Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (27): 4413-4420.doi: 10.12307/2024.558
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease and the potential ameliorative effects of exercise
Kong Jianda1, Xie Yingao2, Ma Wen3, Liu Youhan3, Wang Qinglu3
- 1School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China; 2Clinical Medical College, Jining Medical University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China; 3Sports Science Research Institute, Shandong Sport University, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-07Accepted:2023-11-06Online:2024-09-28Published:2024-01-29 -
Contact:Wang Qinglu, PhD, Professor, Sports Science Research Institute, Shandong Sport University, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Kong Jianda, Master candidate, School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China Xie Yingao, Master candidate, Clinical Medical College, Jining Medical University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Special Funds for Central Guiding Local Science and Technology Development, No. YDZX2022091 (to WQL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Kong Jianda, Xie Yingao, Ma Wen, Liu Youhan, Wang Qinglu. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease and the potential ameliorative effects of exercise[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4413-4420.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
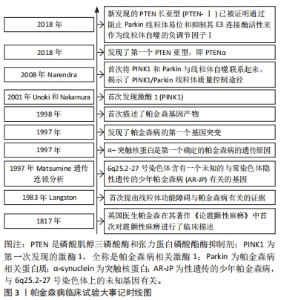
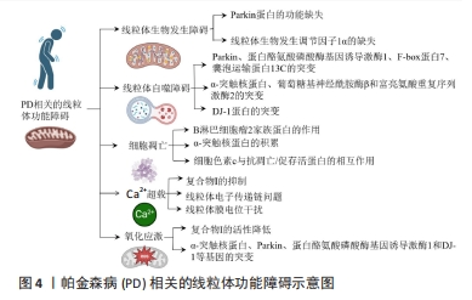
2.1 帕金森病概述及其病理机制 衰老是帕金森病等神经退行性疾病的最大危险因素,易造成运动功能障碍、肌肉僵硬和震颤等不良事件,其发病机制涉及多个方面,包括线粒功能障碍导致[1-2,5-6]。衰老使线粒体更易受到环境危险因素的影响,线粒体功能障碍的可能性增加[2,5]。研究证明,帕金森病患者的线粒体功能存在障碍,包括线粒体呼吸链的紊乱、线粒体自噬减少和线粒体DNA的突变等问题[1,3,7],这些线粒体功能异常引发了细胞氧化应激和细胞凋亡过程,进而导致多巴胺能神经元的死亡和帕金森病的临床症状[3,5-7]。 2.2 帕金森病相关的线粒体功能障碍 图3展示了关于PTEN、PINK1和Parkin与帕金森病相关的重要发现和突破。在1983年,Langston团队首次提出了线粒体功能障碍与帕金森病之间的关联。1997年,Matsumine团队通过遗传连锁分析确定了与性遗传少年帕金森病(AR-JP)相关的基因位点。同年,帕金森病的第一个基因突变也被发现。在1998年,第一个确定的帕金森病遗传原因被发现,即α-突触核蛋白。在2001年,帕金森病相关激酶1 (PINK1)被首次发现,并被发现与帕金森病相关。在2008年,Narendra团队首次将PINK1和Parkin与线粒体自噬联系起来,揭示了PINK1/Parkin线粒体质量控制途径的重要性。2018年新发现的PTEN长亚型(PTEN-Ⅰ)被证明通过阻止Parkin线粒体易位和抑制其E3连接酶活性作为线粒体自噬的负调节因子。此外,2018年还发现了第一个PTEN亚型,即PTENα。通过这些关键发现和突破,可以对帕金森病的病理机制和潜在治疗目标有更深入的了解,这些发现为帕金森病的发展提供了新的研究方向和条件,并为开发更有效的治疗方法提供了新的思路。"

2.2.1 帕金森病相关的线粒体生物发生障碍 线粒体生物发生是一个关键的细胞过程,涉及协调转录、翻译、核编码成分的输入,以及线粒体基因的表达,这些基因用于生成新的线粒体[8]。然而,线粒体生物发生受到Parkin蛋白的重要调控。Parkin蛋白通过诱导Parkin蛋白相互作用底物的蛋白酶体降解,Parkin蛋白相互作用底物在这一过程中充当过氧化物酶体增殖物激活线粒体生物发生调节因子1α的转录抑制因子[9]。线粒体生物发生调节因子1α是促进线粒体生物发生的关键分子,并在特发性帕金森病的病理机制中扮演关键角色[10]。研究表明,在没有Parkin蛋白的情况下,Parkin蛋白相互作用底物结合到线粒体生物发生调节因子1α基因启动子并抑制其表达[11],这说明Parkin的功能缺失会导致Parkin蛋白相互作用底物的积累,进而抑制线粒体生物发生过程。另外,Parkin蛋白相互作用底物在多巴胺神经元黑质致密部中高度表达。研究表明,临时的Parkin基因缺失导致多巴胺神经元的进行性退化,这一过程依赖于Parkin蛋白相互作用底物的表达[12],且Parkin蛋白相互作用底物的过度表达亦导致了黑质致密部中线粒体生物发生调节因子1α的表达减少以及多巴胺神经元的选择性死亡[12-13]。 综合而言,Parkin功能的缺失通过Parkin蛋白相互作用底物的积累抑制了线粒体的生物发生过程,这不仅对细胞功能产生了负面影响,还对神经元的健康产生了不利影响。然而,尚有一些问题需要进一步研究,例如具体的分子机制以及如何在临床上干预这一过程,以帮助治疗特发性帕金森病。 2.2.2 帕金森病相关的线粒体自噬障碍 通过自噬过程,复杂的分子信号能够从细胞中识别和有选择地清除受损的线粒体,这被称为线粒体自噬[14]。PICKRELL等[15]认为,线粒体自噬的减少是导致帕金森病患者出现脑区病理异质性和选择性易感性的主要原因。另外,Parkin和蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1的突变是导致早发性帕金森病的两个重要因素,这种突变遵循常染色体隐性遗传模式[16],这种遗传性突变形式强调了线粒体自噬在疾病发展中的重要性。 F-box蛋白7是一个适配器蛋白,属于E3-泛素连接酶复合物,负责蛋白质的泛素化降解和非降解,其在线粒体中具有多种功能,并且可能通过与蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1和Parkin相互作用来影响线粒体自噬[17],这说明线粒体自噬具有复杂性,受到多种因素影响。另外,囊泡运输蛋白13C的一部分位于线粒体外膜上,其突变亦与导致早发性帕金森病的常染色体隐性遗传有关。如果这一部分蛋白缺失,会导致线粒体电位差降低、代谢异常以及线粒体形态发生变化[18]。另外,囊泡运输蛋白13 C还被认为参与调节线粒体自噬,与Parkin和蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1共同发挥作用[19]。 α-突触核蛋白、葡萄糖基神经酰胺酶β和富亮氨酸重复序列激酶2的突变等亦和线粒体功能障碍密切相关,这些突变可能对自噬过程产生增强或损害作用[20]。其中,WALTER等[21]对富亮氨酸重复序列激酶2突变的细胞进行研究,发现线粒体片段数量增加,且膜电位差减少。另外,初级神经元中线粒体的清除可能是由富亮氨酸重复序列激酶2突变患者纤维细胞中线粒体钙摄取增强、电位差下降和钙紊乱引发的[22]。