Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (30): 4862-4868.doi: 10.12307/2023.470
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of the nanovesicle delivery system in cardiovascular diseases
Peng Fengli, Li Chaofu, Shi Bei
- Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-06-16Accepted:2022-07-25Online:2023-10-28Published:2023-04-03 -
Contact:Shi Bei, Master, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Peng Fengli, Master candidate, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China

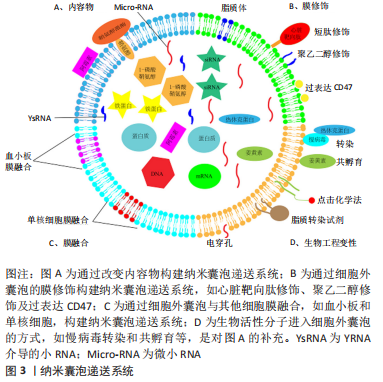
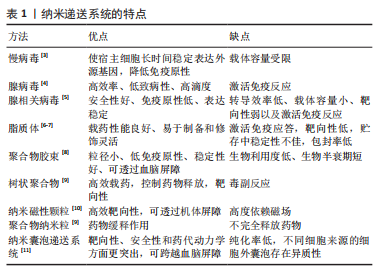
2.1.1 递送内容物改变 细胞外囊泡通过改变递送内容物,成功构建出纳米囊泡递送系统,可将多种生物活性物质递送至靶器官,根据递送物质的来源不同,可将其分为2类,即内源性物质(细胞外囊泡负载同源细胞产生的生物活性物质)与外源性物质(将递送物质在细胞外囊泡分离后装载到细胞外囊泡中,如非编码RNA、蛋白质和药物等),而这些物质由于物理化学性质、进入细胞外囊泡的方式不同,可导致负载效率以及细胞外囊泡膜完整性的差异[19-31]。 2.1.2 细胞外囊泡膜融合 膜融合是一个自然发生的过程,允许细胞质的融合而不发生泄漏或失去脂质双分子层的完整性,且细胞外囊泡表面的特性可以很容易地利用脂质体嵌入多肽或聚乙二醇作为靶向部分,从而构建出纳米囊泡递送系统。该纳米囊泡递送系统不仅可实现生物伪装,逃避免疫清除[32],还可将外源性疏水脂质转运到受体细胞提高膜稳定性及高效负载[33]。 2.1.3 细胞外囊泡膜修饰 为了提高药物疗效、降低药物毒性和减少脱靶效应,靶向配体、免疫逃避分子及刺激反应因子对细胞外囊泡进行表面修饰是靶向器官、组织和细胞最常用的方法。通过大量研究发现,通过聚乙二醇、短肽、水凝胶贴片及磁性靶向、过表达CD47等修饰细胞外囊泡构建的纳米囊泡递送系统[32-45],可以使其生物学功能更加稳定,而未经修饰的细胞外囊泡更容易被单核吞噬系统及网状内皮系统等清除。 2.2 纳米囊泡递送系统与心肌梗死 近年来,干细胞来源的外泌体在治疗心肌梗死等缺血性疾病中均起到重要作用。与干细胞相比,其外泌体不仅具有与干细胞相似生物学功能,而且还可避免触发免疫反应,能够降低异源植入的潜在风险。因此,基于干细胞来源的外泌体己成为治疗缺血性心血管疾病的一种有效策略。但外泌体治疗也存在着一些和干细胞治疗相同的缺点:如血液注射靶向性差、原位注射驻留时间短以及具有特定功能的分子含量不足等,因此,以细胞外囊泡为基础构建的纳米囊泡递送系统显现出尤为重要的作用。 由于衰老和缺血性损伤均可引起相似的分子和下游通路的变化,且Micro-RNA-675作为一种关键的上游分子,可以通过靶定转化生长因子β1-smad2/3信号通路来抑制衰老和损伤诱导的相关表型,但是鉴于Micro-RNA-675在外泌体中表达量较低,因此作者将Micro-RNA-675 模拟物转染到人脐带间充质干细胞中,收集含有大量的Micro-RNA-675的外泌体,并且为了进一步提高Micro-RNA-675功能,作者再使用功能性多肽水凝胶来包封外泌体,该功能性多肽水凝胶富含心脏保护肽GHRP6,可以使被包封的细胞外囊泡靶向心脏,结果表明其可以明显改善心脏功能,抑制炎症反应和纤维化水平[46]。 由于部分Micro-RNA对心脏损伤后的心功能具有修复作用,于是作者将具有心脏保护功能的Micro-RNA通过不同的方式负载到细胞中从而提取其细胞外囊泡发挥作用,如Song等[47]研究人员将抗凋亡的Micro-RNA-21转染到人胚胎肾细胞系中,成功获得了含有Micro-RNA-21的细胞外囊泡,使细胞外囊泡可以更有效地保护Micro-RNA-21不被降解,并保持其他特性不发生改变,并且在小鼠缺血心肌中局部给予过表达Micro-RNA-21后,Micro-RNA-21可被有效地转移到心肌细胞和内皮细胞中,从而抑制细胞凋亡,促进心功能的恢复。同样地,在另一项研究中通过使用脂质体2000实现了Micro-RNA-338转染至间充质干细胞中,并提取其细胞外囊泡注射到心肌梗死部位,发现其可抑制心肌细胞凋亡和改善心肌梗死后的心功能[48]。LI等[49]也使用脂质体方法获得了心肌梗死负载的细胞外囊泡用于心脏输送,从而改善心肌梗死大鼠的心肌功能,减少梗死面积和心肌自噬。除此之外,还可将Micro-RNA-181a通过慢病毒的方式转导至间充质干细胞中,随后分离出Micro-RNA-181a负载的细胞外囊泡,这些细胞外囊泡能够抑制心肌梗死小鼠模型中的炎症反应[50]。 WANG等[22]通过电穿孔将纤维化的关键抑制剂miRNA-101a载入间充质干细胞来源的细胞外囊泡中,以增加细胞外囊泡的治疗潜力,接下来将其经尾静脉注射后,可抑制心肌梗死部位的转化生长因子β和胶原蛋白的产生,促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,发挥抗炎作用,在急性心肌梗死后显示出心脏保护作用。并且DENG等[51]研究发现细胞外囊泡膜上含有鞘氨醇,并且在鞘氨醇激酶1的作用下,鞘氨醇可被催化形成1-磷酸-鞘氨醇,从而导致细胞外囊泡裂解,而1-磷酸-鞘氨醇会被释放到细胞外空间,促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,改善心肌梗死后的心脏损伤。YU等[52]研究人员通过慢病毒过表达热休克蛋白20在细胞外囊泡中,发现热休克蛋白20介导的心肌细胞外囊泡激活AKT信号通路,抑制肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β因子的释放,减轻心脏受损部位的纤维化程度,促血管生成,改善心肌梗死后的心功能。另外,ZHANG等[53]通过生物膜融合的工程化改造手段,设计出的单核细胞仿生物赋予了细胞外囊泡对损伤心脏显著增强的靶向趋化能力,并且,为解决胞外囊泡产量低、归巢少及功效不确切等问题提供了新方法,并且研究人员将提取的单核细胞膜囊泡作为单核细胞仿生物,通过膜融合的工程技术,将其与间充质干细胞细胞外囊泡融合从而达到仿生修饰的目的,最终得到了具有单核细胞靶向趋化能力的纳米囊泡递送系统。