Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (31): 5014-5019.doi: 10.12307/2022.970
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism by which echinacoside delays the senescence of human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Tian Tian, Ouyang·Juyan, Li Yu, Miyesai·Ainiwaer, He Juanli, Li Zhenhua, Wang Hong
- Second Department of Comprehensive Internal Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-12-06Accepted:2022-02-08Online:2022-11-08Published:2022-04-24 -
Contact:Wang Hong, MD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Second Department of Comprehensive Internal Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Tian Tian, Master candidate, Second Department of Comprehensive Internal Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Plan Project of Karamay City, No. 2017RC001A-16 (to WH); Postgraduate Innovatian Entrepreneurship Project of Xinjiang Medical University, No. CXCY2021008 (to TT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Tian, Ouyang·Juyan, Li Yu, Miyesai·Ainiwaer, He Juanli, Li Zhenhua, Wang Hong. Mechanism by which echinacoside delays the senescence of human umbilical vein endothelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5014-5019.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
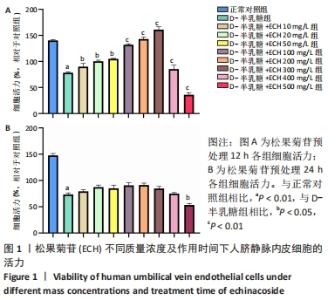
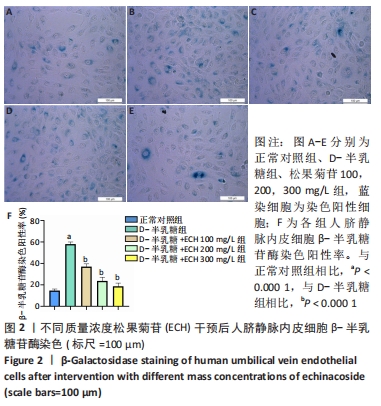
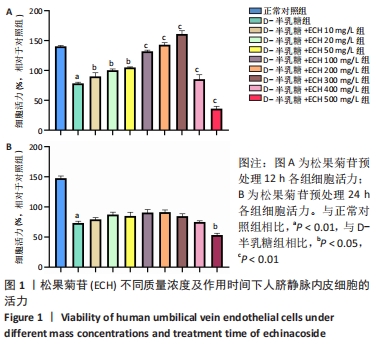
2.1 CCK-8法筛选松果菊苷最佳质量浓度及干预时间 由图1可见,松果菊苷预处理12 h组明显比24 h组细胞存活率高。松果菊苷预处理12 h组中:①与正常对照组相比,D-半乳糖组细胞存活率明显下降,P < 0.000 1,说明D-半乳糖对细胞有一定损伤作用;②与D-半乳糖组相比,松果菊苷100,200,300 mg/L组均促进细胞增殖,其中松果菊苷200 mg/L组与松果菊苷100 mg/L组相比,P < 0.01,松果菊苷300 mg/L组与松果菊苷200 mg/L组相比,P < 0.01,松果菊苷300 mg/L组与松果菊苷100 mg/L组相比,P < 0.001,松果菊苷300 mg/L组促进细胞增殖作用最明显;③随着松果菊苷质量浓度的增加,细胞增殖活力一开始呈上升趋势,松果菊苷300 mg/L组促进细胞增殖作用最明显,但随着松果菊苷质量浓度继续增加,反而抑制细胞增殖活力,说明松果菊苷在一定质量浓度范围内对人脐静脉内皮细胞活性起促进作用,调整松果菊苷质量浓度在适当范围内是延缓人脐静脉内皮细胞衰老的关键。"
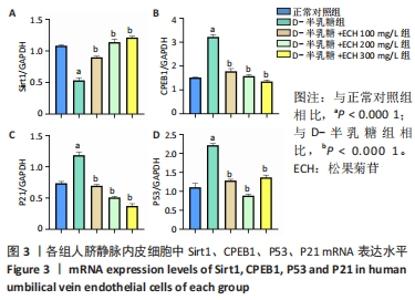
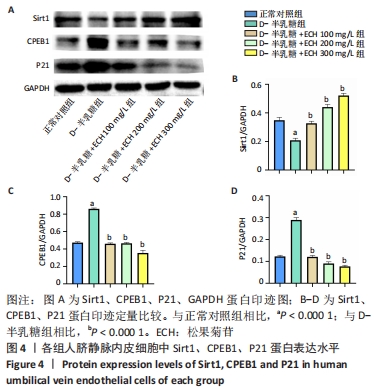
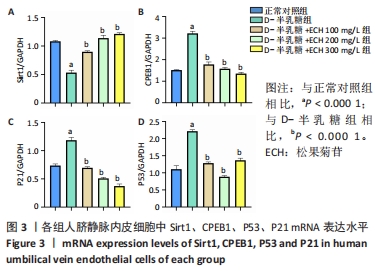
2.3 松果菊苷对人脐静脉内皮细胞中CPEB1、Sirt1、P53、P21 mRNA及蛋白表达水平的影响 如图3所示,与正常对照组相比,D-半乳糖组Sirt1 mRNA表达水平明显下降,CPEB1、P53、P21 mRNA表达水平均升高。与D-半乳糖组相比,松果菊苷100,200,300 mg/L组Sirt1 mRNA表达均不同程度升高,CPEB1、P53、P21 mRNA表达水平均下降。如图4所示,Sirt1、CPEB1、P21蛋白表达趋势与PCR结果一致。这些证据表明松果菊苷可缓解D-半乳糖诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞衰老损伤,这种保护作用可能通过上调Sirt1表达,下调CPEB1、P53、P21表达水平实现。"
| [1] SHEN CY, JIANG JG, YANG L, et al. Anti-ageing active ingredients from herbs and nutraceuticals used in traditional Chinese medicine: pharmacological mechanisms and implications for drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(11):1395-1425. [2] NORTH BJ, SINCLAIR DA. The intersection between aging and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2012;110(8):1097-1108. [3] VAN DEURSEN JM. The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature. 2014; 509(7501):439-446. [4] BRUN C, JEAN-LOUIS F, ODDOS T, et al. Phenotypic and functional changes in dermal primary fibroblasts isolated from intrinsically aged human skin. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25(2):113-119. [5] JOHMURA Y, NAKANISHI M. Multiple facets of p53 in senescence induction and maintenance. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(11):1550-1555. [6] ZHANG R, ADAMS PD. Heterochromatin and its relationship to cell senescence and cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 2007;6(7):784-789. [7] ALIPIEVA K, KORKINA L, ORHAN IE, et al. Verbascoside--a review of its occurrence, (bio)synthesis and pharmacological significance. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(6):1065-1076. [8] WU L, GEORGIEV MI, CAO H, et al. Therapeutic potential of phenylethanoid glycosides: A systematic review. Med Res Rev. 2020; 40(6):2605-2649. [9] LIU J, YANG L, DONG Y, et al. Echinacoside, an Inestimable Natural Product in Treatment of Neurological and other Disorders. Molecules. 2018;23(5):1213. [10] WANG N, JI S, ZHANG H, et al. Herba Cistanches: Anti-aging. Aging Dis. 2017;8(6):740-759. [11] 李欢,宋安齐,薛嘉虹,等.