Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (35): 5670-5675.doi: 10.12307/2021.298
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lentiviral vector overexpressing FNDC5 inhibits proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells
Wang Xiang, Wei Chaojun, Wang Yao, Pan Yujia, Liu Danan
- Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Institute of Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2020-09-18Revised:2020-09-21Accepted:2020-11-13Online:2021-12-18Published:2021-08-05 -
Contact:Liu Danan, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s/Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Institute of Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Xiang, Master candidate, Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Institute of Medical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:The National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660083 (to LDN); Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Talent Team Project, No. (2020)5014 (to LDN); Guizhou Provincial Hundred-level Innovative Talent Cultivation Plan, No. (2015)4026 (to LDN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xiang, Wei Chaojun, Wang Yao, Pan Yujia, Liu Danan. Lentiviral vector overexpressing FNDC5 inhibits proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5670-5675.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
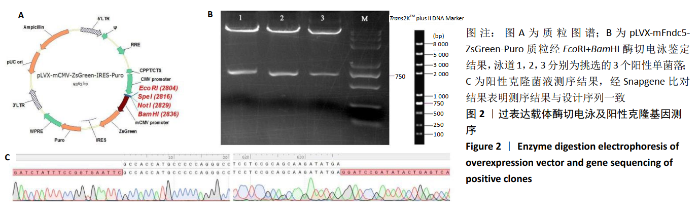
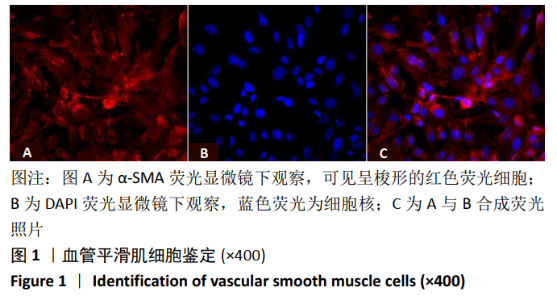
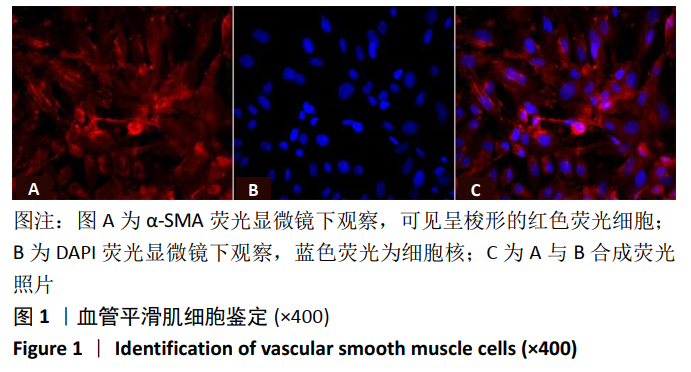
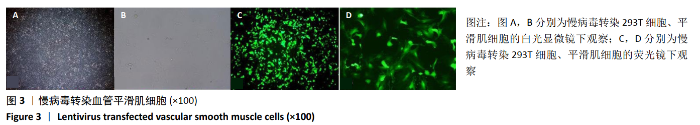
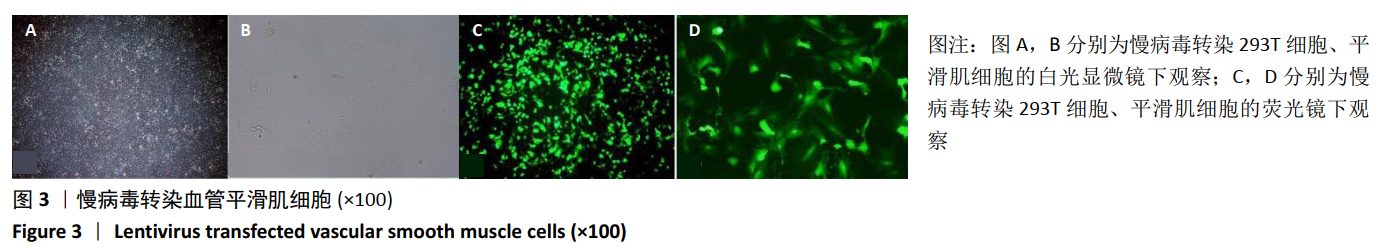
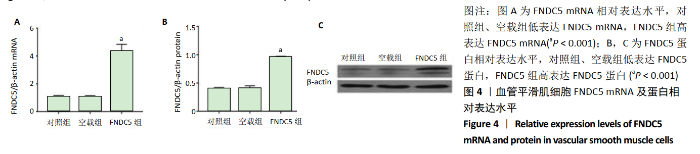
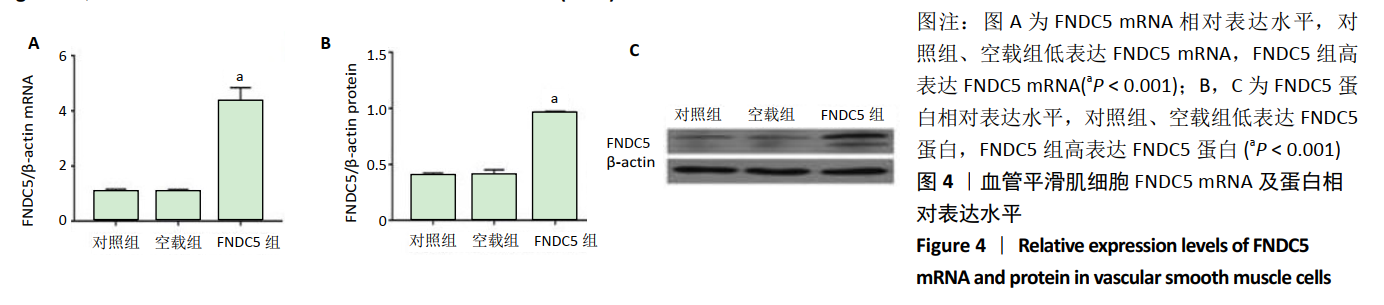
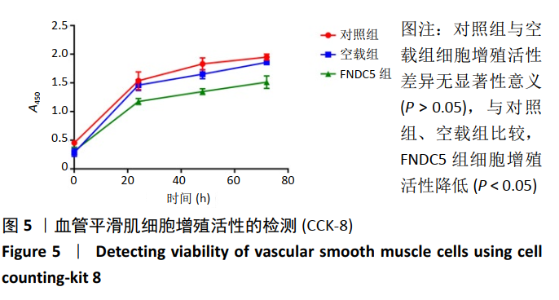
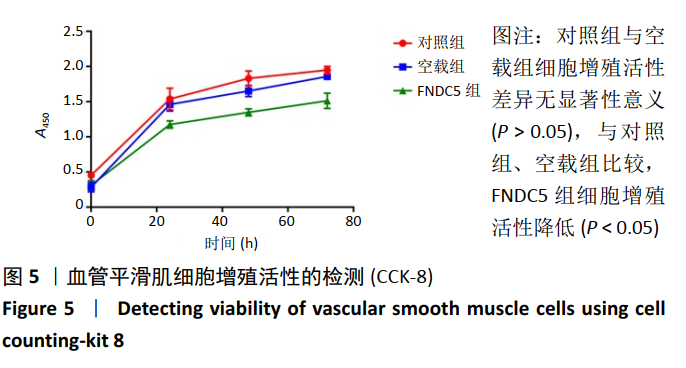
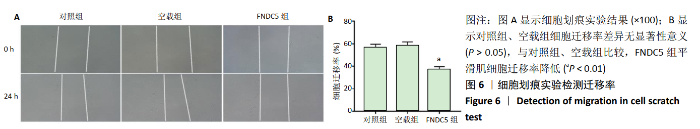
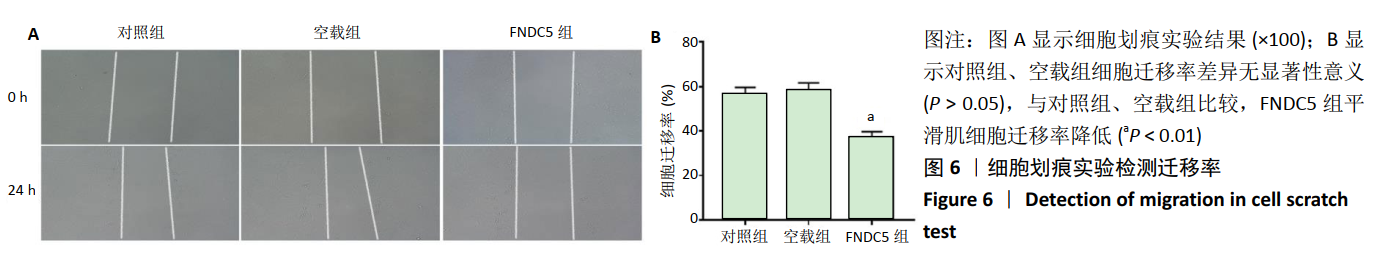
2.2 rLV-mFndc5-ZsGreen-Puro质粒的构建与鉴定 取pLVX-mCMV-ZsGreen-IRES-Puro质粒,该质粒含有EcoRI、BamHI双酶切位点(图2A),将FNDC5克隆到质粒上,双酶切后用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳回收并分析产物片段长度,酶切后电泳结果与预期结果一致(图2B),得到目的基因阳性克隆,送菌液pLVX-mFndc5-ZsGreen-Puro测序,测序结果经Snapgene比对表明测序结果与设计序列一致(图2C),已成功构建FNDC5过表达质粒。 2.3 rLV-mFndc5-ZsGreen-Puro慢病毒包装及转染平滑肌细胞 将质粒pLVX-mFndc5-ZsGreen-Puro导入293T细胞(图3A,C),48 h后收集细胞上清液,通过PCR法定量测定上清液中的病毒滴度为1×108 TU/mL。将慢病毒包装的rLV-mFndc5-ZsGreen-Puro表达质粒按照MOI为10,15,30转染平滑肌细胞,24 h后能明显观察到绿色荧光(图3B,D,MOI=30),得到FNDC5过表达转染的平滑肌细胞株。"

