趋炎因子,这些因子可以介导核转录因子κB信号通路进一步促进炎症相关因子的释放[11]。同时,核转录因子κB信号通路的激活也可以促进中性粒细胞的趋化、黏附和激活。研究表明,脊髓损伤小鼠血液中募集的中性粒细胞通常与继发性组织损伤以及神经功能缺损程度有关,中性粒细胞可以介导多种细胞反应,衔接上下实现促炎或抗炎功能,其效应器功能也可能会导致临近组织的受损以及炎症反应的扩大[23]。"

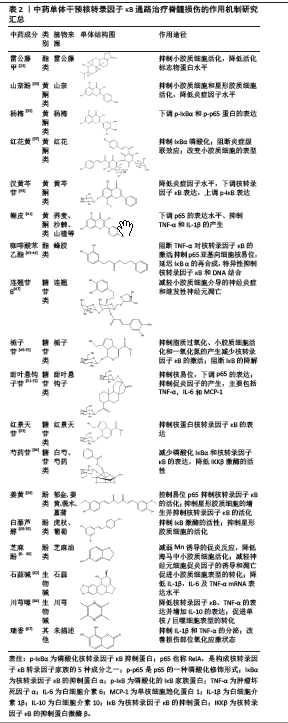
2.2.2 核转录因子κB信号通路与小胶质细胞 核转录因子κB作为中枢调节因子能够调控神经炎症中小胶质细胞表型的极化,小胶质细胞是先天免疫反应的主要调节因子[24],活化状的小胶质细胞不仅可以释放肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素1及白细胞介素6等炎症因子诱导核转录因子κB通路,作为核转录因子κB信号通路的下游因子又可以反过来激活核转录因子κB的表达。HUANG等[25]发现通过抑制核转录因子κB信号通路可以降低小胶质细胞的活性并减少炎性细胞因子的产生。小胶质细胞可以激活核转录因子κB通路参与炎症相关基因的转录与表达,核转录因子κB通路的激活又可以促进小胶质细胞的增殖与转移,进一步扩大炎症。因此,通过抑制核转录因子κB通路的激活和小胶质细胞活化可以促进机体抗炎、减少神经元的死亡,这为神经重建与机体功能的恢复提供了有利条件。 2.2.3 核转录因子κB信号通路与星形胶质细胞 作为中枢神经系统中数量最多的神经胶质细胞,星形胶质细胞不仅具有免疫功能,还能促进神经元存活、维持组织稳态并调节神经干细胞分化[26]。M1型星形胶质细胞分泌的白细胞介素1α等炎症因子会介导p65进入细胞核从而产生抑制轴突再生的胶质,其他产物如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等则介导核转录因子κB通路引起强烈的炎症反应;M2型星形胶质细胞能够促进新髓鞘的产生从而保护神经功能[27]。反应性星形胶质细胞是脊髓损伤后数小时内被激活的、具有高度异质性的星形胶质细胞,其产物白细胞介素17R能够激活核转录因子κB通路,促进促炎递质在损伤区域的进一步聚集。此外,活化的星形胶质细胞对细胞外基质蛋白的沉积效应能有效控制炎症反应[24]。 中枢神经系统的愈合随着反应性星形胶质细胞的长期增生受到损害,抑制核转录因子κB通路中p65的核转位可以减少星形胶质细胞的产生并降低炎症因子的水平[28]。总体来看,星形胶质细胞对神经元的具体影响应根据星形胶质细胞的不同表型及星形胶质细胞在脊髓损伤后不同阶段的功能状态去选择干预方式。 2.2.4 核转录因子κB信号通路与巨噬细胞 脊髓损伤后的巨噬细胞可分为炎症早期的M1型促炎巨噬细胞和炎症晚期的M2型抗炎巨噬细胞。对2001-2021年间巨噬细胞极化的文献计量学和图谱分析表明,M1型巨噬细胞的促炎反应明显依赖于核转录因子κB1的激活,而M2型巨噬细胞则是通过募集STAT3来抑制炎症[29],周金萍等[30]通过对小鼠RAW264.7巨噬细胞的实验发现,德昂酸茶水提物可以显著增加核转录因子κB信号通路负调节因子基因的表达,进一步研究表明,该水提物能显著抑制小鼠RAW264.7巨噬细胞中IκBα和IκBα的磷酸化。LI等[31]发现抑制核转录因子κB信号通路能够减少巨噬细胞的迁移及下游炎症因子的释放,这对于减轻炎症反应有十分重要的意义。综上所述,在减轻神经炎症、减少继发性损伤并恢复神经功能时应注意介入反应的时间、确定正确的巨噬细胞表型。 综上所述,作者在该部分讨论了脊髓损伤过程中核转录因子κB信号通路在炎症细胞聚集、炎症因子释放和损伤加重中的重要作用,具体包括中性粒细胞、小胶质细胞、星形胶质细胞和巨噬细胞在核转录因子κB信号通路中的参与和影响,汇总了通过抑制核转录因子κB信号通路减少促炎细胞因子的释放,阻碍继发性损伤的炎症反应,促进受损脊髓组织的修复等方向的相关研究。作者认为对核转录因子κB信号通路进行干预前应着重考虑细胞类型和炎症反应不同阶段的具体情况,从而更好地减轻神经炎症、减少继发性损伤并促进神经功能的恢复;目前研究多以动物实验水平为主,具体的干预机制也未能完全明晰,未来应探寻更多可能的干预方法,如进一步研究调节核转录因子κB信号通路的治疗策略、该通路针对不同细胞类型干预的切入时机以提高脊髓损伤的治疗效果等,进一步的研究将为未来治疗提供坚实的理论基础,同时为具体的临床应用和治疗方法进一步研究转化为临床实践提供理论策略。 2.3 中药单体干预核转录因子κB信号通路治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展 近年来,大量研究表明中药单体可通过干预核转录因子κB通路来减轻脊髓损伤[32],主要包括黄酮类、酯类、糖苷类、酚类和生物碱类。 2.3.1 黄酮类化合物 山奈酚(Κaempferol)主要来源于姜科植物山奈的根茎,广泛存在于各种蔬菜和水果中。研究发现山奈酚能够抑制小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的活化,通过抑制核转录因子κB信号通路p65的核易位并降低白细胞介素18、白细胞介素1β的产生,从而发挥神经保护作用[33]。此外,山奈酚还具有降低脊髓损伤部位氧化应激水平、减少活性氧的产生和抑制细胞焦亡相关蛋白的表达等能力,进一步保护脊髓功能,对山奈酚药理特性的进一步研究能很好地揭示山奈酚在脊髓损伤后神经功能的保护和潜在机制中的作用。 杨梅素(Myricetin)又称杨梅黄酮、杨梅酮,是从杨梅树皮中提取的黄酮醇类化合物,同时也广泛存在于水果、蔬菜中。杨梅素具有抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤和抗氧化应激等作用[34],李驰等[35]通过利用杨梅素治疗脊髓损伤大鼠的研究表明杨梅素能够显著降低白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的含量,且药效呈剂量依赖性,中高浓度杨梅素的药效与阳性药物地塞米松相当,通过抑制核转录因子κB信号通路促进运动功能的恢复、抑制炎症反应的发生发展。