Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (35): 5694-5701.doi: 10.12307/2021.302
Previous Articles Next Articles
Nrf2-ARE regulated neurovascular interaction is involved in neural repair after spinal cord injury
Tan Rongbang, Wei Bo, Li Guangsheng
- Orthopedics Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-07-10Revised:2020-07-21Accepted:2020-09-15Online:2021-12-18Published:2021-08-06 -
Contact:Li Guangsheng, MD, Attending physician, Orthopedics Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Tan Rongbang, Master candidate, Orthopedics Center, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524001, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2016A030313679 and 2018A0303130105 (both to LGS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tan Rongbang, Wei Bo, Li Guangsheng. Nrf2-ARE regulated neurovascular interaction is involved in neural repair after spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5694-5701.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
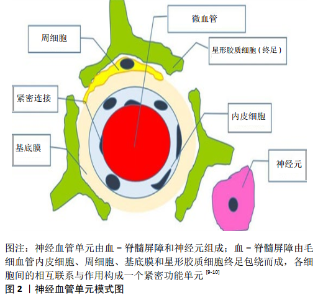
2.1 Nrf2-ARE的分子基础及调控机制 2.1.1 Nrf2-ARE的分子基础 1994年,Moi等首次发现并分离出Nrf2。Nrf2属于Cap ‘n’ Collar (CNC)-bZip转录激活因子家族成员,主要结构包含一个NF-E2样的碱性亮氨酸拉链(basic leucine zipper,bZip)结构域,可与β-珠蛋白基因位点控制区的串联重复序列NF-E2/AP1结合[5]。目前发现的CNC-bZip转录激活因子家族成员有6个,包括NF-F2、Nrf1、Nrf2、Nrf3、Bach1和 Bach2。Nrf2是该家族成员中转录活性最强的转录调节因子,在人体多种组织器官中均有广泛表达[5]。 Nrf2包含6个高度保守的同源结构域(Neh1-Neh6):①Neh1为bZip特异性结构域,Nrf2通过Neh1与伴侣蛋白Maf(包括MafG、MafK和MafF)形成异二聚体,识别并与抗氧化反应元件 (antioxidant response element,ARE)上的DNA基序(GCTGAGTCA)结合,启动目标基因的转录[5];ARE是一个特异性的DNA启动子结合序列,位于细胞保护基因的上游启动子区域,是一种顺式作用元件,可被亲电剂或氧化剂激活;②Neh2的功能区位于N末端区域内,共含有7个赖氨酸残基结构;这些结构含有与Kelch样环氧氯丙烷相关蛋白1 (kelch-Like-ECH associated protein-1,Keap1) 的结合区,可与泛素相结合,它的功能主要为负向调节Nrf2的降解;③Neh3位于羧基端(C-),通过与CHD6的结合调控Nrf2的转录活性;④Neh4 和 Neh5 富含酸性残基,是2个独立激活区,位于Neh1和Neh2之间,需与环磷酸腺苷反应元件结合蛋白(cyclic AMP response element-binding protein,CREB)等辅助因子结合,才能启动基因转录过程;⑤Neh6富含丝氨酸,主要影响Nrf2降解的调控。 2.1.2 Nrf2-ARE的调控机制 Nrf2与小Maf蛋白、cjun、ATF4等形成异二聚体,与ARE上的DNA序列相结合,启动下游目的基因的转录。Keap1和ARE是调控Nrf2稳定性与转录活性的关键影响因子[6]。Keap1是Nrf2最重要的抑制因子,介导Nrf2在胞浆与胞核的合成与泛素化降解[7]。生理条件下,Keap1的C末端区与Nrf2的Neh2区结合,通过胞浆肌动蛋白细胞骨架将Nrf2锚定于胞浆,迅速被泛素化降解,只有极少部分进入细胞核与ARE结合启动转录活性,从而保持低转录水平[8]。在氧化应激条件下,Keap1位点的疏基(-SH)失去电子变成二硫键(-S-S-),与Nrf2解离,Nrf2随后进入胞核与SMP形成异二聚体,识别并与ARE结合,启动Ⅱ相解毒酶与多种抗氧化基因的转录,发挥抗氧化应激损伤、抑制炎症损伤和抗细胞凋亡的作用。 2.2 神经-血管的交互作用 在中枢神经系统中,神经元、神经胶质细胞与毛细血管并非孤立存在,它们之间在结构与功能上相互联系与相互作用,组成中枢神经系统的基本功能单元,即神经血管单元 [9-10](图2)。神经元和血-脊髓屏障是神经血管单元的两大组成要素。神经元是神经信息活动的综合处理中枢;血-脊髓屏障是神经细胞血氧供应的脉络。血-脊髓屏障主要由连续的毛细血管内皮细胞及其内皮间的紧密连接,基膜、周细胞以及星形胶质细胞终足包绕而成(图 2)。内皮细胞作为神经血管单元各组件间的门控屏障,调节血-脊髓屏障通透性的变化与微环境稳态,并在神经细胞-神经细胞、神经细胞-内皮细胞交互作用或信号转导中起着重要作用 [9-10]。 神经元通过释放神经递质,经胶质细胞摄取,调节神经因子转运与神经营养活动,胶质细胞活化调节神经胶质的形成从而影响神经再生;内皮细胞通透性变化调节神经元与神经胶质细胞的血氧供应与抵御神经毒性损害,神经元活动亦可影响微循环血流;星形胶质细胞的终足包绕着内皮细胞,参与维护血-脊髓屏障结构与功能的完整性 [9-10]]。生理条件下,神经元与神经胶质细胞通过血-脊髓屏障与血液进行着密切的物质交换,以维持正常的生命活动。血-脊髓屏障具有高度的选择透过性,可防止有毒物质进入脊髓组织,保护神经元与神经胶质细胞免受毒性物质的损害。病理状态下,血-脊髓屏障结构和功能受到破坏,脊髓缺血缺氧与组织水肿,过氧化物、炎症因子与神经毒性物质侵入,造成脊髓微环境紊乱,使神经元、神经胶质细胞受损或者凋亡,轴突脱髓鞘变性。 2.2.1 神经元-星形胶质细胞 神经元是中枢神经系统的基本结构和功能单位。神经元可直接合成、运输和释放神经递质或神经激素,经胶质细胞摄取,调节神经因子转运与神经营养活动。