| [1] ZHAO D, LIU J, WANG M, et al. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in China: current features and implications. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019;16(4):203-212. [2] NOBUYOSHI M, KIMURA T, NOSAKA H, et al. Restenosis after successful percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: serial angiographic follow-up of 229 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988;12(3):616-623. [3] MINER SE, HEGELE RA, SPARKES J, et al. Homocysteine, lipoprotein(a), and restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: a prospective study. Am Heart J. 2000;140(2):272-278. [4] CLOWES AW, CLOWES MM, KOCHER O, et al. Arterial smooth muscle cells in vivo: relationship between actin isoform expression and mitogenesis and their modulation by heparin. J Cell Biol. 1988;107(5):1939-1945. [5] DESMOULIERE A, RUBBIA-BRANDT L, GABBIANI G. Modulation of actin isoform expression in cultured arterial smooth muscle cells by heparin and culture conditions. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991;11(2):244-253. [6] WANG DD, UHRIN P, MOCAN A, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation as a therapeutic target.Part 1: molecular targets and pathways. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(6):1586-1607. [7] GALLO G, PIERELLI G, FORTE M, et al. Role of oxidative stress in the process of vascular remodeling following coronary revascularization. Int J Cardiol. 2018;268:27-33. [8] PUKAJŁO K, KOLACKOV K, ŁACZMAŃSKI Ł, et al. Irisin--a new mediator of energy homeostasis. 2015:69,233-242. [9] ZHANG Y, SONG H, ZHANG Y, et al. Irisin Inhibits Atherosclerosis by Promoting Endothelial Proliferation Through microRNA126‐5p. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016; 5(9):e004031. [10] FRÜHBECK G, FERNÁNDEZ-QUINTANA B, PANIAGUA M, et al. FNDC4, a novel adipokine that reduces lipogenesis and promotes fat browning in human visceral adipocytes. Metabolism. 2020;108:154261. [11] DU X, JIANG W, LV Z. Lower Circulating Irisin Level in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. 2016:48,644-652. [12] EFE TH, AÇAR B, ERTEM AG, et al. Serum Irisin Level Can Predict the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Stable Angina. 2017:47,44-49. [13] ARONIS KN, MORENO M, POLYZOS SA, et al. Circulating irisin levels and coronary heart disease: association with future acute coronary syndrome and major adverse cardiovascular events. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39(1):156-161. [14] DENG W. Association of Serum Irisin Concentrations with Presence and Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:4193-4197. [15] PARK KH, ZAICHENKO L, BRINKOETTER M, et al. Circulating Irisin in Relation to Insulin Resistance and the Metabolic Syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98(12):4899-4907. [16] 何青松,刘大男,谭娟.鸢尾素对高脂饮食诱导ApoE~(-/-)小鼠动脉粥样硬化形成的影响及其机制[J]. 山东医药,2020,60(22):39-43. [17] 何青松,刘大男,谭娟.冠心病患者血清鸢尾素水平变化观察[J].山东医药, 2020,60(6):69-71. [18] 谭娟,刘大男,何青松,等.鸢尾素对载脂蛋白E基因敲除小鼠动脉粥样硬化的影响[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2017,25(8):773-777. [19] ZHENG G, LI H, ZHANG T, et al. Irisin protects macrophages from oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018;25(5):849-857. [20] 覃铮,刘大男,肖金翠,等. FNDC5过表达慢病毒载体的构建及稳定转染THP-1细胞系[J].重庆医科大学学报,2020,45(2):212-216. [21] ZHANG D, TAN X, TANG N, et al. Review of Research on the Role of Irisin in Tumors. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:4423-4430. [22] 牟仁奎,向水,黄进启,等.鸢尾素通过磷酸腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路调控自噬抑制血管平滑肌细胞炎性反应和增殖的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(6):1020-1023. [23] SESTI G, ANDREOZZI F, FIORENTINO TV, et al. High circulating irisin levels are associated with insulin resistance and vascular atherosclerosis in a cohort of nondiabetic adult subjects. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51(5):705-713. [24] 刘大男,何作云,方颖,等.血红素氧合酶-1/一氧化碳系统对胰岛素样生长因子-Ⅰ诱导的兔血管平滑肌细胞增殖的抑制作用[J].中华心血管病杂志, 2006,34(2):153-158. [25] LIU D, MO X, ZHANG H, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) alleviates vascular restenosis after balloon injury in a rabbit carotid artery model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018;11(5):2479. [26] KURODA H, KUTNER RH, BAZAN NG, et al. Simplified lentivirus vector production in protein-free media using polyethylenimine-mediated transfection. J Virol Methods. 2009;157(2):113-121. [27] BUCHHOLZ CJ, FRIEDEL T, BÜNING H. Surface-Engineered Viral Vectors for Selective and Cell Type-Specific Gene Delivery. Trends Biotechnol. 2015;33(12):777-790. [28] CHIANG CY, LIGUNAS GD, CHIN WC, et al. Efficient Nonviral Stable Transgenesis Mediated by Retroviral Integrase. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020;17:1061-1070. [29] DI PASQUALE E, LATRONICO MV, JOTTI GS, et al. Lentiviral vectors and cardiovascular diseases: a genetic tool for manipulating cardiomyocyte differentiation and function. Gene Ther. 2012;19(6):642-648. [30] THOMAS CE, EHRHARDT A, KAY MA. Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4(5):346-358. [31] BENNETT MR, SINHA S, OWENS GK. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 2016;118(4):692-702. [32] BEAMISH JA, HE P, KOTTKE-MARCHANT K, et al. Molecular regulation of contractile smooth muscle cell phenotype: implications for vascular tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010;16(5):467-491. [33] BOSTROM P, WU J, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481(7382):463-468. [34] ZHANG X, HU C, WU HM, et al. Fibronectin type III domain-containing 5 in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: a promising biomarker and therapeutic target. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00557-5. [35] TENG Y, WANG Z, LI W, et al. Mitoxantrone suppresses vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation and balloon injury-induced neointima formation: An in vitro and in vivo study. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2017;17(4):339-348. [36] WANG KC, CHEN PS, CHAO TH, et al. The role of vascular smooth muscle cell membrane-bound thrombomodulin in neointima formation. Atherosclerosis. 2019;287:54-63. [37] SONG H, XU J, LV N, et al. Irisin reverses platelet derived growth factor-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cells phenotype modulation through STAT3 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;479(2):139-145. [38] ZANG YH, CHEN D, ZHOU B, et al. FNDC5 inhibits foam cell formation and monocyte adhesion in vascular smooth muscle cells via suppressing NFκB-mediated NLRP3 upregulation. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019;121:106579. [39] ZHOU B, QIU Y, WU N, et al. FNDC5 Attenuates Oxidative Stress and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells via Activating the AMPK-SIRT1 Signal Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:6384803. [40] RYKACZEWSKA U, SUUR BE, RÖHL S, et al. PCSK6 Is a Key Protease in the Control of Smooth Muscle Cell Function in Vascular Remodeling. Circ Res. 2020;126(5):571-585. |
