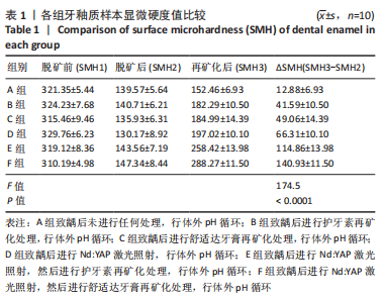
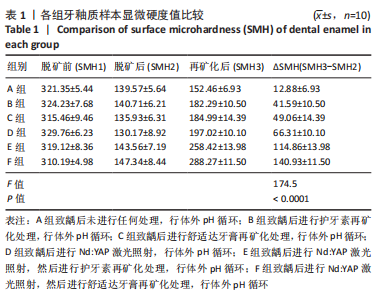
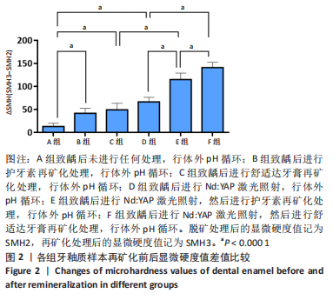
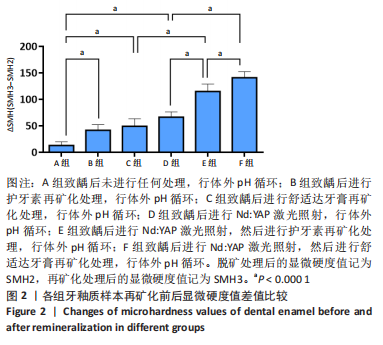
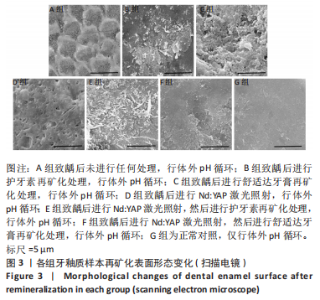
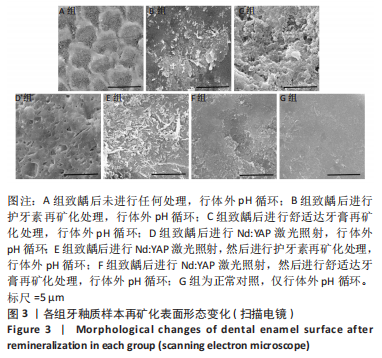
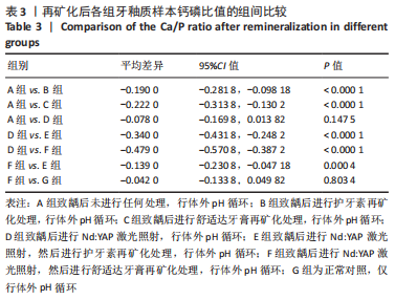
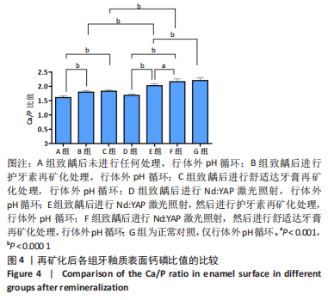
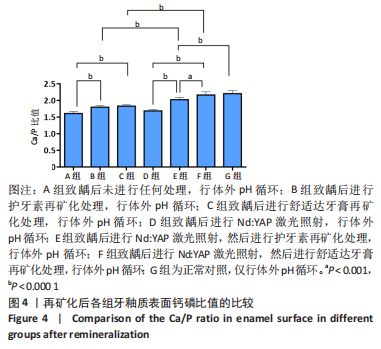
[1] 黎凯歌,严冬,韩文睿,等.不同正畸方式对龈上菌斑中三种致龋菌的早期影响[J].北京口腔医学,2022,30(3):182-188.
[2] 陈锐.固定矫治中不同药物应用对釉质脱矿指数的影响[J].中华全科医学,2017,15(9):1632-1634.
[3] DIDEM N, MEHMET OO, DERYA GC, et al. Prevention of demineralization around orthodontic brackets using two different fluoride varnishes. Eur J Dent. 2013;7:41-47.
[4] SHIVANANDA DH, ANSAR W, DINSHA AR, et al. Effectiveness of Various Dental Varnishes in Prevention of Enamel Demineralization around Orthodontic Brackets: An In Vitro Study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2020;21(6): 621-625.
[5] 招顺秀,李业荣,许碧晖.多乐氟预防固定正畸矫治中牙釉质脱矿的临床研究[J].广东牙病防治,2013,21(8):441-443.
[6] 吴海苗,许衍,叶翠,等. 氟保护漆预防固定正畸牙釉质脱矿的临床观察研究[J].口腔生物医学,2020,11(2):113-115.
[7] 黄少宏.群体氟防龋指导策略[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014,7(7):389-394.
