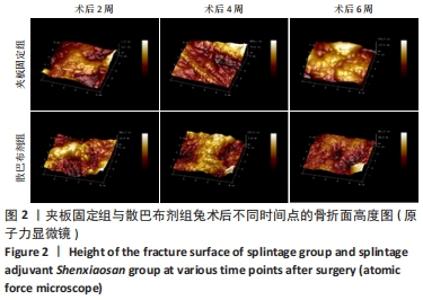
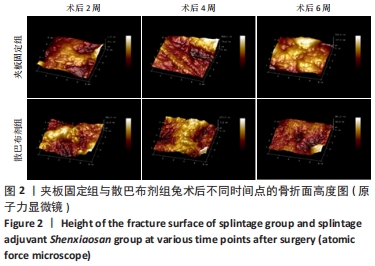
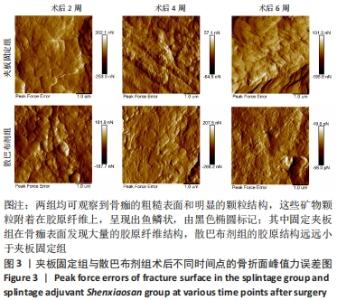
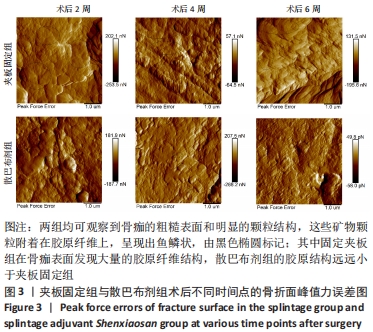
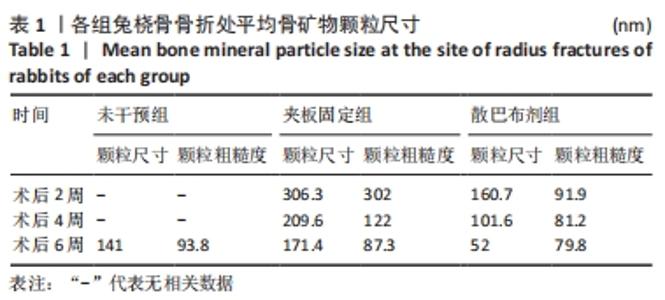
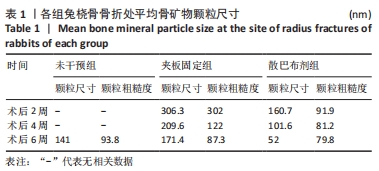
[1] 谢杰伟,林涌鹏.两种不同固定方式对老年桡骨远端骨折腕关节功能康复的评价[J].新中医,2014,46(8):83-84.
[2] 陈功群,郭伯文,谢澄.小夹板与石膏托外固定治疗老年桡骨远端骨折的疗效观察[J].当代医学,2021,27(6):110-113.
[3] 张春燕.钛制弹性髓内钉治疗小儿尺桡骨不稳定骨折的临床效果观察[J].中国医刊,2021,56(3):271-273.
[4] 王遥伟,吴树华,王树金,等.弹性髓内钉修复儿童长骨骨折:固位坚强及产生骨折部位微动促进骨折愈合[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(48):7827-7832.
[5] 叶琪毅,张文广,唐亚飞,等.桡骨远端骨折掌侧接骨板内固定微创手术的疗效分析[J].实用手外科杂志,2020,34(3):329-332.
[6] 胡小祥,何艳.HPLC法同时测定骨折挫伤胶囊中7种成分的含量[J].中药新药与临床药理,2020,31(2):224-228.
[7] 江敏瑜,闫丹,陈娇,等.三七跌打软膏的制备及体外透皮特性研究[J].中草药,2017,48(22):4639-4647.
[8] 胡小祥,何艳.HPLC法同时测定骨折挫伤胶囊中7种成分的含量[J].中药新药与临床药理,2020,31(2):224-228.
[9] 方姝晨,邹季,史政康,等.三七总皂苷对股骨头坏死大鼠股骨头成骨作用影响的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2020,28(6): 6-9+15.
[10] 胡广,关智宇,张开伟.三七总皂苷干预去势骨质疏松性骨折模型大鼠的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):172-177.
[11] 姚懿,陈丑彦,唐发兵,等.大鼠股骨骨折后肾髓质浅层细胞的凋亡及三七总皂苷的保护作用[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2015, 36(4):549-553.
[12] 高安敏,冯颖,曾峰,等.大鼠股骨骨折对肾皮质浅层细胞凋亡的影响及三七总皂苷的保护作用[J].南方医科大学学报,2013,33(11): 1692-1695.
[13] 区泳芳,伏学坤,梅兴莎,等.三七总皂苷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡的抑制作用[J].生理学报,2016,68(3):285-292.
[14] 傅晨,刘雪梅,王凤丽,等.血塞通软胶囊对单侧颈动脉狭窄大鼠脑组织血管新生的作用及其机制[J].北京中医药,2018,37(9):821-824+909.
[15] 王买全,王永功,侯明.氢氟酸表面改性种植体对骨质疏松大鼠骨结合的影响[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2019,33(9):860-864.
[16] GAO J, GONG H, HUANG X, et al. Multi-Level Assessment of Fracture Calluses in Rats Subjected to Low-Magnitude High-Frequency Vibration with Different Rest Periods. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016;44(8): 2489-2504.
[17] 莫钟才,李彦,符方涛.不同时期应用阿仑膦酸钠片对老年股骨颈骨折患者全髋关节置换术后关节功能和骨密度的影响[J].新乡医学院学报,2021,38(3):281-284.
[18] 范永前,沈海敏,朱炯,等.阿仑膦酸钠对小鼠骨质疏松骨折愈合的影响[J].上海医学,2014,37(9):808-810+827.
[19] 吕国先.中西医结合治疗创伤性骨折的临床疗效观察[J].四川解剖学杂志,2020,28(3):39-40.
[20] 罗仕华,万世元,薛彬,等.魏氏手法联合外用三七断骨巴布膏治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的临床研究[J].按摩与康复医学, 2018,9(21):40-42.
[21] 张影,陈小勇.浅谈中药巴布剂的研究现状[J].中医药信息,2015, 32(5):116-118.
[22] MILOVANOVIC P, DJURIC M, RAKOCEVIC Z. Age‐dependence of power spectral density and fractal dimension of bone mineralized matrix in atomic force microscope topography images: potential correlates of bone tissue age and bone fragility in female femoral neck trabeculae. J Anat. 2012;221(5):427-433.
[23] WALLACE JM. Applications of atomic force microscopy for the assessment of nanoscale morphological and mechanical properties of bone. Bone. 2012;50(1):420-427.
[24] BARKARMO S, WENNERBERG A, HOFFMAN M, et al. Nano‐hydroxyapatite‐coated PEEK implants: A pilot study in rabbit bone. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(2):465-471.
[25] 孙强,李峰,伍亮,等.正骨夹板外固定和手术内固定治疗高龄骨质疏松性桡骨远端骨折的效果比较[J].医学信息,2021,34(10):128-130.
|