Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (16): 2541-2547.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3149
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and functional in vitro characteristics of three-dimensional collagen HepaRG microsphere
Li Shao, Liang Yongkang, Gao Yi, Peng Qing
- Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery II, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-07-16Revised:2020-07-21Accepted:2020-08-22Online:2021-06-08Published:2021-01-07 -
Contact:Peng Qing, Professor, Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery II, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Shao, Master, Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery II, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research & Development Program of China, No. 2018YFA0108200 (to PQ); the National Key Research & Development Program of China, No. 2018YFC1106400 (to GY); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31972926 (to GY); the National Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2014A030312013 (to GY); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China, No. 2018A030313128 (to PQ); the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, No. 201803010086 (to PQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Shao, Liang Yongkang, Gao Yi, Peng Qing. Establishment and functional in vitro characteristics of three-dimensional collagen HepaRG microsphere[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2541-2547.
share this article
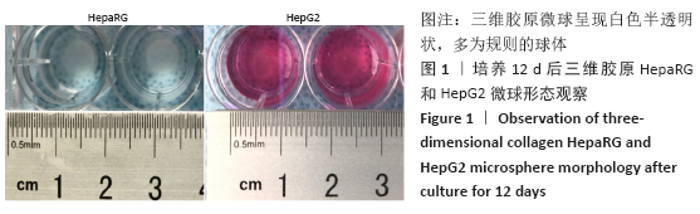
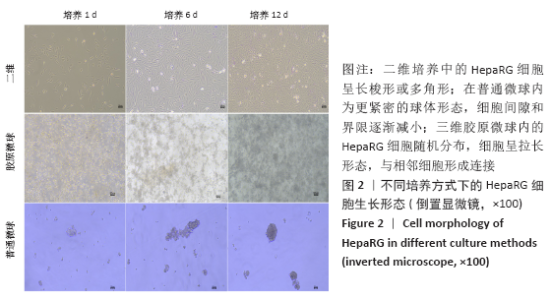
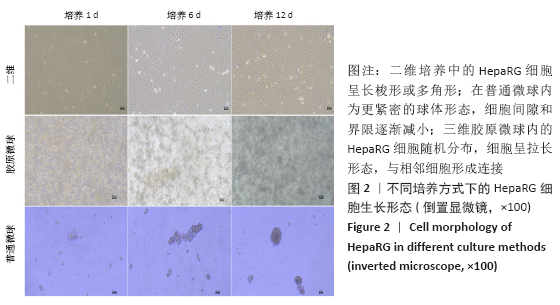
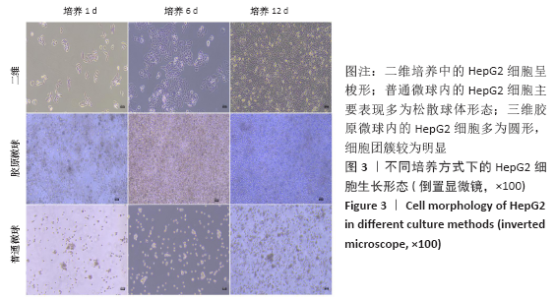
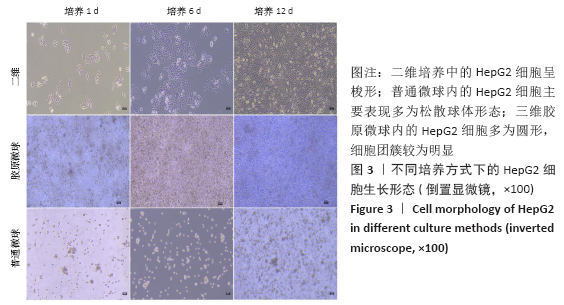
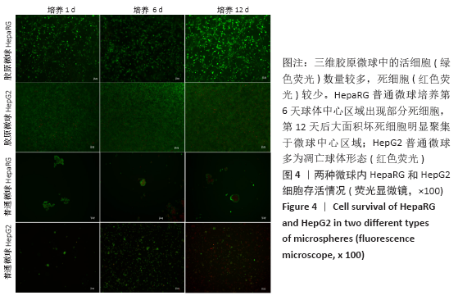
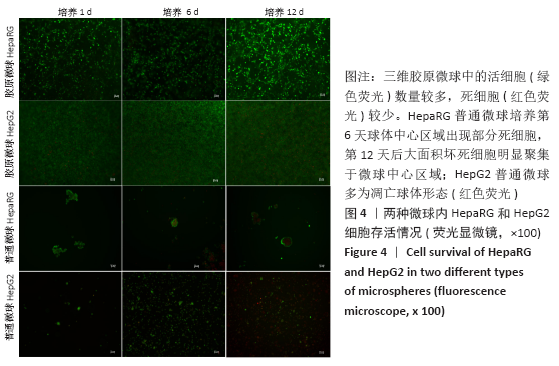
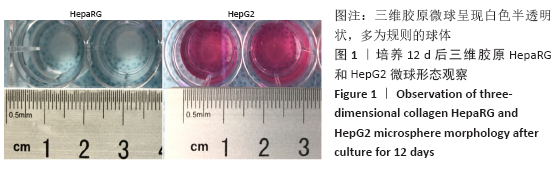
2.1 三维胶原微球中的细胞生长形态和存活情况 三维胶原微球呈现白色半透明状,多为规则的球体,见图1。在二维培养中,HepaRG细胞呈长梭形或多角形;在普通微球内主要表现由松散转变为更紧密的球体形态,细胞间隙和界限逐渐减小;在三维胶原微球内的HepaRG细胞随机分布,细胞呈拉长形态,与相邻细胞形成连接,培养第6天呈现圆形形态,均匀分布胶原微球内,第12天后更多的细胞集中在微球中心形成细胞簇,相邻团簇间形成连接更为紧密,空间上的交联结构,见图2。在二维培养中,HepG2细胞呈梭形;在普通微球内主要表现多为松散球体形态;三维胶原微球内的HepG2细胞多为圆形,细胞团簇较为明显,培养第6天细胞密度显著升高,第12天细胞形态仍为圆形居多且数量增大,集中在微球中心,细胞间连接更为紧密,见图3。死活染色结果显示,在三维胶原微球培养12 d后的活细胞(绿色荧光)数量较多,死细胞(红色荧光)较少,而且中心区域没有出现大面积坏死细胞,具有较高的细胞活率,见图4。 "
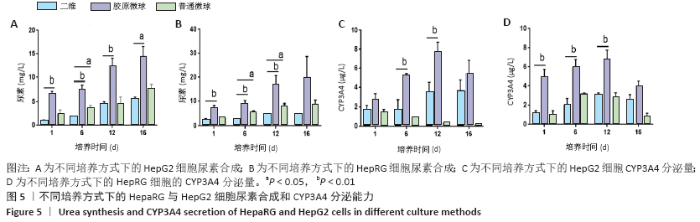
