Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (27): 4417-4422.doi: 10.12307/2022.877
Previous Articles Next Articles
Novel nano-delivery system: engineered small extracellular vesicles
Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Liu Tingjiao, Niu Weidong
- School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-19Accepted:2021-05-08Online:2022-09-28Published:2022-03-12 -
Contact:Niu Weidong, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhang Mi, Master candidate, Physician, School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116041, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82073001 (to LTJ); Natural Science Basic Research Project of the Education Department of Liaoning Province, No. LZ2019038 (to NWD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Liu Tingjiao, Niu Weidong. Novel nano-delivery system: engineered small extracellular vesicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4417-4422.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
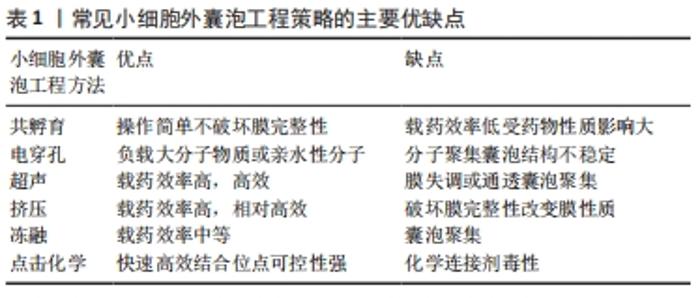
2.1 小细胞外囊泡 自20世纪80年代初期PAN和JOHNSTONE提出外泌体概念以来,外泌体就被视为将细胞垃圾产物运送到细胞外环境的载体[18]。然而,通过多年来对外泌体的大量研究,学者们已经发现了它们的各种关键功能,包括广泛的细胞间通讯[19]、癌症进展和转移[20]、胚胎发生[21]、器官发育[22]、伤口愈合和组织再生[23]、细胞分化[24]、免疫调节及抗原呈递等[25-26],这些功能涉及广泛的生物医学应用,包括癌症治疗和诊断[27]、药物递送[28]、基因治疗[29]、组织再生和疫苗开发等[30-31]。由于目前很难分离出纯度非常高的外泌体亚群,所以依据国际细胞外囊泡协会的建议,通常将纯化得到的粒径小于100 nm或小于200 nm的囊泡称之为小细胞外囊泡[14],这一命名逐渐替代外泌体被广泛接受。尽管天然小细胞外囊泡在医学领域具有多种潜力,但其临床应用仍具有一些固有的局限性,如向组织运输效率低、循环半衰期短、易被单核吞噬细胞系统清除、缺乏靶向细胞选择性等。 各种生物技术方法的迅速发展导致了小细胞外囊泡工程学新领域的出现。小细胞外囊泡工程化旨在通过表面改造或用功能配体修饰实现将内外源性分子、药物、蛋白质或核酸负载到小细胞外囊泡表面或腔内,或实现将小细胞外囊泡靶向特定类型的细胞或组织,从多角度多方面改善小细胞外囊泡的递送性能,在促进小细胞外囊泡的临床应用上具有显著意义[16,32-33]。 2.2 小细胞外囊泡工程化策略 目前小细胞外囊泡的工程改造策略主要概括为2个方向,一是针对亲代细胞即分离前小细胞外囊泡的“细胞工程”,二是针对分离后小细胞外囊泡自身的“小细胞外囊泡工程”。 2.2.1 细胞工程 小细胞外囊泡几乎可由所有细胞分泌,不同细胞来源的小细胞外囊泡具有特定的特征、组成及其对靶细胞的作用[34]。由于特殊的内体分选机制,细胞内含的物质被分拣到小细胞外囊泡内,细胞产生的小细胞外囊泡通过内吞途径、配体-受体相互作用或膜融合等方式实现细胞间的信息传递,故小细胞外囊泡所携带的物质与亲代细胞密切相关,也自然表现出其亲代细胞的特征[35-36]。“细胞工程”是指通过基因工程等技术修饰或改造亲代细胞以使其分泌特殊的小细胞外囊泡,即通过改变亲代细胞的一些遗传特性将功能性分子内化到细胞内部,使其自然地被分拣到小细胞外囊泡中后随着小细胞外囊泡的释放而发挥特定作用。 