重要的是,经工程化改造后,这种杂合间充质干细胞外囊泡的生物学功能并无明显改变,依然保持了显著的心肌保护、促血管化和免疫调节等功效。 LI等[54]通过血小板膜修饰间充质干细胞的细胞外囊泡(记为P-EV),从而劫持循环中的单核细胞,单核细胞继而介导P-EV到缺血心肌处,从而实现靶向递送P-EV到炎症巨噬细胞。首先,血小板膜表面的糖蛋白赋予了P-EV优先结合循环单核细胞的能力,并随着Ly6Chigh单核细胞募集到心肌缺血交界区;单核细胞跨越血管内皮后受到心脏局部微环境的刺激分化成巨噬细胞,其吞噬能力明显增强,可以大量吞噬原本锚定在单核细胞表面的P-EV;随后,P-EV由于继承了细胞外囊泡逃逸溶酶体的能力,与溶酶体发生膜融合将Micro-RNA等活性物质释放到胞浆中,从而使巨噬细胞更多的极化成M2型巨噬细胞,发挥免疫调节的作用。此外,心脏贴片是将干细胞和其他治疗药物输送到心脏的优秀载体,然而,心脏贴片通常需要开胸手术,这对心肌梗死后的心脏稳态至关重要[55-57],并且在临床前研究中,心脏干细胞来源的外泌体已被证明可促进心肌梗死后的心脏再生。 最近的研究通过心肌内注射将心脏干细胞来源的外泌体集中在梗死灶中,虽然这种方法有一定效果,但由于其侵入性,在临床上并不具有吸引力。因此,有科研人员利用心包腔作为一种天然的“模具”,在心包内注射生物相容性水凝胶治疗药物后,原位形成心脏贴片,发现在啮齿动物心肌梗死模型中,水凝胶心脏贴片可以递送含有诱导多能干细胞来源的心脏祖细胞或间充质干细胞来源的外泌体的水凝胶。注射后,通过减轻免疫反应,增加治疗药物的心脏潴留,从而促进心肌梗死后的心功能恢复[58]。此外,LIU等[41]通过心脏特异性重编程因子将诱导多能干细胞定向分化为心肌细胞,从心肌细胞中纯化的细胞外囊泡提供了无细胞疗法,并可将心脏特异性生物分子递送至受伤组织。结果表明,将多功能干细胞衍生的外泌体(记为iPS-EV)和心肌细胞衍生的外泌体(记为iCM-EV)包装进水凝胶贴片中,并置于大鼠心肌梗死部位2周后,iCM-EV减少了心脏扩张并改善了心肌梗死后的心功能;此外,心肌梗死后4周时,iCM-EV的递送显著减少了梗死面积和心肌细胞肥大;总之,iCM-EV可减少受损心脏中的心肌细胞凋亡,且未导致心律失常。树突状细胞来源的外泌体(记为DEXs)可改善心肌梗死后心功能,但鉴于在外周停留时间短和治疗效果弱的限制,于是作者将树突状细胞来源的外泌体与海藻酸水凝胶结合形成DEXs-Gel,发现该海藻酸水凝胶可持续释放DEXs,延长了DEXs的保留时间,并对体内迁移没有不利影响;然后将DEXs-Gel应用于心肌梗死模型小鼠,发现DEXs-Gel可激活调节性T(Treg)细胞,并促进巨噬细胞向修复性M2型巨噬细胞极化,从而显著增强了DEXs对改善心肌梗死后心功能的治疗效果[59]。 来自心脏球源性细胞的外泌体(CDCs-EV)已被证明可以刺激血管生成,诱导内源性心肌细胞增殖,并调节心肌细胞凋亡和肥大。虽然对心脏损伤发挥强大的修复作用,但是由于其有限的靶向性导致其在心脏潴留时间不够,不能充分发挥心脏保护作用。于是,有研究在心脏球源性细胞的外泌体表面表达心脏靶向肽CMP,不仅保留了其天然的物理性质,而且在心肌内注射后有更高的心脏保留率,从而有利于心肌梗死后心功能的恢复[60]。除此之外,心肌内注射心脏驻留祖细胞来源的细胞外囊泡可减少大鼠心肌梗死后的瘢痕形成,从而改善心脏功能[61]。 鉴于心肌原位注射的技术难度大及可导致大鼠死亡率增加,因此作者探索了一种临床相关的方法来增强心肌细胞的归巢能力,这对全身传递细胞外囊泡的治疗效果至关重要。他们在细胞外囊泡膜表面过表达CXCR4,发现其可增加对缺血心脏的生物利用度,提高了血浆注射心脏保护性外心脏祖细胞的疗效。并且通过静脉注射过表达CXCR4的细胞外囊泡可显著改善心脏功能[62]。但是由于细胞外囊泡在外周循环中的保留时间仍是一个复杂的问题,细胞外囊泡比非吞噬细胞更容易被吞噬细胞吞噬,作者研究发现在间充质干细胞源性细胞外囊泡表面过表达CD47可降低其在外周循环中的被识别和吞噬作用,原因是CD47可与SIRPα结合激活“不要吃我”信号,导致免疫逃逸,从而延长细胞外囊泡在外周循环中的保留时间,最终实现尾静脉输送[43-44]。此外,又通过电穿孔技术构建了负载miRNA21的CD47-细胞外囊泡,结果表明,细胞外囊泡通过外周静脉通路成功地将心肌缺血再灌注损伤后的外源性miR-21转运到左心室心肌,并在体内和体外都发挥了令人满意的抗凋亡作用,减轻心脏炎症,改善心脏形态和缺血再灌注心肌的功能恢复[45]。将MiR-183-5p过表达在骨髓间充质干细胞源性的细胞外囊泡中,发现其可靶向抑制FOXO1的表达,减少缺血再灌注后心肌细胞的凋亡和氧化应激,增加左心室射血分数,改善心功能,从而减少心肌梗死后的缺血再灌注损伤[63]。WANG等[64]在间充质干细胞源性的细胞外囊泡过表达可下调抑制细胞增殖的基因hsa-miR-590-3p,并且为了实现细胞外囊泡的靶向心脏特异性位置,又将上述细胞外囊泡经电穿孔以过表达心脏靶向肽CTNI,通过静脉注射到心肌梗死动物模型中,发现其可靶向心脏,并减少心肌细胞的凋亡,改善心肌梗死后心功能。 2.3 纳米囊泡递送系统与动脉粥样硬化 CHEN等[65]研究发现细胞外囊泡负载YsRNAs可以激活细胞死亡途径和炎症反应,在动脉粥样硬化的发生、进展和诊断中发挥重要作用。另有其他研究发现,由代谢综合征患者的细胞外囊泡携带的Rap1参与促进平滑肌细胞的增殖、迁移、促炎以及激活ERK5/p38途径,从而导致血管炎症和重塑以及动脉粥样硬化[66]。除此之外,WU等[67]将5-氨基乙酰丙酸己酯盐酸盐(HAL)经电穿孔负载至M2型巨噬细胞产生的细胞外囊泡中,形成HAL-M2-Exos,对小鼠进行全身给药,发现HAL-M2-Exos可将其表面的趋化因子受体与动脉粥样硬化部位的炎性血管内皮细胞结合,导致内源性抗炎细胞因子和外源性HAL释放,从而减轻动脉粥样硬化的发生。 2.4 纳米囊泡递送系统与心力衰竭 由于慢性缺血性心力衰竭的发生率不断增加和对供体心脏的获取有限,受损心肌的再生是未来治疗的一个重要目标。恢复心脏功能的一个常规治疗方式是从水凝胶中局部传递药物和生物活性物质[68]。有研究通过将间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡包埋到透明质酸水凝胶中,创建并测试了一种可注射的Exo-Gel,将Exo-Gel注入横主动脉收缩诱导的心力衰竭大鼠心包腔中,发现其可减少左室大小和心肌肥厚。并且在猪模型中也进一步证实了Exo-Gel注射液的可行性和安全性[69]。 2.5 纳米囊泡递送系统与肺动脉高压 Kruppel样因子2(KLF2)信号通路的减少是人类肺动脉高压的一个共同特征,于是作者在内皮细胞中过表达KLF2,提取细胞外囊泡发现,Micro-RNA-181和Micro-RNA-324的表达明显上调,并通过影响肿瘤坏死因子α、MAPK、血管内皮生长因子、核转录因子κB、Toll样受体和N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖(GlcNac)的信号转导,显著改善肺内皮细胞的存活,减少炎症反应,限制血管内皮细胞的增殖[70]。 