神经元的死亡或损伤可导致星形胶质细胞退变。神经胶质细胞是中枢神经系统的支持细胞,具有隔离绝缘、分泌、运输营养、摄取化学物质和影响神经修复与再生的作用。星形胶质细胞亦为神经元的正常活动或神经修复提供不可或缺的支持:一方面,星形胶质细胞通过调节Ca2+、环氧二十碳烯酸(EETs)、一氧化氮和环氧化酶2以及炎症因子的表达,影响神经元的生理活动[11-12];另一方面,星形胶质细胞中Nrf2与其下游基因醌氧化还原酶1、血红素加氧酶1、谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶和谷胱甘肽的过表达,可减轻氧化应激反应,延缓运动神经元退变与拮抗神经凋亡,提高神经元存活率[13-16]。此外,在脊髓损伤的修复过程中,反应性星形胶质细胞向脊髓病变区域中心迁移,在其迁移的过程中,反应性星形胶质细胞在STAT3的调控下,增强损伤部位的收缩,使浸润的炎性细胞局限化,从而限制病变区域蔓延,显著提高神经功能的恢复[17-18]。然而,在慢性损伤阶段,反应性星形胶质细胞形成瘢痕,作为物理和化学屏障,却阻碍轴突再生[17,19]。尽管如此,神经元与星形胶质细胞间的交互作用在正常神经活动过程中依然是具有重要作用的,且其在急性脊髓损伤修复中的作用毋容置疑。 2.2.2 内皮细胞-神经元 血-脊髓屏障是神经血管单元的组件之一。在血管分支上属于毛细血管,是神经组织血液供应与物质交换的终末血管。内皮细胞是血-脊髓屏障的主要组成结构,其结构与功能的完整决定血-脊髓屏障通透性的变化。神经元因具有高耗氧和高代谢性,含有丰富的线粒体,生理状况下其能量几乎全部来源于葡萄糖的有氧氧化,故对缺血缺氧环境极其敏感。倘若内皮屏障结构破坏或功能受损,神经元极易受到缺血缺氧与氧化应激、自由基、神经炎症或神经毒性损伤等继发性损害,发生线粒体损伤,导致神经元退变或凋亡 [20]。在缺血环境下,神经元促使星形胶质细胞活化,进而刺激内皮细胞分泌更多血管内皮生长因子,破坏内皮细胞屏障[21]。基于此,学者们尝试使用药物降低模型动物血-脊髓屏障的通透性,结果证明这种策略可在不同程度上减缓神经元退变、损伤或轴突脱髓鞘变性的病理进程[22-24]。 2.2.3 星形胶质细胞-内皮细胞 星形胶质细胞也是神经血管单元中不可或缺的组件之一。在内皮屏障形成过程中,星形胶质细胞和血管内皮细胞相互诱导分化,星形胶质细胞分泌的转化生长因子β、胶质细胞源性营养因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、白细胞介素6等细胞因子可以促进血管内皮细胞的分化,而内皮细胞分泌的白血病抑制因子等细胞因子可以反过来促进星形胶质细胞的分化[25-26]。星形胶质细胞成熟后,其终足与内皮细胞以及基膜紧密相连,共同维护内皮屏障结构完整性与调节其通透性。缺血环境下,活化的星形胶质细胞可使内皮细胞的紧密连接蛋白Occludin和Claudin-5表达下调,使内皮屏障结构与功能受损[21]。星形胶质细胞可能通过介导转化生长因子β1、血管生成素1和血管内皮生长因子调节紧密连接蛋白的表达,从而调控内皮屏障的通透性[27]。然而,内皮屏障的破坏也对胶质细胞产生损害。脊髓损伤后,内皮祖细胞不但可以通过Jagged1依赖性Notch信号调控血管功能,而且可诱导星形胶质细胞胶质形成,促进神经组织修复与再生[28]。 以上可知,神经血管单元各组件在结构与功能上都有紧密的联系。各组件间的交互作用是脊髓行使基本功能的必要条件,同时也是脊髓损伤修复的内源性驱动力。在这些交互作用过程中,以内皮细胞为主要屏障结构的血-脊髓屏障,作为神经细胞的能量源泉与门控,不断调节着内环境的稳态与各组件间的信号转导,影响神经修复。"

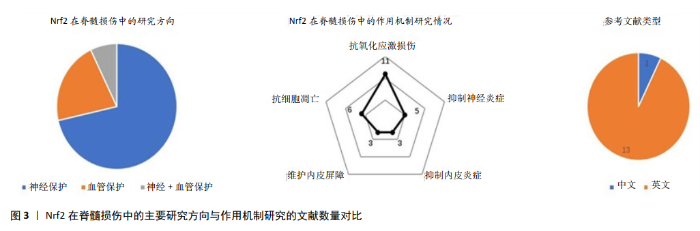
2.3 Nrf2-ARE对神经血管的作用 生理情况下,Nrf2大部分被Keap1锚定在细胞质中,在细胞核中只有很低的转录水平。脊髓损伤后,Nrf2与 Keap1解离,进入细胞核与ARE结合,启动下游靶基因血红素加氧酶1、谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶、谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶、醌氧化还原酶1、超氧化物歧化酶等的转录与表达,这些酶类在机体组织细胞中发挥抗氧化应激、抑制炎症反应与拮抗细胞凋亡的作用。尽管如此,内源性的Nrf2-ARE及其活化的下游分子显然并不足以抵御脊髓损伤所导致的神经-血管功能损害。近几年,使用外源性药物激活Nrf2相关通路成为脊髓损伤治疗的研究热点。目前研究方向主要集中于Nrf2的神经保护作用,血管保护作用其次,而对神经和血管的双重同步作用较少。其中中文文献较少,英文文献较多(图3),然而英文文献中很大部分来源于国内。Nrf2在脊髓损伤中的机制探索依次包括抗氧化应激损伤、抗细胞凋亡和抑制神经炎症,而对内皮损伤和血管再生的研究相对较少(图3)。简而言之,研究结果证明Nrf2的激活具有保护神经与血管的双重作用,但尚缺乏对神经血管单元各组件保护作用的全面性研究。 2.3.1 Nrf2-神经元 神经元是高耗氧和高代谢性的神经细胞,内含丰富的线粒体,满足有氧呼吸与能量代谢的需求,神经元死亡常导致永久性神经功能缺陷。在继发性脊髓损伤中,由谷氨酸盐、超氧化物等毒性物质积聚引发的线粒体氧化损伤或功能障碍是造成神经元死亡的常见原因 [29-30]。Nrf2-ARE通路的激活,主要发挥拮抗线粒体氧化应激损伤、减轻线粒体功能障碍和抑制神经元骨架降解的作用[31-32]。在缺血再灌注脊髓损伤大鼠模型中,神经元胞浆和胞核中内源性Nrf2表达上调对神经元产生保护作用[33-34]。在多发侧索硬化症患者体内,Nrf2在α-运动神经元中的表达上调[35],表明Nrf2对人体运动神经元的氧化损伤也产生积极的反应性保护作用,但由于人体病理研究的局限性,目前鲜有Nrf2的临床相关结果。与之相反,当抑制或下调Nrf2的表达后,神经营养因子与抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达减少,促凋亡因子Bax 和caspase-3表达上调,脊髓前角运动神经元的存活率下降,运动功能恢复受到影响[36]。总之,无论是在体外细胞还是在活体内,当发生氧化应激、炎症反应等刺激时,Nrf2及下游基因血红素加氧酶1、醌氧化还原酶1和GCLC等表达上调,均可发挥拮抗超氧化物引起的线粒体损伤和神经元凋亡的作用,从而提高神经元的存活率[30-31,33,37-39] 。 2.3.2 Nrf2-星形胶质细胞 作为中枢神经系统的支持细胞,星形胶质细胞尚具有分泌和摄取细胞因子的功能,对神经修复与再生产生影响。