目前存在的问题是,杨梅素的水溶性和脂溶性较差,这些客观因素限制了以杨梅素或杨梅素类物质为主的药品的开发与应用,可以尝试合成同类衍生物、联合使用提高药物亲脂性的物质或使用纳米材料充当载体进行试验,为杨梅素治疗相关疾病的分子机制提供可行性。 红花黄素(Safflower Yellow)是从中药红花中提取的主要活性物质,具有抗炎、抗凝和抗氧化等作用[36]。红花黄素在核转录因子κB信号通路中主要通过抑制IκBα磷酸化阻碍核转录因子κB信号通路和p53核易位而实现其抗炎作用[37]。除此以外,现代研究表明红花黄素可以通过多种方式调节核转录因子κB信号通路,如通过肿瘤坏死因子α或白细胞介素1β阻断核转录因子κB在炎症中的级联效应、改变小胶质细胞的表型阻碍Toll样受体 4(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4)/核转录因子κB信号通路等方式[36]。王大伟等[38]研究发现红花黄素能够有效抑制HMGB1/TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路,表现为脊髓损伤后氧化应激损伤程度的降低和炎症递质表达的减少。 汉黄芩苷(Wogonoside)是来源于黄芩的黄酮类苷化合物,具有抗炎、抑制细胞凋亡、调节氧化应激和抗肿瘤等广泛的药理活性。ZHU等[39]研究发现汉黄芩苷能够减少IκB的降解和核转录因子κB蛋白核易位,通过抑制核转录因子κB信号通路的激活保护神经组织,揭示了汉黄芩苷在调节免疫细胞中的关键作用;此外,汉黄芩苷还可以降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8等相关因子的水平。 槲皮素(Quecetin)是一种常见的黄酮类化合物,其生物活性具有抗癌、抗炎、抗氧化应激及抗纤维化等作用,减轻损伤对机体造成的损害。近些年研究发现槲皮素能够促进脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能恢复、保护氧化损伤神经退化模型中的神经组织[40],同时具有减轻神经病理性疼痛并有效减少脊髓空洞及胶质瘢痕的形成、促进轴突再生的作用。王业杨等[41]研究发现槲皮素可以抑制脊髓损伤后TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,减少脊髓损伤后组织中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的产生,同时能够下调c-caspase 3和Bax的表达,上调抑凋亡蛋白Bcl-2的表达,表明槲皮素对脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能的恢复可能是通过降低TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路介导的神经炎症及细胞凋亡过程实现的。 2.3.2 酯类化合物 咖啡酸苯乙酯(Caffeic acid phenethyl ester)是从蜂胶汇总分离出来的咖啡酸天然衍生物,具有抗癌、抗炎、抗氧化和抗真菌等特性,因显著的神经保护作用而被广泛应用[42]。研究证明,咖啡酸苯乙酯作为核转录因子κB活化抑制剂,可通过抑制核转录因子κB的活性有效的抑制炎症[43],最新研究发现脊髓损伤行鞘内注射咖啡酸苯乙酯可以明显降低组织和血清中的白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6等炎症因子的表达,并减轻脊髓的水肿和出血状态[44]。 雷公藤甲素(Triptolide),又名雷公藤内酯,是从卫矛科植物雷公藤的根叶、花果中提取出来的一种环氧二萜内酯化合物、具有抗炎及免疫抑制作用,主要用于治疗炎症性疾病和自身免疫病[45],有研究将雷公藤内酯作用于miR-96/IΚΚβ/核转录因子κB通路后发现雷公藤内酯能够抑制小胶质细胞的活化,降低了小胶质细胞的活化标志物Iba-1和IΚΚβ/核转录因子κB相关蛋白的水平,从而抑制了脊髓组织和脂多糖诱导的小胶质细胞蛋白中炎症细胞因子、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的产生。 2.3.3 糖苷类化合物 连翘苷B(ForsythosideB)是从本犀科植物连翘的叶子或干燥果实中分离出来的一种苯乙烷糖苷,具有抗炎、抗氧化和防腐的特性,能够通过抑制核转录因子κB信号传导有效抑制内源性炎症因子的活化,从而起到有效的神经保护作用[46]。研究发现连翘苷B可以靶向调节核转录因子κB通路并降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和IκB水平,通过抑制核转录因子κB有效减轻小胶质细胞介导的神经炎症和继发性神经元凋亡[47]。除此以外,连翘苷B还能够抑制神经胶质瘢痕形成、缓解脱髓鞘并促进运动功能的恢复。 栀子苷(Geniposide)是从栀子花中提取的单环烯醚萜类苷,具有显著的抗炎和神经元修复能力,除此以外还有抗细胞凋亡、抗血栓形成、抗氧化应激和神经保护等多种生物活性[48]。前期研究发现栀子苷能够通过抑制脂质过氧化、小胶质细胞的活化和一氧化氮的产生发挥抗炎效果,降低肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β的产生和核转录因子κB的激活[49]。近年来还发现栀子苷能够通过阻断IκB的降解抑制核转录因子κB通路、减少环氧化酶2的产生以及抑制IΚΚs/核转录因子κB信号通路来降低脊髓损伤后的炎症反应[50]。 甜叶悬钩子苷(Rubusoside)是甜叶悬钩子中提纯得到的高甜度二萜糖苷,具有减轻炎症、抗氧化和抗肿瘤等功效。研究报道,甜叶悬钩子苷能够抑制血浆中促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和单细胞趋化蛋白1(monocyte chemoattractant protein,MCP-1)的释放[51]。杨爽等[52]通过体外实验观察到甜叶悬钩子苷能够通过抑制核转录因子κB信号通路中核易位过程、下调p65蛋白的表达来减轻小鼠神经炎症细胞模型的炎症反应。 