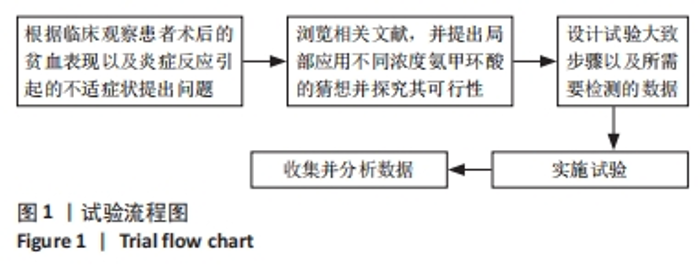
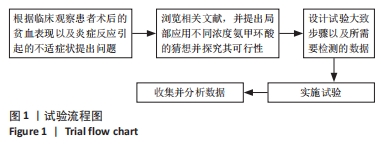
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (21): 3367-3372.doi: 10.12307/2024.092
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of intravenous and topical tranexamic acid on blood loss and inflammatory response after posterior cervical decompressive laminectomy
Tan Yubo, Xia Yingpeng
- Tianjin union medical center, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300000, China, Tianjin 300000, China
-
Received:2023-03-21Accepted:2023-06-25Online:2024-07-28Published:2023-09-27 -
Contact:Xia Yingpeng, MD, Chief physician, Tianjin union medical center, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300000, China, Tianjin 300000, China -
About author:Tan Yubo, Master candidate, Tianjin union medical center, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300000, China, Tianjin 300000, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tan Yubo, Xia Yingpeng. Effects of intravenous and topical tranexamic acid on blood loss and inflammatory response after posterior cervical decompressive laminectomy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3367-3372.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
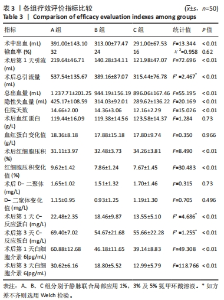
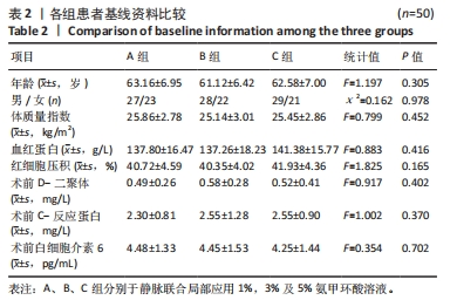
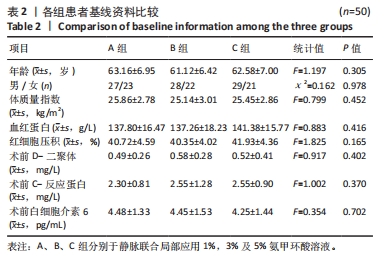
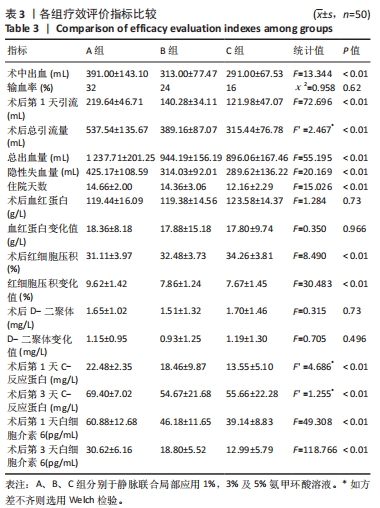
2.4 观察指标统计分析结果 B、C两组的术中出血量、总出血量以及隐性出血量均明显少于A组,且差异有显著性意义;而经过Bonferroni检验显示B、C两组间的术中出血量(P=0.844)、总出血量(P=0.521)、隐性失血量(P=1.00),无统计学差异。颈后路钉棒手术损伤较大,患者术中出血500 mL左右会选择输血,差量主要存在于关闭伤口时给药对于引流管穿刺以及缝合时深层肌肉的出血的影响。3组术后第1天引流量以及总引流量相比差异有显著性意义,其中B、C组相较A组引流量明显减少。此外,3组的住院天数也存在差异,C组较A、B组时间相对缩短(P < 0.001)。3组的手术前后血红蛋白变化值(P=0.966)、D-二聚体变化值(P=0.496)无明显差异,手术前后红细胞压积3组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),后续的Bonferroni检验显示B、C两组之间差异无显著性意义(P=1.00)。3组患者术后第 1,3 天炎症指标包括C-反应蛋白、白细胞介素6与术前相比均有不同程度升高(P < 0.05),随着用药浓度升高其表达降低,3组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001)。见表3。"
| [1] BAKHSHESHIAN J, MEHTA VA, LIU JC. Current Diagnosis and Management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Global Spine J. 2017; 7(6):572-586. [2] LIU B, WANG Y, ZHANG Y. Efficacy of Posterior Cervical Laminectomy and Decompression plus Lateral Mass Screw-Rod Internal Fixation in the Treatment of Multisegment Cervical Spinal Canal Stenosis and Effects on Cervical Curvature and Range of Motion Parameters. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:6001877. [3] MCCORMICK JR, SAMA AJ, SCHILLER NC, et al. Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: A Guide to Diagnosis and Management. J Am Board Fam Med. 2020;33(2):303-313. [4] AL BARBARAWI MM, ALLOUH MZ. Cervical lateral mass screw-rod fixation: Surgical experience with 2500 consecutive screws, an analytical review, and long-term outcomes. Br J Neurosurg. 2015;29(5): 699-704. [5] WU DZ, GU ZF, MENG DJ, et al. Bridging the cervicothoracic junction during posterior cervical laminectomy and fusion for the treatment of multilevel cervical ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: a retrospective case series. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1): 446. [6] 郭强, 张宏其.脊柱围手术期隐性出血的研究进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2015,13(3):186-188. [7] YU CC, GAO WJ, YANG JS, et al. Can tranexamic acid reduce blood loss in cervical laminectomy with lateral mass screw fixation and bone grafting: a retrospective observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(5):e6043. [8] WILLNER D, SPENNATI V, STOHL S, et al. Spine Surgery and Blood Loss: Systematic Review of Clinical Evidence. Anesth Analg. 2016;123(5): 1307-1315. [9] NIELSEN VG, FORD PM. The ratio of concentrations of aminocaproic acid and tranexamic acid that prevent plasmin activation of platelets does not provide equivalent inhibition of plasmatic fibrinolysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2018;46(3):365-370. [10] WALKER PF, FOSTER AD, ROTHBERG PA, et al. Tranexamic acid decreases rodent hemorrhagic shock-induced inflammation with mixed end-organ effects. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0208249. [11] DUNN CJ, GOA KL. Tranexamic acid: a review of its use in surgery and other indications. Drugs. 