Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (31): 4921-4927.doi: 10.12307/2021.131
Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: a single-arm clinical study
Xu Huimin, Zhang Suping, Cao Weijie, Li Li, Zhang Ran, Wang Yiran, Wan Dingming
- Department of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-28Revised:2020-10-30Accepted:2020-12-18Online:2021-11-08Published:2021-04-25 -
Contact:Wan Dingming, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Xu Huimin, Master candidate, Department of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Major Scientific Research Project of Henan Provincial Universities, No. 20A320021 (to ZR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Huimin, Zhang Suping, Cao Weijie, Li Li, Zhang Ran, Wang Yiran, Wan Dingming. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: a single-arm clinical study[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4921-4927.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

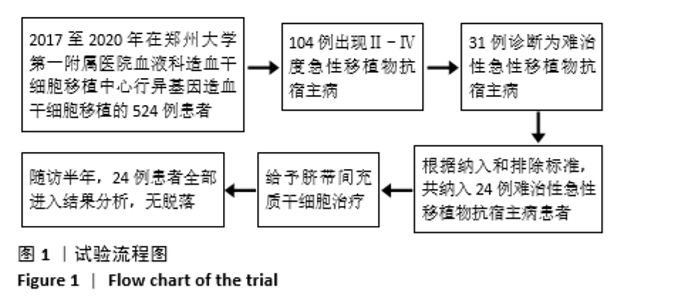
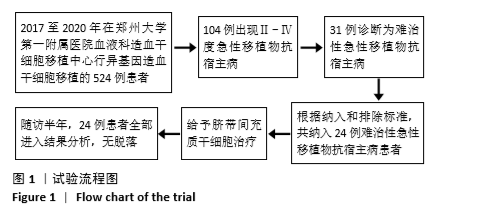
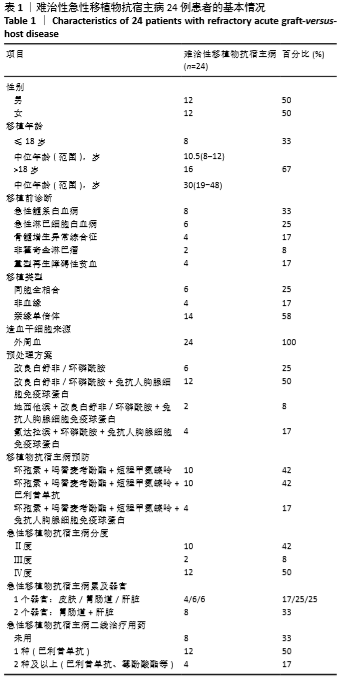
共纳入24例TR-aGVHD患者。预处理方案:6例采用“改良白舒非/环磷酰胺”方案,12例采用“改良白舒非/环磷酰胺+兔抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白”方案,2例采用“地西他滨+改良白舒非/环磷酰胺+兔抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白”方案,4例采用“氟达拉滨/环磷酰胺+兔抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白”方案。GVHD预防:10例应用“环孢素+吗替麦考酚酯+短程甲氨蝶呤”预防,10例应用“环孢素+吗替麦考酚酯+短程甲氨蝶呤+巴利昔单抗”预防,4例应用“环孢素+吗替麦考酚酯+短程甲氨蝶呤+兔抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白”预防。TR-aGVHD分度:Ⅱ度10例,Ⅲ度2例,Ⅳ度12例。16例患者仅累及单个器官,其中累及皮肤4例(均为Ⅱ度),胃肠道6例(均为Ⅳ度),肝脏6例(Ⅱ度/Ⅲ度/Ⅳ度分别为2例/2例/2例);8例患者同时累及胃肠道及肝脏,其中Ⅱ度4例,Ⅳ度4例。aGVHD二线治疗用药情况:8例患者未应用二线药物治疗,12例患者应用1种二线药物治疗(均为巴利昔单抗),4例患者应用2种及以上二线药物治疗如巴利昔单抗、甲氨蝶呤、硫唑嘌呤、兔抗人胸腺细胞免疫球蛋白等,见表1。"
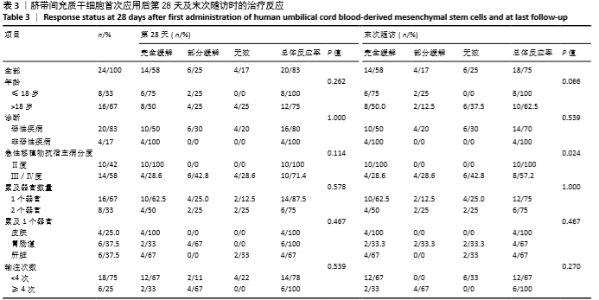
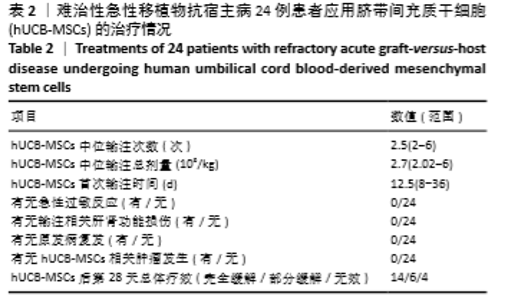
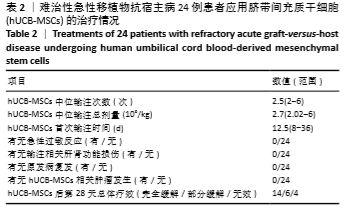
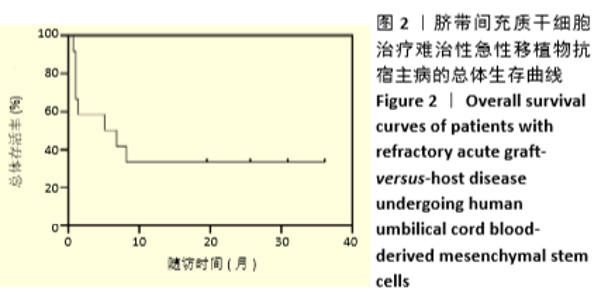
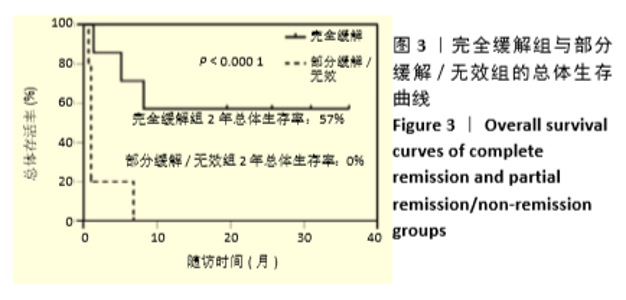
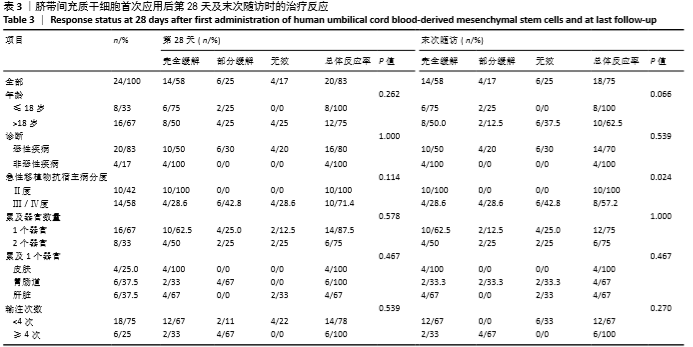
首次hUCB-MSCs应用后第28天的总体治疗反应率为83%(20/24),其中完全缓解14例、部分缓解4例、一过性部分缓解2例;末次随访时间的总体治疗反应率为75%(18/24),其中完全缓解14例、部分缓解4例,见表3。 从发病年龄分析,儿童和成人治疗后第28天的总体治疗反应率分别为100%(8/8)和75%(12/16),两者差异无显著性意义(P=0.262);末次随访时的总体治疗反应率分别为100%(8/8)和63%(10/16),两者差异无显著性意义(P=0.066),见表3。 从疾病类型分析,恶性血液病与非恶性血液病治疗后第28天的总体治疗反应率分别为80%(16/20)和100%(4/4),两者差异无显著性意义(P=1.000);末次随访时的总体治疗反应率分别为70%(14/20)和100%(4/4),两者差异无显著性意义(P=0.539),见表3。 从aGVHD分度分析,Ⅱ度和Ⅲ-Ⅳ度治疗后第28天的总体治疗反应率分别为100%(10/10)和71%(10/14),两者差异无显著性意义(P=0.114);末次随访时的总体治疗反应率分别为100%(10/10)和57%(8/14),两者差异有显著性意义(P=0.024),见表3。 从aGVHD累及器官数量分析,累及单个器官和累及2个器官治疗后第28天的总体治疗反应率分别为88%(14/16)和75%(6/8),两者差异无显著性意义(P=0.578);末次随访时的总体治疗反应率分别为75%(12/16)和75%(6/8),两者差异无显著性意义(P=1.000)。aGVHD仅累及单个器官共16例,治疗后第28天评估疗效:皮肤、胃肠道、肝脏总体治疗反应率分别为100%(4/4),100%(6/6),67%(4/6),三者间差异无显著性意义(P=0.467);末次随访时评估疗效:皮肤、胃肠道、肝脏总体治疗反应率分别为100%(4/4),67%(4/6),67%(4/6),三者间差异无显著性意义(P=0.467),见表3。 从hUCB-MSCs输注次数分析,输注次数<4次和输注次数≥4次患者治疗后第28天的总体治疗反应率分别为78%(14/18)和100%(6/6),两者间差异无显著性意义(P=0.539);末次随访时的总体治疗反应率分别为67%(12/18)和100%(6/6),两者间差异无显著性意义(P=0.27),见表3。 "