红景天苷(Salidroside)是景天科红景天属多年生草本植物的共有成分,具有收涩止血、散瘀消肿的功效。研究表明,红景天苷不仅具有抗炎、抗纤维化的功能,还能够延缓衰老、降血糖。周彬彬等[53]在脂多糖诱导雄性大鼠脑内炎症反应的实验中发现,红景天苷能够激活PI3K/Akt信号通路,通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和诱导性一氧化氮合成酶等炎症因子的表达,促进Akt蛋白磷酸化,从而减少核蛋白核转录因子κB的表达。考虑到该项研究中造模给药与取材时间较短,实验结果可能会存在误差,若进一步规范给药剂量和给药后取材时间并进行细胞实验,将进一步验证红景天苷对核转录因子κB蛋白表达的影响。 芍药苷(Paeoniflorin)是中药芍药、白芍中的主要活性成分,是一种水溶性的单萜类糖苷,具有清热凉血、散瘀止痛等功效,同时也因其抗炎、抗氧化及不良反应低等药理作用而被广泛使用。陈剑平等[54]发现芍药苷对脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能的改善具有剂量-时间依赖性,同时,芍药苷干预能够显著减少磷酸化I-κBα和核转录因子κB的表达,IKKβ激酶的活性下降近50%。 2.3.4 酚类化合物 姜黄素(Curcumin)被证明可以通过控制易位p65抑制核转录因子κB的活化,对核转录因子κB通路的抑制作用表现在能够显著抑制瘢痕的形成,姜黄素也可以通过抑制TAΚ1/核转录因子κB途径显示出良好的抗炎和抗氧化效应[55]。最新研究表明,姜黄素在抑制星形胶质细胞的增生的同时能够显著抑制核转录因子κB的活化,减少肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β等促炎递质的释放,从而为轴突的恢复提供良好的环境[56]。李建设等[57]通过姜黄素干预新生SD大鼠大脑皮层中原代培养的星形胶质细胞补充了姜黄素在神经炎症过程中对星形胶质细胞的影响,但该实验未进一步对比姜黄素浓度在动物体内实验中的影响及相关蛋白的表达,因此,姜黄素的浓度及动物实验的效果仍需深入探讨。 白藜芦醇(Resveratrol)是一种天然多酚,具有抗炎、抗氧化、抗血管生成等多种特性,白藜芦醇对核转录因子κB通路的抑制主要表现在抑制IκB激酶的活性上,同时,白藜芦醇还可以通过抑制核转录因子κB信号通路减少前白细胞介素1β的产生,白藜芦醇的这些作用可以减轻脊髓损伤后神经炎症的反应程度[58-59],抑制星形胶质细胞的活化并增强修复能力。 芝麻酚(Sesamol)是从芝麻油中提取而来的一种活性成分,现代研究已证明其抗炎、抗氧化应激和神经保护功能。WU等[60]研究证明芝麻酚可以通过抑制小胶质细胞cGAS-STING/核转录因子κB通路来减弱Mn诱导的促炎反应,明显降低海马中小胶质细胞的活化、同时保护神经细胞。此外,WANG等[6]研究发现芝麻酚能够通过调节核转录因子κB通路减轻氧化应激所诱导的神经元细胞中促炎因子的凋亡,显著调节细胞存活率。 2.3.5 生物碱类 石蒜碱(Lycorine)是石蒜提取物中最主要的活性物质之一,主要存在于石蒜科植物石蒜鳞茎中,具有调节肿瘤细胞周期、促进肿瘤细胞凋亡、抑制COVID-19病毒的复制和抑制炎症相关诱导酶的合成等作用[61]。抗晶晶等[62]通过检测石蒜碱对小胶质细胞活性、mRNA及核转录因子κB关键蛋白核转录因子κB p65、p-核转录因子κB p65表达水平的检测表明石蒜碱或许可通过抑制TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路减轻小胶质细胞炎症反应,保护神经系统。 川芎嗪(Tetramethylpyrazine)是从中药川芎根茎中提取出的生物碱,因其活血化瘀、疏通血脉常用于心脑血管疾病和中枢神经系统疾病的治疗,ZHANG等[63]在脑脊髓膜炎中的研究中发现川芎嗪能够通过核转录因子κB信号通路调节小胶质细胞的极化状态,通过抑制促炎因子的释放、保护血脊髓屏障改善机体脊髓损伤后的微循环障碍。张厚君等[64]通过腹腔注射盐酸川芎嗪注射液对大鼠脊髓横断模型进行干预,发现川芎嗪能够显著降低核转录因子κB、肿瘤坏死因子α的表达并增加白细胞介素10的表达,促进单核/巨噬细胞表型的转化。肖志满等[65]通过检测核转录因子κB和I-κB证实了川芎嗪能够阻断I-κB磷酸化的信号传导抑制核转录因子κB的活化,通过下调炎性基因的表达抑制炎症反应。 2.3.6 其他 瑞香素(Daphnetin)是一种天然香豆素的衍生物,研究表明其具有抗氧化应激、抗肿瘤等作用,临床上常用于心脑血管疾病的治疗,同时也有一部分文献基于瑞香素的抗氧化应激、抗炎和抗凋亡等作用致力于对脊髓损伤等神经系统疾病的研究[66]。吴军等[67]探究了瑞香素在脊髓损伤模型大鼠中对TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路的调节作用,实验表明瑞香素能调节脑源性神经生长因子/Trk B信号通路和TLR4/核转录因子κB信号通路,其主要药理作用表现为抑制白细胞介素1β的分泌、改善损伤部位氧化应激状态并提升实验大鼠下肢运动功能。 以上研究表明,中药单体可以通过调节IκB的活化与降解、相关炎症因子水平及关键蛋白的含量从而调控核转录因子κB信号通路,发挥治疗脊髓损伤后神经炎症、保护神经功能的作用。上述中药单体来源及调控机制见表2。"
