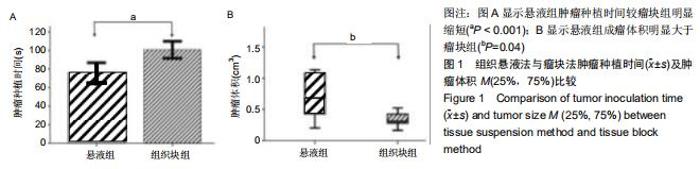
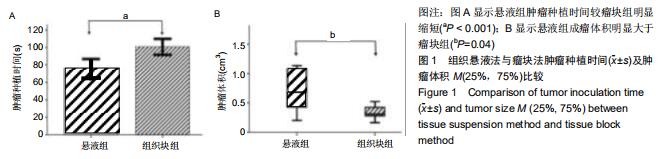
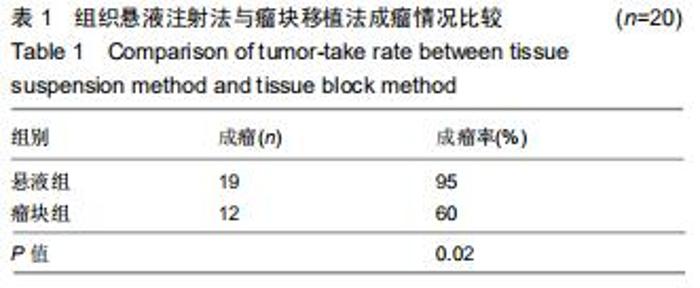
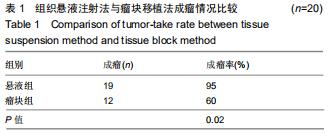
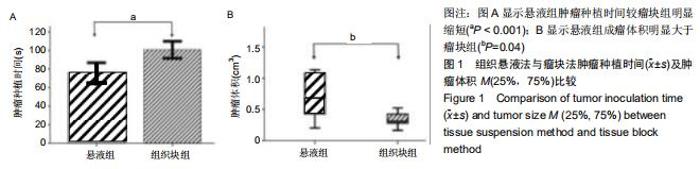
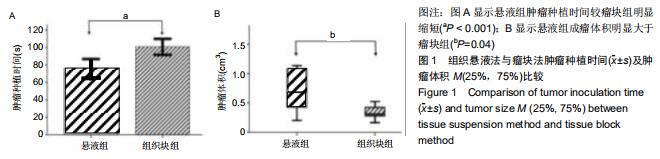
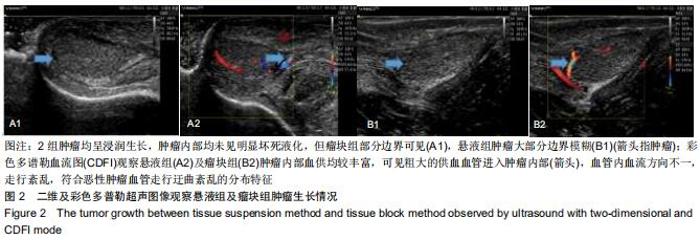
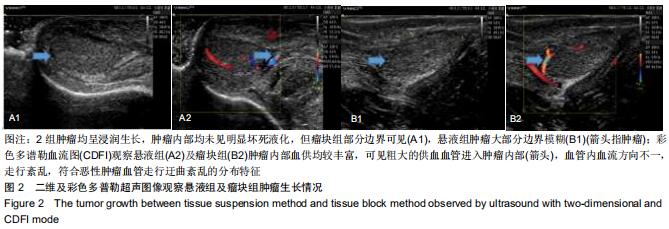
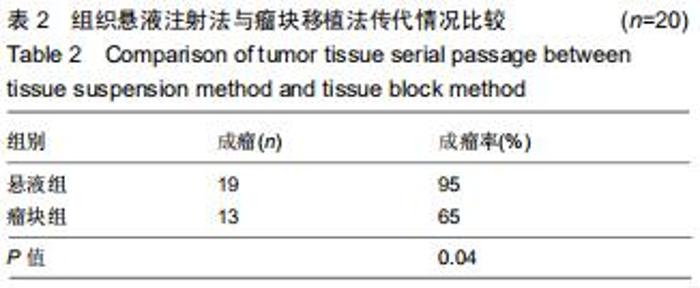
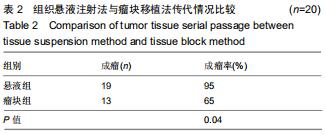
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (32): 5173-5178.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2867
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparing tumor suspension injection and tissue explant to establish rabbit VX2 subcutaneous tumor model
Liu Ya, Feng Shuang, Yi Cuo, Yu Yanlan, Liu Zheng
- Department of Ultrasound, Xinqiao Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing 400037, China
-
Received:2019-10-28Revised:2019-10-31Accepted:2019-12-13Online:2020-11-18Published:2020-09-25 -
Contact:Liu Zheng, MD, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Ultrasound, Xinqiao Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing 400037, China -
About author:Liu Ya, Attending physician, Department of Ultrasound, Xinqiao Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing 400037, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Project of China, No. 2017YFC0107300
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Ya, Feng Shuang, Yi Cuo, Yu Yanlan, Liu Zheng. Comparing tumor suspension injection and tissue explant to establish rabbit VX2 subcutaneous tumor model[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5173-5178.
share this article
|