这表明,富亮氨酸重复序列激酶2突变与线粒体功能异常有关,但尚不清楚富亮氨酸重复序列激酶2突变如何导致线粒体数量增加和膜电位差减少以及其与线粒体钙摄入增强、电位差下降和钙离子紊乱之间的具体关系。另外,磷酸化的动力相关蛋白1在富亮氨酸重复序列激酶2突变中亦会促进线粒体分裂和过度自噬[23]。 帕金森病蛋白,又称DJ-1,其突变罕见且通常表现为隐性家族性帕金森病[24]。DJ-1的变化通过激活蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1/Parkin途径,产生活性氧,进而提高线粒体自噬水平[25]。然而,目前尚不清楚DJ-1的积累是通过蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1/Parkin信号途径还是独立的功能来调节线粒体功能。另外,甾醇调节元件结合蛋白1与帕金森病风险相关,亦能够影响线粒体自噬[26]。另外,心磷脂是一种特异于线粒体内膜的脂质,在蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1突变体中,其增强表现得更加明显[27]。而神经元的表达突变α-突触核蛋白则显示出线粒体碎片和线粒体外膜中暴露的心磷脂,这会引发线粒体自噬[28]。α-突触核蛋白在路易体的主要组成部分,并会在线粒体膜中积累[29]。另外,心磷脂与多巴胺一起有助于形成含有α-突触核蛋白和细胞色素c的路易体样复合物,这可能有助于阻止受损神经线粒体的凋亡信号传递[30]。这些证据表明,心磷脂与增强线粒体自噬、α-突触核蛋白积累和路易体样复合物的形成有关,但对其具体作用机制的认识仍有待完善。 综上所述,虽然当前研究主要集中在探索线粒体自噬与帕金森病发病机制的关联以及相关蛋白的功能和变化如何影响这一过程,但线粒体自噬在帕金森病中的调控网络仍不清楚,需要进一步研究来揭示线粒体自噬与其他遗传突变和相关疾病因素之间的关系。 2.2.3 帕金森病相关的细胞凋亡 在帕金森病的黑质致密部位,可能出现线粒体依赖的凋亡通路激活,这对于多巴胺神经退行性变发挥着重要的作用[31]。这一通路包括多个关键步骤[32]:①增强活性氧生成导致细胞色素c释放到细胞质;②线粒体外膜通透性增加激活caspase-9和caspase 3;③三磷酸腺苷的耗竭。另外,在线粒体介导的细胞凋亡中,主要外膜蛋白的通透性通常被认为是不可逆的[32]。因此,Bcl-2家族蛋白在调控这些主要外膜蛋白方面发挥着至关重要的作用,这一家族包括抗凋亡蛋白(如Bcl-2和B细胞淋巴瘤-XL)、促凋亡蛋白(如Bcl-2相关X蛋白和促凋亡蛋白BAK),以及仅包含BH3结构域的蛋白[32]。其中,Bcl-2相关X蛋白和促凋亡蛋白BAK在线粒体外膜内形成通道,导致通透性增加,与此同时,Bcl-2蛋白能够结合Bcl-2相关X蛋白和促凋亡蛋白BAK,进而减少线粒体外膜通透性的增加[32]。这说明Bcl-2相关X蛋白等促凋亡蛋白在外膜蛋白中发挥关键作用,但其中的确切机制仍然存在争议,特别是关于其如何转位和插入线粒体膜,以及如何引发线粒体外膜通透性增加的机制,这需要进一步研究。另外,细胞色素c在caspase激活中起着重要作用。细胞色素c释放到细胞质中时能够引发线粒体介导的细胞凋亡[33]。多项证据表明,细胞色素c结合到caspase适配器分子Apaf-1会形成多聚Apaf-1/细胞色素c复合物,该复合物进一步吸引了caspase-9,进而形成凋亡体[31-32,34]。然而,尚然不清楚细胞色素c与抗凋亡/促存活蛋白之间的具体互作机制,以及其如何诱导线粒体介导的细胞凋亡。 α-突触核蛋白与线粒体之间亦存在相互作用。研究表明,α-突触核蛋白存在于线粒体内膜上,并具有高度亲和力,其寡聚化和聚集会导致复合体I活性的降低,并减少三磷酸腺苷的产生,进而引发内膜去极化,导致细胞色素c等线粒体凋亡因子会被释放到细胞质中,细胞色素c进入细胞质后与抗凋亡蛋白和促存活蛋白相互作用,最终促使线粒体介导的细胞凋亡的发生[35]。然而,关于α-突触核蛋白对线粒体寡聚化和聚集如何导致复合体Ⅰ活性下降以及线粒体功能受损的具体机制仍然不明确,需进一步研究。 总之,线粒体依赖的凋亡通路在帕金森病的发病机制中扮演着关键角色,但仍存在许多不明确的细节,包括Bcl-2相关X蛋白等促凋亡蛋白的确切机制、细胞色素c与抗凋亡/促存活蛋白之间的互作机制以及α-突触核蛋白与线粒体相互作用的分子细节。这需要进一步的研究来深入探讨其在帕金森病中的作用和意义。 2.2.4 帕金森病相关的Ca2+超载 线粒体的功能障碍和帕金森病的兴奋性毒性密切相关。一个关键方面是降低细胞的三磷酸腺苷水平[36],例如,复合物Ⅰ的抑制会妨碍能量和ATP的生成,导致部分神经元去极化,并减少Na+/K+-ATP的活性[36],这一过程是帕金森病发展的关键机制。 另一方面,线粒体在调节细胞内Ca2+浓度方面发挥着重要作用。线粒体膜电位上的Ca2+单转运体起关键作用,能够快速吸收细胞质中的Ca2+。然而,当线粒体的电子传递链功能出现问题时,活性氧会产生,并对线粒体膜造成损害,破坏Ca2+的吸收和储存机制。这进一步导致细胞内Ca2+水平上升,加剧了兴奋性毒性的严重程度[37]。此外,干扰了线粒体膜电位还会增加对Ca2+超载的敏感性,进一步加剧了这一过程[38]。 因此,线粒体驱动的兴奋性毒性在帕金森病的发展中起着重要作用。然而,如何精确调节线粒体功能以减轻帕金森病的兴奋性毒性,以及如何更有效地干预这些机制以改善帕金森病的病情,仍需要进一步研究。 2.2.5 帕金森病相关的氧化应激 除了线粒体功能障碍,帕金森病还涉及到氧化应激的问题。复合物Ⅰ在线粒体呼吸链中扮演着重要角色,其活性降低与帕金森病的发病密切相关[38-40]。复合物Ⅰ的抑制不仅会降低三磷酸腺苷的合成,还会增加活性氧的产生,进而导致呼吸衰竭和氧化应激的发生[40]。复合物Ⅰ的部分抑制也会进一步增加线粒体产生活性氧的能力,形成一个恶性循环[41]。然而,目前对复合物Ⅰ活性降低的具体机制尚不清楚,需要进一步的研究。α-突触核蛋白、Parkin、蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1和DJ-1等基因的突变也与帕金森病相关的氧化应激密切相关[42]。研究发现,在多巴胺神经元中,α-突触核蛋白的积累会降低复合物Ⅰ的活性,增加活性氧的产生,并导致神经元的丧失[43]。α-突触核蛋白的聚集也会增加多巴胺神经元的线粒体氧化应激[44]。在少突胶质细胞中,氧化应激会增加细胞外α-突触核蛋白的积累和摄取,进而增加多巴胺的毒性[45]。此外,WOOD-KACZMAR等[46]认为,蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1的基因缺失会导致活性氧产生增加和细胞膜电位降低。在反应性星形胶质细胞中的DJ-1重要蛋白,在氧化应激增加时也会得到增强[47-48]。然而,在散发性帕金森病中,反应性星形胶质细胞中DJ-1的过度表达可能会产生不利影响,干扰氧化应激对神经的保护作用,解除失衡反应并损害复合物Ⅰ,从而对神经功能造成干扰[49]。尽管这些研究揭示了多个蛋白基因突变与帕金森病相关氧化应激之间的关系,在氧化应激过程中这些蛋白的具体调节机制和相互作用仍需进一步研究。 综上所述,在帕金森病相关的氧化应激中,复合物Ⅰ活性降低和α-突触核蛋白的积累备受关注。然而,仍然对复合物Ⅰ活性降低的具体机制以及氧化应激和线粒体功能障碍之间的相互关系缺乏清晰的了解。对于α-突触核蛋白、Parkin、蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶基因诱导激酶1和DJ-1等在氧化应激过程中的具体调节机制和相互作用也需要进一步的研究。 2.3 运动对帕金森病相关线粒体功能障碍的潜在改善作用 前述内容详细回顾了与帕金森病相关的线粒体功能障碍,故了解如何解决这些问题至关重要。运动对于改善帕金森病相关的线粒体功能障碍有着潜在的积极影响,可作为一种潜在的解决策略。证据表明,运动能够通过激活不同的细胞内信号通路来促进线粒体的生物学发生,但这种影响可能取决于运动的强度水平。另外,运动还能够诱导线粒体自噬,以清除受损的线粒体,进而改善线粒体的质量和功能。运动还能够通过激活特定的分子机制影响线粒体的形状,以调控线粒体的形态。另外,运动还能够通过调节线粒体呼吸链的塑性来调节线粒体功能。运动还能够抑制氧化应激和炎症过程来改善线粒体功能。接下来的内容将详细回顾运动对帕金森病相关的线粒体功能障碍的潜在影响。 2.3.1 运动对线粒体生物发生的影响 运动能够对线粒体生物发生一定的改善作用,并以多种方式影响所有器官的线粒体动力学和功能[4]。然而,这些影响可能会受到运动强度的影响而有所不同。