| 1] KHORASANIZADEH M, YOUSEFIFARD M, ESKIAN M, et al. Neurological recovery following traumatic spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. Spine. 2019. doi: 10.3171/2018.10.SPINE18802. [2] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17018. [3] MALLON S, KWIECIEN JM, KARIS JP. Imaging of neurotrauma in acute and chronic settings. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(8):1178-1190. [4] BUKOWSKA A, NIKONOVA Y, WOLKE C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of endothelin receptor blockade in left atrial tissue of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022;42:101088. [5] ANJUM A, YAZID MDI, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, multimolecular interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533. [6] WANG N, YU H, SONG Q, et al. Sesamol-loaded stearic acid-chitosan nanomicelles mitigate the oxidative stress-stimulated apoptosis and induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines in motor neuronal of the spinal cord through NF-ĸB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;186:23-32. [7] HAYDEN MS, GHOSH S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008; 132(3):344-362. [8] YU H, LIN L, ZHANG Z, et al. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020; 5(1):209. [9] JIMI E, FEI H, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB signaling regulates physiological and pathological chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275. [10] 索宗武,魏凯欣,徐依,等.天然产物通过调控神经炎症改善阿尔茨海默病的研究进展[J].中草药,2023,54(7):2284-2300. [11] DING Y, CHEN Q. The NF-κB Pathway: a focus on inflammatory responses in spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(9):5292-5308. [12] MUKHAMEDSHINA YO, AKHMETZYANOVA ER, MARTYNOVA EV, et al. Systemic and local cytokine profile following spinal cord injury in rats: a multiplex analysis. Front Neurol. 2017;8:581. [13] LIU H, ZHANG J, XU X, et al. SARM1 promotes neuroinflammation and inhibits neural regeneration after spinal cord injury through NF-κB signaling. Theranostics. 2021;11(9):4187-4206. [14] TANG R, BOTCHWAY BOA, MENG Y, et al. The inhibition of inflammatory signaling pathway by secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor can improve spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40(7):1067-1073. [15] SEN R, BALTIMORE D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986;46(5):705-716. [16] SHAKHOV AN, COLLART MA, VASSALLI P, et al. Kappa B-type enhancers are involved in lipopolysaccharide-mediated transcriptional activation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha gene in primary macrophages. J Exp Med. 1990;171(1):35-47. [17] BETHEA JR, CASTRO M, KEANE RW, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation. J Neurosci. 