Nrf2对星形胶质细胞的作用主要体现如下:①减轻星形胶质细胞氧化损伤:Nrf2诱导星形胶质细胞中醌氧化还原酶1、血红素加氧酶1和谷胱甘肽的表达,下调细胞内活性氧产生,减轻氧化损伤与线粒体功能障碍[40-41];②抑制星形胶质细胞炎症反:Nrf2通过抑制IκBα磷酸化进而抑制核因子κB活化,降低下游炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1 β表达水平,抑制炎症损伤蔓延[42-43];③调控神经胶质形成,影响神经修复与再生:Nrf2下调胶质纤维酸性蛋白、Vim、CSPG等因子的生成,进而抑制胶质瘢痕形成[44];在脊髓损伤后期Nrf2还可促进GAP-43的表达,增强神经轴突的再生能力[44];④介导星形胶质细胞与神经元的交互作用,改善神经元存活率:Nrf2通过介导自噬溶酶体通路,减少α-突触核蛋白的积聚,减轻氧化应激反应和神经胶质形成,延缓运动神经元退变[45];或通过诱导靶基因表达增加神经元的抗氧化损伤能力以减缓神经元退变,提高神经元的存活率[16]。 2.3.3 Nrf2-内皮细胞 血管内皮屏障结构或功能的损害参与脊髓损伤病理生理损伤过程的主要环节[46-47]。Nrf2主要通过以下几点对内皮细胞产生作用:①拮抗内皮细胞的氧化损伤:Nrf2-ARE通过激活靶基因血红素加氧酶1、醌氧化还原酶1、谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶、TRX、谷胱甘肽和超氧化物歧化酶的表达,拮抗氧化应激对血管内皮细胞的损伤,从而维护血-脊髓屏障的完整性[22,24,48];②抑制内皮细胞的炎症损伤:Nrf2-ARE通过上调血红素加氧酶1,抑制炎症因子核因子κB、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1 β、白细胞介素18、基质金属蛋白酶9和巨噬细胞移动抑制因子等的表达[22,24,48-49],减轻内皮细胞的炎症损伤;③维护内皮屏障结构功能的完整性:Nrf2通过促进紧密连接蛋白ZO-1和Occludin合成,促进血脊髓屏障损伤后的修复[22,48,50];④促进内皮的增殖分化:Nrf2通过促进血红素加氧酶1的表达,诱导内皮细胞的增殖、分化和迁移,促进血管结构的形成[51-52]。由此可见,在脊髓损伤后,一方面,Nrf2通过其下游靶基因的抗氧化应激损伤与抗炎作用来保护内皮细胞,同时促进紧密连接蛋白的产生以恢复血-脊髓屏障的完整性,维持内环境稳态[53];另一方面,Nrf2也可以通过调控新生血管的形成,改善脊髓微循环的血液供应,促进脊髓损伤修复。"
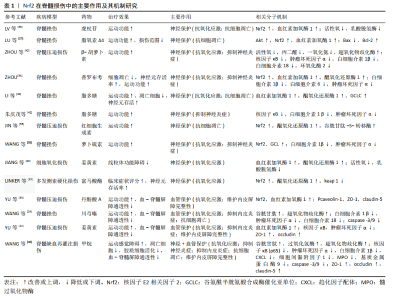
2.4 Nrf2-ARE的神经血管保护机制 在神经保护作用方面,Nrf2的激活主要通过以下几点发挥作用(表1):①通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路,上调抗氧化蛋白谷氨酸半胱氨酸连接酶、GCLC、谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶、醌氧化还原酶1、谷胱甘肽、过氧化氢酶和超氧化物歧化酶的表达,保护神经细胞免受超氧化物损 伤[30,32,35,40,48,54-58];②下调细胞内活性氧和乳酸脱氢酶等 产物的产生[40,43,56],减轻对神经细胞DNA、蛋白与细胞器膜结构的氧化损伤,特别是线粒体的损伤,但具体机制尚未明确;③通过调控核因子κB信号通路,下调炎症相关因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1 β、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素18表达,减轻炎症损伤[22,24,42,48,54-55];④通过Akt/Nrf2/HO-1信号通路下调凋亡基因Bax和促凋亡蛋白caspase-3,9的表达,并上调抗凋亡基因Bcl-2以抑制神经元凋亡,从而提高神经元存活率[48,57]。"
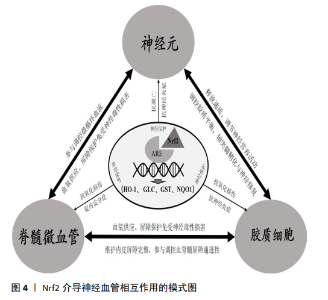
在血管保护作用方面,Nrf2的激活主要通过以下信号通路发挥作用(表1):①通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路上调抗氧化蛋白谷胱甘肽、超氧化物歧化酶、血红素加氧酶1和CAT表达,提高血管内皮抗氧化损伤能力[22,24,48,50];②通过核因子κB信号通路,下调炎症相关因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1 β、白细胞介素18和基质金属蛋白酶9的表达,抑制内皮细胞炎症损伤[27,29,50,57];③上调紧密连接蛋白ZO-1、occludin、claudin-5或 Pcaveolin-1的表达,降低内皮屏障的通透性[22,48,50],其具体机制尚待进一步阐明;④Nrf2促进脊髓血管再生的机制尚不明确,研究显示Nrf2可通过HIF-1α/VEGF或SDF-1激活PI3K、ERK1/2 和Akt,促进内皮细胞分化、增殖、迁移以及血管样结构的形成[52,59-60]。 综上所述,神经细胞与微血管内皮细胞在结构与功能上的相互联系与相互作用是脊髓行使正常神经功能的基础;Nrf2-ARE信号通路具有抗氧化应激损伤、抑制炎症损伤和抗凋亡的作用,它参与脊髓损伤与神经修复的病理生理过程,并可能通过共同通路对神经细胞与血管内皮细胞产生双重的保护作用(图4)。 由于Nrf2-ARE对脊髓损伤具有多重的保护机制,其在维护毛细血管内皮屏障稳定性与调控新生血管形成中的机制尚未完全明确,特别是Nrf2-ARE介导其下游靶基因调控神经细胞与血管内皮细胞交互作用的机制研究较少,还需要更加深入的研究。"
| [1] TRAN AP, WARREN PM, SILVER J. The Biology of Regeneration Failure and Success After Spinal Cord Injury. Physiol Rev. 2018; 98(2):881-917. [2] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282. [3] LOY K, BAREYRE FM. Rehabilitation following spinal cord injury: how animal models can help our understanding of exercise-induced neuroplasticity. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(3):405-412. [4] IADECOLA C. The Neurovascular Unit Coming of Age: A Journey Through Neurovascular Coupling in Health and Disease.Neuron. 2017;96(1): 17-42. [5] TONELLI C,CHIO IIC,TUVESON DA.Transcriptional Regulation by Nrf2.