2.6 纳米囊泡递送系统与心律失常 在将Micro-RNA-320d模拟物转染至细胞外囊泡中,与房颤小鼠的心肌细胞共培养,发现可通过STAT3信号通路减少心肌细胞凋亡,促进心肌细胞存活,改善心功能[71]。 2.7 纳米囊泡递送系统与心肌炎 SiRNA可以发挥心脏保护作用,但如何递送SiRNA至特定的组织或细胞类型,同时避免非特异性递送到其他器官,特别是肝脏,仍然具有挑战性。于是有研究将编码心脏靶向肽CTP-Lamp2b的载体引入人胚肾细胞系中,生成了高表达心脏靶向肽(CTP)-Lamp2b的细胞外囊泡,发现其在大鼠心肌细胞中的摄取率明显增加,增强了外泌体向心脏细胞和心脏组织的传递,但是肝脏对其的摄取并没有明显改变。因此,高表达心脏靶向肽(CTP)-Lamp2b的细胞外囊泡可能被作为心脏病的治疗工具[72]。随后有研究发现通过过表达高水平的心脏靶向肽CTP的细胞外囊泡可以传递小干扰RNA(siRNA)靶向RAGE(晚期糖基化终末产物的受体),而RAGE的药理和遗传抑制都可以缓解心肌炎[40],表现出对心脏功能保护的作用。 2.8 纳米囊泡递送系统减轻心脏毒性 众所周知,化疗仍然是对癌症患者有效的策略之一,其中阿霉素是一种常用于治疗各种癌症的化疗药物。然而,显著的心脏毒性限制了其持续的临床应用(如心肌病和充血性心力衰竭),并且化疗相关的心脏毒性正成为癌症患者预后的最大障碍之一,因此,提供保护性Micro-RNA为心脏毒性的预防和治疗提供了希望,因此作者使用iRGD肽修饰的细胞外囊泡将化疗药物阿霉素靶向传递到小鼠实体肿瘤中,可显著抑制肿瘤生长,但不引起明显的心脏毒性[73]。但是由于其在心脏靶向给药的效率仍远未达到预期,迫切需要进一步提高给药效率。SCHINDLER等[74]将阿霉素通过共孵育及电穿孔的手段负载至细胞外囊泡中,构建纳米囊泡递送系统,发现该系统可以增加细胞对阿霉素的摄取,并且与脂质体载体相比,该纳米囊泡递送系统介导细胞对阿霉素的摄取速度更快、更有效。 有研究发现在超声靶向微泡破坏技术的帮助下,细胞外囊泡介导的Micro-RNA可以显著传递到心脏,且在阿霉素诱导的心脏毒性小鼠模型中,超声靶向微泡破坏技术辅助细胞外囊泡负载Micro-RNA-21进入心脏显著降低了细胞死亡,并恢复了心脏功能[75]。鉴于细胞外囊泡在外周易被单核巨噬系统清除,因此可提出“先阻断,再治疗”的想法;由于网格蛋白重链是一种在包被囊泡形成中起重要作用的蛋白质,同时介导肝脏和脾脏对外泌体的内吞作用显著;因此先通过脂质体介导的转染显著敲除网格蛋白重链,接下来通过用Micro-RNA-21负载的外泌体注射到由阿霉素诱导的心脏毒性模型中,可发现该治疗方式可明显减轻阿霉素所致的心脏毒性;总之预先注射装载siRNA敲除网格蛋白重链的外泌体可以显著阻断单核吞噬细胞系统在脾脏和肝脏中的内吞功能,从而显著改善随后注射的治疗性外泌体在其他靶向器官的体内分布[76]。 2.9 纳米囊泡递送系统与心脏移植 作者前期证实过表达吲哚胺2,3双加氧酶的骨髓源性间充质干细胞可以有效抑制免疫排异反应[77]。但经过基因改造的骨髓源性间充质干细胞应用于临床仍然遥遥无期。有研究将吲哚胺2,3双加氧酶过表达于大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中收集细胞外囊泡,将其经尾静脉注射到腹腔异位移植心脏术后3 d的大鼠模型中,发现其可促进Treg细胞增加,减少移植心脏局部淋巴细胞的浸润,从而改善大鼠腹腔异位移植心脏存活[78]。"

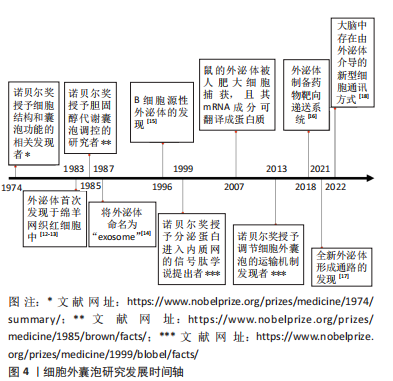
| [1] DE JONG OG, KOOIJMANS SAA, MURPHY DE, et al. Drug delivery with extracellular vesicles: from imagination to innovation. Acc Chem Res. 2019;52(7):1761-1770. [2] De Jong OG, Van Balkom BW, Schiffelers RM, et al. Extracellular vesicles: potential roles in regenerative medicine. Front Immunol. 2014;5:608. [3] 张阳.慢病毒载体的研究进展[J].福建医科大学学报,2014,48(6):407-410. [4] 吴清胜,李媛媛.腺病毒载体的研究及应用进展[J].国际生物制品学杂志, 2021,44(6):353-360. [5] 翟贯星,傅卫辉,徐建青,等.腺相关病毒载体优化的研究进展[J].复旦学报(医学版),2021,48(6):827-833. [6] RAYAMAJHI S, NGUYEN TDT, MARASINI R, et al. Macrophage-derived exosome-mimetic hybrid vesicles for tumortargeted drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2019;94: 482-494. [7] 董丽娜,蔡璐璐,赵明明,等.生物大分子载体在肿瘤纳米靶向药物研发中的应用研究进展[J].山东医药,2019,59(35):83-87. [8] 翟宏强,丁维明,李桂玲.聚合物胶束注射给药系统的研究进展[J].中国医药生物技术,2015,10(5):441-447. [9] 侯天宇,赖芳芳,李青山.载药纳米聚合物研究进展[J].江西化工,2011(2): 12-15. [10] SILVA AK, LUCIANI N, GAZEAU F, et al. Combining magnetic nanoparticles with cell derived microvesicles for drug loading and targeting. Nanomedicine. 