| [1] 中华医学会血液学分会干细胞应用学组.中国异基因造血干细胞移植治疗血液系统疾病专家共识(Ⅲ)——急性移植物抗宿主病(2020年版)[J].中华血液学杂志,2020,41(7):529-536. [2] MUNNEKE JM, SPRUIT MJ, CORNELISSEN AS, et al. The Potential of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as Treatment for Severe Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease: A Critical Review of the Literature. Transplantation. 2016;100(11):2309-2314. [3] 许兰平,黄晓军.我如何治疗造血干细胞移植后急性移植物抗宿主病[J].中华血液学杂志,2017,38(8):649-655. [4] PENACK O, MARCHETTI M, RUUTU T, et al. Prophylaxis and management of graft versus host disease after stem-cell transplantation for haematological malignancies: updated consensus recommendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(2):e157-e167. [5] RUUTU T, GRATWOHL A, DE WITTE T, et al. Prophylaxis and treatment of GVHD: EBMT-ELN working group recommendations for a standardized practice. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(2):168-173. [6] DEEG HJ. How I treat refractory acute GVHD. Blood. 2007;109(10): 4119-4126. [7] DOTOLI GM, DE SANTIS GC, ORELLANA MD, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell infusion to treat steroid-refractory acute GvHD III/IV after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(6):859-862. [8] LE BLANC K, RASMUSSON I, SUNDBERG B, et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004;363(9419):1439-1441. [9] 巫丹,尹宇.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗不同疾病的研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2020,30(8):125-130. [10] 王佃亮.脐带间充质干细胞的临床应用[J].中国生物工程杂志,2020, 40(5):125-129. [11] SCHOEMANS HM, LEE SJ, FERRARA JL, et al. EBMT-NIH-CIBMTR Task Force position statement on standardized terminology & guidance for graft-versus-host disease assessment. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(11):1401-1415. [12] PRZEPIORKA D, WEISDORF D, MARTIN P, et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995; 15(6):825-828. [13] FORMAN SJ, NEGRIN RS, JOSEPH H, et al. Thomas’ Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Stem Cell Transplantation.5th Ed. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 2015:1012-1019. [14] 王佃亮.脐带间充质干细胞制剂的质量管理及有效性和安全性[J].转化医学杂志,2020,9(2):65-69. [15] HOLTAN SG, PASQUINI M, WEISDORF DJ. Acute graft-versus-host disease: a bench-to-bedside update. Blood. 2014;124(3):363-373. [16] MARKEY KA, MACDONALD KP, HILL GR. The biology of graft-versus-host disease: experimental systems instructing clinical practice. Blood. 2014;124(3):354-362. [17] 许兰平,韩婷婷.异基因造血干细胞移植术后移植物抗宿主病的研究进展[J].临床内科杂志,2011,28(11):725-728. [18] 惠玉,周凡,张毅.MSC治疗aGVHD相关机制及临床应用研究进展[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2017,25(4):1245-1249. [19] 刘茂兰,史明霞.间充质干细胞治疗急性移植物抗宿主病机制及应用进展[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(11):1850-1853. [20] WANG L, GU Z, ZHAO X, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released from Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevent Life-Threatening Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease in a Mouse Model of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(24):1874-1883. [21] DENG Y, YI S, WANG G, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells instruct dendritic cells to acquire tolerogenic phenotypes through the IL-6-mediated upregulation of SOCS1. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(17):2080-2092. [22] LIU Y, YIN Z, ZHANG R, et al. MSCs inhibit bone marrow-derived DC maturation and function through the release of TSG-6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;450(4):1409-1415. [23] DAVIES LC, HELDRING N, KADRI N, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretion of Programmed Death-1 Ligands Regulates T Cell Mediated Immunosuppression. Stem Cells. 2017;35(3):766-776. [24] GUO H, ZHAO N, GAO H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Interleukin-35 Propagate Immunosuppressive Effects in Mice. Scand J Immunol. 2017;86(5):389-395. [25] BOISSEL L, TUNCER HH, BETANCUR M, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells increase expansion of cord blood natural killer cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(9):1031-1038. [26] WILLIAMS AR, HARE JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: biology, pathophysiology, translational findings, and therapeutic implications for cardiac disease. Circ Res. 2011;109(8):923-940. [27] LE BLANC K, FRASSONI F, BALL L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1579-1586. [28] ZHAO K, LOU R, HUANG F, et al. Immunomodulation effects of mesenchymal stromal cells on acute graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(1):97-104. [29] ZHAO K, LIU Q. The clinical application of mesenchymal stromal cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Hematol Oncol. 2016; 9(1):46. [30] MUROI K, MIYAMURA K, OKADA M, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (JR-031) for steroid-refractory grade III or IV acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II/III study. Int J Hematol. 2016;103(2):243-250. [31] ERBEY F, ATAY D, AKCAY A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment for Steroid Refractory Graft-versus-Host Disease in Children: A Pilot and First Study from Turkey. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1641402. [32] VON DALOWSKI F, KRAMER M, WERMKE M, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Treatment of Acute Steroid-Refractory Graft Versus Host Disease: Clinical Responses and Long-Term Outcome. Stem Cells. 2016;34(2):357-366. [33] HASHMI S, AHMED M, MURAD MH, et al. Survival after mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2016;3(1):e45-52. [34] CHEN X, WANG C, YIN J, et al. Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136991. [35] BADER P, KUÇI Z, BAKHTIAR S, et al. Effective treatment of steroid and therapy-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease with a novel mesenchymal stromal cell product (MSC-FFM). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(7):852-862. [36] KURTZBERG J, PROCKOP S, TEIRA P, et al. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cell therapy (remestemcel-L, Prochymal) as a rescue agent for severe refractory acute graft-versus-host disease in pediatric patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(2):229-235. |
