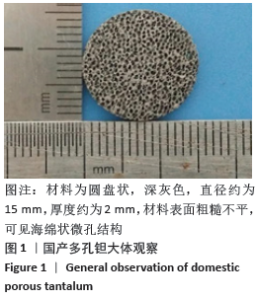
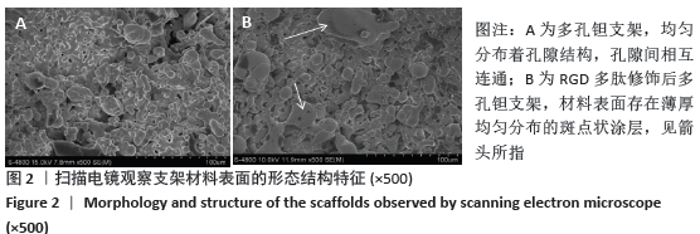
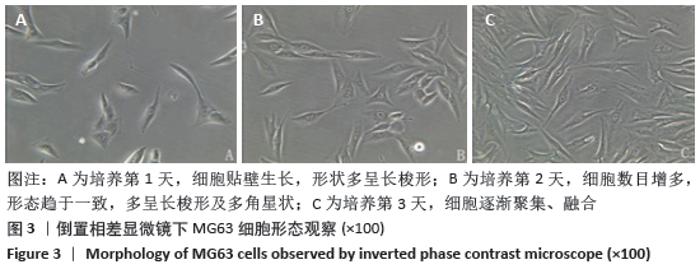
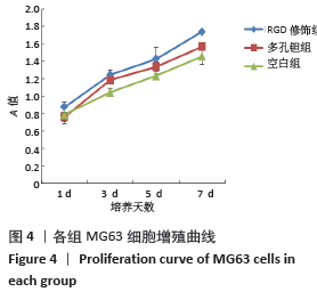
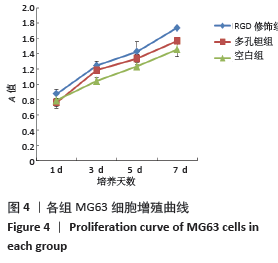
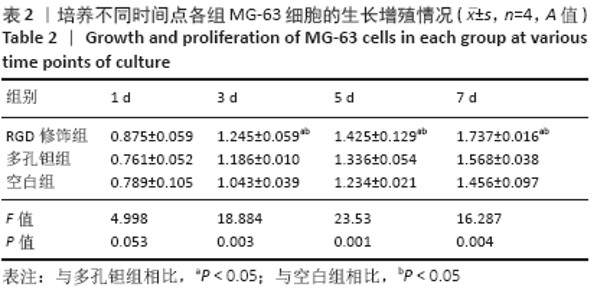
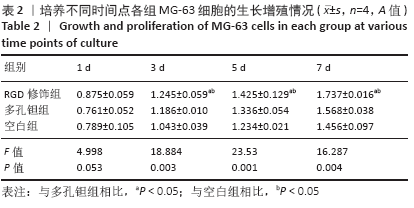
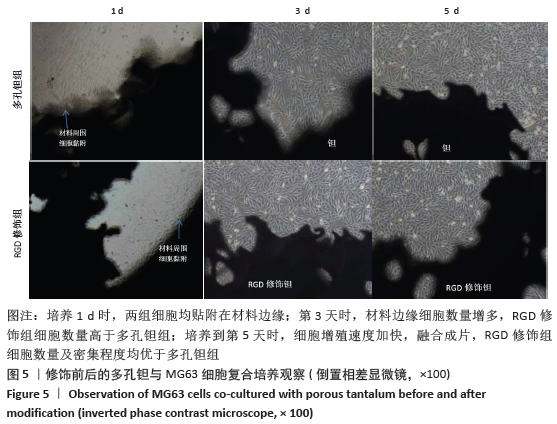
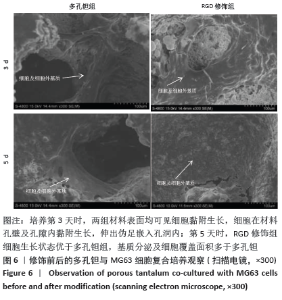
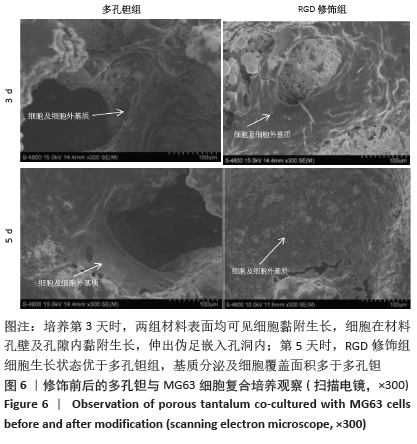
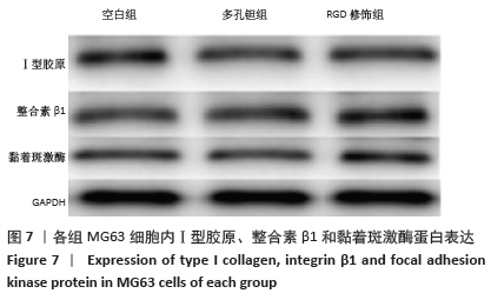
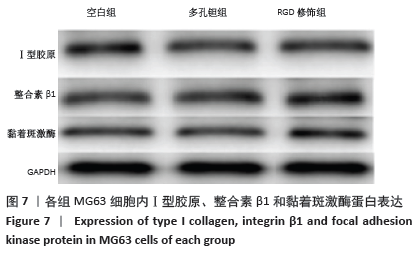
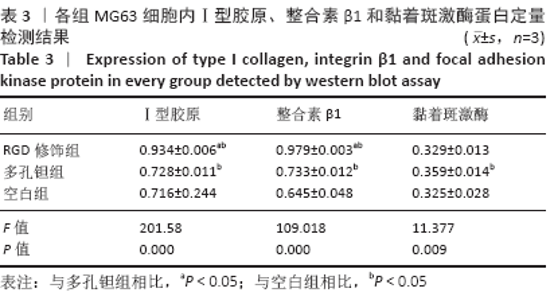
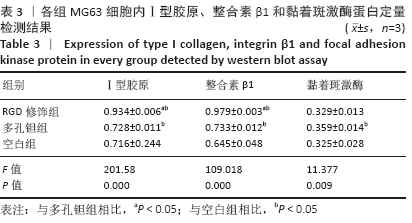
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (16): 2535-2540.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3117
Previous Articles Next Articles
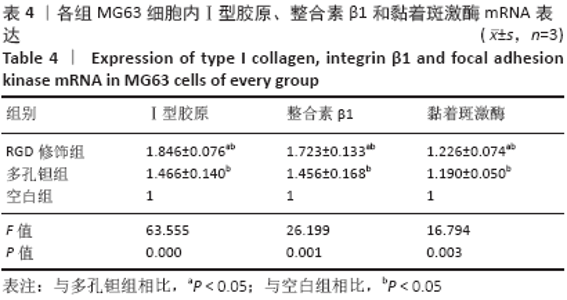
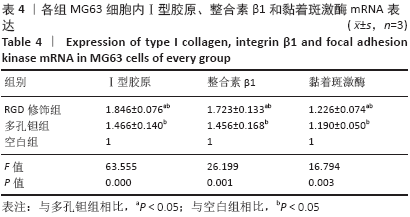
Porous tantalum coated with RGD polypeptide can activate the integrin/focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway of MG63 cells
Zhang Hui1, Wang Shaohua2, Wang Qian3, Wang Hui4, Gan Hongquan5, Cui Yishuang3, Li Qijia3, Wang Zhiqiang5
- 1First Department of Joint Surgery, Second Hospital of Tangshan, Hebei Province, China; 2Tianjin Emergency Center, China; 3Medical Research Center, North China University of Science and Technology, Hebei Province, China; 4First Department of Hand Surgery, Second Hospital of Tangshan, Hebei Province, China; 5Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North China of Science and Technology, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2020-07-30Revised:2020-07-31Accepted:2020-08-25Online:2021-06-08Published:2021-01-07 -
Contact:Wang Zhiqiang, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of North China of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China Wang Qian, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Medical Research Center, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063210, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhang Hui, MD, Associate chief physician, First Department of Joint Surgery, Second Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Project supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, No. 2012BAE06B03 (to WZQ); Hebei Province Science and Technology Support Project, No. 16277776D (to LQJ); Hebei Provincial Medical Research Project, No. 20160225 (to WZQ); the Project Supported by the Foundation of Doctoral Research of North China University of Science and Technology, No. 28606299 (to WQ); the Project Supported by Hebei Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission, No. 20180733 (to WQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Hui, Wang Shaohua, Wang Qian, Wang Hui, Gan Hongquan, Cui Yishuang, Li Qijia, Wang Zhiqiang. Porous tantalum coated with RGD polypeptide can activate the integrin/focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway of MG63 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2535-2540.
