Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (16): 2510-2515.doi: 10.12307/2022.249
Previous Articles Next Articles
Gelatin collagen composite hydrogel and inducible factor regulate differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells
Yuan Yihang, Xu Menghan, Niu Xufeng
- Key Laboratory of Biomechanics and Force Biology of Ministry of Education, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Biomedical Engineering, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China
-
Received:2020-12-11Revised:2020-12-18Accepted:2021-01-23Online:2022-06-08Published:2021-12-22 -
Contact:Niu Xufeng, Professor, Key Laboratory of Biomechanics and Force Biology of Ministry of Education, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Biomedical Engineering, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China -
About author:Yuan Yihang, Master candidate, Key Laboratory of Biomechanics and Force Biology of Ministry of Education, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Biomedical Engineering, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100083, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 11872097 (to NXF), Beijing Natural Science Foundation-Haidian Original Innovation Joint Fund, No. L182017 (to NXF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yuan Yihang, Xu Menghan, Niu Xufeng. Gelatin collagen composite hydrogel and inducible factor regulate differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2510-2515.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

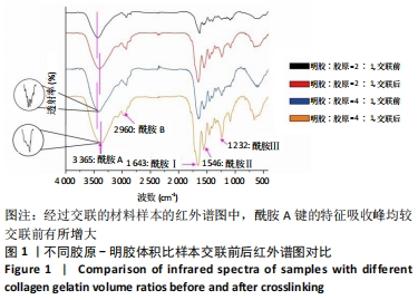
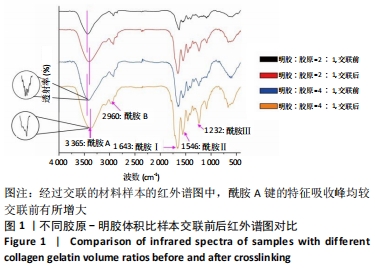
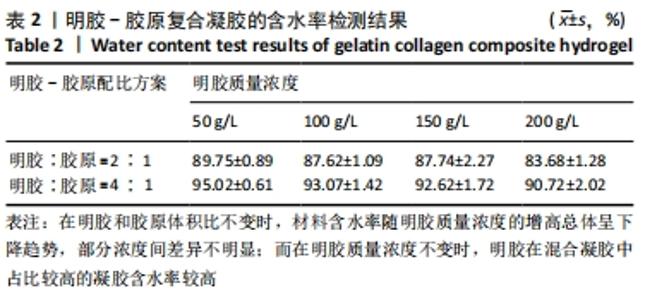
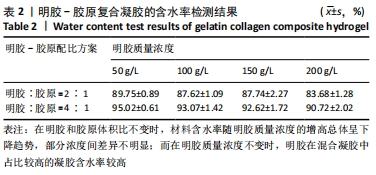
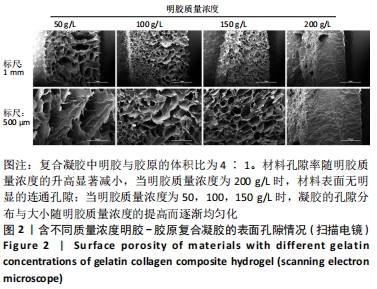
在明胶和胶原体积比不变时,材料含水率随明胶质量浓度的增高总体呈下降趋势,部分浓度间差异不明显;而在明胶质量浓度不变时,明胶在混合凝胶中占比较高的实验组含水率较高。用于细胞培养时,含水率较高的材料吸水性能较好,能被培养基更充分地浸润,从而增强材料的细胞相容性;另一方面,含水率较高也能侧面反映出材料的孔隙率更大,更有利于细胞的吸附和生长。综合以上考量,排除第二组材料配比,后续实验中仅对第三组进行进一步表征。 2.4 扫描电镜表征结果及配方筛选 样本孔隙率和孔隙结构结果,见图2。材料孔隙率随明胶质量浓度的升高显著减小,当明胶质量浓度为200 g/L时,由于明胶浓度过高材料表面已无明显的连通孔隙;当明胶质量浓度为50,100,150 g/L时,凝胶的孔隙分布与大小随明胶质量浓度的提高而逐渐均匀化,50 g/L组的孔隙结构松散且不规则、有大片连通破损的沟壑状结构;100 g/L组总体孔隙比较均匀,但仍有部分孔隙破损;150 g/L组孔隙大小一致且均匀分布,无明显可见的破损结构。出于细胞培养考虑,希望材料表面应在孔隙率较高的情况下尽量平整,故选取明胶与胶原体积比为4∶1、明胶质量浓度为150 g/L为制备凝胶的最终配方。"
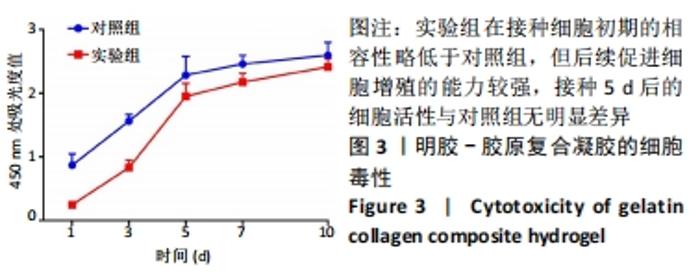
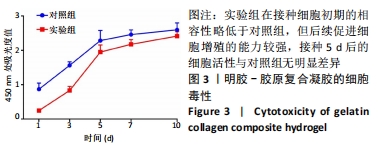
实验组第1,3,5,7,10天相对于对照组的细胞活性比值分别为28.25%,53.10%,85.33%,88.41%,92.98%。采用明胶-胶原复合凝胶作为基底培养的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的活性略低于直接采用培养基培养的对照组,其中接种细胞的前5 d二者差值较大,5 d后差值逐渐缩小。结合二者细胞活性比值分析,在接种细胞后实验组与对照组的细胞活性差异逐渐减小,说明采用复合凝胶培养的细胞增殖速度高于对照组;接种后第5天,实验组的细胞活性为对照组的85.33%,随后至第10天已达对照组的92.98%,两组细胞活性已基本无差异。添加明胶-胶原复合凝胶的实验组在接种细胞初期的相容性略低于对照组,但实验组后续促进细胞增殖的能力较强,接种5 d后的细胞活性与对照组无明显差异,证明其细胞毒性较低。 2.6 肝向诱导实验白蛋白分泌水平检测结果 空白组培养至21 d时细胞形态无变化且部分凋亡,故未展示其白蛋白分泌水平。实验组与对照组诱导不同时间点的白蛋白分泌水平检测结果,见图4。"
