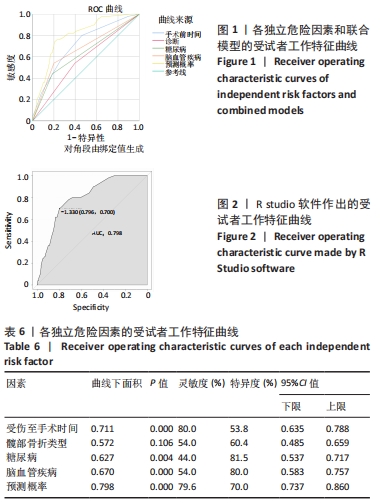
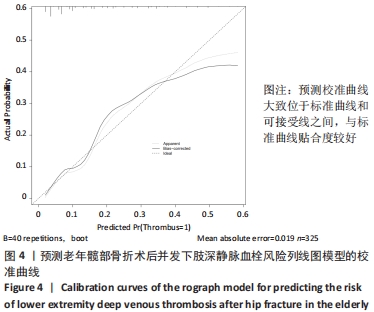
[1] 李兴国,邓叶龙,刘朝晖,等.中国老年髋部骨折流行性病学特征分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2021,27(7):601-606.
[2] 谢添,马彬彬,李荥娟,等.加速康复外科在老年髋部骨折的研究现状[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(8):1038-1046.
[3] SOFFIN EM, YADEAU JT. Enhanced recovery after surgery for primary hip and knee arthroplasty: a review of the evidence. Br J Anaesth. 2016;117(suppl 3):i62-i72.
[4] AASVANG EK, LUNA IE, KEHLET H. Challenges in postdischarge function and recovery: the case of fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115(6):861-866.
[5] 刘春香,成传芳,赵晨,等.骨折联络服务在老年髋部脆性骨折患者中的应用[J].中华护理杂志,2019,54(9):1343-1348.
[6] KYRLE PA, EICHINGER S. Deep vein thrombosis. Lancet. 2005;365(9465): 1163-1174.
[7] WAKEFIELD TW, MYERS DD, HENKE PK. Mechanisms of venous thrombosis and resolution.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28(3): 387-391.
[8] Pannucci CJ, dSandra L, Dimick JB, et al. A validated risk model to predict 90-day VTE events in postsurgical patients. Chest. 2014;145(3): 567-573.
[9] SCHAEFER JK, JACOBS B, WAKEFIELD TW, et al. New biomarkers and imaging approaches for the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Curr Opin Hematol. 2017;24(3):274-281.
[10] ENDEN T, HAIG Y, KLOW NE, et al. Long-term outcome after additional catheter-directed thrombolysis versus standard treatment for acute iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis (the CaVenT study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;379(9810):31-38.
[11] 李浩,窦群立,范秀风,等.七味三芎汤治疗髋部骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓[J].长春中医药大学学报,2019,35(3):483-486.
[12] 籍芳华,何云霞,刘晓宁.老年髋部骨折患者围手术期下肢深静脉血栓阳性率及影响因素[J].河北医药,2021,43(12):1805-1808+1813.
[13] 郝鹏飞,高智,党培业,等.抗凝时间对老年髋部骨折患者围术期深静脉血栓发生率的影响[J].血栓与止血学,2021,28(2):290-291.
[14] 胡钢,李刚,殷铭,等.预测老年髋部骨折深静脉血栓风险的列线图模型构建[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2021,29(6):26-31.
[15] 刘大伟,牛帅.老年粗隆间骨折后发生下肢深静脉血栓的多因素分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2020,6(3):128-135.
[16] 岳睿,李晓玉,杨明辉,等.高龄老年髋部骨折患者术前下肢深静脉血栓形成的危险因素[J].首都医科大学学报,2020,41(3):458-463.
[17] 张猛,刘刚,于广洋,等.髋关节骨折患者术前深静脉血栓形成的危险因素分析[J].局解手术学杂志,2021,30(8):708-712.
[18] 李杰. 创伤下肢骨折患者深静脉血栓发生时间规律及危险因素的临床研究[D].延安:延安大学,2020.
[19] 侯玉芬,刘政.下肢深静脉血栓形成诊断及疗效标准(2015年修订稿)[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2016,22(5):520-521.
[20] 张英泽.老年髋部骨折—中国骨科医师面临的机遇和挑战[J].中华创伤杂志,2014,30(3):193-195.
[21] REZZADEH K, BEHERY OA, KESTER BS, et al. Patellofemoral arthroplasty: short-term complications and risk factors. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(9): 912-918.
[22] PERRIER A, BOUNAMEAUX H. Cost-effective diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86(1): 475-487.
[23] ELF JL, STRANDBERG K, SVENSSON PJ. The diagnostic performance of APC-PCI complex determination compared to D-dimer in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2010; 29(4):465-470.
[24] RIVA N, CAMPORESE G, IOTTI M, et al. Age-adjusted D-dimer to rule out deep vein thrombosis: findings from the PALLADIO algorithm. J Thromb Haemost. 2018;16(2):271-278.
[25] RIVA N, RIGHINI M, CAMPORESE G, et al. Accuracy of age-adjusted D-dimer to rule out deep vein thrombosis in the elderly. Thromb Res. 2019;174:148-150.
[26] ZHANG W, HUAI Y, WANG W, et al.A Retrospective cohort study on the risk factors of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) for patients with traumatic fracture at Honghui Hospital. BMJ Open. 2019;9(3): e024247.
[27] 中国老年医学学会骨与关节分会创伤骨科学术工作委员会.老年髋部骨折诊疗专家共识(2017)[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(11): 921-927.
[28] 李树灏,张堃,冯东旭,等.髋部骨折24小时内及延迟入院的下肢深静脉血栓发生情况分析[J].骨科,2019,10(4):307-313.
[29] XING F, LI L, LONG Y, et al. Admission prevalence of deep vein thrombosis in elderly Chinese patients with hip fracture and a new predictor based on risk factors for thrombosis Screening. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):444.
[30] 马俊,沈彬,杨静,等.人工全髋关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的危险因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(13):965-969.
[31] 许凤云.髋关节置换术患者深静脉血栓形成危险因素分析及风险评估[J].湖南师范大学学报(医学版),2018,15(3):107-110.
[32] 苏其朱,陈仕雄,孟志斌.髋关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的危险因素分析[J].解放军医药杂志,2018,30(5):66-69.
[33] 胡炎权,张国超.下肢骨折患者深静脉血栓形成的影响因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016(9):1001-1003.
[34] 邱天,郭曙光,方伟,等.下肢深静脉血栓发病的高危因素[J].中华医学志,2013,93(29):2279-2282.
[35] 肖湘,冯凯强,袁宇,等.老年骨质疏松性髋部骨折患者术前下肢深静脉血栓患病率及危险因素分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(11): 1084-1090.
[36] 马华山,刘金山,田玲,等.下肢关节手术患者行硬膜外麻醉及全麻的凝血相关指标及血栓发生率观察[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2016,22(5):464-467.
[37] 马华山,刘金山,田玲,等.老年全膝关节置换中全麻和硬膜外麻醉对凝血功能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(35): 5610-5614.
[38] 王晨,王鹏飞,宋哲,等.股骨颈骨折术后发生下肢深静脉血栓的相关研究[J].国际外科学杂志,2018,45(7):452-455.
[39] MACKMAN N. New insights into the mechanisma of wenous thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(7):2331-2336.
[40] 郭云云.全髋关节置换术后患者深静脉血栓形成的logistic回归分析[J].中国校医,2015,29(1):45-46.
|