1998;18(9):3251-3260. [18] KIM H, SEO JY, KIM KH. NF-kappaB and cytokines in pancreatic acinar cells. J Korean Med Sci. 2000;15 Suppl(Suppl):S53-S54. [19] BRAMBILLA R, BRACCHI-RICARD V, HU WH, et al. Inhibition of astroglial nuclear factor kappaB reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Exp Med. 2005;202(1):145-156. [20] PAN YD, GUO QL, WANG E, et al. Intrathecal infusion of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate for the prevention and reversal of neuropathic pain in rats using a sciatic chronic constriction injury model. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010;35(3):231-237. [21] CHEN S, YE J, CHEN X, et al. Valproic acid attenuates traumatic spinal cord injury-induced inflammation via STAT1 and NF-κB pathway dependent of HDAC3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):150. [22] JIANG Z, ZENG Z, HE H, et al. Lycium barbarum glycopeptide alleviates neuroinflammation in spinal cord injury via modulating docosahexaenoic acid to inhibiting MAPKs/NF-kB and pyroptosis pathways. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):770. [23] LEY K, HOFFMAN H M, KUBES P, et al. Neutrophils: new insights and open questions. Sci Immunol. 2018;3(30):eaat4579. [24] MAHESHWARI S, DWYER LJ, SÎRBULESCU RF. Inflammation and immunomodulation in central nervous system injury-B cells as a novel therapeutic opportunity. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;180:106077. [25] HUANG Y, ZHU N, CHEN T, et al. Triptolide suppressed the microglia activation to improve spinal cord injury through miR-96/IKKβ/NF-κB pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(12):E707-E714. [26] LIDDELOW SA, MARSH SE, STEVENS B. Microglia and astrocytes in disease: dynamic duo or partners in crime? Trends Immunol. 2020;41(9):820-835. [27] VEREMEYKO T, YUNG AWY, DUKHINOVA M, et al. The role of neuronal factors in the epigenetic reprogramming of microglia in the normal and diseased central nervous system. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:453. [28] WANG L, PEI S, HAN L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce a1 astrocytes via downregulation of phosphorylated NFκB P65 subunit in spinal cord injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1535-1559. [29] SONG L, ZHANG J, MA D, et al. A bibliometric and knowledge-map analysis of macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis from 2001 to 2021. Front Immunol. 2022;13:910444. [30] 周金萍,罗程,李海燕,等.德昂酸茶水提物对小鼠RAW264.7巨噬细胞抗炎作用的研究[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2023,38(3): 431-438. [31] LI M, RONG ZJ, CAO Y, et al. Utx regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway of natural stem cells to modulate macrophage migration during spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(3):353-364. [32] QIN F, ZHANG H, LIU A, et al. Analgesic effect of zanthoxylum nitidum extract