由于帕金森病不仅是一种神经疾病,也涉及肌肉病变和线粒体功能异常,因此有必要观察运动对大脑和骨骼肌中线粒体生物发生的影响。 已有研究表明,急性运动会激活多个与线粒体生物发生调节因子1α相关的信号通路,包括Ca2+钙调蛋白依赖性蛋白激酶、p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、AMP活化蛋白激酶和肿瘤抑制蛋白53信号通路,从而调控线粒体的生物发生[50]。具体而言,细胞质中Ca2+浓度的增加能够促进L6肌肉细胞中PPARγ共激活因子1α(Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α,PGC-1α)、核呼吸因子1、核呼吸因子2和线粒体转录因子A的表达增加[51],而p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路则通过增强PGC-1α启动子的活性来促进线粒体的生物发生[52]。然而,研究结果也显示,高强度的耐力训练可能会抑制骨骼肌线粒体的生物合成[53],这表明细胞质中Ca2+浓度的变化在线粒体生物发生中起着重要的调节作用,但高强度的运动可能会抑制线粒体的生物合成。此外,研究还发现p53参与调控线粒体生物发生[54]。研究证实,p53的缺失会降低线粒体的呼吸功能,并导致耐力下降[54-55],p53还通过调节线粒体的迁移和激活TFAM来破坏糖酵解和氧化途径之间的平衡[56]。另外,小鼠实验表明,运动有助于促进p53与其靶基因TFAM、SCO2基因、p53上调凋亡调控因子和Bcl-2相关X蛋白启动子的结合,但青年小鼠的骨骼肌自噬与线粒体有关基因对运动的响应比成年小鼠低[57],这表明年龄可能影响着这一机制。然而,该研究仅发现了年龄对运动改善线粒体生物发生的影响,对于不同训练强度对其差异性的认识仍不充分。 综上所述,运动对线粒体生物发生具有一定改善作用,并以多种方式影响所有器官的线粒体动力学和功能。已确认多个与线粒体生物发生调控相关的信号通路,但其间的相互作用及其对线粒体功能的影响仍不清楚。此外,年龄对运动改善线粒体生物发生的影响已有证据支持,但不同训练强度对其差异性的了解尚有限。表1中列出了相关研究对运动对线粒体生物发生的影响进行的调查。"

2.3.2 运动诱导线粒体自噬 运动能够诱导线粒体自噬并促进线粒体周转,有助于提高线粒体质量和功能[4,58]。骨骼肌的急性运动被证明可以激发自噬反应,而长期的运动训练则有助于引导线粒体自噬并清除受损的线粒体[53]。这些研究结果表明,运动对线粒体自噬系统产生积极效果,维持了线粒体的健康和功能,从而减轻了潜在的由线粒体引发的细胞损伤和疾病风险。 不同类型的运动对线粒体自噬的影响存在差异。许多研究显示,耐力训练可以提高骨骼肌中的线粒体自噬过程[59-61],这种影响通常是通过测量微管相关蛋白轻链3-Ⅱ与轻链3-Ⅰ比值来评价的。然而,这种评价方法可能存在一定的局限性,因为并未观察到p62蛋白的积累变化。另一项研究由KIM等[62]进行,发现耐力训练对老年肌肉产生了一系列影响,其中包括自噬相关基因7和Beclin-1的表达增加,以及溶酶体相关膜蛋白2A编码基因呈现相似的趋势。这表明耐力训练可能在老年人的肌肉中促进自噬,但需要进一步的研究来明确其影响。此外,运动能够维持细胞器(如Ca2+超载和三磷酸腺苷产生的细胞器)的纤维形态和超微结构,并通过再神经支配拯救了肌纤维的大小,并降低了与自噬和活性氧清除有关的基因的表达[63]。 然而,抗阻训练引起的自噬反应可能与耐力训练不同。OGBORN等[64]发现,在老年人进行了一次抗阻训练后,肌肉中微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ与轻链3-Ⅰ比例降低,而p62蛋白积累增加。另外,LUO等[65]对老年大鼠进行了为期6周的爬梯运动训练,发现大鼠肌肉中微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ与轻链3-Ⅰ比例降低,同时p62蛋白的丰度下降,但其他自噬标志物,如Beclin-1、自噬相关基因7和组织蛋白酶L的表达却呈上调趋势,这表明抗阻训练可能会随着年龄的增长而加速自噬,但具体的机制尚不清楚。 总的来说,运动对线粒体自噬有一定的影响,并有助于维持细胞的健康。然而,不同类型的运动可能会引起不同的自噬反应,因此需要进一步的研究来深入了解其机制和潜在益处。运动对帕金森病相关线粒体自噬潜在诱导作用相关的研究见表2。"

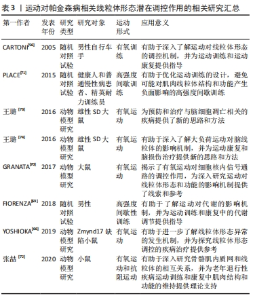
2.3.3 运动对线粒体形态的调控 帕金森病作为一种既涉及神经系统又涉及肌肉系统的疾病,线粒体形态的调控对其发病机制具有重要意义。虽然存在较少关于帕金森病患者脑组织中线粒体形态调控的研究,但通过研究与帕金森病相关的肌肉组织可以提供一些线索。运动是一种对肌肉产生积极影响的重要干预手段,而骨骼肌和心肌的运动对线粒体形态的调控已相对较多地得到研究。然而,需要进一步分析这些研究结果,以探究运动对脑组织中线粒体形态的影响。 运动能够通过激活特定的分子机制来影响线粒体形态[4]。例如,YOSHIOKA等[66]的研究发现,在快速糖酵解肌肉中,肌肉特异性基因Zmynd17在线粒体质量方面发挥了重要作用,而对其他肌肉类型中的调控机制尚未充分研究。一些研究表明,急性运动能够通过激活线粒体生物发生调节因子1α/雌激素相关受体α通路,增加骨骼肌中丝裂素的表达,并促进线粒体融合的过程[56]。此外,运动可以诱导线粒体生物发生调节因子1α的表达,过度表达这一因子会使线粒体更加致密,从而提高肌肉的耐力[67],这表明运动具有显著的积极作用,可以改善肌肉功能和体能水平。有研究还发现,不同的运动方案能够诱导线粒体融合的发生,并增加线粒体融合蛋白2的表达水平[68]。此外,在健康和中度活动的受试者中,进行运动后动力相关蛋白1和线粒体融合蛋白2的基因表达水平也会迅速增加[70-71],这些证据表明,线粒体在适应运动和提高体能方面起着关键作用。然而,急性运动以β-肾上腺素能依赖的方式减少线粒体裂变,这主要是由于动力相关蛋白1的失活[67]。运动还能够控制骨骼肌的裂变和融合过程,并影响Ca2+的处理。PLACE等[71]的研究发现,高强度间歇训练导致利亚诺定受体1碎片化,进而增加了细胞质中Ca2+的释放,这是急性运动的典型效应。此外,张喆等[72]的研究发现,在安静状态下,线粒体分裂蛋白1参与慢肌中线粒体的分裂并维持线粒体密度,而在混合肌中则保持正常的线粒体形态以防止线粒体肿胀。但在线粒体分裂蛋白1在力竭运动中维持骨骼肌内质网的正常形态并保护线粒体功能,从而维持小鼠的运动能力,这说明运动通过线粒体分裂蛋白1的调控来维持线粒体形态。然而,线粒体分裂蛋白1在不同肌肉类型和不同运动状态下对线粒体形态的调控机制尚不清楚。 此外,王璐等[73]的研究发现,进行4周的游泳训练前的运动预处理能够改变大鼠额叶线粒体的形态结构,增强其对运动性缺血缺氧的耐受力,并减轻了一次性力竭运动对大鼠额叶造成的缺血缺氧性损伤。另外,王璐等[73]的研究还发现,一次性高负荷游泳运动导致大鼠额叶神经元凋亡以及神经元线粒体形态结构的异常,这种异常在运动后的48 h内呈现出动态性变化。通过调控线粒体融合分裂基因、动力相关蛋白1和线粒体融合蛋白2的表达,机体可能影响大鼠额叶线粒体的形态结构和功能,调控额叶神经元凋亡的发生和发展[74]。 综上所述,运动对线粒体形态的调控与肌肉类型、运动方案等因素密切相关。作为同时涉及神经疾病和肌肉疾病的帕金森病,运动对线粒体形态的调控具有重要意义。尽管已取得一些关于运动对线粒体形态调控的研究进展,但仍有许多问题需要进一步探索和解答。未来的研究可以重点研究运动对线粒体形态调控的分子机制,以及其在不同肌肉类型和不同运动方案中的差异等方面的问题。相关的运动对帕金森病相关线粒体形态潜在调控作用的研究见表3。"

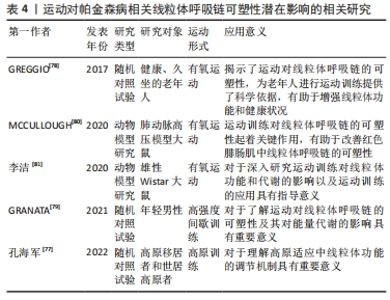