常见的“细胞工程”手段之一是用编码与特定功能分子融合的小细胞外囊泡膜蛋白的重组质粒转染供体细胞,以达到在小细胞外囊泡表面上载入功能性分子的目的[37],使用小细胞外囊泡信号肽是最常见的方法[38]。溶酶体相关膜蛋白2b(Lamp2b)是具有小细胞外囊泡信号肽的小细胞外囊泡表面蛋白,ALVAREZ-ERVITIL等[39]将Lamp2b与一种神经元特异性靶向肽——狂犬病毒糖蛋白融合构建质粒,并转染未成熟的树突状细胞,以将狂犬病毒糖蛋主动载入细胞分泌的小细胞外囊泡,获得小细胞外囊泡-狂犬病毒糖蛋,当这些小细胞外囊泡-狂犬病毒糖蛋被全身给药时,表面的狂犬病毒糖蛋导致这些小细胞外囊泡在小鼠的神经元和大脑中积聚,在使小细胞外囊泡获得靶向性的同时也有效利用了小细胞外囊泡可穿越血脑屏障的优势,向大脑递送了内含物质。目的蛋白与Lamp2b的融合非常常见,很多学者利用上述类似的方式,将蛋白作为靶向部分,配体或受体表达在小细胞外囊泡表面,以在一定程度上提高小细胞外囊泡与受体细胞表面受体或配体的亲和力,进一步提高小细胞外囊泡的靶向性,有效递送药物至靶向位置以发挥药物功效[40]。其他一些可以作为工程化小细胞外囊泡表面修饰的常用分子还包括四跨膜蛋白(CD63、CD9、CD81)、血小板衍生生长因子受体、糖基磷脂酰肌醇等[41-43];此外,由于与水泡性口炎病毒糖蛋白相似的结构域参与细胞内体和小细胞外囊泡的形成,故水泡性口炎病毒糖蛋白也可作为小细胞外囊泡表面载入功能性配体的锚定结构[44]。 除了小细胞外囊泡的表面修饰手段,如何成功将功能性核酸或蛋白质等治疗性分子载入小细胞外囊泡内部也是“细胞工程”的主要追求目标。 具有代表性的“细胞工程”手段是基于泛素化的蛋白质递送策略。早期研究表明,含L-结构域的蛋白质通过泛素途径与内体分选复合物(ESCRT)成分相互作用,参与小细胞外囊泡中的生物发生及蛋白质分选等过程[45]。Nedd4家族相互作用蛋白1(Ndfip1)包含3个已知与Nedd4泛素连接酶家族WW结构域相互作用的高度保守的L结构域基序(PPxY),STERZENBACH等[46]利用在目的蛋白上插入WW标签的手段,使目的蛋白与Ndfip1相互作用并介导目的蛋白的泛素化,以将蛋白质成功负载入小细胞外囊泡内部;他们将Cre重组酶与2个WW标签融合,构建WW-Cre质粒,转染Ndfip1+小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞72 h后收集上清,利用超速离心法结合蔗糖密度梯度离心法成功分离了含WW-Cre的小细胞外囊泡,其在被受体细胞摄取后显示出显著的Cre重组酶活性,动物实验结果表明该工程化小细胞外囊泡可以成功将Cre重组酶递送至小鼠大脑部分组织中。 YIM等[47]利用受蓝光控制的可逆蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用开发了一种在细胞内递送蛋白质的新策略,他们将拟南芥蓝光受体CRY2与目的蛋白融合,再将与CRY2相互作用的截短的基本螺旋-环-螺旋1(CIBN)与小细胞外囊泡标志性跨膜蛋白CD9融合,连续蓝光诱导CIBN和CRY2融合蛋白之间可逆的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用,以将目的蛋白引导至细胞内早期内体的表面,当目的蛋白通过内源性生物发生过程引入至小细胞外囊泡中时,就可以通过去除光源将它们与结合了CD9的CIBN分离,从而将目的蛋白成功释放至小细胞外囊泡内。 与上述蛋白质递送手段相类似,RNA结合蛋白通常被用作“细胞工程”的RNA分选模块。人抗原R(HuR)是一种与miR-155强烈结合的RNA结合蛋白,LI等[48]利用基因工程手段将HuR与小细胞外囊泡标志蛋白CD9融合(CD9-HuN),再用miR-155和CD9-HuN共转染HEK293T细胞,利用HuR与miR-155的高亲和力成功将miR-155载入小细胞外囊泡内部,且此工程化小细胞外囊泡将miR-155有效递送至受体细胞中。 2.2.2 小细胞外囊泡工程 “小细胞外囊泡工程”是指通过一些物理化学方法直接在分离后的小细胞外囊泡引入功能配体,如一些小核酸分子及治疗性药物分子,以进一步提高小细胞外囊泡载体性能。与基于亲代细胞的“细胞工程”方法相比,小细胞外囊泡工程技术相对简单,近些年被广泛用于基因或药物的递送。常见的小细胞外囊泡工程技术包括共孵育、电穿孔、超声、挤压、冻融、点击化学法、抗体结合法等[5,49]。常见小细胞外囊泡工程策略的主要优缺点,见表1。"
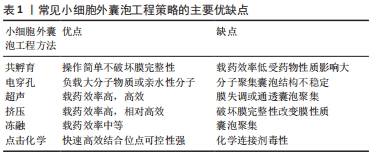