in inflammatory pain models through targeting of ERK and NF-κB signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:359. [33] LIU Z, YAO X, SUN B, et al. Pretreatment with kaempferol attenuates microglia-mediate neuroinflammation by inhibiting MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;168:142-154. [34] HAN SH, LEE JH, WOO JS, et al. Myricetin induces apoptosis and autophagy in human gastric cancer cells through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Heliyon. 2022;8(5):e09309. [35] 李驰,郭中华,杨锐,等.杨梅素调控NF-κB和MAPK信号通路对大鼠脊髓损伤的保护作用研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2020,37(11): 1980-1986. [36] WANG C, GAO Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Safflower yellow alleviates osteoarthritis and prevents inflammation by inhibiting PGE2 release and regulating NF-κB/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine. 2020;78:153305. [37] WANG L, BOTCHWAY BOA, LIU X. The repression of the HMGB1-TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway by safflower yellow may improve spinal cord injury. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:803885. [38] 王大伟,胡培,吴迎爽,等.红花黄素对脊髓损伤大鼠的保护作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(6):1313-1319. [39] ZHU Y, ZHU H, WANG Z, et al. Wogonoside alleviates inflammation induced by traumatic spinal cord injury by suppressing NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(4):3304-3308. [40] LIU YW, LIU XL, KONG L, et al. Neuroprotection of quercetin on central neurons against chronic high glucose through enhancement of Nrf2/ARE/glyoxalase-1 pathway mediated by phosphorylation regulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:2145-2154. [41] 王业杨,李贵涛,王明森,等.槲皮素抑制TLR4/NF-κB通路介导的炎症反应减轻脊髓损伤[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(14):1311-1316. [42] TAYSI S, ALGBURI FS, TAYSI ME, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester: a review on its pharmacological importance, and its association with free radicals, COVID-19, and radiotherapy. Phytother Res. 2023;37(3):1115-1135. [43] KASAI M, FUKUMITSU H, SOUMIYA H, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester reduces spinal cord injury-evoked locomotor dysfunction. Biomed Res. 2011;32(1):1-7. [44] AKGUN B, OZTURK S, ARTAS G, et al. Effects of intrathecal caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on IL-6 and TNF-α levels and local inflammatory responses in spinal cord injuries. Turk Neurosurg. 2018;28(4):625-629. [45] GAO J, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al. Triptolide: pharmacological spectrum, biosynthesis, chemical synthesis and derivatives. Theranostics. 