2015;11(3):645-55. [11] HERRMANN IK, WOOD MJA, FUHRMANN G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021;16:748-759. [12] HARDING C, HEUSER J, STAHL P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97:329-39. [13] PAN BT, JOHNSTONE RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983; 33:967-978. [14] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Turbide, Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420. [15] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGRL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med 1996;183:1161-1172. [16] CAO HQ, WANG H, HE XY, et al. Bioengineered macrophages can responsively transform into nanovesicles to target lung metastasis. Nano Lett. 2018;18:4762-4770. [17] WEI DG, ZHAN WX, GAO Y, et al. RAB31 marks and controls an ESCRT-independent exosome pathway. Cell Res. 2021;31:157-177. [18] SCHIAPPARELLI LM, SHARMA P, HE HY, et al. Proteomic screen reveals diverse protein transport between connected neurons in the visual system. Cell Rep. 2022;38:110287. [19] SUN D, ZHUANG X, XIANG X, et al. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: theanti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated inexosomes. Mol Ther. 2010;18(9):1606-1614. [20] WALKER S, BUSATTO S, PHAM A, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Theranostics. 2019;9(26):8001-8017. [21] O’LOUGHLIN AJ, MAGER I, DE JONG OG, et al. Functional delivery of lipid-conjugated siRNA by extracellular Vesicles. Mol Ther. 2017;25:1580-1587. [22] WANG J, LEE CJ, DECI MB, et al. MiR-101a loaded extracellular nanovesicles as bioactive carriers for cardiac repair. Nanomedicine. 2020;27:102201. [23] SATO YT, UMEZAKI K, SAWADA S, et al. Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21933. [24] OSKOUIE MN, AGHILI MOGHADDAM NS, BUTLER AE, et al. Therapeutic use of curcumin-encapsulated and curcumin-primed exosomes. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(6):8182-8191. [25] KANG JY, KIM H, MUN D, et al. Co-delivery of curcumin and miRNA-144-3p using heart-targeted extracellular vesicles enhances the therapeutic efficacy for myocardial infarction. J Control Release. 2021;331:62-73. [26] HANEY MJ, KlYACHKO NL, ZhAO Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207:18-30. [27] JAMUR MC, OLIVER C. Permeabilization of cell membranes. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;588:63-66. [28] FUHRMANN G, SERIO A, MAZO M, et al. Active loading into extracellular vesicles significantly improves the cellular uptake and photodynamic effect of porphyrins. J Control Release. 2015;205:35-44. [29] YI G, SON J, YOO J, et al. Application of click chemistry in nanoparticle modification and its targeted delivery. Biomater Res. 2018;22:13. [30] HOOD JL. Post isolation modification of exosomes for nanomedicine applications. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016;11:1745-1756. [31] SINGH A, TRIVEDI P, JAIN NK. Advances in siRNA delivery in cancer therapy. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46:274-283. [32] PIFFOUX M, SILVA AKA, WILHELM C, et al. Modification of extracellular vesicles by fusion with liposomes for the design of personalized biogenic drug delivery systems. ACS Nano. 2018;12(7):6830-6842. [33] ESCUDE MARTINEZ DE CASTILLA P, TONG L, HUANG C, et al. Extracellular vesicles as a drug delivery system: a systematic review of preclinical studies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;175:113801. [34] KOOIJMANS SAA, FLIERVOET LAL, VAN DER MEEL R, et al. PEGylated and targeted extracellular vesicles display enhanced cell specificity and circulation time. J Control Release. 