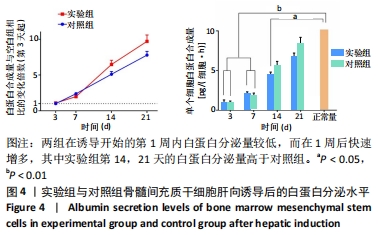
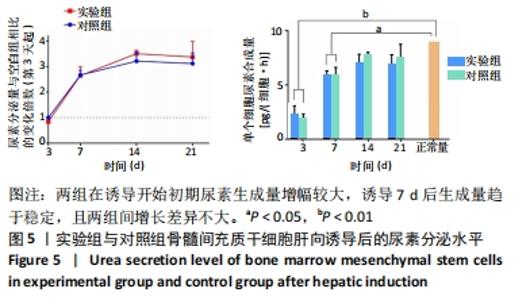
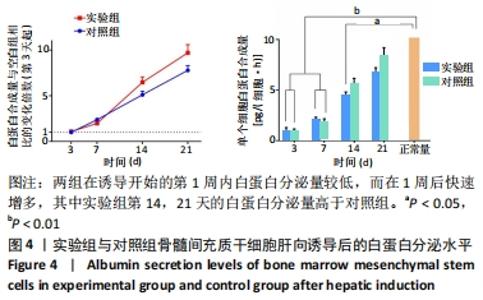
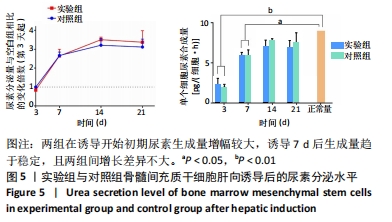
两组在诱导开始的第1周内白蛋白分泌量较低,而在1周后快速增多,其中实验组第14,21天的白蛋白分泌量高于对照组。与正常肝细胞单位时间单个细胞白蛋白分泌量[约10 pg/(细胞·h)]相比[40-41],诱导后1周内两组均与正常值有极显著差异;诱导第14天时,实验组和正常合成水平已无明显差异,而对照组仍和正常水平有显著差异;诱导第21天时,两组与正常水平均无明显差异。该结果说明,两组肝向诱导的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞在加入诱导因子后均可分泌白蛋白,其合成量随诱导时间增加而逐渐增大;实验组定向诱导的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞白蛋白分泌量增长更快。上述结果证明,实验所用的分步诱导方案能使大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向肝样细胞分化并行使物质合成功能,且明胶-胶原复合凝胶可促进其分化和白蛋白分泌。 2.7 肝向诱导实验尿素分泌水平检测结果 空白组培养至21 d时细胞形态无变化且部分凋亡,故未展示其尿素分泌水平。实验组与对照组的尿素分泌水平检测结果,见图5。"
| [1] DU T, NIU X, HOU S, et al. Apatite minerals derived from collagen phosphorylation modification induce the hierarchical intrafibrillar mineralization of collagen fibers. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(11): 2403-2413. [2] NIU X, FAN R, TIAN F, et al. Calcium concentration dependent collagen mineralization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;73:137-143. [3] NIU X, FAN R, GUO X, et al. Shear-mediated orientational mineralization of bone apatite on collagen fibrils. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(46):9141-9147. [4] DU T, NIU X, LI Z, et al. Crosslinking induces high mineralization of apatite minerals on collagen fibers. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;113: 450-457. [5] DE BARTOLO L, SALERNO S, MORELLI S, et al. Long-term maintenance of human hepatocytes in oxygen-permeable membrane bioreactor. Biomaterials. 2006;27(27):4794-4803. [6] HOFFMAN AS. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64:18-23. [7] 张林,孙磊,徐梦浛,等.可吸收胶原膜的体内免疫反应评价[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2018,44(4):879-886. [8] 孙磊,袁源,牛睿,等.辐照和EO灭菌对SIS材料免疫原性的对比研究[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2020,46(12):2245-2252. [9] JOSHI S, SINGH V. Gelatin–rosin gum complex nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and colon targeted delivery of 5-fluorouracil. Chem Pap. 2020;74(12):4241-4252. [10] LIU J, WANG Q, SUN Y, et al. A core-shell structured collagen hydrogel microsphere with removable superparamagnetic alginate coating for cell coculture and rapid separation. Materials Letters. 2019;249:49-52. [11] ZHAO X, WU H, GUO B, et al. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials. 2017;122: 34-47. [12] YOUNG S, WONG M, TABATA Y, et al. Gelatin as a delivery vehicle for the controlled release of bioactive molecules. J Control Release. 2005; 109(1-3):256-274. [13] WANG J, TABATA Y, BI D, et al. Evaluation of gastric mucoadhesive properties of aminated gelatin microspheres. J Control Release. 