2.3.4 运动对线粒体呼吸链的可塑性影响 作为既涉及神经系统又涉及肌肉系统的疾病,帕金森病线粒体呼吸链的可塑性对其发病机制具有重要意义。运动通过改变线粒体呼吸链的可塑性来调节线粒体功能[4]。电子在不同的代谢反应中被引导到线粒体电子传递链上,为线粒体氧化磷酸化过程提供动力所必需。线粒体电子传递链结构由包含OXPHOS复合物Ⅰ到Ⅳ的电子传递链组成,对线粒体功能起关键作用。线粒体超复合物是指在线粒体电子传递链中可塑性变化,从自由移动的复合物到超组装的结构[75]。ROBERTS等[76]认为,线粒体超复合物的形成可以减少电子泄漏,增加电子流动通道,从而提高线粒体效率并减少产生活性氧。此外,线粒体超复合物的形成受能量需求变化的影响。孔海军等[77]的研究发现,在高原居住时间逐渐延长的高原移居者中,外周血单个核细胞线粒体自噬水平下降,而外周血单个核细胞线粒体呼吸酶活性逐渐增加,特别是复合物Ⅱ和复合物Ⅲ的水平明显降低。这表明环境条件可以影响线粒体超复合物的形成,从而影响对线粒体呼吸链的可塑性。GREGGIO等[78]的研究发现,运动影响老年人体内的线粒体超复合物形成。然而,GRANATA等[79]的研究表明,高强度训练并不会导致呼吸链的重组。另外,研究还发现,耐力训练可以促进骨骼肌电子传递链超级复合物的组装[80]。这说明,不同类型的运动对线粒体超复合物产生多种效应。对于线粒体呼吸链的动态代谢方面,李洁等[81]的研究发现,极高负荷运动训练能有效提高骨骼肌线粒体能量代谢,这表明线粒体呼吸链的功能可能在不同负荷下的运动中存在差异。然而,仍需进一步研究运动如何调节不同组织中线粒体可塑性的机制。 综上所述,运动对线粒体呼吸链的可塑性具有重要影响,但仍需进一步的研究,以探究不同类型的运动对线粒体功能的影响、调节机制以及不同组织中的调节作用。相关运动对帕金森病相关线粒体呼吸链可塑性潜在影响的研究见表4。"

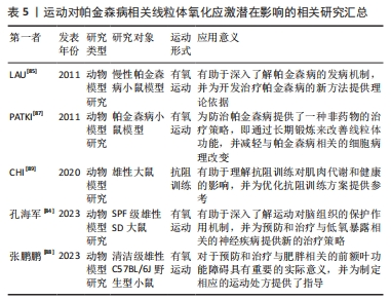
2.3.5 运动对氧化应激影响 帕金森病作为一种涉及神经系统和肌肉系统的疾病,与氧化应激密切相关[82]。氧化应激主要由线粒体产生的活性氧负责,长期的活性氧生成可能导致氧化损伤,并参与许多病理状态的发展。运动的剧烈或长时间进行可能会增加活性氧的产生量,导致肌肉和血液中的氧化损伤生物标志物增加[83]。活性氧的产生取决于运动的模式、强度和持续时间,从而影响氧化损伤的适应性信号反应类型[83]。然而,研究发现运动预适应可能通过激活特定信号通路来调节脑组织的氧化应激并减轻损伤程度,改善低氧暴露大鼠的神经行为功能[84]。但是,目前对脑组织氧化应激的分子细节尚需进一步研究。 研究发现,长期进行运动不仅有助于促进慢性帕金森病模型中黑质纹状体神经元的神经营养活动,还能够预防慢性帕金森病相关的神经行为障碍和线粒体缺陷[85]。神经元作为高度活跃的细胞,需要持续供能以执行各种功能,如调节神经传递、受体、离子通道、蛋白质运输和突触活动,因此线粒体对维持神经元功能的稳态和完整性至关重要,而线粒体功能障碍被认为是帕金森病相关神经元死亡的一个重要因素[86]。研究证据表明,长期的运动训练能够改善帕金森病的症状,并增加神经元的存活[86]。此外,运动能够通过适应过程抑制全身的氧化应激,增加抗氧化剂和氧化损伤修复酶(如超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶)的水平和活性[87]。然而,对运动对线粒体功能和氧化应激的具体影响以及遗传因素是否对其起作用的了解还比较有限,需要进一步研究。 运动还能够抑制炎症过程,从而减少氧化应激和线粒体功能障碍。研究发现,持续运动和间歇运动都能通过抑制炎症和氧化应激来缓解肥胖引起的前额叶损伤和认知功能障碍,其中间歇运动的效果更佳[88]。此外,运动能够抑制促炎细胞因子如白细胞介素6的表达,促进抗炎因子的表达,从而减少氧化剂的产生[89]。 综上所述,运动对氧化应激和线粒体功能具有积极影响,其可以减少线粒体活性氧的产生量,改善神经元的存活,降低氧化应激水平,修复线粒体功能紊乱,并抑制炎症过程。然而,对于运动对线粒体功能的具体影响以及遗传因素是否起作用的了解还相对不足,需要进一步研究。同时,还需要更多的人体研究来验证运动对帕金森病患者的益处,并深入研究其具体的机制。鉴于运动在改善线粒体氧化应激方面的潜力,今后的研究可以进一步探索如何优化运动模式、强度和持续时间,以获得最佳的治疗效果。更多关于运动对帕金森病想线粒体氧化应激潜在影响的相关研究见表5。"

| [1] BLOEM BR, OKUN MS, KLEIN C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2021;397(10291): 2284-2303. [2] PARK JS, DAVIS RL, SUE CM. Mitochondrial dysfunction in parkinson’s disease: new mechanistic insights and therapeutic perspectives. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2018;18(5):21. [3] RANGO M, BRESOLIN N. Brain Mitochondria, Aging, and Parkinson’s Disease. Genes (Basel). 2018;9(5):250. [4] 李雪,孙君志,金毓,等.运动干预脑衰老:新进展与再认识[J].科技导报, 2022,40(10):49-59. [5] 李玉娟,王丹巧.线粒体功能障碍与帕金森病关系的研究进展.中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2013,27(4):727-730. [6] MORADI VASTEGANI S, NASROLAHI A, GHADERI S, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and parkinson’s disease: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(8):2285-2308. [7] PRASUHN J, DAVIS RL, KUMAR KR. Targeting mitochondrial impairment in parkinson’s disease: challenges and opportunities. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;8:615461. [8] CHANDRA G, SHENOI RA, ANAND R, et al. Reinforcing mitochondrial functions in aging brain: an insight into Parkinson’s disease therapeutics. J Chem Neuroanat. 2019;95:29-42. [9] LIN CY, HUANG YN, FU RH, et al. Promotion of mitochondrial biogenesis via the regulation of PARIS and PGC-1α by parkin as a mechanism of neuroprotection by carnosic acid. Phytomedicine. 2021;80:153369. [10] WANG Y, CHEN C, HUANG W, et al. Beneficial effects of PGC-1α in the substantia nigra of a mouse model of MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(20):8937-8950. [11] 陈溪. PGC-1α过表达对PD模型细胞的线粒体和在体多巴胺能神经元的影响[D].石家庄:河北师范大学,2017. [12] LEE Y, STEVENS DA, KANG SU, et al. PINK1 primes parkin-mediated ubiquitination of PARIS in dopaminergic neuronal survival. Cell Rep. 2017;18(4):918-932. [13] ZHENG L, BERNARD-MARISSAL N, MOULLAN N, et al. Parkin functionally interacts with PGC-1α to preserve mitochondria and protect dopaminergic neurons. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(3):582-598. [14] FIVENSON EM, LAUTRUP S, SUN N, et al. Mitophagy in neurodegeneration and aging. Neurochem Int. 2017;109:202-209. [15] PICKRELL AM, YOULE RJ. The roles of PINK1, parkin, and mitochondrial fidelity in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2015;85(2):257-273. [16] MAGALHÃES JD, CARDOSO SM. Mitochondrial signaling on innate immunity activation in Parkinson disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2023;78:102664. [17] LEONG YQ, KOH RY, CHYE SM, et al. Unravelling the genetic links between Parkinson’s disease and lung cancer. Biol Chem. 2023;404(6):551-567. [18] LESAGE S, DROUET V, MAJOUNIE E, et al. Loss of VPS13C function in autosomal-recessive Parkinsonism causes mitochondrial dysfunction and increases PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy. Am J Hum Genet. 2016;98(3):500-513. [19] KUMAR N, LEONZINO M, HANCOCK-CERUTTI W, et al. VPS13A and VPS13C are lipid transport proteins differentially localized at ER contact sites. J Cell Biol. 2018;217(10):3625-3639. [20] 胡安霞,尹昌浩,郭一鸣,等.线粒体功能障碍和氧化应激在帕金森病中的作用[J].医学综述,2021,27(15):2929-2934. [21] WALTER J, BOLOGNIN S, ANTONY PMA, et al. Neural stem cells of parkinson’s disease patients exhibit aberrant mitochondrial morphology and functionality. Stem Cell Reports. 2019;12(5):878-889. [22] VERMA M, CALLIO J, OTERO PA, et al. Mitochondrial calcium dysregulation contributes to dendrite degeneration mediated by PD/LBD-associated LRRK2 mutants. J Neurosci. 2017;37(46):11151-11165. [23] 肖琪,樊慧杰,李艳荣,等.帕金森病发病机制研究进展[J].解放军医学杂志, 2023,48(8):983-992. [24] 倪晓晨,于世龙,刘延庆,等.DJ-1调控线粒体功能研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2023,39(8):1406-1411. [25] SALAZAR C, RUIZ-HINCAPIE P, RUIZ LM. The interplay among PINK1/PARKIN/Dj-1 network during mitochondrial quality control in cancer biology: protein interaction analysis. Cells. 2018;7(10):154. [26] IVATT RM, SANCHEZ-MARTINEZ A, GODENA VK, et al. Genome-wide RNAi screen identifies the Parkinson disease GWAS risk locus SREBF1 as a regulator of mitophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(23):8494-8499. [27] 马学虎,马莉花,苟妍,等.线粒体功能障碍引起的相关炎性疾病及靶向治疗[J].生物技术通报,2023,39(6):119-125. [28] RYAN T, BAMM VV, STYKEL MG, et al. Cardiolipin exposure on the outer mitochondrial membrane modulates α-synuclein. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):817. [29] HAQUE ME, AKTHER M, AZAM S, et al. Targeting α-synuclein aggregation and its role in mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2022; 179(1):23-45. [30] 朱睿放,张宇,卢应梅.小胶质细胞及其介导的神经炎症在帕金森病中的作用[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2023,43(4):569-576. [31] EREKAT NS. Apoptosis and its Role in Parkinson’s Disease. In: Stoker TB, Greenland JC, eds. Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects[D]. Brisbane (AU): Codon Publications. 2018. [32] WOLF P, SCHOENIGER A, EDLICH F. Pro-apoptotic complexes of BAX and BAK on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022; 1869(10):119317. [33] SEMENOVA MA, CHERTKOVA RV, KIRPICHNIKOV MP, et al. Molecular Interactions between neuroglobin and cytochrome c: possible mechanisms of antiapoptotic defense in neuronal cells. Biomolecules. 2023;13(8):1233. [34] HE C, BASSIK MC, MORESI V, et al. Exercise-induced BCL2-regulated autophagy is required for muscle glucose homeostasis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):511-515. [35] LUDTMANN MHR, ANGELOVA PR, HORROCKS MH, et al. α-synuclein oligomers interact with ATP synthase and open the permeability transition pore in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2293. [36] 刘家岐,楚世峰,张大永,等.钙离子与帕金森病的研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2018,32(9):690-691. [37] CARBONE C, COSTA A, PROVENSI G, et al. The hyperpolarization-activated current determines synaptic excitability, calcium activity and specific viability of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017;11:187. [38] VOS M. Mitochondrial complex i deficiency: guilty in Parkinson’s disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):136. [39] WRIGHT JJ, BINER O, CHUNG I, et al. Reverse electron transfer by respiratory complex I catalyzed in a modular proteoliposome system. J Am Chem Soc. 2022; 144(15):6791-6801. [40] TRYPHENA KP, NIKHIL US, PINJALA P, et al. Mitochondrial complex I as a pathologic and therapeutic target for Parkinson’s disease. ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 2023, 14(8):1356-1368. [41] HAJAM YA, RANI R, GANIE SY, et al. Oxidative stress in human pathology and aging: Molecular mechanisms and perspectives. Cells. 2022;11(3):552. [42] 吴悦,唐业忠,方光战.帕金森病步态障碍发生机制及动物模型[J].科学通报,2023,68(23):3043-3051. [43] MARTIN LJ, PAN Y, PRICE AC, et al. Parkinson’s disease alpha-synuclein transgenic mice develop neuronal mitochondrial degeneration and cell death. J Neurosci. 2006;26(1):41-50. [44] DRYANOVSKI DI, GUZMAN JN, XIE Z, et al. Calcium entry and α-synuclein inclusions elevate dendritic mitochondrial oxidant stress in dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci. 2013;33(24):10154-10164. [45] XIANG W, SCHLACHETZKI JC, HELLING S, et al. Oxidative stress-induced posttranslational modifications of alpha-synuclein: specific modification of alpha-synuclein by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal increases dopaminergic toxicity. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013;54:71-83. [46] WOOD-KACZMAR A, GANDHI S, YAO Z, et al. PINK1 is necessary for long term survival and mitochondrial function in human dopaminergic neurons. PLoS One. 2008;3(6):e2455. [47] RIZOR A, PAJARILLO E, JOHNSON J, et al. Astrocytic oxidative/nitrosative stress contributes to Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis: the dual role of reactive astrocytes. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(8):265. [48] FRØYSET AK, EDSON AJ, GHARBI N, et al. Astroglial DJ-1 over-expression up-regulates proteins involved in redox regulation and is neuroprotective in vivo. Redox Biol. 2018;16:237-247. [49] DI NOTTIA M, MASCIULLO M, VERRIGNI D, et al. DJ-1 modulates mitochondrial response to oxidative stress: clues from a novel diagnosis of PARK7. Clin Genet. 2017;92(1):18-25. [50] 任翔宇,沈飞,金玲,等.运动促进骨骼肌健康的新视角:基于Rac1/PAK1/p38 MAPK信号通路改善肌生成和糖代谢的研究进展与展望[J].中国体育科技,2023,59(5):79-87. [51] ISLAM H, HOOD DA, GURD BJ. Looking beyond PGC-1α: emerging regulators of exercise-induced skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis and their activation by dietary compounds. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2020;45(1):11-23. [52] MEMME JM, ERLICH AT, PHUKAN G, et al. Exercise and mitochondrial health. J Physiol. 2021;599(3):803-817. [53] 张国华,陈淑妆,李素萍.大强度耐力运动抑制骨骼肌线粒体的生物合成[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(46):7419-7424. [54] FERREIRA R, VITORINO R, PADRÃO AI, et al. Lifelong exercise training modulates cardiac mitochondrial phosphoproteome in rats. J Proteome Res. 2014;13(4): 2045-2055. [55] ROH J, RHEE J, CHAUDHARI V, et al. The role of exercise in cardiac aging: from physiology to molecular mechanisms. Circ Res. 2016;118(2):279-295. [56] CARTONI R, LÉGER B, HOCK MB, et al. Mitofusins 1/2 and ERRalpha expression are increased in human skeletal muscle after physical exercise. J Physiol. 2005; 567(Pt 1):349-358. [57] 漆正堂,刘静霞,钱帅伟,等.不同运动能力小鼠在定制负荷运动适应中骨骼肌的基因转录响应——以细胞自噬与线粒体有关基因为例[J].武汉体育学院学报,2022,56(2):93-100. [58] WOHLGEMUTH SE, LEES HA, MARZETTI E, et al. An exploratory analysis of the effects of a weight loss plus exercise program on cellular quality control mechanisms in older overweight women. Rejuvenation Res. 2011;14(3):315-324. [59] WHITE Z, TERRILL J, WHITE RB, et al. Voluntary resistance wheel exercise from mid-life prevents sarcopenia and increases markers of mitochondrial function and autophagy in muscles of old male and female C57BL/6J mice. Skelet Muscle. 