2016;224:77-85. [35] WAN Y, WANG L, ZHU C, et al, Aptamer-conjugated extracellular nanovesicles for targeted drug delivery. Cancer Res. 2018;78(3):798-808. [36] KIM MS, HANEY MJ, ZHAO Y, et al. Engineering macrophage-derived exosomes for targeted paclitaxel delivery to pulmonary metastases: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(1):195-204. [37] DAMS ET, LAVERMAN P, OYEN WJ, et al. Accelerated blood clearance and altered biodistribution of repeated injections of sterically stabilized liposomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;292(3):1071-1079. [38] ISHIDA T, MAEDA R, ICHIHARA M, et al. Accelerated clearance of PEGylated liposomes in rats after repeated injections. J Control Release. 2003;88(1):35-42. [39] FAN J, PAN J, ZHANG X, et al. A peptide derived from the N-terminus of charged multivesicular body protein 6 (CHMP6) promotes the secretion of gene editing proteins via small extracellular vesicle production. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):4702-4716. [40] KIM H, MUN D, KANG JY, et al. Improved cardiac-specific delivery of RAGE siRNA within small extracellular vesicles engineered to express intense cardiac targeting peptide attenuates myocarditis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:1024-1032. [41] LIU B, LEE BW, NAKANISHI K, et al. Cardiac recovery via extended cell-free delivery of extracellular vesicles secreted by cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018; 2(5):293-303. [42] HEALLEN TR, MARTIN JF. Heart repair via cardiomyocyte-secreted vesicles. Nat Biomed Eng, 2018;2:271-272. [43] LE BRAS A. Exosome-based therapy to repair the injured heart. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(7):382. [44] WEI Z, CHEN Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Mononuclear phagocyte system blockade using extracellular vesicles modified with CD47 on membrane surface for myocardial infarction reperfusion injury treatment. Biomaterials. 2021;275:121000. [45] MURPHY DE, DE TONG OG, BROUWER M, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: natural versus engineered targeting and trafficking. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(3):1-12. [46] 韩超珊. MiR--675和水凝胶对间充质干细胞外泌体的改造和应用研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2019. [47] SONG Y, ZHANG C, ZHANG J, et al. Localized injection of miRNA-21-enriched extracellular vesicles effectively restores cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2019;9;2346-2360. [48] FU DL, JIANG H, LI C, et al. MicroRNA-338 in MSCs-derived exosomes inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis in myocardial infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24;10107-10117. [49] LI