Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 5425-5431.doi: 10.12307/2024.826
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of time-restricted diet on infrapatellar fat pad in high-fat diet-induced obese rats and relevant mechanisms
Ding Yukun, Zhu Cuiling, Zhang Xiaodong
- Department of Medical Imaging, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-23Accepted:2024-01-09Online:2024-12-08Published:2024-03-14 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaodong, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Medical Imaging, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Ding Yukun, Master, Department of Medical Imaging, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81801653 (to ZXD); General Project of President’s Foundation of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, No. YM2021012 (to ZXD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ding Yukun, Zhu Cuiling, Zhang Xiaodong. Effect of time-restricted diet on infrapatellar fat pad in high-fat diet-induced obese rats and relevant mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5425-5431.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

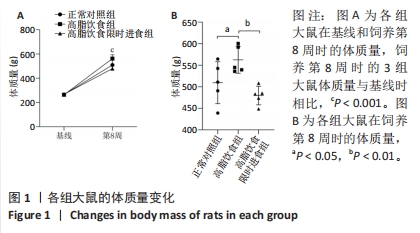
2.3 各组大鼠脂肪组织PDFF值变化 饲养第8周时,3组间髌下脂肪垫的PDFF值的差异有显著性意义(F=14.19,P < 0.001),见图2A,3A,多重比较发现高脂饮食组大鼠髌下脂肪垫的PDFF明显大于正常对照组(P < 0.001)和高脂饮食限时进食组(P=0.004),并且高脂饮食限时进食组髌下脂肪垫的PDFF值明显大于正常对照组(P=0.042)。然而,3组间皮下脂肪组织的PDFF值差异无显著性意义,见图2B,3B。此外,3组大鼠髌下脂肪垫的PDFF(43.82%-66.88%)均明显小于皮下脂肪组织的PDFF(91.53%-99.55%,F=619.45,P < 0.001)。"


PDFF测量值的可靠性和一致性分析结果显示,同一观察者2次测量脂肪组织PDFF值的组内相关系数ICC=0.989(95%CI:0.981-0.994,P < 0.001);观察者间测量脂肪组织PDFF的组内相关系数ICC=0.986(95%CI:0.987-0.996,P < 0.001)。 2.4 各组大鼠血清脂肪因子水平 如图4所示,饲养第8周时,3组间大鼠的血清瘦素差异有显著性意义(F=4.54,P=0.034),正常对照组(P=0.030)和高脂饮食限时进食组(P=0.018)的血清瘦素水平明显低于高脂饮食组。此外,高脂饮食组的血清脂联素水平明显低于正常对照组(P=0.022);虽然高脂饮食限时进食组血清脂联素含量的平均值(P=0.231)高于高脂饮食组,但两组之间差异无显著性意义。"


2.5.3 瘦素在髌下脂肪垫中的表达 瘦素定位于脂肪细胞的胞质中,呈现棕黄色为阳性表达,所有切片染色背景清晰,阴性对照不着色。3组间的髌下脂肪垫瘦素相对表达水平差异有显著性意义(F=26.16,P < 0.001),高脂饮食组的髌下脂肪垫中瘦素相对表达明显高于正常对照组(P < 0.001)和高脂饮食限时进食组(P < 0.001),高脂饮食限时进食组的髌下脂肪垫中瘦素相对表达明显高于正常对照组(P=0.029),见图7A,B。 2.5.4 脂联素在髌下脂肪垫中的表达 脂联素定位于脂肪细胞的胞质中,呈现棕黄色为阳性表达,所有切片染色背景清晰,阴性对照不着色。高脂饮食组的髌下脂肪垫中脂联素相对表达明显低于正常对照组(P=0.011)和高脂饮食限时进食组(P=0.049),见图7A,B。 2.5.5 肿瘤坏死因子α在髌下脂肪垫中的表达 实验中所有大鼠的髌下脂肪垫中均未观察到肿瘤坏死因子α的阳性表达,见图7A。"

| [1] ELMALEH-SACHS A, SCHWARTZ JL, BRAMANTE CT, et al. Obesity management in adults: a review. JAMA. 2023;330(20):2000-2015. [2] BATUSHANSKY A, ZHU S, KOMARAVOLU RK, et al. Fundamentals of OA. An initiative of osteoarthritis and cartilage. Obesity and metabolic factors in OA. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(4):501-515. [3] COLLINS KH, LENZ KL, POLLITT EN, et al. Adipose tissue is a critical regulator of osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(1): e2021096118. [4] CHANG J, LIAO Z, LU M, et al. Systemic and local adipose tissue in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(7):864-871. [5] ZENG N, YAN ZP, CHEN XY, et al. Infrapatellar fat pad and knee osteoarthritis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5):1317-1328. [6] ZHOU S, MALEITZKE T, GEISSLER S, et al. Source and hub of inflammation: the infrapatellar fat pad and its interactions with articular tissues during knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(7):1492-1504. [7] BARBOZA E, HUDSON J, CHANG WP, et al. Profibrotic infrapatellar fat pad remodeling without m1 macrophage polarization precedes knee osteoarthritis in mice with diet-induced obesity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(6):1221-1232. [8] EYMARD F, PIGENET A, CITADELLE D, et al. Knee and hip intra-articular adipose tissues (IAATs) compared with autologous subcutaneous adipose tissue: a specific phenotype for a central player in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):1142-1148. [9] IOAN-FACSINAY A, KLOPPENBURG M. Osteoarthritis: Inflammation and fibrosis in adipose tissue of osteoarthritic joints. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(6):325-326. [10] GIBBS AJ, GRAY B, WALLIS JA, et al. Recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review of clinical practice guidelines. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023;31(10):1280-1292. [11] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578. [12] MESSIER SP, GUTEKUNST DJ, DAVIS C, et al. Weight loss reduces knee-joint loads in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(7):2026-2032. [13] HALL M, CASTELEIN B, WITTOEK R, et al. Diet-induced weight loss alone or combined with exercise in overweight or obese people with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;48(5):765-777. [14] JARAMILLO AP, CASTELLS J, IBRAHIMLI S, et al. Time-restricted feeding and intermittent fasting as preventive therapeutics: a systematic review of the literature. Cureus. 2023;15(7):e42300. [15] LIU D, HUANG Y, HUANG C, et al. Calorie restriction with or without time-restricted eating in weight loss. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(16): 1495-1504. [16] AOUICHAT S, CHAYAH M, BOUGUERRA-AOUICHAT S, et al. Time-restricted feeding improves body weight gain, lipid profiles, and atherogenic indices in cafeteria-diet-fed rats: role of browning of inguinal white adipose tissue. Nutrients. 2020;12(8):2185. [17] HATORI M, VOLLMERS C, ZARRINPAR A, et al. Time-restricted feeding without reducing caloric intake prevents metabolic diseases in mice fed a high-fat diet. Cell Metab. 2012;15(6):848-860. [18] CHAIX A, ZARRINPAR A, MIU P, et al. Time-restricted feeding is a preventative and therapeutic intervention against diverse nutritional challenges. Cell Metab. 2014;20(6):991-1005. [19] MEHUS AA, RUST B, IDSO JP, et al. Time-restricted feeding mice a high-fat diet induces a unique lipidomic profile. J Nutr Biochem. 2021;88: 108531. [20] ARBLE DM, BASS J, LAPOSKY AD, et al. Circadian timing of food intake contributes to weight gain. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;17(11): 2100-2102. [21] CHAIX A, MANOOGIAN ENC, MELKANI GC, et al. Time-restricted eating to prevent and manage chronic metabolic diseases. Annu Rev Nutr. 2019;39:291-315. [22] SUN K, TORDJMAN J, CLEMENT K, et al. Fibrosis and adipose tissue dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2013;18(4):470-477. [23] DEBARI MK, ABBOTT RD. Adipose tissue fibrosis: mechanisms, models, and importance. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6030. [24] HARASYMOWICZ NS, CLEMENT ND, AZFER A, et al. Regional differences between perisynovial and infrapatellar adipose tissue depots and their response to class II and class III obesity in patients with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(7):1396-1406. [25] LIU Y, LI Y, LIANG J, et al. The mechanism of leptin on inhibiting fibrosis and promoting browning of white fat by reducing ITGA5 in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12353. [26] DE GOEDE P, HELLINGS TP, COOPMANS TV, et al. After-effects of time-restricted feeding on whole-body metabolism and gene expression in four different peripheral tissues. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2020;28 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S68-S80. [27] OUCHI N, PARKER JL, LUGUS JJ, et al. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(2):85-97. [28] HUI W, LITHERLAND GJ, ELIAS MS, et al. Leptin produced by joint white adipose tissue induces cartilage degradation via upregulation and activation of matrix metalloproteinases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71(3):455-462. [29] CHEN TH, CHEN L, HSIEH MS, et al. Evidence for a protective role for adiponectin in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1762(8):711-718. [30] HARIRI N, THIBAULT L. High-fat diet-induced obesity in animal models. Nutr Res Rev. 2010;23(2):270-299. [31] JUNE RK, LIU-BRYAN R, LONG F, et al. Emerging role of metabolic signaling in synovial joint remodeling and osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(12):2048-2058. |
| [1] | Li Yongjie, Fu Shenyu, Xia Yuan, Zhang Dakuan, Liu Hongju. Correlation of knee extensor muscle strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters with peak knee flexion/adduction moment in female patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1354-1358. |
| [2] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [3] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [4] | Cheng Jie, Wang Jihong, Zhang Pei. Functional exercise for tendon adhesion in a model of deep flexor tendon II injury of the third toe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1161-1167. |
| [5] | Shen Jiangyong, He Xi, Tang Yuting, Wang Jianjun, Liu Jinyi, Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Xinyi, Liu Tong, Sun Haoyuan. RAS-selective lethal small molecule 3 inhibits the fibrosis of pathological scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1168-1173. |
| [6] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [7] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [8] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 499-504. |
| [9] | Hu Guangzhi, Lu Hongyan. Changes in pulmonary pericytes and tube formation of pulmonary vascular endothelial cells in mouse models of broncho-pulmonary dysplasia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 522-527. |
| [10] | Lou Xinqi, Zhong Hao, Wang Xiyu, Feng Haoyu, Li Pengcui, Wei Xiaochun, Wang Yanqin, Wu Xiaogang, Chen Weiyi, Xue Yanru. Possible mechanisms of multi-pathway biological effects of laser therapy for knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5521-5527. |
| [11] | Huang Keqi, Li Jiagen, Chen Shangtong, Rong Xiangbin. Mechanisms of long non-coding RNA in osteoarthritis and traditional Chinese medicine intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5571-5576. |
| [12] | Yu Guangwen, Xie Junjie, Liang Jiajian, Liu Wengang, Wu Huai, Li Hui, Hong Kunhao, Li Anan, Guo Haopeng. Role and significance of deep learning in intelligent segmentation and measurement analysis of knee osteoarthritis MRI images [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5382-5387. |
| [13] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Wang Xixi, Chen Xu. Autophagy, ferroptosis-related targets and renal function progression in patients with chronic kidney disease: bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5122-5129. |
| [14] | Ren Weiliang, Jiao Yongwei, Zhang Jian, Yang Liying, Yang Qi. Modulatory effect of resveratrol on oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in the joint fluid of rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5154-5158. |
| [15] | Hou Zengtao, Dong Zhiwei, Zhang Jinfeng, Yang Xiaohui, Fan Xiao. Platelet-rich fibrin regulates apoptosis to promote cartilage repair in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5167-5171. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||