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;29(17):1727-1745. [6] 李慧,杨林.Nrf2抗氧化的分子调控机制[J].生物信息学,2018, 16(1):1-6. [7] BELLEZZA I, GIAMBANCO I, MINELLI A, et al. Nrf2-Keap1 Signaling in Oxidative and Reductive Stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865(5):721-733. [8] YAMAMOTO M, KENSLER TW, MOTOHASHI H. The KEAP1-NRF2 System: A Thiol-Based Sensor-Effector Apparatus for Maintaining Redox Homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(3):1169-1203. [9] YU X, JI C, SHAO A. Neurovascular Unit Dysfunction and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:334. [10] BROWN LS,FOSTER CG,COURTNEY JM,et al.Pericytes and Neurovascular Function in the Healthy and Diseased Brain. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019; 13:282. [11] WANG K, LI H, WANG H, et al. Irisin Exerts Neuroprotective Effects on Cultured Neurons by Regulating Astrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:9070341. [12] MARINA N, CHRISTIE IN, KORSAK A, et al. Astrocytes Monitor Cerebral Perfusion and Control Systemic Circulation to Maintain Brain Blood Flow. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):131. [13] XU J, HUANG G, ZHANG K, et al. Nrf2 Activation in Astrocytes Contributes to Spinal Cord Ischemic Tolerance Induced by Hyperbaric Oxygen Preconditioning. J Neurotrauma. 2014;31(15):1343-1353. [14] COLOMBO E, BASSANI C, DE ANGELIS A, et al. Siponimod (BAF312) Activates Nrf2 While Hampering NFκB in Human Astrocytes, and Protects From Astrocyte-Induced Neurodegeneration. Front Immunol. 2020;11:635. [15] HOANG TT, JOHNSON DA, RAINES RT, et al. Angiogenin activates the astrocytic Nrf2/antioxidant-response element pathway and thereby protects murine neurons from oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(41):15095-15103. [16] ASANUMA M, OKUMURA-TORIGOE N, MIYAZAKI I, et al. Region-Specific Neuroprotective Features of Astrocytes Against Oxidative Stress Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):598. [17] OKADA S, HARA M, KOBAYAKAWA K, et al. Astrocyte reactivity and astrogliosis after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res. 2018;26:39-43. [18] RENAULT-MIHARA F, MUKAINO M, SHINOZAKI M, et al. Regulation of RhoA by STAT3 coordinates glial scar formation. J Cell Biol. 2017; 216(8):2533-2550. [19] LI X, YANG B, XIAO Z, et al. Comparison of subacute and chronic scar tissues after complete spinal cord transection. Exp Neurol. 2018;306: 132-137. [20] RUIZ A, ALBERDI E, MATUTE C. Mitochondrial Division Inhibitor 1 (mdivi-1) Protects Neurons Against Excitotoxicity Through the Modulation of Mitochondrial Function and Intracellular Ca 2+ Signaling. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:3. [21] LI YN, PAN R, QIN XJ, et al. Ischemic neurons activate astrocytes to disrupt endothelial barrier via increasing VEGF expression. J Neurochem. 