Y, YANG R, GUO B, et al. Exosomal miR-301 derived from mesenchymal stem cells protects myocardial infarction by inhibiting myocardial autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;514:323-328. [50] WEI Z, QIAO S, ZHAO J, et al. miRNA-181a over-expression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes inflfluenced inflflammatory response after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 2019; 232:116632. [51] DENG S, ZHOU X, Ge Z, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;114:105564. [52] YU DW, GE PP, LIU AL, et al. HSP20-mediated cardiomyocyte exosomes improve cardiac function in mice with myocardial infarction by activating Akt signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(11):4873-4881. [53] ZHANG N, SONG Y, HUANG ZC, et al. Monocyte mimics improve mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle homing in a mouse MI/RI model. Biomaterials. 2020;255:120168. [54] LI Q, HUANG Z, WANG Q, et al. Targeted immunomodulation therapy for cardiac repair by platelet membrane engineering extracellular vesicles via hitching peripheral monocytes. Biomaterials. 202;284:121529. [55] HUANG K, OZPINAR EW, SU T, et al. An off-the-shelf artifificial cardiac patch improves cardiac repair after myocardial infarction in rats and pigs. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(538):eaat9683. [56] GAO L, KUPFER ME, JUNG JP, et al. Myocardial tissue engineering with cells derived from humaninduced pluripotent stem cells and a native-like, high-resolution, 3- dimensionally printed scaffold. Circ Res. 2017;120(8):1318-1325. [57] TANG J, VANDERGRIFF A, WANG Z, et al. A regenerative cardiac patch formed by spray painting of biomaterials onto the heart. Tissue Eng Part C. 2017;23(3):146-155. [58] ZHU D, LI Z, HUANG K, et al. Minimally invasive delivery of therapeutic agents by hydrogel injection into the pericardial cavity for cardiac repair. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1412. [59] ZHANG Y, CAI Z, SHEN Y, et al. Hydrogel-load exosomes derived from dendritic cells improve cardiac function via Treg cells and the polarization of macrophages following myocardial infarction. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):271. [60] MENTKOWSKI KI, LANG JK. Exosomes engineered to express a cardiomyocyte binding peptide demonstrate improved cardiac retention in vivo. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1):10041. [61] VANDERGRIFF A, HUANG K, SHEN D, et al. Targeting regenerative exosomes to myocardial infarction using cardiac homing peptide. Theranostics. 018;8(7):1869-1878. [62] CIULLO A, BIEMMI V, MILANO G, et al. Exosomal expression of CXCR4 targets cardioprotective vesicles to myocardial infarction and improves outcome after systemic administration. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):468. [63] MAO S, ZHAO J, ZHANG ZJ, et al. MiR-183-5p overexpression in bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting FOXO1. Immunobiology. 