2016;6(1):45. [60] GARVEY SM, RUSS DW, SKELDING MB, et al. Molecular and metabolomic effects of voluntary running wheel activity on skeletal muscle in late middle-aged rats. Physiol Rep. 2015;3(2):e12319. [61] KIM YA, KIM YS, OH SL, et al. Autophagic response to exercise training in skeletal muscle with age. J Physiol Biochem. 2013;69(4):697-705. [62] KIM YA, KIM YS, SONG W, et al. Autophagic response to a single bout of moderate exercise in murine skeletal muscle. J Physiol Biochem. 2012;68(2):229-235. [63] ZAMPIERI S, PIETRANGELO L, LOEFLER S, et al. Lifelong physical exercise delays age-associated skeletal muscle decline. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015; 70(2):163-173. [64] OGBORN DI, MCKAY BR, CRANE JD, et al. Effects of age and unaccustomed resistance exercise on mitochondrial transcript and protein abundance in skeletal muscle of men. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015;308(8):R734-R741. [65] LUO L, LU AM, WANG Y, et al. Chronic resistance training activates autophagy and reduces apoptosis of muscle cells by modulating IGF-1 and its receptors, Akt/mTOR and Akt/FOXO3a signaling in aged rats. Exp Gerontol. 2013;48(4):427-436. [66] YOSHIOKA K, FUJITA R, SEKO D, et al. Distinct roles of Zmynd17 and PGC1α in mitochondrial quality control and biogenesis in skeletal muscle. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:330. [67] CASUSO RA, HUERTAS JR. The emerging role of skeletal muscle mitochondrial dynamics in exercise and ageing. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;58:101025. [68] 林建健,宋洁.运动调控线粒体动力学变化的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(11):1767-1771. [69] FIORENZA M, GUNNARSSON TP, HOSTRUP M, et al. Metabolic stress-dependent regulation of the mitochondrial biogenic molecular response to high-intensity exercise in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2018;596(14):2823-2840. [70] GRANATA C, OLIVEIRA RS, LITTLE JP, et al. Sprint-interval but not continuous exercise increases PGC-1α protein content and p53 phosphorylation in nuclear fractions of human skeletal muscle. Sci Rep. 2017;7:44227. [71] PLACE N, IVARSSON N, VENCKUNAS T, et al. Ryanodine receptor fragmentation and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leak after one session of high-intensity interval exercise. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(50):15492-15497. [72] 张喆,丁树哲.线粒体分裂蛋白1在安静状态下和力竭运动中对骨骼肌线粒体质量的调控作用[J].北京体育大学学报,2020,43(10):104-113. [73] 王璐,邓文骞,袁琼嘉,等.运动预处理影响线粒体形态变化以及相关因子表达干预力竭运动后大鼠额叶细胞凋亡[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(8): 719-725. [74] 王璐,邓文骞.大负荷游泳运动后大鼠额叶神经元凋亡和线粒体形态变化及Drp1、Mfn2表达的研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2016,42(4):76-81. [75] ACIN-PEREZ R, ENRIQUEZ JA. The function of the respiratory supercomplexes: the plasticity model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1837(4):444-450. [76] ROBERTS FL, MARKBY GR. New insights into molecular mechanisms mediating adaptation to exercise; a review focusing on mitochondrial biogenesis, mitochondrial function, mitophagy and autophagy. Cells. 2021;10(10):2639. [77] 孔海军,王凤华,李新龙,等.PBMC线粒体自噬对高原移居人群运动能耗、线粒体呼吸链复合酶活性的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2022,38(6): 655-660. [78] GREGGIO C, JHA P, KULKARNI SS, et al. Enhanced respiratory chain supercomplex formation in response to exercise in human skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2017; 25(2):301-311. [79] GRANATA C, CARUANA NJ, BOTELLA J, et al. High-intensity training induces non-stoichiometric changes in the mitochondrial proteome of human skeletal muscle without reorganisation of respiratory chain content. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):7056. [80] MCCULLOUGH DJ, KUE N, MANCINI T, et al. Endurance exercise training in pulmonary hypertension increases skeletal muscle electron transport chain supercomplex assembly. Pulm Circ. 2020;10(2):2045894020925762. [81] 李洁,黄彩云,王艳.不同负荷运动训练对大鼠肝脏及骨骼肌线粒体呼吸链功能的影响[J].上海体育学院学报,2020,44(10):68-74. [82] DEUS CM, TEIXEIRA J, RAIMUNDO N, et al. Modulation of cellular redox environment as a novel therapeutic strategy for Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2022;52(10):e13820. [83] POWERS SK, DEMINICE R, OZDEMIR M, et al. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Friend or foe? J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5):415-425. [84] 孔海军,李新龙,王凤华,等.运动预适应介导氧化应激调控PI3K/Akt和Nrf2/HO-1通路对大鼠认知和学习障碍的影响[J].康复学报,2023,33(3): 231-240. [85] LAU YS, PATKI G, DAS-PANJA K, et al. Neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of exercise in a chronic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease with moderate neurodegeneration. Eur J Neurosci. 2011;33(7):1264-1274. [86] BHAT AH, DAR KB, ANEES S, et al. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases: a mechanistic insight. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;74:101-110. [87] PATKI G, LAU YS. Impact of exercise on mitochondrial transcription factor expression and damage in the striatum of a chronic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2011;505(3):268-272. [88] 张鹏鹏.持续和间歇运动上调PGC-1α/Irisin/BDNF表达改善肥胖小鼠认知功能障碍[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2023,39(9):1346-1355 [89] CHI CP, HOU CW, WU YY, et al. Night time resistance exercise alters muscular IL-6-related protein signaling, but not muscle growth after 10 weeks of resistance training in male rats. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2020;39(1):89-98. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [3] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [4] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [5] | Qi Xue, Li Jiahui, Zhu Yuanfeng, Yu Lu, Wang Peng. Abnormal modification of alpha-synuclein and its mechanism in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1301-1306. |
| [6] | Cheng Jie, Wang Jihong, Zhang Pei. Functional exercise for tendon adhesion in a model of deep flexor tendon II injury of the third toe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1161-1167. |
| [7] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [8] | Ruan Rong, Lou Xujia, Jin Qiguan, Zhang Libing, Xu Shang, Hu Yulong. Effect of resveratrol on gluconeogenesis in exercise-induced fatigue rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1229-1234. |
| [9] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [10] | Zhuge Xiaoxuan, Li Ce, Bao Guangjie, Kang Hong. Potential value of canonical and non-canonical roles of connexin 43 in disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1130-1136. |
| [11] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [12] | Sun Teng, Han Yu, Wang Shuang, Li Jialei, Cao Jimin. miR-20a regulates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1021-1028. |
| [13] | Liu Zhiyang, Fu Zeting, Xia Yu, Ding Haili. The role of BMAL1 and MyoD in exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 510-515. |
| [14] | Zhu Xiaofeng, Chen Weiwei, Huang Jian. Effects of maternal high-fat diet and exercise intervention on insulin sensitivity and the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in male offspring mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 556-561. |
| [15] | Wang Shijie, Wen Dengtai, Wang Jingfeng, Gao Yinghui. Mammalian target of rapamycin in relation to exercise, high fat/high salt diet, and aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 574-580. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||