Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 5413-5418.doi: 10.12307/2024.836
Effect of hydrogen-rich gas on proprioception and muscle endurance after high-intensity exercise
Dong Gengxin1, Li Yiting1, Hong Yinglu1, Bao Dapeng2
- 1School of Sport Medicine and Physical Therapy, 2China Institute of Sport and Health Science, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2023-11-16Accepted:2024-01-16Online:2024-12-08Published:2024-03-14 -
Contact:Bao Dapeng, Researcher, China Institute of Sport and Health Science, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Dong Gengxin, PhD candidate, School of Sport Medicine and Physical Therapy, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dong Gengxin, Li Yiting, Hong Yinglu, Bao Dapeng. Effect of hydrogen-rich gas on proprioception and muscle endurance after high-intensity exercise[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5413-5418.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
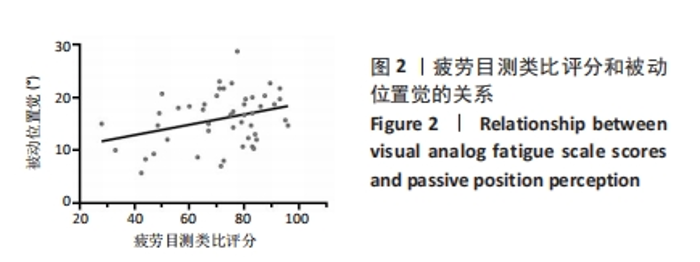
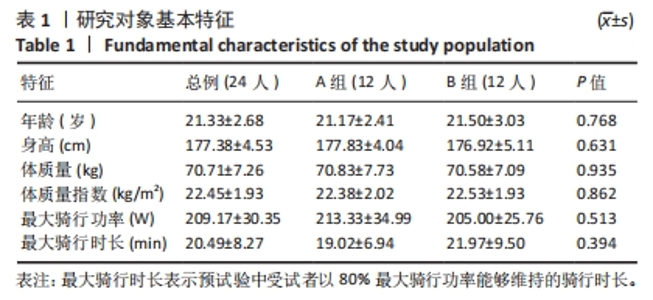
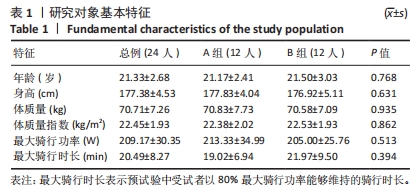
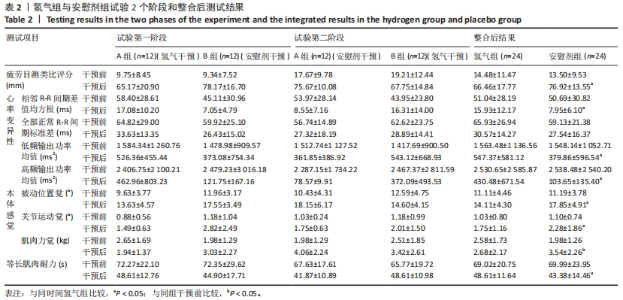
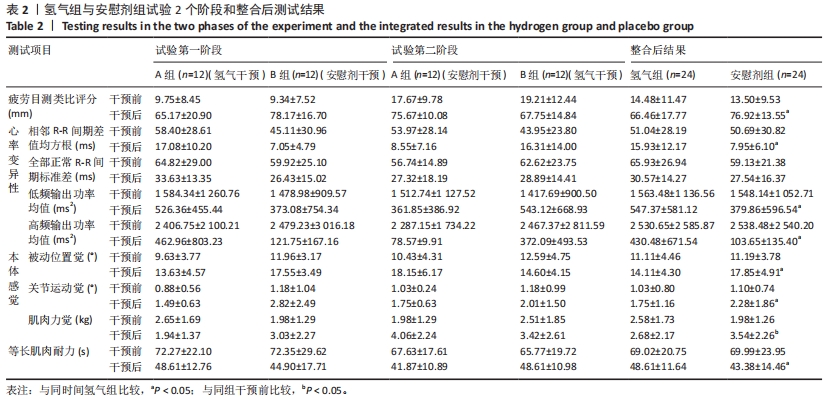
干预前,试验两个阶段的 A、B 组组间所有测试结果比较差异均无显著性意义 (P > 0.05)。在试验的第一阶段,干预后A组的疲劳目测类比评分有低于B组的趋势,相邻R-R 间期差值均方根、低频输出功率均值、高频输出功率均值和等长肌肉耐力值均有大于B组的趋势,被动位置觉、关节运动觉和肌肉力觉有优于B组的趋势。在试验的第二阶段,B组与A组干预后所有测试结果的差异趋势同试验的第一阶段。 2.4 整合后氢气组和对照组的测试结果 整合交叉前后2个阶段的结果,氢气组和安慰剂组所有干预前测试结果比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。 疲劳目测类比评分的交互效应显著(时间×组别)(F=9.395,P=0.005,偏η2=0.290)。组别的主效应显著(F=8.260,P=0.009,偏η2=0.264),时间的主效应显著(F=310.585,P < 0.001,偏η2=0.931)。干预后氢气组受试者疲劳目测类比评分显著低于安慰剂组(F=11.392,P=0.003,偏η2=0.331)。 相邻R-R间期差值均方根的交互效应不显著(时间×组别)(F=3.786,P=0.066,偏η2=0.159)。组别的主效应显著(F=4.654,P=0.043,偏η2=0.189),时间的主效应显著(F=50.463,P < 0.001,偏η2=0.716)。干预后氢气组受试者相邻R-R间期差值均方根显著高于安慰剂组(F=9.574,P=0.006,偏η2=0.324)。 全部正常R-R间期标准差的交互效应不显著(时间×组别)(F=0.710,P=0.409,偏η2=0.034)。组别的主效应不显著(F=2.460,P=0.132,偏η2=0.110),时间的主效应显著(F=55.080,P < 0.001,偏η2=0.734)。干预后氢气组和安慰剂组受试的全部正常R-R间期标准差比较差异无显著性意义(F=0.756,P=0.395,偏η2=0.036)。 低频输出功率均值的交互效应不显著(时间×组别)(F=0.349,P=0.561,偏η2=0.017)。组别的主效应不显著(F=0.429,P=0.520,偏η2=0.021),时间的主效应显著(F=28.761,P < 0.001,偏η2=0.590)。干预后氢气组受试者低频输出功率均值显著大于安慰剂组(F=7.783,P=0.011,偏η2=0.280)。 高频输出功率均值的交互效应不显著(时间×组别)(F= 0.941,P =0.344,偏η2=0.045)。组别的主效应不显著(F=0.796,P=0.383,偏η2=0.038),时间的主效应显著(F=17.380,P < 0.001,偏η2=0.465)。干预后氢气组受试者高频输出功率均值显著大于安慰剂组(F=5.198,P=0.034,偏η2=0.206)。 被动位置觉的交互效应显著(时间×组别)(F=9.158,P=0.006,偏η2=0.285)。组别的主效应不显著(F=3.303,P=0.082,偏η2=0.126),时间的主效应显著(F=57.047,P < 0.001,偏η2=0.713)。干预后氢气组受试者被动位置觉(与目标角度的差值)显著优于安慰剂组(F=7.905,P=0.010,偏η2=0.256)。 关节运动觉的交互效应不显著(时间×组别)(F=2.249,P=0.147,偏η2=0.089)。组别的主效应显著(F=5.987,P=0.022,偏η2=0.207),时间的主效应显著(F=25.288,P < 0.001,偏η2=0.524)。干预后氢气组受试者关节运动觉(与起始角度的差值)显著优于安慰剂组(F=4.355,P=0.048,偏η2=0.159)。 肌肉力觉的交互效应显著(时间×组别)(F=4.865,P=0.038,偏η2=0.175)。组别的主效应不显著(F=0.106,P=0.747,偏η2=0.005),时间的主效应显著(F=8.548,P=0.008,偏η2=0.271)。氢气组受试者干预前后的肌肉力觉(与目标力量的差值)比较差异无显著性意义(F=0.046,P=0.831,偏η2=0.002),安慰剂组受试者干预后的肌肉力觉显著差于干预前(F=14.675,P=0.001,偏η2=0.390)。 伸膝等长肌肉耐力的交互效应显著(时间×组别)(F=5.193,P=0.032,偏η2=0.184)。组别的主效应不显著(F=0.829,P=0.372,偏η2=0.035),时间的主效应显著(F=45.239,P < 0.001,偏η2=0.663)。干预后氢气组受试者等长肌肉耐力显著大于安慰剂组(F=5.197,P=0.032,偏η2=0.184)。 2.5 线性回归分析结果 对受试者干预后的疲劳状况(用疲劳目测类比评分指标代表)和本体感觉情况(用被动位置觉数据代表,即与目标角度的差值)进行线性回归分析。结果显示疲劳目测类比评分和被动位置觉显著相关(r=0.327,P=0.023),即在高强度运动后主观疲劳程度越高被动位置觉结果越差,见图2。"