共孵育法是将小细胞外囊泡与药物以一定比例简单混合后一起孵育,使得小细胞外囊泡负载药物,因为其操作简单,对小细胞外囊泡的结构、含量等不产生重要影响且适用于各种性质的药物负载,所以是使用最广泛的方法。该方法的主要缺点是负载效率较低,受药物分子疏水性影响较大。有研究表明,与皂苷等膜透化剂一起孵育可以使膜通透性增加,显著提高小细胞外囊泡的负载能力。但皂苷具有体内溶血活性,应严格控制用于载药的皂苷浓度,并在与皂苷孵育后进一步纯化载药小细胞外囊泡[50]。 电穿孔是指通过向悬浮在导电溶液中的小细胞外囊泡施加电场,电流干扰小细胞外囊泡磷脂双分子层,使小细胞外囊泡膜上瞬时形成可修复的小孔,从而使药物载入小细胞外囊泡中。该方法被广泛用于载入小干扰RNA及微RNA等较大的分子物质或亲水性小分子。由于电压、脉冲数、电容器容量等参数具有可控性,因而电穿孔技术具有广泛的应用前景,但电穿孔可能会导致RNA聚集和小细胞外囊泡不稳定,从而导致较低的负载效率。JOHNSEN等[51]曾报道,在优化的缓冲液(如海藻糖二糖)中进行电穿孔可以帮助维持结构完整性,并可以抑制脂肪干细胞来源的小细胞外囊泡的聚集。 超声法是将小细胞外囊泡与药物混合后使用均化器探针进行超声处理,超声产生的机械剪切力破坏小细胞外囊泡的膜完整性,使药物在这种膜变形过程中扩散到小细胞外囊泡中。研究表明,在超声处理后小细胞外囊泡膜的微黏度显著降低,但这种程度的膜变形不会对小细胞外囊泡表面膜结合蛋白或脂质的含量产生显著影响,且在孵育过程中小细胞外囊泡膜的完整性可以恢复。超声法负载的药物可同时存在于小细胞外囊泡膜中或小细胞外囊泡内部,所以药物释放存在“二阶段释放”效应,即附着于小细胞外囊泡膜中的药物于第一阶段释出,随后是包裹在小细胞外囊泡内的药物缓慢释放。超声法具有高效、载药率高等优点,但有学者认为超声处理会导致小细胞外囊泡膜失调和通透,可能导致囊泡聚集,降低小细胞外囊泡的免疫活性[52]。 挤压法是在受控温度下将小细胞外囊泡与药物的混合物装入具有100-400 nm多孔膜的脂质挤出机中挤出,使得小细胞外囊泡膜破裂并与药物剧烈混合,是一种常用且相对高效的手段,但挤压过程产生的强机械力是否会改变膜的性质及囊泡结构尚存在争议。FUHRMANN等[53-54]曾报道使用挤压法将卟啉负载于从MDA-MB231乳腺癌细胞提取的小细胞外囊泡中,改变了小细胞外囊泡的Zeta电位并产生了细胞毒性;而另一项报道将过氧化氢酶通过10次挤压负载到RAW264.7细胞衍生的小细胞外囊泡中,与共孵育产生的载药小细胞外囊泡相比,其并未产生细胞毒性且显示出更大的神经保护活性。 冻融法是指将小细胞外囊泡与药物在室温下孵育一定时间后在-80 ℃或液氮中快速冷冻,随后在室温下解冻,此过程至少重复3次。该方法的负载效率通常低于超声或挤压法,但有研究发现通过反复冻融可以实现小细胞外囊泡与脂质体之间的膜融合。但是,该方法易诱导小细胞外囊泡的聚集,从而导致载药小细胞外囊泡较大的粒径分布范围[55]。 点击化学法是指通过铜催化的叠氮化物炔烃环加成反应将生物分子直接缀合至小细胞外囊泡表面,该方法具有快速高效、结合位点可控性强、相容性高的特点,对小细胞外囊泡的结构完整性及功能没有明显影响,是生物大分子及小分子化合物载入小细胞外囊泡的理想选择[56]。 2.2.3 仿生小细胞外囊泡 细胞分泌的小细胞外囊泡数量是有限的,这极大阻碍了以小细胞外囊泡为对象的研究和临床试验的发展。近来有研究报道,可以通过细胞挤压或用细胞膜包裹聚合物纳米颗粒等方法来生产大量的人工纳米囊泡,其具有类似于天然小细胞外囊泡的结构和物理特征,他们将这些纳米囊泡称之为仿生小细胞外囊泡或小细胞外囊泡模拟物。 JANG等[57]在化学治疗剂存在下通过使用孔径逐渐减小(10,5,1 μm)的过滤器将单核细胞或巨噬细胞连续挤压分解,生产出载有药物的仿生纳米囊泡,并使用密度梯度离心法分离囊泡,这些细胞衍生的纳米囊泡与同源小细胞外囊泡具有相似的特性,且载有化学治疗药物的仿生小细胞外囊泡表现出与天然小细胞外囊泡相似的体内抗肿瘤活性,但囊泡产量却提高了近100倍。类似地,通过将细胞经纳米级多孔膜挤出并与聚合物纳米颗粒融合以制备仿生小细胞外囊泡,利用天然细胞膜的特性掩藏人工纳米粒,有效延长了纳米颗粒在血液中的半衰期及循环滞留时间。血小板膜覆盖的纳米颗粒有效减少了巨噬细胞的摄取,并可以选择性地黏附于受损的脉管系统[58]。间充质干细胞膜包裹的纳米颗粒将抗肿瘤药物sTRAIL成功递送至肿瘤组织并抑制了体内肿瘤的生长,与之相比,脂质体包裹的sTRAIL没有显示出任何抗肿瘤作用[59]。YOON等[60]提出了另一种产生小细胞外囊泡模拟物的方法,在细胞流过标准化微流控系统的同时,用500 nm的微细氮化硅叶片将活细胞切成薄片,切片后膜碎片自发组装形成纳米囊泡,在切片过程中同时添加聚苯乙烯胶乳珠粒,最终将珠粒封装在纳米囊泡中的效率高达30%。 近年来,关于仿生小细胞外囊泡的研究逐渐证明了这些方法用于大规模生产纳米递送载体的潜力。