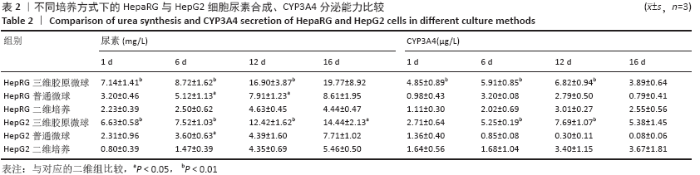
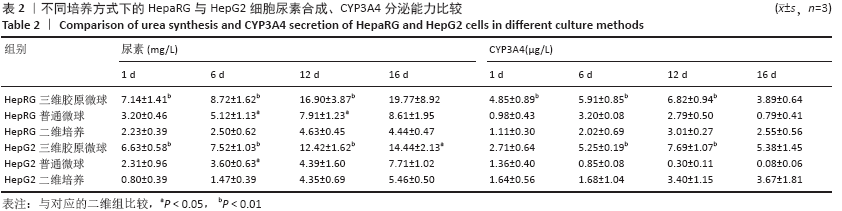
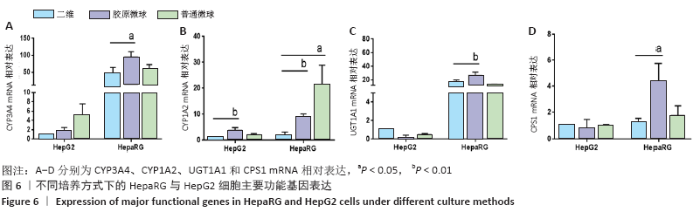
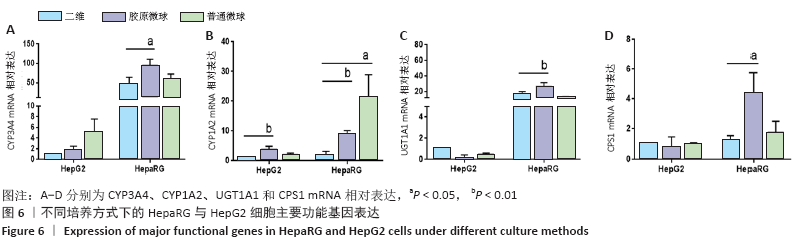
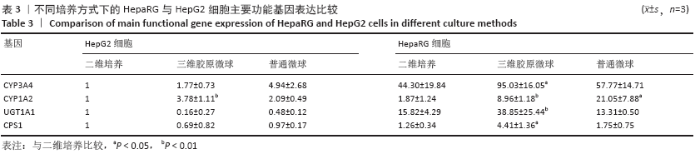
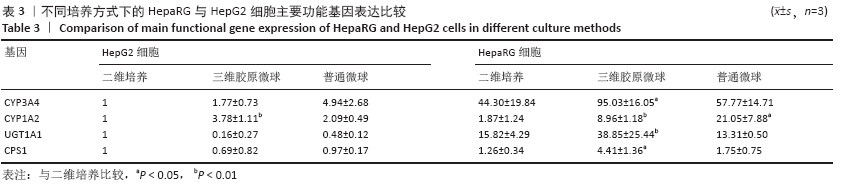
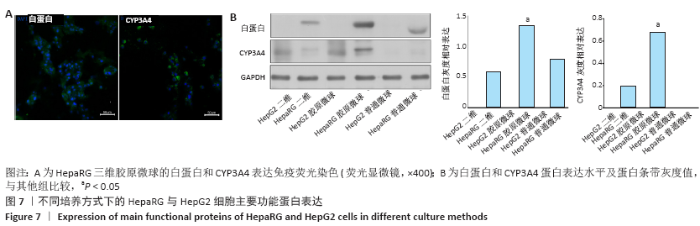
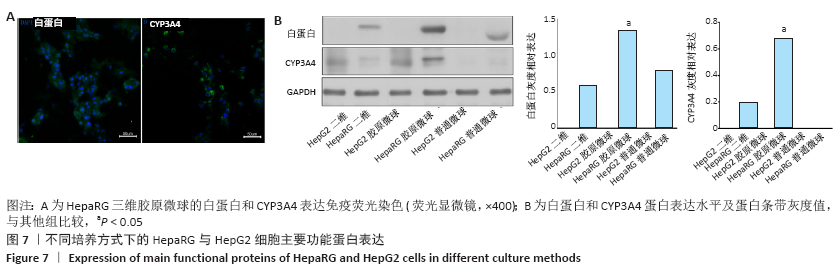
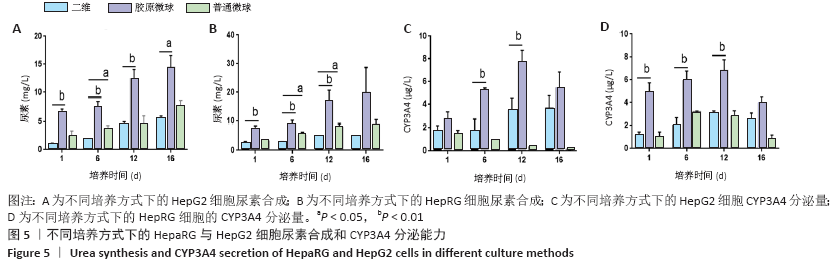
HepaRG普通微球培养第6天球体中心区域出现部分死细胞,培养第12天后大面积坏死细胞明显聚集于微球中心区域,仅有外表层可见部分存活细胞;HepG2普通微球多为凋亡球体形态(红色荧光),见图4。上述结果表明,在连续12 d培养中,三维胶原微球内HepaRG细胞呈现出多个细胞簇紧密连接的交联结构,同时细胞活率维持较好,中心坏死细胞量少。 2.2 三维胶原微球的尿素合成和CYP3A4分泌功能 HepaRG三维胶原微球培养1,6,12 d后的尿素含量高于HepaRG二维培养(P < 0.05),HepaRG普通微球培养6,12 d后的尿素含量高于HepaRG二维培养(P < 0.05),培养16 d后3组尿素含量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。HepG2三维胶原微球培养1,6,12,16 d后的尿素含量高于HepG2二维培养(P < 0.05),HepG2普通胶原微球培养6 d后的尿素含量高于二维培养(P < 0.05)。HepaRG三维胶原微球各时间点的尿素含量与HepG2三维胶原微球比较差异无显著性意义 (P > 0.05),见图5,表2。 HepaRG三维胶原微球培养1,6,12 d后的CYP3A4分泌量高于HepaRG二维培养(P < 0.05),HepG2三维胶原微球培养6,12 d后的CYP3A4分泌量高于HepG2二维培养(P < 0.05)。HepaRG三维胶原微球各时间点的CYP3A4分泌量与HepG2三维胶原微球比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图5,表2。 "
| [1] CHISTIAKOV DA. Liver regenerative medicine: advances and challenges. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196(4):291-312. [2] DZOBO K, THOMFORD NE, SENTHEBANE DA, et al. Advances in Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering: Innovation and Transformation of Medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:2495848. [3] HOSSEINI V, MAROUFI NF, SAGHATI S, et al. Current progress in hepatic tissue regeneration by tissue engineering. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):383. [4] ZHOU Y, SHEN JX, LAUSCHKE VM. Comprehensive Evaluation of Organotypic and Microphysiological Liver Models for Prediction of Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1093. [5] DUVAL K, GROVER H, HAN LH, et al. Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture. Physiology (Bethesda). 2017;32(4):266-277. [6] MIRBAGHERI M, ADIBNIA V, HUGHES BR, et al. Advanced cell culture platforms: a growing quest for emulating natural tissues. Materials Horizons. 2019;6(1):45-71. [7] AMELIAN A, WASILEWSKA K, MEGIAS D, et al. Application of standard cell cultures and 3D in vitro tissue models as an effective tool in drug design and development. Pharmacol Rep. 2017;69(5):861-870. [8] EDMONDSON R, BROGLIE JJ, ADCOCK AF, et al. Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2014;12(4):207-218. [9] MATTEI G, MAGLIARO C, PIRONE A, et al. Bioinspired liver scaffold design criteria. Organogenesis. 2018;14(3):129-146. [10] YE S, BOETER JWB, PENNING LC, et al. Hydrogels for Liver Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering (Basel). 2019;6(3):59. [11] CATOIRA MC, FUSARO L, DI FRANCESCO D, et al. Overview of natural hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(10):115. [12] WANG Y, KIM MH, SHIRAHAMA H, et al. ECM proteins in a microporous scaffold influence hepatocyte morphology, function, and gene expression. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37427. [13] LEAL-EGAÑA A, FRITSCH A, HEIDEBRECHT F, et al. Tuning liver stiffness against tumours: an in vitro study using entrapped cells in tumour-like microcapsules. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;9:113-121. [14] NAGARAJAN SR, PAUL-HENG M, KRYCER JR, et al. Lipid and glucose metabolism in hepatocyte cell lines and primary mouse hepatocytes: a comprehensive resource for in vitro studies of hepatic metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019;316(4):E578-E589. [15] ZEILINGER K, FREYER N, DAMM G, et al. Cell sources for in vitro human liver cell culture models. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016;241(15):1684-1698. [16] NATARAJAN V, BERGLUND EJ, CHEN DX, et al. Substrate stiffness regulates primary hepatocyte functions. RSC Adv. 2015;5(99):80956-80966. [17] GUO L, DIAL S, SHI L, et al. Similarities and differences in the expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes between human hepatic cell lines and primary human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(3):528-538. [18] KHOLODENKO IV, YARYGIN KN. Cellular Mechanisms of Liver Regeneration and Cell-Based Therapies of Liver Diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017: 8910821. [19] WONG N, LAI P, PANG E, et al. A comprehensive karyotypic study on human hepatocellular carcinoma by spectral karyotyping. Hepatology. 2000;32(5):1060-1068. [20] LEE JH, HO KL, FAN SK. Liver microsystems in vitro for drug response. J Biomed Sci. 2019; 26(1):88. [21] NGUYEN DG, FUNK J, ROBBINS JB, et al. Bioprinted 3D Primary Liver Tissues Allow Assessment of Organ-Level Response to Clinical Drug Induced Toxicity In Vitro. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0158674. [22] HEYDARI Z, NAJIMI M, MIRZAEI H, et al. Tissue Engineering in Liver Regenerative Medicine: Insights into Novel Translational Technologies. Cells. 2020;9(2):304. [23] GUILLOUZO A, CORLU A, ANINAT C, et al. The human hepatoma HepaRG cells: a highly differentiated model for studies of liver metabolism and toxicity of xenobiotics. Chem Biol Interact. 2007;168(1):66-73. [24] TASCHER G, BURBAN A, CAMUS S, et al. In-Depth Proteome Analysis Highlights HepaRG Cells as a Versatile Cell System Surrogate for Primary Human Hepatocytes. Cells. 2019;8(2): 192. [25] JACKSON JP, LI L, CHAMBERLAIN ED, et al. Contextualizing Hepatocyte Functionality of Cryopreserved HepaRG Cell Cultures. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016;44(9):1463-1479. [26] KAMMERER S, KÜPPER, JAN-HEINER. Human hepatocyte systems for in vitro toxicology analysis. J Cell Biot. 2018;3(2):85-93. [27] NWOSU ZC, BATTELLO N, ROTHLEY M, et al. Liver cancer cell lines distinctly mimic the metabolic gene expression pattern of the corresponding human tumours. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):211. [28] TAKAHASHI Y, HORI Y, YAMAMOTO T, et al. 3D spheroid cultures improve the metabolic gene expression profiles of HepaRG cells. Biosci Rep. 2015;35(3):e00208. [29] RAMAIAHGARI SC, WAIDYANATHA S, DIXON D, et al. From the Cover: Three-Dimensional (3D) HepaRG Spheroid Model With Physiologically Relevant Xenobiotic Metabolism Competence and Hepatocyte Functionality for Liver Toxicity Screening. Toxicol Sci. 2017;159(1): 124-136. [30] MANDON M, HUET S, DUBREIL E, et al. Three-dimensional HepaRG spheroids as a liver model to study human genotoxicity in vitro with the single cell gel electrophoresis assay. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10548. [31] LIAW CY, JI S, GUVENDIREN M. Engineering 3D Hydrogels for Personalized In Vitro Human Tissue Models. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(4):10. [32] 王敏,兰亚,胡皓,等.以胶原水凝胶为支架构建肝细胞三维培养系统[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(29):5323-5330. [33] JIA Z, CHENG Y, JIANG X, et al. 3D Culture System for Liver Tissue Mimicking Hepatic Plates for Improvement of Human Hepatocyte (C3A) Function and Polarity. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6354183. [34] CORONADO RE, SOMARAKI-CORMIER M, NATESAN S, et al. Decellularization and Solubilization of Porcine Liver for Use as a Substrate for Porcine Hepatocyte Culture: Method Optimization and Comparison. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(12):1840-1854. [35] YUAN M, LEONG KW, CHAN BP. Three-dimensional culture of rabbit nucleus pulposus cells in collagen microspheres. Spine J. 2011; 11(10): 947-960. [36] YUAN Z, MEMARZADEH K, STEPHEN AS, et al. Development of a 3D Collagen Model for the In Vitro Evaluation of Magnetic-assisted Osteogenesis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16270. [37] BOMO J, EZAN F, TIAHO F, et al. Increasing 3D Matrix Rigidity Strengthens Proliferation and Spheroid Development of Human Liver Cells in a Constant Growth Factor Environment. J Cell Biochem. 2016;117(3):708-720. [38] KUNA L, BOZIC I, KIZIVAT T, et al. Models of Drug Induced Liver Injury (DILI) - Current Issues and Future Perspectives. Curr Drug Metab. 2018;19(10): 830-838. [39] FUNK C, ROTH A. Current limitations and future opportunities for prediction of DILI from in vitro. Arch Toxicol. 2017;91(1):131-142. [40] 孟镇锴.HepaRG和HepG2聚球体模型的建立及药物体外肝毒性检测的对比研究[D].北京:军事科学院,2019. [41] 李晓旭,孟镇锴,荣斌,等.3D HepaRG聚球体模型的建立[J].中国新药杂志,2019,28(22):2709-2717. [42] SUN P, ZHANG G, SU X, et al. Maintenance of Primary Hepatocyte Functions In Vitro by Inhibiting Mechanical Tension-Induced YAP Activation. Cell Rep. 2019;29(10):3212-3222. [43] 李朋彦,崔鹤蓉,李婷婷,等.基于3D培养技术的体外肝毒性评价模型研究进展[C].2016年第六届全国药物毒理学年会论文集, 2016: 392-393. [44] MIHARA H, KUGAWA M, SAYO K, et al. Improved Oxygen Supply to Multicellular Spheroids Using A Gas-permeable Plate and Embedded Hydrogel Beads. Cells. 2019;8(6):525. [45] HUANG G, LI F, ZHAO X, et al. Functional and Biomimetic Materials for Engineering of the Three-Dimensional Cell Microenvironment. Chem Rev. 2017;117(20):12764-12850. [46] CHOI YY, SEOK JI, KIM DS. Flow-Based Three-Dimensional Co-Culture Model for Long-Term Hepatotoxicity Prediction. Micromachines (Basel). 2019;11(1):36. [47] DENG J, WEI W, CHEN Z, et al. Engineered Liver-on-a-Chip Platform to Mimic Liver Functions and Its Biomedical Applications: A Review. Micromachines (Basel). 2019;10(10):676. [48] NICOLAS J, MAGLI S, RABBACHIN L, et al. 3D Extracellular Matrix Mimics: Fundamental Concepts and Role of Materials Chemistry to Influence Stem Cell Fate. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(6):1968-1994. [49] BAZE A, PARMENTIER C, HENDRIKS DFG, et al. Three-Dimensional Spheroid Primary Human Hepatocytes in Monoculture and Coculture with Nonparenchymal Cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2018;24(9): 534-545. [50] COHEN M, LEVY G, NAHMIAS Y. Coculture and Long-Term Maintenance of Hepatocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1250:161-173. |
| [1] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [2] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [3] | Zhang Bin, Sun Lihua, Zhang Junhua, Liu Yusan, Cui Caiyun. A modified flap immediate implant is beneficial to soft tissue reconstruction in maxillary aesthetic area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 707-712. |
| [4] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [5] | Li Chenjie, Lü Linwei, Song Yang, Liu Jingna, Zhang Chunqiu. Measurement and statistical analysis of trabecular morphological parameters of titanium alloy peri-prosthesis under preload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 516-520. |
| [6] | Sun Qi, Zhou Yanan, Dong Xin, Li Ning, Yan Jiazhen, Shi Haojiang, Xu Sheng, Zhang Biao. Metal-ceramic interface characteristics of Co-Cr alloy fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 521-525. |
| [7] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [9] | Zhang Guomei, Zhu Jun, Hu Yang, Jiao Hongwei. Stress of three-dimensional finite element models of E-MAX porcelain inlay [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [10] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [11] | Li Quanxi, Shen Yu, Wan Wei, Sun Shanzhi. Changes of abdominal wall mechanics and pain after tension-free inguinal hernia repair with polypropylene mesh [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 548-552. |
| [12] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [13] | Ma Zhijie, Li Jingyu, Cao Fang, Liu Rong, Zhao Dewei. Influencing factors and biological property of novel biomedical materials: porous silicon carbide coated with bioactive tantalum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 558-563. |
| [14] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [15] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||