Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (32): 5173-5178.doi: 10.12307/2022.941
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone metabolism in a rat model of diabetes mellitus intervened by Xianling Gubao Capsules
Jiao Yinghua1, Bao Kairan2, Song Jieqiong2, Xing Lei1, Cui Lihua2, Gao Jingyuan1, Qi Ning1, Liu Xiangyu1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 2North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-06Accepted:2021-02-22Online:2022-11-18Published:2022-05-14 -
Contact:Xing Lei, Master, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Jiao Yinghua, Master, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Government Funded Project for Provincial Clinical Medical Talents in 2017 (to JYH); a grant from Hebei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 2016, No. 2016083 (to JYH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiao Yinghua, Bao Kairan, Song Jieqiong, Xing Lei, Cui Lihua, Gao Jingyuan, Qi Ning, Liu Xiangyu. Bone metabolism in a rat model of diabetes mellitus intervened by Xianling Gubao Capsules[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5173-5178.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
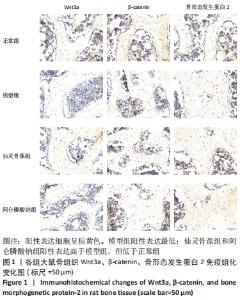
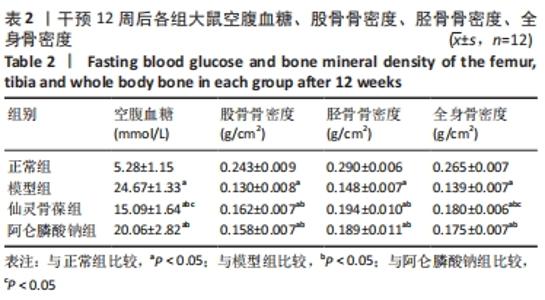
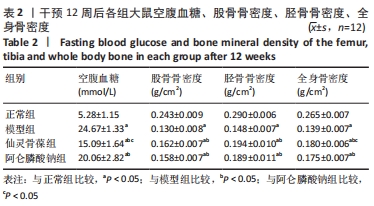
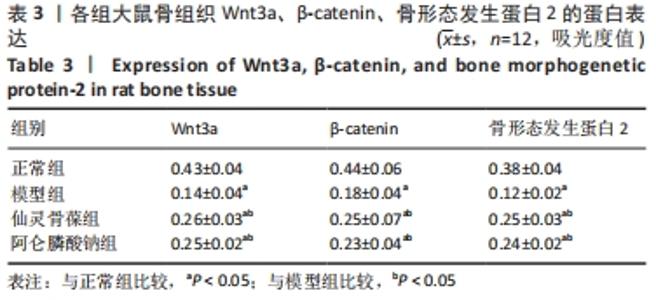
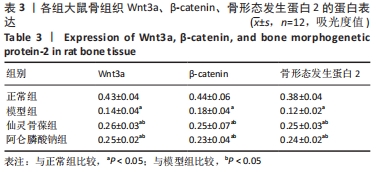
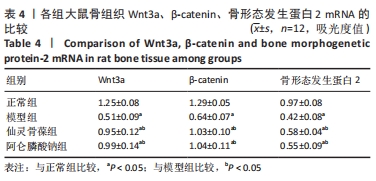
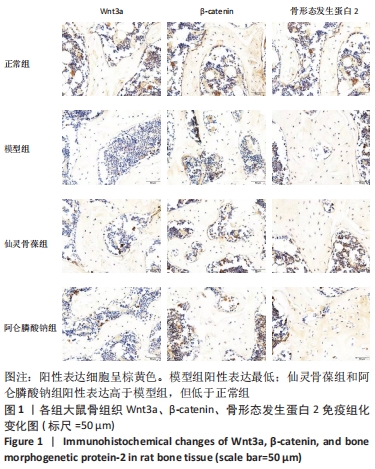
2.3 大鼠骨组织病理学观察结果 正常组大鼠骨质完整、规则,有多个小梁,厚度适中,小梁裂缝狭窄,髓腔宽度小;模型组大鼠骨小梁的完整性受到损害,导致骨小梁的排列欠规则,骨小梁的数量明显减少,相较于正常组,骨小梁的厚度明显减少,髓腔的宽度较大并且大部分被脂肪细胞填充;仙灵骨葆组和阿仑膦酸钠组的大鼠组织病理学变化明显改善,骨小梁局部缺失,布列较不规整,骨小梁的数目明显多于模型组,骨小梁的厚度较适中。 2.4 免疫组织化学法检测骨组织中的成骨标志物因子 Wnt3a、β-catenin、骨形态发生蛋白2的蛋白表达 骨组织中Wnt3a、β-catenin、骨形态发生蛋白2免疫组化阳性表达细胞呈棕黄色。模型组阳性表达最低;仙灵骨葆组和阿仑膦酸钠组阳性表达高于模型组,但低于正常组,见图1,表3。"
| [1] ISHTAYA GA, ANABTAWI YM, ZYOUD SH, et al. Osteoporosis knowledge and beliefs in diabetic patients: a cross sectional study from Palestine. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):43. [2] KURRA S, FINK DA, SIRIS ES. Osteoporosis-associated fracture and diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2014;43(1):233-243. [3] CHANDRAN M, TAY D, HUANG XF, et al. The burden of inpatient care for diabetic and non-diabetic patients with osteoporotic hip fractures—does it differ? An analysis of patients recruited into a fracture liaison service in Southeast Asia. Arch Osteoporos. 2018;13(1):27. [4] WU J, LI W, YE B, et al. The efficacy and safety of Xianling Gubao capsules in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A protocol for a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021; 100(36):e27086. [5] INDRAN IR, LIANG RLZ, MIN TE, et al. Preclinical studies and clinical evaluation of compounds from the genus Epimedium for osteoporosis and bone health. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;162:188-205. [6] LI WD, YAN CP, WU Y, et al. Osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation stimulating activities of the main components of Fructus Psoraleae corylifoliae. Phytomedicine.2014;21(4):400-405. [7] NIU YB, LI YH, KONG XH, et al. The beneficial effect of Radix Dipsaci total saponins on bone metabolism in vitro and in vivo and the possible mechanisms of action. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(11):2649-2660. [8] XING Y, BI HY, ZHANG QN. Introduction of common Chinese patent medicines for the treatment of osteoporosis. Chin J Osteoporos. 2013; 19(1):83-85. [9] ZHU HM, QIN L, GARNERO P, et al. The first multicenter and randomized clinical trial of herbal Fufang for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(4):1317-1327. [10] RAWADI G, ROMAN-ROMAN S. Wnt signalling pathway: a new target for the treatment of osteoporosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005;9(5): 1063-1077. [11] MANOLAGAS SC, ALMEIDA M. Gone with the Wnts: β-catenin, T-cell factor, forkhead box O, and oxidative stress in age-dependent diseases of bone, lipid, and glucose metabolism. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(11): 2605-2614. [12] NIE X, WEI X, MA H, et al. The complex role of Wnt ligands in type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications. J Cell Mol Med. 2021; 25(14):6479-6495. [13] LI X, LIU D, LI J, et al. Wnt3a involved in the mechanical loading on improvement of bone remodeling and angiogenesis in a postmenopausal osteoporosis mouse model.FASEB J. 2019;33(8):8913-8924. [14] WANG BW, FANG WJ, SHYU KG. Micro RNA‐145 regulates disabled‐2 and Wnt3a expression in cardiomyocytes under hyperglycaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48(1). doi: 10.1111/eci.12867. [15] CHEN G, DENG C, LI YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):272-288. [16] ZHANG JM, YU RQ, WU FZ, et al. BMP‑2 alleviates heart failure with type 2 diabetes mellitus and doxorubicin‑induced AC16 cell injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(2):897. [17] ISLAM MS. Experimental rodent models of type 2 diabetes: a review. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2009;31(4):249-261. [18] INABA M, TERADA M, KOYAMA H, et al. Influence of high glucose on 1, 25‐dihydroxyvitamin D3‐induced effect on human osteoblast‐like MG‐63 cells.J Bone Miner Res. 1995;10(7):1050-1056. [19] MACDONALD BT, TAMAI K, HE X. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009;17(1):9-26. [20] KRISHNAN V, BRYANT HU, MACDOUGALD OA.Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling.J Clin Invest. 2006;116(5):1202-1209. [21] BARON R, KNEISSEL M. WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):179-192. [22] KOBAYASHI Y, UEHARA S, UDAGAWA N, et al. Regulation of bone metabolism by Wnt signals. J Biochem. 2016;159(4):387-392. [23] INOUE J, IHARA Y, TSUKAMOTO D, et al. Identification of BCL11B as a regulator of adipogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32750. [24] FIORENZANO A, PASCALE E, D’ANIELLO C, et al. Cripto is essential to capture mouse epiblast stem cell and human embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12589. [25] MALEKI DANA P, SADOUGHI F, MANSOURNIA MA, et al. Targeting Wnt signaling pathway by polyphenols: implication for aging and age-related diseases. Biogerontology. 2021;22(5):479-494. [26] DAY TF, YANG Y. Wnt and hedgehog signaling pathways in bone development.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 1:19-24. [27] KURRA S, FINK DA, SIRIS ES. Osteoporosis-associated fracture and diabetes.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2014;43(1):233-243. [28] GARCÍA-MARTÍN A, ROZAS-MORENO P, REYES-GARCÍA R, et al. Circulating levels of sclerostin are increased in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(1):234-241. [29] MA R, WANG L, ZHAO B, et al. Diabetes perturbs bone microarchitecture and bone strength through regulation of Sema3A/IGF-1/β-catenin in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(1):55-66. [30] XIONG Y, ZHANG Y, XIN N, et al. 1α, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes osteogenesis by promoting Wnt signaling pathway. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;174:153-160. [31] Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, et al. Wnt proteins are lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature. 2003; 423(6938):448-452. [32] Shimizu H, Julius MA, Giarre M, et al. Transformation by Wnt family proteins correlates with regulation of beta-catenin. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8(12):1349-1358. [33] RAWADI G, VAYSSIÈRE B, DUNN F, et al. BMP‐2 controls alkaline phosphatase expression and osteoblast mineralization by a Wnt autocrine loop. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(10):1842-1853. [34] CHEN Y, WANG G, MA Z, et al. Adverse effects of high glucose levels on somite and limb development in avian embryos.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014;71:1-9. [35] MA XY, FENG YF, MA ZS, et al. The promotion of osteointegration under diabetic conditions using chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite coating on porous titanium surfaces. Biomaterials. 2014;35(26):7259-7270. [36] SHAO X, YANG Y, TAN Z, et al. Amelioration of bone fragility by pulsed electromagnetic fields in type 2 diabetic KK-Ay mice involving Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021;320(5): E951-E966. [37] SCHMITT B, RINGE J, HÄUPL T, et al. BMP2 initiates chondrogenic lineage development of adult human mesenchymal stem cells in high-density culture. Differentiation. 