2014;129(1):120-129. [22] YU DS, CAO Y, MEI XF, et al. Curcumin improves the integrity of blood-spinal cord barrier after compressive spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurol Sci. 2014; 346(1-2):51-59. [23] WINKLER EA, SENGILLO JD, SAGARE AP, et al. Blood-spinal cord barrier disruption contributes to early motor-neuron degeneration in ALS-model mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(11): E1035-1042. [24] WANG C, WANG P, ZENG W, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine improves the recovery of spinal cord injury via Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016;26(4):1287-1291. [25] ABBOTT NJ. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions and blood-brain barrier permeability. J Anat. 2002;200:629-638. [26] ABBOTT NJ, RONNBACK L, HANSSON E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41-53. [27] YOU T, BI Y, LI J, et al. IL-17 Induces Reactive Astrocytes and Up-Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Through JAK/STAT Signaling. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41779. [28] KAMEI N, KWON SM, ISHIKAWA M, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells promote astrogliosis following spinal cord injury through Jagged1-dependent Notch signaling. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(29):1758-1769. [29] OLIVEIRA KM, BINDA NS, LAVOR MSL, et al.Conotoxin MVIIA Improves Cell Viability and Antioxidant System After Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0204948. [30] ZHU J, YANG LK, CHEN WL, et al. Activation of SK/K Ca Channel Attenuates Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Anti-oxidative Activity and Inhibition of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Rabbits. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:325. [31] MILLER DM, SINGH IN, WANG JA, et al. Nrf2-ARE activator carnosic acid decreases mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative damage and neuronal cytoskeletal degradation following traumatic brain injury in mice. Exp Neurol. 2015;264:103-110. [32] LI W, JIANG D, LI Q, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced preconditioning protects against traumatic spinal cord injury by upregulating Nrf2 expression in rats. Life Sci. 2016;162:14-20. [33] BOBINAC M, ĆELIĆ T, VUKELIĆ I, et al. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and choline acetyltransferase co-expression in rat spinal cord neurons after ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2018;32(4):803-813. [34] FU J, SUN H, ZHANG Y, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Luteolin Against Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Attenuation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. J Med Food. 2018;21(1):13-20. [35] LINKER RA, LEE DH, RYAN S, et al. Fumaric acid esters exert neuroprotective effects in neuroinflammation via activation of the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 3):678-692. [36] SHAO Z, LV G, WEN P, et al. Silencing of PHLPP1 promotes neuronal apoptosis and inhibits functional recovery after spinal cord injury in mice. Life Sci. 2018;209:291-299. [37] WAN T, WANG Z, LUO Y, et al. FA-97, a New Synthetic Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Derivative, Protects against Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neuronal Cell Apoptosis and Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impairment by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:8239642. [38] KWON SH, LEE SR, PARK YJ, et al. Suppression of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Stress by Hyperoside Via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in Dopaminergic Neurons. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5832. [39] LIN X, ZHU J, NI H, et al. Treatment With 2-BFI Attenuated Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Apoptosis via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:567. [40] JIANG H, TIAN X, GUO Y, et al. Activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 cytoprotective signaling by curcumin protect primary spinal cord astrocytes against oxidative toxicity. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011; 34(8):1194-1197. [41] LEE EJ, PARK JS, LEE YY, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of an MMP-8 inhibitor in lipoteichoic acid-stimulated rat primary astrocytes: involvement of NF-κB, Nrf2, and PPAR-γ signaling pathways. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):326. [42] 朱庆茂,蒋电明,唐溧,等.低剂量脂多糖预处理上调Nrf2表达减轻大鼠脊髓损伤的炎症反应[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2015, 31(4):437-442. [43] ZHOU L, OUYANG L, LIN S, et al. Protective role of β-carotene against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:92-99. [44] 廖小俊. Nrf2对小鼠脊髓损伤后胶质瘢痕形成的影响及机制研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2016. [45] GAN L, VARGAS MR, JOHNSON DA, et al. Astrocyte-specific Overexpression of Nrf2 Delays Motor Pathology and Synuclein Aggregation throughout the CNS in the Alpha-synuclein Mutant (A53T) Mouse Model. J Neurosci. 2012;32(49):17775-17787. [46] 戴国宇,刘吉松,李坚,等.MiRNA-125a-5p对大鼠脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障及运动功能的影响[J].解剖学杂志,2019,42(3):225-230. [47] 余正然,王晓波,龙厚清.血-脊髓屏障修复在脊髓损伤治疗中作用的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(2):179-184. [48] WANG L, YAO Y, HE R, et al. Methane ameliorates spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activity mediated by Nrf2 activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;103:69-86. [49] CHANG HC, YANG HL, PAN JH, et al. Hericiumerinaceus Inhibits TNF-α-Induced Angiogenesis and ROS Generation through Suppression of MMP-9/NF-κB Signaling and Activation of Nrf2-Mediated Antioxidant Genes in Human EA. hy926 Endothelial Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;8257238. [50] YU DS, WANG YS, BI YL, et al.Salvianolic acid A ameliorates the integrity of blood-spinal cord barrier via miR-101/Cul3/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Brain Res. 2017;1657:279-287. [51] VALCARCEL-ARES MN, GAUTAM T, WARRINGTON JP, et al. Disruption of Nrf2 Signaling Impairs Angiogenic Capacity of Endothelial Cells: Implications for Microvascular Aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67(8):821-829. [52] FLORCZYK U, JAZWA A, MALESZEWSKA M, et al. Nrf2 Regulates Angiogenesis: Effect on Endothelial Cells, Bone Marrow-Derived Proangiogenic Cells and Hind Limb Ischemia. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;20(11):1693-1708. [53] DU F, WANG X, SHANG B, et al. Gastrodin ameliorates spinal cord injury via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Acta Biochim Pol. 2016;63(3):589-593. [54] ZHOU Z, LIU C, CHEN S, et al. Activation of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway by probucol contributes to inhibiting inflammation and neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Oncotarget. 2017;8(32): 52078-52093. [55] JIN W, MING X, HOU X, et al. Protective effects of erythropoietin in traumatic spinal cord injury by inducing the Nrf2 signaling pathway activation. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014;76(5):1228-1234. [56] LV R, DU L, ZHANG L, et al. Polydatin attenuates spinal cord injury in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and microglia apoptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Life Sci. 2019;217:119-127. [57] LU T, WU X, WEI N, et al. Lipoxin A4 protects against spinal cord injury via regulating Akt/nuclear factor (erythroid-derived2)-like 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:905-910. [58] WANG XL, DE RV, WANG HD, et al. Activation of the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element pathway is neuroprotective after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29:936-945. [59] FAN J, LV H, LI J, et al. Roles of Nrf2/HO-1 and HIF-1α/VEGF in lung tissue injury and repair following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):7695-7707. [60] JAYASURIYA R, DHAMODHARAN U, AMIN KN, et al. Role of Nrf2 in MALAT1/ HIF-1α loop on the regulation of angiogenesis in diabetic foot ulcex. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;S0891-5849(20)30626-30632. [61] HUTSON TH, DI GIOVANNI S. The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(12):732-745. [62] CHEN CM, CHEN WL, YANG ST, et al. New Synthetic 3-Benzoyl-5-Hydroxy-2H-Chromen-2-One (LM-031) Inhibits Polyglutamine Aggregation and Promotes Neurite Outgrowth through Enhancement of CREB, NRF2, and Reduction of AMPKα in SCA17 Cell Models. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:3129497. [63] PUKOS N, GOODUS MT, SAHINKAYA FR, et al. Myelin status and oligodendrocyte lineage cells over time after spinal cord injury: What do we know and what still needs to be unwrapped? Glia. 2019;67(11): 2178-2202. [64] LIU Z, ZHANG H, XIA H, et al. CD8 T Cell-Derived Perforin Aggravates Secondary Spinal Cord Injury Through Destroying the Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;512(2):367-372. [65] PARK CS, LEE JY, CHOI HY, et al. Protocatechuic Acid Improves Functional Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury by Attenuating Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Disruption and Hemorrhage in Rats. Neurochem Int. 2019;124:181-192. [66] BUENDIA I, MICHALSKA P, NAVARRO E, et al. Nrf2-ARE Pathway: An Emerging Target Against Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;157:84-104. |