松果菊苷对血管内皮细胞损伤的保护作用[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2013,34(3):387-392. [12] DONATO AJ, MORGAN RG, WALKER AE, et al. Cellular and molecular biology of aging endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;89(Pt B): 122-135. [13] LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO MA, PARTRIDGE L, et al. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013;153(6):1194-1217. [14] 庞明,刘展,李韶山,等.同型半胱氨酸对血管内皮细胞衰老的影响[J].新疆医学,2020,50(7):670-674. [15] LAMICHANE S, BAEK SH, KIM YJ, et al. MHY2233 Attenuates Replicative Cellular Senescence in Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells via SIRT1 Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:6492029. [16] PANG J, XIONG H, OU Y, et al. SIRT1 protects cochlear hair cell and delays age-related hearing loss via autophagy. Neurobiol Aging. 2019; 80:127-137. [17] XIE L, HUANG R, LIU S, et al. A positive feedback loop of SIRT1 and miR17HG promotes the repair of DNA double-stranded breaks. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(17):2110-2123. [18] NAKAGAWA T, GUARENTE L. SnapShot: sirtuins, NAD, and aging. Cell Metab. 2014;20(1):192. [19] KASZUBOWSKA L, FOERSTER J, KWIATKOWSKI P, et al. NKT-like cells reveal higher than T lymphocytes expression of cellular protective proteins HSP70 and SOD2 and comparably increased expression of SIRT1 in the oldest seniors. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2018;56(4):231-240. [20] GUO Y, XING L, QIAN C, et al. Involvement of Flavonoids from the Leaves of Carya cathayensis Sarg. in Sirtuin 1 Expression in HUVEC Senescence. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:8246560. [21] SHEN P, DENG X, CHEN Z, et al. SIRT1: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12:779177. [22] FANG Y, WANG X, YANG D, et al. Relieving Cellular Energy Stress in Aging, Neurodegenerative, and Metabolic Diseases, SIRT1 as a Therapeutic and Promising Node. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13: 738686. [23] YAO H, RAHMAN I. Perspectives on translational and therapeutic aspects of SIRT1 in inflammaging and senescence. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84(10):1332-1339. [24] RAMIS MR, ESTEBAN S, MIRALLES A, et al. Caloric restriction, resveratrol and melatonin: Role of SIRT1 and implications for aging and related-diseases. Mech Ageing Dev. 2015;146-148:28-41. [25] MAEDA M, TSUBOI T, HAYASHI T. An Inhibitor of Activated Blood Coagulation Factor X Shows Anti-Endothelial Senescence and Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects. J Vasc Res. 2019;56:181-190. [26] WARBOYS CM, DE LUCA A, AMINI N, et al. Disturbed flow promotes endothelial senescence via a p53-dependent pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:985-995. [27] BIAN W, JING X, SUN Y, et al. Downregulation of LncRNA NORAD promotes Ox-LDL-induced vascular endothelial cell injury and atherosclerosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(7):6385-6400. [28] RYAN KM, PHILLIPS AC, VOUSDEN KH. Regulation and function of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13(3):332-337. [29] MORGAN RG, IVES SJ, LESNIEWSKI LA, et al. Age-related telomere uncapping is associated with cellular senescence and inflammation independent of telomere shortening in human arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;305(2):H251-258. [30] CASELLA G, MUNK R, KIM KM, et al. Transcriptome signature of cellular senescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(14):7294-7305. [31] FERNÁNDEZ-MIRANDA G, MÉNDEZ R. The CPEB-family of proteins, translational control in senescence and cancer. Ageing Res Rev. 2012; 11(4):460-472. [32] BURNS DM, RICHTER JD. CPEB regulation of human cellular senescence, energy metabolism, and p53 mRNA translation. Genes Dev. 2008;22(24):3449-3460. [33] BURNS DM, D’AMBROGIO A, NOTTROTT S, et al. CPEB and two poly(A) polymerases control miR-122 stability and p53 mRNA translation. Nature. 