| [1] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [2] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [3] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [4] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [5] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [6] | Liu Yanlu, Hu Wei, Aikebaier, Yiliya, Huang Yifei. Inhibition of galectin-3 promotes apoptosis of cartilage endplate cells and induces intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5599-5603. |
| [7] | Shi Shujuan, Li Cheng, Qiao Lingyan, Yang Binyi, Li Tang. Construction of human SMARCAL11 gene over-expressed lentiviral vector and its effect on proliferation of embryonic kidney cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5682-5687. |
| [8] | Chen Dong, Jiang Xin. Effect of Kartogenin/Pluronic F127 micelles on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5473-5477. |
| [9] | Liu Lei, Di Haiping, Guo Haina, Cao Dayong, Niu Xihua, Xia Chengde. Changes in biological characteristics of platelet-rich fibrin by freeze-drying technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4995-4999. |
| [10] | Zheng Weipeng, Hu Weijian, Zhao Guoyuan, Wei Hewei, Liu Zhijun, Wan Lei, Chen Sheng, Liao Zhihao. Effects of Bushen Jianpi Huoxue Recipe on cell proliferation and alkaline phosphatase activity in Beclin-1 overexpressing and silencing MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4650-4655. |
| [11] | Zhou Jianwei, Zhou Jing, Li Mao, Chi Cheng, Wang Fei. A hydrogel based on acellular decalcified bone matrix/erythropoietin promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(28): 4454-4459. |
| [12] | Zheng Feng, Zhang Fucai, Xu Zhe. MicroRNA-98-5p promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation: possibilities and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4112-4117. |
| [13] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [14] | Xu Guilan, Song Jiansheng, Yang Shijiang. Regulation of S100A4 gene silencing by ultrasound microbubbles on the stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of gastric cancer stem cells#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4025-4031. |
| [15] | Tang Xiaokai, Li Weiming. Role and mechanism of Nel-like molecule-1 in promoting bone fusion after spinal fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3914-3920. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||