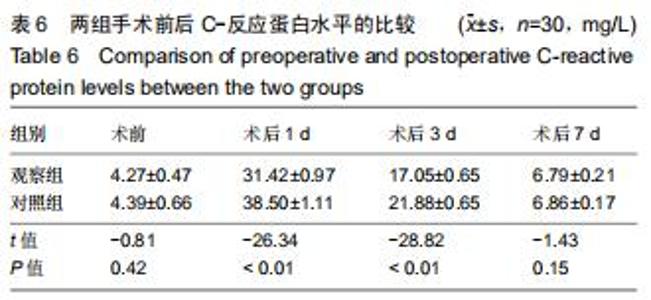
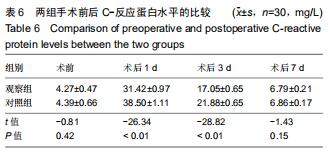
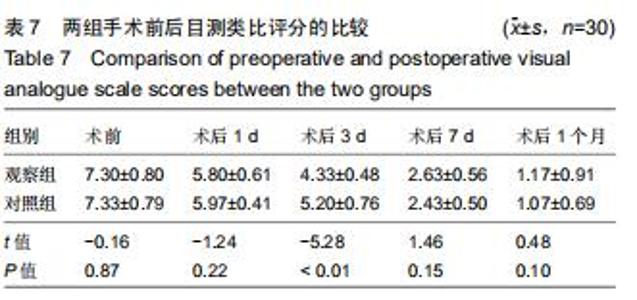
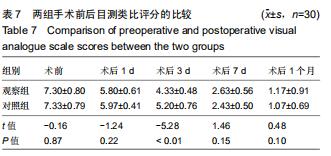
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (36): 5812-5817.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2931
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of tranexamic acid combined with tourniquet optimization program in total knee arthroplasty
Peng Ruhui, Zhou Dechun
- Department of Bone Surgery, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Meishan City, Meishan 620010, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2020-02-10Revised:2020-02-15Accepted:2020-03-18Online:2020-12-28Published:2020-10-27 -
Contact:Zhou Dechun, Chief physician, Department of Bone Surgery, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Meishan City, Meishan 620010, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Peng Ruhui, Master, Attending physician, Department of Bone Surgery, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Meishan City, Meishan 620010, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Peng Ruhui, Zhou Dechun. Application of tranexamic acid combined with tourniquet optimization program in total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5812-5817.
share this article
|
[1] 裴福兴.加速康复外科是现代骨外科发展的趋势[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2017,6(12):881-882.
[2] STARKS I, WAINWRIGHT TW, LEWIS J, et al. Older patients have the most to gain from orthopaedic enhanced recovery programmes.Age Ageing.2014;43(5):642-648.
[3] 谢锦伟,岳辰,裴福兴.氨甲环酸在全髋关节置换术中的有效性与安全性研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(20): 1856-1860.
[4] AUYONG DB, ALLEN CJ, PAHANG JA, et al. Reduced length of hospitalization in primary total knee arthroplasty patients using an updated enhanced recovery after orthopedic surgery (ERAS) pathway.J Arthroplasty.2015; 30(10):1705-1709.
[5] 周宗科,黄泽宇,杨惠林,等.中国骨科手术加速康复围手术期氨甲环酸与抗凝血药应用的专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2019,12(2):81-88.
[6] 周宗科,翁习生,曲铁兵,等.中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复——围术期管理策略专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(1): 1-9.
[7] 岳辰,周宗科,裴福兴,等.中国髋、膝关节置换术围术期抗纤溶药序贯抗凝血药应用方案的专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2015,8(4):281-285. [8] TIWARI MK, VAISHYA R, AGARWAL AK. Tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty: a review.Apollo Med.2017;14(1):8-11.
[9] MUTLU S, GULER O, MUTLU H. Tourniquet use during total knee arthroplasty does not offer significant benefit:a retrospective cohort study.Int J Surg.2015;18(1):123-127.
[10] OLIVECRONA C, LAPIDUS LJ, BENSON L. Tourniquet time affects postoperative complications after knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2013;37(5):827-832.
[11] RASMUSSEN LE, HOLM HA, KRISTENSEN PW. Tourniquet time in total knee arthroplasty.Knee.2018;25(2):306-313.
[12] 杨建平,蒋涛,吕正祥.止血带优化对全膝关节置换术快速康复的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(1):33-37.
[13] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[14] DAWSON J, LINSELL L, ZONDERVAN K, et al. Epidemiology of hip and knee pain and its impact on overall health status in older adults.Rheumatology.2004;43(4):497-504.