| [1] 邹利民,毛丽娟,伍勰,等.疲劳与非预期效应对女子足球运动员侧切动作中膝关节生物力学的影响[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(7):14-21. [2] 张颖慧,丁昊阳,苏健蛟.运动性疲劳对横踢技术动作特征及其击打速度的影响研究[J].武汉体育学院学报,2020,54(6):87-94. [3] 岳文雨.运动性疲劳特征的研究综述[J].中国体育科技,2003,39(10):51-54. [4] WRIGHT CJ, ARNOLD BL. Fatigue’s effect on eversion force sense in individuals with and without functional ankle instability. J Sport Rehabil. 2012;21(2): 127-136. [5] 张秋霞,张林,王国祥.局部肌肉疲劳对踝关节本体感觉的影响[J].体育科学,2011,31(3): 68-73,80. [6] GERLACH KE, WHITE SC, BURTON HW, et al. Kinetic changes with fatigue and relationship to injury in female runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(4):657-663. [7] HIEMSTRA LA, LO IK, FOWLER PJ. Effect of fatigue on knee proprioception: implications for dynamic stabilization. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2001;31(10):598-605. [8] 颜天民,郭层城.我国竞技体操落地稳定性的现状与应重视的问题——析肌肉耐力对落地稳定性的影响[J].中国体育科技,1992(8):21-27,37,49. [9] OHSAWA I, ISHIKAWA M, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 2007;13(6):688-694. [10] OHTA S. Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;144(1):1-11. [11] OSTOJIC SM. Molecular hydrogen in sports medicine: new therapeutic perspectives. Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(4):273-279. [12] OSTOJIC SM. Hydrogen Gas as an Exotic Performance-Enhancing Agent: Challenges and Opportunities. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(5):723-730. [13] LEBARON TW, LAHER I, KURA B, et al. Hydrogen gas: from clinical medicine to an emerging ergogenic molecule for sports athletes 1. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;97(9):797-807. [14] AOKI K, NAKAO A, ADACHI T, et al. Pilot study: Effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water on muscle fatigue caused by acute exercise in elite athletes. Med Gas Res. 2012;2:12. [15] SHIBAYAMA Y, DOBASHI S, ARISAWA T, et al. Impact of hydrogen-rich gas mixture inhalation through nasal cannula during post-exercise recovery period on subsequent oxidative stress, muscle damage, and exercise performances in men. Med Gas Res. 2020;10(4):155-162. [16] DONG G, FU J, BAO D, et al. Short-Term Consumption of Hydrogen-Rich Water Enhances Power Performance and Heart Rate Recovery in Dragon Boat Athletes: Evidence from a Pilot Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(9):5413. [17] BOTEK M, KHANNA D, KREJČÍ J, et al. Molecular Hydrogen Mitigates Performance Decrement during Repeated Sprints in Professional Soccer Players. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):508. [18] HOLGADO D, TROYA E, PERALES JC, et al. Does mental fatigue impair physical performance? A replication study. Eur J Sport Sci. 2021;21(5):762-770. [19] BARZEGARPOOR H, AMOOZI H, RAJABI H, et al. The Effects of Performing Mental Exertion during Cycling Exercise on Fatigue Indices. Int J Sports Med. 2020;41(12):846-857. [20] LEE KA, HICKS G, NINO-MURCIA G. Validity and reliability of a scale to assess fatigue. Psychiatry Res. 1991;36(3):291-298. [21] 王兴泽,于杰,陈佩杰.基于心率变异性监测中医刮痧抗运动性疲劳的效果[J].上海体育学院学报,2021,45(7):76-83. [22] HEBISZ RG, HEBISZ P, ZATOŃ MW. Heart Rate Variability After Sprint Interval Training in Cyclists and Implications for Assessing Physical Fatigue. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(2):558-564. [23] 崔小珠,王人卫.应用心率变异性指标评价优秀耐力运动员机能状态研究进展[J].体育科学,2015,35(12):75-79+93. [24] 王大武,白定群,邵岚,等.下肢康复机器人训练对脑卒中偏瘫侧膝关节本体感觉的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(9):950-954. [25] 李玉周,胡英琪,李国平.本体感觉测试的敏感性角度指标选取研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(8):696-701. [26] PROSKE U. What is the role of muscle receptors in proprioception? Muscle Nerve. 2005;31(6):780-787. [27] FORESTIER N, TEASDALE N, NOUGIER V. Alteration of the position sense at the ankle induced by muscular fatigue in humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(1):117-122. [28] JAVORAC D, STAJER V, RATGEBER L, et al. Short-term H2 inhalation improves running performance and torso strength in healthy adults. Biol Sport. 2019;36(4):333-339. [29] KOROVLJEV D, STAJER V, JAVORAC D, et al. Hydrogen inhalation positively affects cardiometabolic risk factors in men and women aged 65 years or older: a preliminary report. Eur Geriatr Med. 2018;9(5):729-730. [30] BLOOMER RJ. Effect of exercise on oxidative stress biomarkers. Adv Clin Chem. 2008;46: 1-50. [31] REID MB, HAACK KE, FRANCHEK KM, et al. Reactive oxygen in skeletal muscle. I. Intracellular oxidant kinetics and fatigue in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1992;73(5):1797-1804. [32] COOMBES JS, ROWELL B, DODD SL, et al. Effects of vitamin E deficiency on fatigue and muscle contractile properties. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2002;87(3):272-277. [33] GOLDFARB AH. Nutritional antioxidants as therapeutic and preventive modalities in exercise-induced muscle damage. Can J Appl Physiol. 1999;24(3):249-266. [34] EVANS WJ. Vitamin E, vitamin C, and exercise. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72(2 Suppl):647S-652S. [35] FINAUD J, LAC G, FILAIRE E. Oxidative stress : relationship with exercise and training. Sports Medicine (Auckland, N.Z.). 2006;36(4):327-358. [36] POWERS SK, DEMINICE R, OZDEMIR M, et al. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Friend or foe? J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5):415-425. [37] PEDERSEN J, LÖNN J, HELLSTRÖM F, et al. Localized muscle fatigue decreases the acuity of the movement sense in the human shoulder. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31(7):1047-1052. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Zhang Xihui, Li Zhengrong, Li Shineng, Xing Zengyu, Wang Jiao. Effect of rehabilitation training guided by Pro-kin balance system on proprioception and balance function of the affected knee after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1259-1264. |