2021;11(15):7199-7221. [46] KONG FG, JIANG X, WANG R, et al. “Forsythoside B attenuates memory impairment and neuroinflammation via inhibition on NF-κB signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):305. [47] XIA M, ZHANG Y, WU H, et al. Forsythoside B attenuates neuro-inflammation and neuronal apoptosis by inhibition of NF-κB and p38-MAPK signaling pathways through activating Nrf2 post spinal cord injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109120. [48] CHEN L, LI M, YANG Z, et al. Gardenia jasminoides Ellis: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological and industrial applications of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;257:112829. [49] NAM KN, CHOI YS, JUNG HJ, et al. Genipin inhibits the inflammatory response of rat brain microglial cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010;10(4):493-499. [50] LI Y, QIU H, YAO S, et al. Geniposide exerts protective effects on spinal cord injury in rats by inhibiting the IKKs/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108158. [51] LI L, JIANG M, LI Y, et al. 1H-NMR metabolomics analysis of the effect of rubusoside on serum metabolites of golden hamsters on a high-fat diet. 2020;25(6):1274. [52] 杨爽,董明鑫,姜新,等.甜叶悬钩子苷通过NF-κB和MAPK信号通路抑制小鼠神经炎症细胞模型炎症反应[J].中国病理生理杂志,2023, 39(4):616-622. [53] 周彬彬,郑雪蕊,谢志扬,等.红景天苷对LPS诱导的脑内炎症反应的抑制作用机制研究[J].中国药理学通报,2023,39(11):2096-2101. [54] 陈剑平,廖祥萍,李正南,等.芍药苷基于IKK/NF-κB信号通路对大鼠脊髓损伤后继发性损害的保护作用[J].广东医学,2019,40(18):2578-2582. [55] SHARMA N, NEHRU B. Curcumin affords neuroprotection and inhibits α-synuclein aggregation in lipopolysaccharide-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Inflammopharmacology. 2018;26(2):349-360. [56] YUAN J, ZOU M, XIANG X, et al. Curcumin improves neural function after spinal cord injury by the joint inhibition of the intracellular and extracellular components of glial scar. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):235-245. [57] 李建设,何文龙,孟珂,等.姜黄素对LPS诱导的大鼠星形胶质细胞NF-κB炎症因子信号通路的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(5):1081-1085. [58] FAN R, ZHANG Y, BOTCHWAY BOA, et al. Resveratrol can attenuate astrocyte activation to treat spinal cord injury by inhibiting inflammatory responses. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(11):5799-5813. [59] BREUSS JM, ATANASOV AG, UHRIN P. Resveratrol and its effects on the vascular system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1523. [60] WU J, CHEN H, GUO T, et al. Sesamol alleviates manganese-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment via regulating the microglial cGAS-STING/NF-κB pathway. Environ Pollut. 