2003;71(9-10):567-577. [38] INTINI G, NYMAN JS. Dkk1 haploinsufficiency requires expression of Bmp2 for bone anabolic activity. Bone. 2015;75:151-160. [39] RUAN W, XUE Y, ZONG Y, et al. Effect of BMPs and Wnt3a co-expression on the osteogenetic capacity of osteoblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(5): 4328-4334. [40] DUMIC-CULE I, PERIC M, KUCKO L, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins in fracture repair. Int Orthop. 2018;42(11):2619-2626. [41] LEE EJ, NA W, KANG MK, et al. Hydroxycoumarin scopoletin inhibits bone loss through enhancing induction of bone turnover markers in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Biomedicines. 2021;9(6):648. [42] KARIM K, GIRIBABU N, SALLEH N. Marantodes pumilum Var Alata (Kacip Fatimah) ameliorates derangement in RANK/RANKL/OPG pathway and reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in the bone of estrogen-deficient female rats with type-2 diabetes. Phytomedicine. 2021;91:153677. [43] SHAO H, WU R, CAO L, et al. Trelagliptin stimulates osteoblastic differentiation by increasing runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2): a therapeutic implication in osteoporosis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1): 960-968. [44] DONG C, YANG H, WANG Y, et al. Anagliptin stimulates osteoblastic cell differentiation and mineralization. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020; 129:109796. [45] XUE S, GAO P, TAN X, et al. Effect of Down-Regulating AK045490 on Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BMSCs) Under High Glucose Environment by Targeting Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated (FTO). Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering. 2020;10(10):1541-1547. [46] FATCHIYAH F, SETIAWAN B, SASASE T, et al. The amelioration of T2DM rat femoral bone achieved by anti-osteoporosis of caprine CSN1S2 protein through bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathway. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021;68(2):265-275. |
| [1] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [3] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [4] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [5] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [6] | Zhang Lichuang, Gao Huali, Wang Jingchao, Lin Huijun, Wu Chonggui, Ma Yinghui, Huang Yunfei, Fang Xue, Zhai Weitao. Effect of tendon manipulation with equal emphasis on muscles and bones on accelerating the functional rehabilitation of quadriceps femoris after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1383-1389. |
| [7] | Du Xueting, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Yanjun, Wang Mei, Chen Wubiao, Huang Wenhua. Application of compressed sensing technology in two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1396-1402. |
| [8] | You Zhengqiu, Zhang Zhongzu, Wang Qunbo. Early symptomatic intervertebral disc pseudocysts after discectomy detected on MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1403-1409. |
| [9] | Li Chao, Zhang Peipei, Xu Mengting, Li Linlin, Ding Jiangtao, Liu Xihua, Bi Hongyan. Respiratory training improves morphological changes of the multifidus muscle in patients with chronic nonspecific lower back pain assessed by musculoskeletal ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1417-1421. |
| [10] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [11] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [12] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [13] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [14] | Li Mengfei, Zhang Hong, Zhao Shaojian, Yin Guanghao, Wang Qibao. Expression of forkhead box protein 3 in refractory periapical periodontitis in rats with Enterococcus faecalis infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1187-1192. |
| [15] | Zhao Lu, Zhao Yifei, Gao Da, Liu Yanfang, Fu Tingting, Xu Jiangyan. Expression of suppressor of Zeste 12 in kidney tissues of rats with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||