share this article
| [1] LI HL, YAO Z, ZHANG J, et al. The progress on physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of tantalum-based metal bone implants. SN Appl Sci. 2020;2(3):38-40. [2] BERMUDEZ MD, CARRION FJ, MARTINEZ NG, et al. Erosion–corrosion of stainless steels,titanium, tantalum and zirconium. Wear. 2005;258(1-4):693-700. [3] OH IH, NOMURA N, MASAHASHI N, et al. Mechanical properties of porous titanium compacts prepared by powder sintering. Scr Mater. 2003;49(12): 1197-1202. [4] COHEN R. A porous tantalum trabecular metal: basic science. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2002;31(4):216-217. [5] LING TX, LI JL, ZHOU K, et al. The use of porous tantalum augments for the reconstruction of acetabular defect in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):453-459. [6] KONAN S, DUNCAN CP, MASRI BA, et al. Porous tantalum uncemented acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty: a minimum ten-year clinical, radiological and quality of life outcome study. Bone Joint J. 2016;98B:767-771. [7] LING TX, LI JL, ZHOU K, et al. The use of porous tantalum augments for the reconstruction of acetabular defect in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):453-459. [8] WITEK L, ALIFARAG AM, TOVAR N, et al. Osteogenic parameters surrounding trabecular tantalum metal implants in osteotomies prepared via osseodensification drilling. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2019;24(6): e764-e769. [9] ZHAO DW, MA ZJ, WANG TN, et al. Biocompatible Porous Tantalum Metal Plates in the Treatment of Tibial Fracture. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):325-329. [10] 徐基亮,夏荣.精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸修饰钛材料表面的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2016,43(2):190-194. [11] MAS-MORUNO C, GARRIDO B, RODRIGUEZ D, et al. Biofunctionalization strategies on tantalum-based materials for osseointegrative applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(2): 1-12. [12] DUQUE-SANCHEZ L, BRACK N, POSTMA A, et al. Engineering the Biointerface of Electrospun 3D Scaffolds with Functionalized Polymer Brushes for Enhanced Cell Binding. Biomacromolecules. 2019;20(2):813-825. [13] HAMDAN F, BIGDELI Z, ASGHARI SM, et al. Synthesis of Modified RGD-Based Peptides and Their in vitro Activity. ChemMedChem. 2019;14(2):282-288. [14] 谢玉,周诺.Ⅰ型胶原诱导骨髓间充质干细胞及成骨细胞的成骨分化机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(21):3417-3423. [15] BLANDIN AF, RENNER G, LEHMANN M, et al. β1 Integrins as Therapeutic Targets to Disrupt Hallmarks of Cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6(157):279. [16] GOODMAN SL, PICARD M. Integrins as therapeutic targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012;33(7):405. [17] TAPIAL MARTÍNEZ P, LÓPEZ NAVAJAS P, LIETHA D. FAK Structure and Regulation by Membrane Interactions and Force in Focal Adhesions. Biomolecules. 2020;10(2):179. [18] Kroese-Deutman HC, van den Dolder J, Spauwen PH, et al. Influence of RGD-loaded titanium implants on bone formation in vivo. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(11-12):1867-1875. [19] ELMENGAARD B, BECHTOLD JE, SØBALLE K. In vivo study of the effect of RGD treatment on bone ongrowth on press-fit titanium alloy implants. Biomaterials. 2005;26(17):3521-3526. [20] 甘洪全,王茜,张辉,等.精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸多肽表面修饰多孔钽对软骨细胞黏附、增殖和分泌功能的促进作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2015,41(3):510-516. [21] 王少华. RGD修饰多孔钽对人成骨细胞增殖及COL-Ⅰ、Integrinβ1、FAK表达影响的实验研究[D].河北:华北理工大学,2018. [22] 魏晨旭,何怡文,王聃,等.