| [1] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [2] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [3] | Zhai Haoyan, Zhao Yuan, Fan Dengying, Liu Chunyan. The role of reactive oxygen species in periodontitis and periodontal tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2254-2260. |
| [4] | Peng Yingnan, Bian Zhilei, Zhang Suping, Li Li, Cao Weijie, Wan Dingming. Effect of CD34+ cell dose on haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for treating malignant hematological diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 1-6. |
| [5] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [6] | Zheng Bo, Zhang Xiuli, Zhou Hao, He Zebi, Zhou Jin, Zhou Weiyun, Li Peng. Arthroscopy-assisted locking hollow screw fixation and open reduction plate internal fixation in the treatment of Schatzker II-III tibial plateau fractures: early CT evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1410-1416. |
| [7] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [8] | Huang Guijiang, Ji Yuwei, Zhao Xin, Yang Yi, Zhao Yulan, Wang Peijin, Tang Wei, Jiao Jianlin. Effect and mechanism of different administration routes of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of tree shrews with osteoporotic fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 909-914. |
| [9] | Guo Zhuotao, Zhang Kai, Zha Guochun, Guo Kaijin. A matched controlled trial of lumbar fusion effect on mid-term outcomes after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5801-5805. |
| [10] | Xiong Wei, Yuan Lingmei, Qian Guowen, Huang Jinyang, Pan Bin, Guo Ling, Zeng Zhikui. Value of a critical bone defect animal model in evaluating osteogenic efficacy of bone tissue engineering scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5714-5720. |
| [11] | Qin Jing, Zhang Suping, Li Li, Zhang Ran, Peng Yingnan, Gao Siyu, Fan Jinpeng, Bian Zhilei, Wan Dingming. Analysis of risk factors for varicella-zoster virus infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5292-5297. |
| [12] | Xu Rongwei, Wang Hao, Fu Qiuyue, Lan Xingming, Yang Kun. Bidirectional interaction between inflammatory factors and dental pulp stem cells during bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5385-5393. |
| [13] | Zhang Qingmei, Zhang Lupeng, Du Xiujuan, Li Bing. Application of carbon dots-based materials in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4883-4889. |
| [14] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [15] | Daniyar·Saderden, Huang Xiaoxia, Chen Jiangtao, Tian Zheng, Akbar·Yunus. 3D-printed prostheses for large bone defect reconstruction following bone tumor surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4628-4634. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||