2022;227(3):152204. [64] WANG Y, DING N, GUAN G, et al. Rapid delivery of Hsa-miR-590-3p using targeted exosomes to treat acute myocardial infarction through regulation of the cell cycle. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2018;14:968-977 [65] CHEN W, LI L, WANG J, et al. Extracellular vesicle YsRNA in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2021;517:15-22. [66] PERDOMO L, VIDAL-GOMEZ X, SOLETI R, et al. Large Extracellular vesicle-associated rap1 accumulates in atherosclerotic plaques, correlates with vascular risks and is involved in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2020;127(6):747-760. [67] WU GH, ZHANG JF, ZHAO QR, et al. molecularly engineered macrophage-derived exosomes with inflammation tropism and intrinsic heme biosynthesis for atherosclerosis treatment. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020;59:4068-4074. [68] PAPE AC, BAKKER MH, TSENG CC, et al. An injectable and drug-loaded supramolecular hydrogel for local catheter injection into the pig heart. J Vis Exp. 2015;(100):e52450. [69] CHENG G, ZHU D, HUANG K, et al. Minimally invasive delivery of a hydrogel-based exosome patch to prevent heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;169:113-121. [70] SINDI HA, RUSSOMANNO G, SATTA S, et al. Therapeutic potential of KLF2-induced exosomal microRNAs in pulmonary hypertension. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1185. [71] LIU LN, ZHANG HR, MAO HY, et al. Exosomal miR-320d derived from adipose tissue-derived MSCs inhibits apoptosis in cardiomyocytes with atrial fibrillation (AF). Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47:3976-3984. [72] KIM H, YUN N, MUN D, et al. Cardiac-specific delivery by cardiac tissue-targeting peptide-expressing exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;499(4):803-808. [73] TIAN Y, Li S, SONG J, et al. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2383-2390. [74] SCHINDLER C, COLLISON A, MATTHEWS C, et al. Exosomal delivery of doxorubicin enables rapid cell entry and enhanced in vitro potency. PLoS One. 2019;14(3):e0214545. [75] SUN W, ZHAO P, ZHOU Y, et al. Ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction assisted exosomal delivery of miR-21 protects the heart from chemotherapy associated cardiotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;532(1):60-67. [76] WAN Z, ZHAO L, LU F, et al. Mononuclear phagocyte system blockade improves therapeutic exosome delivery to the myocardium. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):218-230. [77] LASSER C, ELDH M, LOTVALL J. Isolation and characterization of RNA-containing exosomes. J Vis Exp. 2012;(59):e3037. [78] 贺继刚,韩金秀,撒亚莲,等.过表达IDO骨髓间充质干细胞分泌外泌体改善移植心脏存活[J].安徽医科大学学报,2018,53(9):1383-1387. [79] GHARPURE KM, WU SY, LI C, et al. Nanotechnology: future of oncotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(14):3121-3130. [80] BORRELLI DA, YANKSON K, SHUKLA N, et al. Extracellular vesicle therapeutics for liver disease. J Control Release. 