然而,目前尚不能明确这些细胞来源的小细胞外囊泡模拟囊泡是否仍然具备天然小细胞外囊泡的预期优势,但不可否认的是,仿生小细胞外囊泡的出现为新型纳米递送系统的发展提供了新的思路和方法,也在一定程度上弥补了天然小细胞外囊泡的部分局限性。 2.3 工程小细胞外囊泡的应用 目前,由于小细胞外囊泡自身具备的独特能力以及各项生物技术水平的迅速发展,工程化小细胞外囊泡逐渐成为癌症治疗、免疫疗法、再生医学等重要领域的一项研究前景广泛的重要治疗手段。 通过不同的小细胞外囊泡工程化方法使小细胞外囊泡表面显示靶向模块,可使小细胞外囊泡有效靶向特定组织或细胞,以递送治疗性分子。LEE等[61]用Ⅱ类反式激活因子(CIITA)基因转染B16F1鼠类黑色素瘤细胞系致MHC-Ⅱ在其表面过度表达,从而使类黑色素瘤细胞产生了富含MHC-Ⅱ及肿瘤抗原TRP2的小细胞外囊泡,此工程化小细胞外囊泡可靶向T细胞并增强了对癌细胞1型T辅助细胞(TH1)的反应,以剂量依赖性方式显著抑制肿瘤生长。有学者设计了基于GE11的靶向工程小细胞外囊泡用于乳腺癌治疗,他们通过改造供体细胞以表达融合至GE11肽的血小板源性生长因子受体的跨膜结构域来实现靶向[43]。GE11肽对表皮生长因子受体具有很强的亲和力,通过靶向该受体,几种类型实体癌中的表皮生长因子受体上调,因此,表达GE11的小细胞外囊泡可以将药物递送至表达表皮生长因子受体的癌组织,显示出极大的癌症治疗潜力[62]。 由于小细胞外囊泡可穿越包括血脑屏障在内的各种生物屏障,所以神经退行性疾病和相关恶性肿瘤的治疗也是工程化小细胞外囊泡治疗的主要目标之一。有研究表明,小细胞外囊泡表面叶酸受体α(FRα)的过度表达可使此工程化小细胞外囊泡特异性结合脑实质,表面显示狂犬病毒糖蛋白的工程小细胞外囊泡可通过递送siRNA抑制β-分泌酶1以治疗阿尔茨海默病[39,63]。JIA等[64]将超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子和姜黄素加载到小细胞外囊泡中,再通过点击化学法将小细胞外囊泡与神经纤毛蛋白1靶向肽(RGE)偶联,以获得靶向神经胶质瘤具有成像及治疗功能的的新型纳米粒子。结果表明,这些工程化小细胞外囊泡可以顺利穿越血脑屏障,在肿瘤组织中蓄积,为神经胶质瘤等颅内肿瘤的靶向成像和治疗提供了一种新途径。 从不同组织间充质干细胞分离的小细胞外囊泡已被广泛用于组织再生和伤口愈合。有研究表明,诱导性多能干细胞衍生的心肌细胞分泌的小细胞外囊泡,可通过提供诸如簇蛋白miR-21、miR-126和miR-210之类的心脏保护因子对促进心脏梗死的恢复产生实质性影响,但小细胞外囊泡内容物的复杂性和缺乏靶向性仍然是修复应用中急待解决的主要问题[65]。WANG等[66]在急性心肌梗死的治疗中,将缺血性心肌靶向肽与Lamp2b融合,缺血性心肌靶向肽工程化小细胞外囊泡在缺血性心肌区域积聚,导致炎症和细胞凋亡减弱、纤维化减少、血管生成增强和心脏功能增强。KIM等[67]还通过将糖基化序列连接至心脏靶向肽(CTP-Lamp2b)获得同样在缺血心肌聚集的工程小细胞外囊泡。 有文献报道,利用水果来源的小细胞外囊泡可将姜黄素递送至结肠组织,且小细胞外囊泡有效增加了药物的稳定性和血液浓度,诱导了药物向炎性细胞的特异性递送[68],为治疗结肠癌提供了新思路。针对相关研究,詹姆斯·格雷厄姆·布朗癌症中心发起了2项Ⅰ期临床试验,以测试植物小细胞外囊泡对头颈癌和结肠癌的治疗效果(NCT01668849,NCT01294072)。此外,针对小细胞外囊泡的临床研究,关于癌症无细胞免疫疗法的多项临床试验正在进行中,以期在将来开发出有效的癌症疫苗[69]。"

| [1] ZHU GY, LU BY, PENG Q, et al. Antibiofilm effect of drug-free and cationic poly (D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles via nano-bacteria interactions. Nanomedicine (Lond.). 2018;13(10):1093-1106. [2] SHAO XR, WEI XQ, PENG Q, et al. Effects of Micro-environmental pH of Liposome on Chemical Stability of Loaded Drug. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017;12(1):504. [3] LIU J, DONG J, PENG Q, et al. Graphene-based nanomaterials and their potentials in advanced drug delivery and cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2018;286:64-73. [4] PENG Q, ZHANG ZR, LIN YF, et al. Nanocomplex based on biocompatible phospholipids and albumin for long-circulation applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(16):13730-13737. [5] LUAN X, YUAN H, SUN D, et al. Engineering exosomes as refined biological nanoplatforms for drug delivery. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017; 38(6):754-763. [6] HAQUE S, WHITTAKER MR, KAMINSKAS LM, et al. Disposition and safety of inhaled biodegradable nanomedicines: Opportunities and challenges. Nanomedicine. 2016;12:1703-1724. [7] SHAO XR, WEI XQ, PENG Q, et al. Independent effect of polymeric nanoparticle zeta potential/surface charge, on their cytotoxicity and affinity to cells. Cell Prolif. 2015;48(4):465-474. [8] AHN J, PARK TE, JEON NL, et al. Investigation on vascular cyto-toxicity and extravascular transport of cationic polymer nanoparticles using perfusable 3D microvessel model. Acta Biomater. 2018;76:154-163. [9] THERY C, AMIGORENA S, CLAYTON A, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;23(1):1-29. [10] LAI RC, YEO RW, LIM SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin. Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88. [11] SKOGBERG G, LUNDBERG V, EKWALL O, et al. Human thymic epithelial primary cells produce exosomes carrying tissue-restricted antigens. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015;93(8):727-734. [12] BENITO-MARTIN A, CEDER S, PEINADO H, et al. The new deal: a potential role for secreted vesicles in innate immunity and tumor progression. Front. Immunol. 2015;6:66. [13] PEGTEL DM, GOULD SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88: 487-514. [14] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. [15] 姜承耀,陈文娟,韩树萍,等.母乳外泌体载药用于新生儿相关疾病治疗的研究进展[J].医学综述,2020,26(19):3769-3773+3779. [16] JAFARI D, FOROUZANDEH MOGHADAM M, SAMADIKUCHAKSARAEI A, et al. Designer Exosomes: A New Platform for Biotechnology Therapeutics. BioDrugs. 