[15] BOURNE RB, CHESWORTH BM, DAVIS AM, et al. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty:who is satisfied and who is not.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010;468(1):57-63.
[16] TOUZOPOULOS P, VERVERIDIS A, MPOGIATZIS C. The use of tourniquet may influence the cement mantle thickness under the tibial implant during total knee arthroplasty.Eur J Orthop Surg Traum.2019;356(1):65-73.
[17] ZHANG F, YU X, LIU Y, et al. Clinical effects of applying a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty on blood loss.Chin Med J.2010;123(21):3030-3033.
[18] PARVIZI J, DIAZ-LEDEZMA C. Total knee replacement with the use of a tourniquet: more pros than cons.Bone Joint J. 2013;95(11_Supple_A):133-134.
[19] LEDIN H, ASPENBERG P, GOOD L. Tourniquet use in total knee replacement does not improve fixation, but appears to reduce final range of motion: A randomized RSA study involving 50 patients.Acta orthopaedica.2012;83(5):499-503.
[20] 方月,杨翠,李运明.加速康复护理在骨科手术患者中的应用[J].西南军医,2018,20(5):579-581.
[21] 陈佳丽,宁宁,屈俊宏,等.骨科加速康复外科新视角[J].华西医学, 2018,33(9):1068-1072.
[22] 李强,刘益锋,木热提·卡哈尔,等.加速康复外科在骨科中的应用[J].海南医学,2019,30(18):2415-2417. [23] 孙旭,李庭,杨明辉,等.加速康复外科的发展与在骨科的应用[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2017,2(2):114-116.
[24] IRWIN A, KHAN SK, JAMESON SS, et al. Oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid in enhanced-recovery primary total hip and knee replacement: results of 3000 procedures. Bone Joint J.2013;95(11):1556-1561.
[25] 徐飞,董永辉,任晔,等.关节腔局部注射氨甲环酸对初次全膝关节置换术后失血量的影响[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2017, 14(5):29-32.
[26] 陈群群,陈建发,周驰,等.关节腔内加压灌注氨甲环酸与初次全膝关节置换后失血量的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(44): 6564-6569.
[27] JENNINGS JD, SOLARZ MK, HAYDEL C. Application of tranexamic acid in trauma and orthopedic surgery.Orthop Clin.2016;47(1):137-143.
[28] KIM C, PARK SSH, DAVEY JR. Tranexamic acid for the prevention and management of orthopedic surgical hemorrhage: current evidence.J Blood Med.2015;6:239.
[29] LIN ZX, WOOLF SK. Safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of tranexamic acid in orthopedic surgery.Orthopedics.2016; 39(2):119-130.
[30] 孙啸,王浩洋,康鹏德.TKA术中不同时机使用止血带对患者造成的损伤比较[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2016,47(1):135-137, 143.
[31] 谢小伟,岳辰,黄泽宇,等.全膝关节置换术应用与不应用止血带的随机对照研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(17):1572-1576.
[32] YAVARIKIA A, AMJAD GG, DAVOUDPOUR K. The influence of tourniquet use and timing of its release on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty.Pak J Biol Sci.2010;13(5):249.
[33] FARHANG B, LESIAK AC, IANNO DJ. Venous pressure during intravenous regional anesthesia:implications for setting tourniquet pressure.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2018; 34(4):507-512.
[34] WANG K, NI S, LI Z. The effects of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty:a randomized, controlled trial.Knee Surg Sports Trauma Arthroscopy.2016;25(9):1-9. [35] MAYER C, FRANZ A, HARMSEN JF. Soft-tissue damage during total knee arthroplasty: Focus on tourniquet-induced metabolic and ionic muscle impairment.J Orthop. 2017;14(3): 347-353. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [4] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [5] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [6] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [7] | Zheng Bo, Zhang Xiuli, Zhou Hao, He Zebi, Zhou Jin, Zhou Weiyun, Li Peng. Arthroscopy-assisted locking hollow screw fixation and open reduction plate internal fixation in the treatment of Schatzker II-III tibial plateau fractures: early CT evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1410-1416. |
| [8] | Li Chao, Zhang Peipei, Xu Mengting, Li Linlin, Ding Jiangtao, Liu Xihua, Bi Hongyan. Respiratory training improves morphological changes of the multifidus muscle in patients with chronic nonspecific lower back pain assessed by musculoskeletal ultrasound [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1417-1421. |
| [9] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [10] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [11] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [12] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [13] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [14] | Zhang Qiming, Bao Sairong, Shan Sharui, Zhong Zhiliang, Liu Chunlong. Effect of deep muscle stimulation on muscle tone and stiffness of erector spinaes in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: a digital muscle testing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1250-1256. |
| [15] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||