组织工程学中骨修复材料的研究热点与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(10):1615-1621. [23] NOORI A, ASHRAFI SJ, VAEZ-GHAEMI R, et al. A review of fibrin and fibrin composites for bone tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12: 4937-4961. [24] OLIVEIRA MN, SCHUNEMANN WVH, MATHEW MT, et al. Can degradation products released from dental implants affect peri‐implant tissues? J Periodontal Res. 2018;53(1):1-11. [25] NAGELS J, STOKDIJK M, ROZING PM. Stress shielding and bone resorption in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(1):35-39. [26] ANSELME K. Biomaterials and interface with bone.Osteoporos Int. 2011; 22(6):2037-2042. [27] BOBYN JD, STACKPOOL GJ, HACKING SA, et al. Characteristics of bone ingrowth and interface mechanics of a new porous tantalum biomaterial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(5):907-914. [28] 李琪佳,王茜,甘洪全,等.多孔钽材料细胞毒性、生物相容性及体内成骨性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(9):954-961. [29] GRUSKIN E, DOLL BA, FUTRELL FW, et al. Demineralized bone matrix in bone repair:history and use. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1063-1077. [30] DOLATSHAHI-PIROUZ A, JENSEN T, KRAFT DC, et al. Fibronectin adsorption, cell adhesion, and proliferation on nanostructured tantalum surfaces. ACS Nano. 2010;4(5):2874-2882. [31] RANA D, ZREIQAT H, ENKIRANE-JESSEL N, et al. Development of decellularized scaffolds for stem cell-driven tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;11(4):942-965. [32] 赵宏坤,李琪佳,王茜,等.细胞外基质成分修饰骨科植入物的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(11):1390-1394. [33] 张雅杰,张云涛,王云浩,等. RGD多肽修饰种植体的不同方法及其成骨性研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2016,10(18):2799-2802. [34] WANG H, LI QJ, WANG Q, et al. Enhanced repair of segmental bone defects in rabbit radius by porous tantalum scaffolds modified with the RGD peptide. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(3):50. [35] 李倩男,洪莉.胶原代谢相关信号通路研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2017, 14(10):56-59. [36] HASAN A, PANDEY LM. Surface modification of Ti6Al4V by forming hybrid self-assembled monolayers and its effect on Collagen-I adsorption, osteoblast adhesion and integrin expression. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;505:144611. [37] 杨青,洪莉.整合素的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2015(6):1023-1025. [38] LI Z, LIU T, YANG J, et al. Characterization of adhesion properties of the cardiomyocyte integrins and extracellular matrix proteins using atomic force microscopy. J Mol Recognit. 2020;33(4):e2823. [39] GONZALEZ-PUJANA A, SANTOS-VIZCAINO E, GARCÍA-HERNANDO M, et al. Extracellular matrix protein microarray-based biosensor with single cell resolution: Integrin profiling and characterization of cell-biomaterial interactions. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2019;299:126954. [40] 李长文,郑启新, 郭晓东,等.RGD多肽修饰的改性PLGA仿生支架材料对骨髓间充质干细胞粘附、增殖及分化影响的研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2006,25(2):142-146. |
| [1] | Che Yanjun, Hu Dan, Si Weibing, Gu Xueping, Hao Yuefeng. Bone cement interval perfusion in hyperextension position for treatment of senile osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1555-1561. |
| [2] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [4] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [5] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [6] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [7] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [8] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [9] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [10] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [11] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [12] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [13] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [14] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [15] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||