1999;57(6):1005-1032. [12] NADLER SB, HIDALGO JH, BLOCH T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51(2):224-232. [13] GROSS JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;58(3):277-280. [14] SEHAT KR, EVANS RL, NEWMAN JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(4): 561-565. [15] ELWATIDY S, JAMJOOM Z, ELGAMAL E, et al. Efficacy and safety of prophylactic large dose of tranexamic acid in spine surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(24):2577-2580. [16] XIE J, LENKE LG, LI T, et al. Preliminary investigation of high-dose tranexamic acid for controlling intraoperative blood loss in patients undergoing spine correction surgery. Spine J. 2015;15(4):647-654. [17] BARRACHINA B, LOPEZ-PICADO A, REMON M, et al. Tranexamic Acid Compared with Placebo for Reducing Total Blood Loss in Hip Replacement Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesth Analg. 2016; 122(4):986-995. [18] KIMURA OS, FREITAS EH, DUARTE ME, et al. Tranexamic acid use in high-risk blood transfusion patients undergoing total hip replacement: a randomised controlled trial. Hip Int. 2021;31(4):456-464. [19] RAHMANI R, SINGLETON A, FULTON Z, et al. Tranexamic acid dosing strategies and blood loss reduction in multilevel spine surgery: A systematic review and network meta-analysis: Tranexamic acid for multilevel spine surgery. N Am Spine Soc J. 2021;8:100086. [20] O’BRIEN JG, BATTISTINI B, ZAHARIA F, et al. Effects of tranexamic acid and aprotinin, two antifibrinolytic drugs, on PAF-induced plasma extravasation in unanesthetized rats. Inflammation. 2000;24(5):411-429. [21] XIE J, HU Q, MA J, et al. Multiple boluses of intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce hidden blood loss and the inflammatory response following enhanced-recovery primary total hip arthroplasty: a randomised clinical trial. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-b(11):1442-1449. [22] XU D, ZHUANG Q, LI Z, et al. A randomized controlled trial on the effects of collagen sponge and topical tranexamic acid in posterior spinal fusion surgeries. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):166. [23] OU Y, WEI J, LI R, et al. Clinical Research of Combined Intravenous Administration and Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid to a Surgical Wound During Posterior Lumbar Fusion. Surg Innov. 2018;25(2):128-135. [24] LIU X, LIU J, SUN G. A comparison of combined intravenous and topical administration of tranexamic acid with intravenous tranexamic acid alone for blood loss reduction after total hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2017;41:34-43. [25] WATTS CD, HOUDEK MT, SEMS SA, et al. Tranexamic Acid Safely Reduced Blood Loss in Hemi- and Total Hip Arthroplasty for Acute Femoral Neck Fracture: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(7):345-351. [26] GONG M, LIU G, CHEN L, et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Tranexamic Acid in Reducing Surgical Blood Loss in Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion for the Adult: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;122:559-568. [27] KIM KT, KIM CK, KIM YC, et al. The effectiveness of low-dose and high-dose tranexamic acid in posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled randomized study. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(11):2851-2857. [28] CHERIYAN T, MAIER SP, 2ND, BIANCO K, et al. Efficacy of tranexamic acid on surgical bleeding in spine surgery: a meta-analysis. Spine J. 2015; 15(4):752-761. [29] BUSUTTIL SJ, PLOPLIS VA, CASTELLINO FJ, et al. A central role for plasminogen in the inflammatory response to biomaterials. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2(10):1798-1805. [30] YOSHIZAKI S, KIJIMA K, HARA M, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces heme cytotoxicity via the TLR4/TNF axis and ameliorates functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):160. [31] WANG C, XU GJ, HAN Z, et al. Topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2015;15:134-139. [32] XIONG H, LIU Y, ZENG Y, et al. The efficacy and safety of combined administration of intravenous and topical tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):321. [33] BOLAM SM, O’REGAN-BROWN A, PAUL MONK A, et al. Toxicity of tranexamic acid (TXA) to intra-articular tissue in orthopaedic surgery: a scoping review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(6): 1862-1871. [34] CHEN C, YE YY, CHEN YF, et al. Comparison of blood loss between tranexamic acid-soaked absorbable Gelfoam and topical retrograde injection via drainage catheter plus clamping in cervical laminoplasty surgery. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):668. [35] PARKER JD, LIM KS, KIESER DC, et al. Is tranexamic acid toxic to articular cartilage when administered topically? What is the safe dose? Bone Joint J. 2018;100-b(3):404-412. [36] MANJI RA, GROCOTT HP, LEAKE J, et al. Seizures following cardiac surgery: the impact of tranexamic acid and other risk factors. Can J Anaesth. 2012;59(1):6-13. [37] KEYL C, UHL R, BEYERSDORF F, et al. High-dose tranexamic acid is related to increased risk of generalized seizures after aortic valve replacement. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;39(5):e114-e121. [38] 顾力军,张洪美,张斌,等.脊柱手术发生氨甲环酸相关型癫痫1例[J].中国骨伤,2018,31(3):276-278. [39] EIKEBROKK TA, VASSMYR BS, AUSEN K, et al. Cytotoxicity and effect on wound re-epithelialization after topical administration of tranexamic acid. BJS Open. 2019;3(6):840-851. [40] CUELLAR JM, YOO A, TOVAR N, et al. The effects of Amicar and TXA on lumbar spine fusion in an animal model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39(19):E1132-E1137. |
| [1] | Wang Zhikun, Bai Shaoxuan, Zhao Wei, Wang Chenyu. Exercise preconditioning combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for myocardial infarction in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 65-73. |
| [2] | Zhang Xingzhou, Wei Ming, Dong Guoqiang, Du Wei, Luo Yiwen, Zhang Nan . Mechanism of postoperative abdominal adhesion formation and therapeutic prospect of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 147-155. |
| [3] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [4] | Du Changling, Shi Hui, Zhang Shoutao, Meng Tao, Liu Dong, Li Jian, Cao Heng, Xu Chuang. Efficacy and safety of different applications of tranexamic acid in high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1409-1413. |
| [5] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [6] | Zhao Yan, Wu Fan, Li Hong, Wan Shengyu, He Jin, Zhu Binren, Jiang Congbing. Prolonging use of tranexamic acid is helpful to reduce perioperative hidden blood loss in senile patients with intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5858-5864. |
| [7] | Li Qiang, Ji Yuqin, Ye Qiang. Effect of cold water immersion dose on the recovery of skeletal muscle fatigue induced by exercise: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5732-5740. |
| [8] | Wu Yuwei, Zhu Jiang, Zheng Bing, Wu Zonghui. Mechanism by which exercise controls uric acid level [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5552-5557. |
| [9] | Yu Jingwen, Guo Minfang, Zhang Bingxin, Mu Bingtao, Meng Tao, Zhang Huiyu, Ma Cungen, Yin Jinzhu, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong. Astragaloside inhibits astrocyte activation and inflammatory response induced by inflammation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5022-5028. |
| [10] | Yang Pan, Dong Wantao, Liu Jingyi, Qiu Shiming, Yuan Peng. Mechanical stress affects occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by regulating Hippo pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4902-4908. |
| [11] | Tian Yong, Zhou Ying, Gu Yongxiang, Yang Guohui. Metformin pretreatment induces cardiac autophagy to reduce myocardial injury in septic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4469-4476. |
| [12] | Chen Ying, Xia Tianqin, Hua Jianlin, Yin Jinzhu, Song Lijuan, Wang Qing, Yu Jiezhong, Huang Jianjun, Ma Cungen. The role and mechanism of TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in multiple sclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4578-4585. |
| [13] | Guo Xiangying, Peng Zifu, He Yimin, Fang Hongbo, Jiang Ning. MiRNA-122 contributes to the effect of exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 272-279. |
| [14] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [15] | Li Bowei, Pan Wenjie, Xu Chao, Huang Yuanchi, Ma Jianbing. Effect analysis of a modified topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2852-2858. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||