2018;273:86-98. [81] WIKLANDER OP, NORDIN JZ, O’LOUGHLIN A, et al. Extracellular vesicle in vivo biodistribution is determined by cell source, route of administration and targeting. Journal of extracellular vesicles. 2015;4:26316. [82] SUH A, PHAM A, CRESS MJ, et al. Adipose-derived cellular and cell-derived regenerative therapies in dermatology and aesthetic rejuvenation. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;54:100933. [83] AMIRI A, BAGHERIFAR R, ANSARI DEZFOULI E, et al. Exosomes as bio-inspired nanocarriers for RNA delivery:preparation and applications. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):125. |
| [1] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Cao Yue, Ye Xinjian, Li Biyao, Zhang Yining, Feng Jianying. Effect of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1523-1530. |
| [3] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [4] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [5] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [6] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [7] |
Sun Guanghan, Xie Zhencong, Sun Mi, Xu Yang, Guo Dong.
Therapeutic effect and mechanism by which Trichosanthis Fructus-Allii Macrostemonis Bulbus regulates gut microbiota in a rat model of coronary heart disease #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 917-927.
|
| [8] |
Fu Changxi, He Ruibo, Ma Gang, Zhu Zheng, Ma Wenchao.
Effect and mechanism of different training modes on skeletal muscle remodeling in rats with heart failure induced by myocardial infarction
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 221-230.
|
| [9] | Li Yang, Fu Lili, Yang Jiantang. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome attenuates radiation-induced oral mucositis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 31-37. |
| [10] | Zhou Jiaxin, Tao Jiang. A bibliometric analysis of non-coding RNA and mesenchymal stem cell research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 87-94. |
| [11] | Zhang Xingzhou, Wei Ming, Dong Guoqiang, Du Wei, Luo Yiwen, Zhang Nan . Mechanism of postoperative abdominal adhesion formation and therapeutic prospect of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 147-155. |
| [12] | Li Jiao, Li Xiaofeng, Li Jianping. Isolation technique and application of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles from platelet-rich plasma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 156-163. |
| [13] | Qian Yan, Liu Qisong. Enhancing potential of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes for osteoarthritis by adjusting cell culture condition [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 164-174. |
| [14] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [15] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 1199
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 864
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||