| [1] | Zhou Bangyu, Li Jie, Ruan Yushang, Geng Funeng, Li Shaobo. Effects of Periplaneta americana powder on motor function and autophagic protein Beclin-1 in rats undergoing spinal cord hemisection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1223-1228. |
| [2] | Zeng Fanzhuo, Li Yuxin, Sun Jiachen, Gu Xinyang, Wen Shan, Tian He, Mei Xifan. Efficient strategies for microglia replacement in spinal cord injury models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [3] | Liu Tao, Zhang Wenkai, Ma Ziqian, Zhang Yan, Chen Xueming. Riluzole interferes with the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia of rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1036-1042. |
| [4] | Chen Zepeng, Hou Yonghui, Chen Shudong, Hou Yu, Lin Dingkun. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid treats spinal cord injury by reducing apoptosis of spinal cord neurons under glucose and oxygen deprivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [5] | Xu Zihan, Bi Yunfeng, Li Jiang, Zhang Zongliang, Song Chen, Dong Jie, Liu Dong. Repetitive magnetic stimulation of S3 nerve root and M1 area for treating urinary retention after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1719-1723. |
| [6] | Shang Wenya, Ren Yafeng, Li Bing, Wei Huilin, Zhang Zhilan, Huang Xiaomeng, Huang Jing. Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for pyroptosis after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1772-1779. |
| [7] | Wu Yangpeng, Yang Xiaohui, Lao Kecheng, Dai Shiyou, Fan Xiao. Characterization and repair effect of supramolecular conducting hydrogel carrying ligustrazine on spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1505-1511. |
| [8] | Zheng Mingkui, Xue Chenhui, Guan Xiaoming, Ma Xun. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce the permeability of blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 50-55. |
| [9] | Long Qingxi, Zhang Pingshu, Liu Qing, Ou Ya, Zhang Lili, Yuan Xiaodong. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the heterogeneity of astrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 139-146. |
| [10] | He Wanyu, Cheng Leping. Strategies and advance on stem cell transplantation for repair of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [11] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [12] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [13] | Hao Liufang, Duan Hongmei, Wang Zijue, Hao Fei, Hao Peng, Zhao Wen, Gao Yudan, Yang Zhaoyang, Li Xiaoguang. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of ependymal cells after spinal cord injury in transgenic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [14] | Li Xiaoyin, Yang Xiaoqing, Chen Shulian, Li Zhengchao, Wang Ziqi, Song Zhen, Zhu Daren, Chen Xuyi. Collagen/silk fibroin scaffold combined with neural stem cells in the treatment of traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
| [15] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||