2023;319:120988. [61] LV X, ZHANG M, YU S, et al. Antiviral and virucidal activities of lycorine on duck tembusu virus in vitro by blocking viral internalization and entry. Poult Sci. 2021;100(10):101404. [62] 抗晶晶,曹翔.石蒜碱通过TLR4/NF-κB途径抑制LPS诱导的原代小胶质细胞炎症反应[J].天津医药,2022,50(9):897-901. [63] ZHANG L, LU X, GONG L, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine protects blood-spinal cord barrier integrity by modulating microglia polarization through activation of STAT3/SOCS3 and inhibition of NF-кB signaling pathways in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41(4):717-731. [64] 张厚君,蒋昇源,邓博文,等.川芎嗪改善脊髓损伤模型大鼠炎性微环境的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(11):1701-1707. [65] 肖志满,胡建中,吕红斌,等.川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后巨噬细胞移动抑制因子表达的影响[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2012,37(10):1031-1036. [66] ZHI J, DUAN B, PEI J, et al. Daphnetin protects hippocampal neurons from oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3): 4132-4139. [67] 吴军,关涛,田峰,等.瑞香素对脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能改善作用的TRL4/NF-κB信号通路机制研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2021,31(4):84-90. |
| [1] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [4] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [5] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [6] | Su Xiaoyang, Chen Wenting, Fu Yidan, Zhao Yan, Lan Danfeng, Yang Qiuping. Correlation between Mer receptor tyrosine kinase and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1593-1599. |
| [7] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [8] | Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617. |
| [9] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [10] | Jing Ruyi, Chen Yingxin, Cao Lei . Prognosis of deep lamellar keratoplasty versus penetrating keratoplasty in the treatment of stromal corneal dystrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1626-1633. |
| [11] | Wang Xuanqiang, Zhang Wenyang, Li Yang, Kong Weiqian, Li Wei, Wang Le, Li Zhongshan, Bai Shi. Effects of chronic exposure to low-frequency pulsed magnetic fields on contractility and morphology of the quadriceps muscle in healthy adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1634-1642. |
| [12] | Zhang Yuxin, Yu Cong, Zhang Cui, Ding Jianjun, Chen Yan. Differences in postural control ability between older adults with mild cognitive impairment and those with normal cognition under different single-task and dual-task conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1643-1649. |
| [13] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [14] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [15] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||