2001; 73(2-3):223-231. [14] KIM EH, KIM JW, HAN GD, et al. Biocompatible, drug-loaded anti-adhesion barrier using visible-light curable furfuryl gelatin derivative. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120:915-920. [15] BUIE T, MCCUNE J, COSGRIFF-HERNANDEZ E. Gelatin Matrices for Growth Factor Sequestration. Trends Biotechnol. 2020;38(5):546-557. [16] CHOWDHURY DK, MITRA AK. Kinetics of in vitro release of a model nucleoside deoxyuridine from crosslinked insoluble collagen and collagen–gelatin microspheres. Int J Pharm.1999;193(1):113-122. [17] JIANG J, LIU A, CHEN C, et al. An efficient two-step preparation of photocrosslinked gelatin microspheres as cell carriers to support MC3T3-E1 cells osteogenic performance. Colloids and Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;188:110798. [18] PARK C, VO CLN, KANG T, et al. New method and characterization of self-assembled gelatin–oleic nanoparticles using a desolvation method via carbodiimide/N-hydroxysuccinimide (EDC/NHS) reaction. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;89:365-373. [19] WISSINK MJB, BEERNINK R, PIEPER JS, et al. Immobilization of heparin to EDC/NHS-crosslinked collagen. Characterization and in vitro evaluation. Biomaterials. 2001;22(2):151-163. [20] BHATIA SN, UNDERHILL GH, ZARET S, et al. Cell and tissue engineering for liver disease. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(245):245sr2-245sr2. [21] ZHANG J, ZHAO X, LIANG L, et al. A decade of progress in liver regenerative medicine. Biomaterials. 2018;157:161-176. [22] HUCH M, DORRELL C, BOJ SF, et al. In vitro expansion of single Lgr5+ liver stem cells induced by Wnt-driven regeneration. Nature. 2013; 494(7436):247-250. [23] LORVELLEC M, PELLEGATA AF, MAESTRI A, et al. An In Vitro Whole-Organ Liver Engineering for Testing of Genetic Therapies. iScience. 2020;23(12):101808. [24] WU G, WU D, LO J, et al. A bioartificial liver support system integrated with a DLM/GelMA-based bioengineered whole liver for prevention of hepatic encephalopathy via enhanced ammonia reduction. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(10):2814-2824. [25] MONA S , MOHAMMAD B , RASOUL G , et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells-conditioned medium improves diabetic wound healing mainly through modulating fibroblast behaviors. Arch Dermatol Res. 2020;312(5):325-336. [26] GEMA VALLÉS, FÁTIMA BENSIAMAR, MAESTRO-PARAMIO L , et al. Influence of inflammatory conditions provided by macrophages on osteogenic ability of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):1-15. [27] YAO S, HE F, CAO Z, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Laden Hydrogel Microfibers for Promoting Nerve Fiber Regeneration in Long-Distance Spinal Cord Transection Injury. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(2):1165-1175. [28] JAYARAMAYYA K, MAHALAXMI I, SUBRAMANIAM MD, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem-cell-derived exosomes for COVID-19 treatment. BMB Rep. 2020;53(8):400-412. [29] YAN L, SHA L, FENG Y, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell treatment for end stage liver disease: A case report. Asian J of Surg. 2020;43(2):454-455. [30] EISSA M, ELARABANY N, HYDER A. In vitro efficacy of liver microenvironment in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(4):341-348. [31] MATTA A, DYM M ZK, HODA GERAMI BS, et al. Study comparing NTG-101, a growth factor-based therapy with mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) based treatment of degenerative disc disease (DDD) in pre-clinical rodent model. Spine J. 2020;20(9):S105-S106. [32] NITTA S, KUSAKARI Y, YAMADA Y, et al. Conversion of mesenchymal stem cells into a canine hepatocyte-like cells by Foxa1 and Hnf4a. Regen Ther. 2020;14:165-176. [33] CHRIST B, BRÜCKNER S, WINKLER S. The Therapeutic Promise of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Liver Restoration. Trends Mol Med. 2015; 21(11):673-686. [34] DUNCAN AW, DORRELL C, GROMPE M. Stem Cells and Liver Regeneration. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(2):466-481. [35] SHI D, XIN J, LU Y, et al. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Distinct Phenotype of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Hepatocyte-like cells. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17(2):263-273. [36] LIN N, LIN J, BO L, et al. Differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells in an alginate scaffold. Cell Prolif. 2010;43(5):427-434. [37] LI J, TAO R, WU W, et al. 3D PLGA Scaffolds Improve Differentiation and Function of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell–Derived Hepatocytes. Stem Cells and Dev. 2010;19(9):1427-1436. [38] JOSSÉ R, ANINAT C, GLAISE D, et al. Long-Term Functional Stability of Human HepaRG Hepatocytes and Use for Chronic Toxicity and Genotoxicity Studies. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008;36(6):1111-1118. [39] SANCHO-BRU P, ROELANDT P, NARAIN N, et al. Directed differentiation of murine-induced pluripotent stem cells to functional hepatocyte-like cells. J Hepatol. 2011;54(1):98-107. [40] TOSTÕES RM, LEITE SB, MIRANDA JP, et al. Perfusion of 3D encapsulated hepatocytes-A synergistic effect enhancing long-term functionality in bioreactors. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011;108(1):41-49. [41] UKAIRO O, KANCHAGAR C, MOORE A, et al. Long-Term Stability of Primary Rat Hepatocytes in Micropatterned Cocultures. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2013;27(3):204-212. [42] SCHWARTZ RE, REYES M, KOODIE L, et al. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. J Clin Invest. 2002;109(10):1291-1302. [43] JANG M, NEUZIL P, VOLK T, et al. On-chip three-dimensional cell culture in phaseguides improves hepatocyte functionsin vitro. Biomicrofluidics. 2015;9(3):034113. [44] ANIRUDHAN TS, MOHAN AM. Novel pH sensitive dual drug loaded-gelatin methacrylate/methacrylic acid hydrogel for the controlled release of antibiotics. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;110:167-178. |
