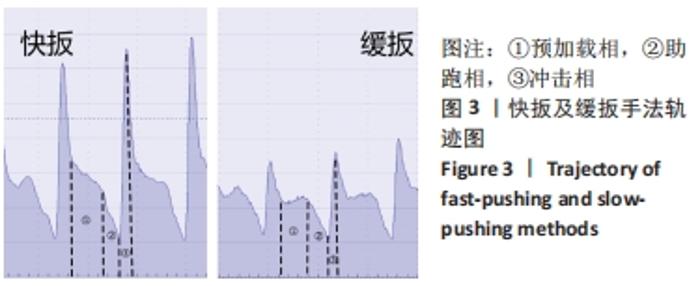
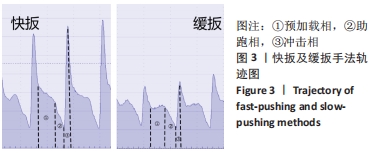
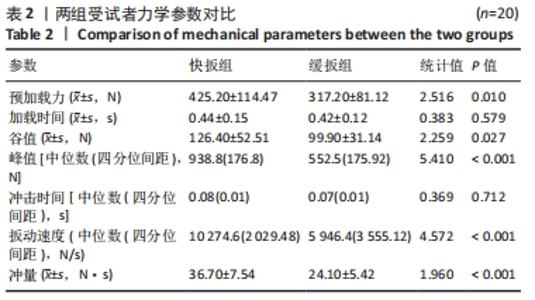
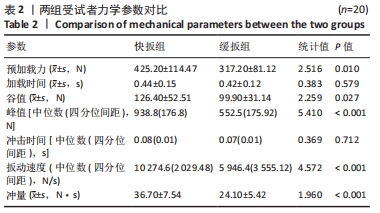
[1] 范志勇,李黎,郭汝松,等.吴山治疗筋伤病的特色经验及正骨手法介绍[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2016,11(8):1067-1069+1076.
[2] 董春苗,黄帆,范志勇,等.基于精准正骨推拿理念侧卧定点踩跷法治疗急性腰椎间盘突出症的临床思考[J].中国中医急症,2020, 29(8):1436-1439.
[3] 吴山,蓝石坚,李涛,等.基于生物力学探讨侧卧定点踩跷法治疗极外侧型腰椎间盘突出症的临床思考[J].世界中医药,2019,14(12): 3406-3409.
[4] 叶武汉,范志勇,黄腾达.侧卧定点踩跷法配合电针治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效观察[J].新中医,2017,49(8):76-78.
[5] 吴震南,范志勇.岭南林氏正骨推拿流派诊治脊柱筋伤病的临床经验[J].环球中医药,2020,13(10):1754-1756.
[6] 胡有谷.腰椎间盘突出症[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2011: 226-230.
[7] 吴震南.侧卧定点踩跷法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床疗效观察[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2020.
[8] 范志勇,蔡敏.吴山诊治筋伤学术思想及临证经验[M].北京:科学卫生出版社,2018:109.
[9] DOWNIE AS, VEMULPAD S, BULL PW. Quantifying the high-velocity, low-amplitude spinal manipulative thrust:A systematic review. J Manip Physiol Ther. 2010;33(7):542-553.
[10] TRIANO JJ, ROGERS CM, COMBS S, et al. Quantitative feedback versus standard training for cervical and thoracic manipulation. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2003;26(3):131-138.
[11] 王景梅,王钲,李兵.按动踩跷法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床研究[J].中国中医急症,2018,27(8):1355-1357.
[12] 齐凤军.踩跷踩法探讨[J].按摩与导引,2001,17(6):14-17.
[13] 李庆兵.踩跷法治疗腰椎间盘突出症医患两者的表面肌电图实验研究[D].成都:成都中医药大学, 2013.
[14] 刘晓瑜,严森,谢慰,等.踩跷推拿技术治疗腰椎间盘突出症30例临床观察[J].湖南中医杂志,2019,35(2):74-75.
[15] 李俊毅,孔赏,马虎升,等.手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的作用机制研究进展[J].中医正骨,2019,31(4): 40-42.
[16] 李庆兵,何成奇,罗才贵.踩跷法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的研究概况[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2021,30(31):3526-3530.
[17] 叶鑫,吕立江,李增图,等.踩跷法联合中药外敷对腰椎间盘突出症患者症状改善情况及炎症因子和TXB2水平的影响[J].中国现代医生,2020,58(22):7-12.
[18] 卢钰,郑太才,王琪,等.不同体位下斜扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(36):5872-5877.
[19] SHU XN, MU WZ, CHEN JF, et al. Comparison of biomechanical effect between oblique Ban-pulling manipulation and lumbar erection-rotation manipulation in sitting position for lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. J Acupunct Tuina Sci. 2017;15(5): 317-321.
[20] 张延海,曹金凤,吕杰,等.基于多刚体力学模型腰椎推拿斜扳法的优化[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(2):277-283.
[21] 刘元华,冯跃,李庆兵,等.基于三维运动捕捉技术的踩跷法运动学参数特征研究[J].北京中医药大学学报,2018,41(3):235-241.
[22] 韩磊.腰部斜扳手法在体运动力学测试及治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床试验研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2012.
[23] 李庆兵,何成奇,冯跃,等.峨眉伤科踩跷法运动学参数分析[J].时珍国医国药,2018,29(10):2560-2562.
[24] HESSELL BW, HERZOG W, CONWAY PJ, et al. Experimental measurement of the force exerted during spinal manipulation using the Thompson technique. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1990;13(8):448-453.
[25] NOUGAROU F, DUGAS C, LORANGER M, et al. The role of preload forces in spinal manipulation: experimental investigation of kinematic and electromyographic responses in healthy adults. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2014;37(5):2872-2893.
|