2020;34(5):567-586. [17] VADER P, MOL EA, SCHIFFELERS RM, et al. Extracellular vesicles for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;106(Pt A):148-156. [18] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, TURBIDE C, et al.Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420. [19] PAOLICELLI RC, BERGAMINI G, RAJENDRAN L. Cell-to-cell communication by extracellular vesicles: focus on microglia. Neuroscience. 2019;405:148-157. [20] WESTON WW, GANEY T, TEMPLE HT. The relationship between exosomes and cancer: implications for diagnostics and therapeutics. BioDrugs. 2019;33(2):137-158. [21] ALMIÑANA C, TSIKIS G, BAUERSACHS S, et al. Deciphering the oviductal extracellular vesicles content across the estrous cycle: implications for the gametesoviduct interactions and the environment of the potential embryo. BMC Genom. 2018;19(1):622. [22] JIANG N, XIANG L, WANG C, et al. Exosomes mediate epithelium-mesenchyme crosstalk in organ development. ACS Nano. 2017;11(8): 7736-7746. [23] SUN B, PENG J, ZHANG Z, et al. Applications of stem cell-derived exosomes in tissue engineering and neurological diseases. Rev Neurosci. 2018;29(5):531-546.
[24] HUANG CC, ALAPATI S, RAVINDRAN S, et al. Exosomes as biomimetic tools for stem cell diferentiation: applications in dental pulp tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;111:103-115. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Zhu Meiying, Jiang Liming, Liu Shuangwei, Ma Mingqi, Yang Yutong. Application of drug delivery system in the field of periodontal tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4423-4428. |
| [14] | Yun Xiao, Ding Tong, Yang Weiqiang, Guo Xinjun. Nano hydroxyapatite/chitosan scaffold loaded with Akebia saponin D in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4293-4299. |
| [15] | Hu Qiuyu, Yang Long, Yang Yong, Song Shenchao. Aligned poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/type I collagen fibers promote tendon-bone healing after anterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4314-4319. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||