| [1] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [2] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [3] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [4] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [5] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [6] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [7] | Tan Guozhong, Tu Xinran, Guo Liyang, Zhong Jialin, Zhang Yang, Jiang Qianzhou. Biosafety evaluation of three-dimensional printed gelatin/sodium alginate/58S bioactive glass scaffolds for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 521-527. |
| [8] | Wang Kun, He Benxiang. Asperosaponin VI therapy for Achilles tendinopathy in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 211-217. |
| [9] | Cao Wei, Mao Furong, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. N-6 methyladenosine RNA methylation regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 266-270. |
| [10] | Fan Danyang, Fu Runze, Mi Jiajing, Liu Chunyan. Expression and role of cannabinoid receptors during bone remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 283-288. |
| [11] | Zhang Hongmei, Sun Xirao, Wang Chengyue. Effect of polymethyl methacrylate/mineralized collagen/Mg-Ca composite material on osteogenic differentiation of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2498-2503. |
| [12] | Li Mingxin, Li Jun, Wang Wenchao, Song Ping, Lei Haoyuan, Gui Xingyu, Zhang Chengyun, Zhou Changchun, Liu Lei. Cell-carrying porous methacrylate anhydride gelatin three-dimensional scaffolds and their effects on cell behavior [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2532-2539. |
| [13] | Yang Xue, Wang Baoqun, Jiang Xiaowen, Zou Shengcan, Ming Jinfa, Lin Shasha. Preparation and properties of biodegradable plant polysaccharide hemostatic microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2487-2491. |
| [14] | Zhang Luwen, Dai Pengxiu, Zhang Yihua, Chen Yijing, Wang Jinglu, Li Jiakai. SV40 large T gene induces immortalization of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 1969-1973. |
| [15] | Xu Xiang, Wu Yimin, Li Shuwen, Ma Libo, Wang Yupeng, Yu Yingnan, Sun Tao, Zhang Yuan, Ren Wei, Yin Heping. Histological comparison between goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and adhesive fibrin for the repair of annulus fibrosus defect of intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 1974-1978. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||