[8] ERDEM AP, SEPET E, AVSHALOM T, et al. Effect of CPP-ACP and APF on Streptococcusmutans biofilm: a laboratory study. Am J Dent. 2011;24(2): 119-123.
[9] PINHEIRO SL, AZENHA GR, ARAUJO G, et al. Effectiveness of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate and lysozyme, lactoferrin, and lactoperoxidase in reducing Streptococcus mutans counts in dentinal caries. Gen Dent. 2017;65(2):47-50.
[10] GJORGIEVSKA E, NICHOLSON JW. Prevention of enamel demineralization after tooth bleaching by bioactive glass in corporated into toothpaste. Aust Dent J. 2011;56(2):193-200.
[11] 方萍,陈燕,周嫣,等.护牙素对正畸牙面脱矿修复的临床效果观察[J].广西医学,2012,34(8):978-980.
[12] 黄汝祥,邓文正,高健全,等.CPP-ACP与氟保护漆联合应用预防鼻咽癌患者放射性龋齿的临床研究[J]. 中国医药指南,2017,15(4):15-16.
[13] 王瑜,龚玲,郑丽纯,等.几种再矿化牙膏对釉质再矿化影响的体外研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(7):394-396.
[14] HENCH LL. The story of Bioglass. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(11):967.
[15] JAFARI N, HABASHI MS, HASHEMI A, et al. Application of bioactive glasses in various dental fields. Biomater Res. 2022;26(1):31.
[16] 黄贤圣,李蓉,冯云枝,等.生物活性玻璃Novamin诱导脱矿牙本质再矿化[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2018,43(6):619-624.
[17] 江蓉,张齐梅.激光协同CPP-ACP对乳牙早期釉质龋再矿化影响的临床研究[J].医学综述,2019,25(22):4585-4588.
[18] 杜伟.激光在牙本质过敏治疗中的应用进展[J].中国医疗器械信息, 2019,25(11):51-52.
[19] LIU J F, LIU Y, STEPHEN HC. Optimal Er:YAG laser energy for preventing enamel demineralization. J Dent. 2006;34(1):62-66.
[20] 刘雪阳,刘海江.不同功率铒,铬:钇钪镓石榴石激光照射对牙釉质表面再矿化效果比较的实验研究[J].转化医学杂志,2017,6(1):22-25.
[21] YASSAEI S, AGHILI H, SHAHRAKI N, et al. Efficacy of erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser with casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium phosphate with and without fluoride for remineralization of white spot lesions around orthodontic brackets. Eur J Dent. 2018;12(2):210-216.
[22] NAMOUR A, GEERTS S, ZEINOUN T, et al. Safety Irradiation Parameters of Nd:YAP Laser Beam for Endodontic Treatments: An In Vitro Study. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:4741516.
[23] MOSHONOV J, PERETZ B, BROWN T, et al. Cleaning of the rool canal using Nd:YAP Laser and its effect on the mineral content of the dentin. J Clin Laser Med Sur. 2004;22:87-89.
[24] 时晨,杨清岭,李宝花.渗透树脂联合CPP-ACP对年轻恒牙早期脱矿的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(4):208-211.
[25] 伍廷芸,阮琼,李智,等.纳米级护牙剂对于釉质酸蚀后再矿化效果的定量分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022,38(2):75-78.
[26] 方谦,穆玉,徐晓南,等.不同浓度生物活性玻璃对早期釉质龋再矿化的作用[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2015,25(12):729-731.
[27] 程亚楠,吴毓聪,毛秋华,等.渗透树脂联合生物活性玻璃修复脱矿牙釉质的效果及稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22):3522-3526.
[28] 董峻池,郑慧玲,卫羽雯,等.生物活性玻璃的抗菌机制及其影响因素[J].口腔医学,2022,42(6): 551-556.
[29] LUK K, ZHAO IS, YU OY, et al. Effects of 10,600 nm Carbon Dioxide Laser on Remineralizing Caries: A Literature Review. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2020;38(2):59-65.
[30] 梁潇月,邹朝晖,董晓曦,等.钕激光、半导体激光对窝洞消毒产热及抑菌效果的体外实验[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(34):5432-5438.
[31] 汪婷,朱亚琴.Nd:YAP激光与Er:YAG激光在口腔医学的应用现状[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2018,27(4):225-228.
[32] 刘耀然,赵继志,孔亚群.Nd:YAG激光与Nd:YAP激光在口腔医学应用中的比较[J].中国激光医学杂志,2016,25(3):153-159.
[33] NAMOUR A, NAMMOUR S, PEREMANS A, et al. Treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity by means of Nd:YAP Laser: apreliminary in vitro study. ScientificWorld J. 2014;2014:323-604.
[34] FORNAINI C, BRULAT-BOUCHARD N, MEDIONI E, et al. Nd:YAP laser in the treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity: An ex vivo study. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020;203:111740.
|