2011;473(7345):105-108. [34] XU K, REN G. Depletion of CPEB1 protects against oxidized LDL-induced endothelial apoptosis and inflammation though SIRT1/LOX-1 signalling pathway. Life Sci. 2019;239:116874. [35] GROISMAN I, IVSHINA M, MARIN V, et al. Control of cellular senescence by CPEB. Genes Dev. 2006;20(19):2701-2712. [36] HU GS, HUR YJ, JIA JM, et al. Effects of 2-aminoindan-2-phosphonic acid treatment on the accumulation of salidroside and four phenylethanoid glycosides in suspension cell culture of Cistanche deserticola. Plant Cell Rep. 2011;30(4):665-674. [37] YOU SP, MA L, ZHAO J, et al. Phenylethanol Glycosides from Cistanche tubulosa Suppress Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Block the Conduction of Signaling Pathways in TGF-β1/smad as Potential Anti-Hepatic Fibrosis Agents. Molecules. 2016;21(1):102. [38] 艾江,余扬,费蒙辉,等.松果菊苷对人增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞TGF-β1/Smads信号通路影响的实验研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2021,32(3):187-189. [39] ZHU H, CHENG C, ZHANG C, et al. Echinacoside suppresses cellular senescence of human fibroblastic cells by down-regulation of p53. J Chin Pharm Sci. 2011;1(5):523-528. |
| [1] | Pan Baoshun, Fang Zhen, Gao Mingjie, Fang Guiming, Chen Jinshui. Design for posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation system with fusion cage based on imaging data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1372-1376. |
| [2] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [3] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [4] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [5] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [6] | Xu Kuishuai, Zhang Liang, Chen Jinli, Ren Zhongkai, Zhao Xia, Li Tianyu, Yu Tengbo. Effect of force line changes on lower limb joints after medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 821-826. |
| [7] | Pan Xian, Liang Simin, Liu Bingxia, Song Tianzeng, Ma He, Wu Peng, Ge Zhaohui. Correlation between pelvic incidence-lumbar lordosis and clinical outcome in patients with degenerative lumbar scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5370-5375. |
| [8] | Sun Ying, Xiang Guangda, Xu Xiaoli. Effects of myeloid-derived growth factor on ventricular remodeling in aging mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5020-5025. |
| [9] | Zhan Yuanbo, Liu Xinpeng, Xu Wenxia, Miao Nan, Mu Sen, Zhang Ruimin, Li Ying. Expression of histone deacetylase 9 in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells during senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4762-4766. |
| [10] | Lin Bo, Chen Xinyu, Jin Qiu, Zhu Zhiman, Zhao Wenhui. Effects of miR-126-3p from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell released exosomes on human umbilical vein endothelial cell glucolipotoxicity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4773-4779. |
| [11] | Zhang Jian, Lin Jianping, Zhou Gang, Fang Yehan, Wang Benchao, Wu Yongchang. Semi-quantitative MRI evaluation of cartilage degeneration in early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 425-429. |
| [12] | Liu Yubo, Zhang Huizeng, Zhang Tongrun, Sui Gengyi, Ma Nan, Cheng Xu, Gao Xupeng, Xu Jing, Wang Chaoliang. Correlation analysis between the morphological changes of ankle acupoints and the ankle function after ankle fracture surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 440-445. |
| [13] | Zhou Zhiwei, Niu Wanqiong, Ren Lijuan, Wang Zhenhua. Effect of grain boundary segregation on low-temperature aging of 3% yttrium oxide stabilized zirconia ceramics co-doped with GeO2 and TiO2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4320-4324. |
| [14] | Wang Yuyin, Wei Wenyue, Guo Minfang, Li Hongxia, Zhang Jing, Gu Qingfang, Liu Xiaoqin, Guo Xiaoping, Song Lijuan, Chai Zhi, Ma Cungen, Wei Jiezhong. Bushen Yizhi Anti-aging Prescription improves cognitive function of APP/PS1 mice by regulating microglia and macrophage polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4166-4172. |
| [15] | Zeng Yuwei, Huang Chuang, Wei Jianguo, Duan Dongming, Wang Le. Tracing transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rat calvarial defect by bioluminescence imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3968-3973. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||