| [3] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [4] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [5] | Wang Yueguang, Mu Xiaohong, Jiang Shengyuan, Deng Bowen, Kang Ximei, Su Jianguang. Correlation between early serum markers and AISA grading in patients with acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5494-5499. |
| [6] | Ren Weiliang, Jiao Yongwei, Zhang Jian, Yang Liying, Yang Qi. Modulatory effect of resveratrol on oxidative stress and inflammatory factors in the joint fluid of rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5154-5158. |
| [7] | Song Wenxue, Liao Yidong, Ming Jiang, He Longcai, Chen Guangtang, Chen Chen, Wang Zili, Xiong Mingsong, Cui Junshuan, Xu Kaya. Intracranial transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates rat brain ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5036-5041. |
| [8] | Li Yue, Qiao Hua. miRNA derived from mesenchymal stem cells and its derivatives in treatment of pathological scar [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5042-5047. |
| [9] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Effect of gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel loaded with salvianolic acid B on intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 380-386. |
| [10] | Qian Longjie, Su Wenli, Zhu Wenxian, Wang Yixin. SRT1720, an activator of silent information regulator 1, alleviates acute traumatic brain injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4447-4454. |
| [11] | Zhou Minghan, Zhang Hui, Zheng Xianbo, Xu Wuji. Significance of PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway expression in nucleus pulposus cells at different oxygen concentrations in delaying intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4491-4497. |
| [12] | Chen Chen, Zheng Runquan, Zhang Guichun. Effects of emodin on the proliferation, apoptosis and oxidative stress of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4528-4534. |
| [13] | Ma Jianglei, Zhang Huijie, Zhang Chenfang, Yang Xitong, Cheng Jianjie, Wang Guangming. Neuroprotective mechanism by which fenofibrate regulates superoxide dismutase 2 expression in transgenic C57BL/6J mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4547-4552. |
| [14] | Liu Xu, Chen Bo, Ning Ke, Chen Xiaohong. Mechanism and potential of vitamin C supplementation in sarcopenia prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4405-4412. |
| [15] | Kong Jianda, Xie Yingao, Ma Wen, Liu Youhan, Wang Qinglu. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease and the potential ameliorative effects of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4413-4420. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||