[1] ROUS P, KIDD JG, SMITH WE. Experiments on the cause of the rabbit carcinomas derived from virus-induced papillomas. II. Loss by the Vx2 carcinoma of the power to immunize hosts against the papilloma virus. J Exp Med. 1952;96(2):159-174.
[2] 侯佳慧,荆慧,秋程,等. CEUS联合声触诊组织成像定量检测兔VX2乳腺癌转移前哨淋巴结[J].医学影像学杂志,2019,29(3): 487-490.
[3] CAO H, JIN Y, ZHAO J, et al. An improved biopsy technique for rabbits with VX2 bone tumors.Oncol Lett. 2018;16(2): 2299-2304.
[4] 王攀鸽,谭红娜,王博,等. MR淋巴造影显影兔VX2乳腺癌模型内乳前哨淋巴结[J].中国医学影像技术,2018,34(5):641-645.
[5] FU X, LUO RG, QIU W, et al. Sustained release of arsenic trioxide benefits interventional therapy on rabbit VX2 liver tumor. Nanomedicine. 2019;24(1):102-118.
[6] 陈宇,朱成楚,孔敏,等.组织块悬液法建立兔食管VX2移植瘤模型的研究[J].医学研究杂志,2013,42(7):84-86.
[7] MINE H, NAKAMURA T. Mode of lymph node metastases in esophageal cancer induced in rabbits with Vx2 carcinoma. Jpn J Surg.1983;13(3):236-245.
[8] YANG Q, CHEN J, ZHU Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate the Remodeling of Bladder VX2 Tumor Interstitial Microenvironment by TGFbeta1-Smad Pathway. J Cancer. 2019;10(19):4532-4539.
[9] 王梓旭,孟鑫,周蕾,等. VX-2组织悬液原位种植与Panc-1细胞悬液原位种植在家兔胰腺癌模型建立中的效果比较[J].医学研究生学报, 2017,30(3):302-305.
[10] FURUKAWA T, KUBOTA T, WATANABE M, et al. A novel "patient-like" treatment model of human pancreatic cancer constructed using orthotopic transplantation of histologically intact human tumor tissue in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1993; 53(13):3070-3072.
[11] 魏强,方亮,杨继金,等.兔肝脏、肌肉、皮下VX_2肿瘤模型的建立和对比研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2013,22(11):931-935.
[12] 苏畅,张惠中,李文海,等.兔VX2肿瘤的离体培养及有关生物学特性[J]. 第四军医大学学报,2006,1(9):844-847.
[13] HU S, SUN C, WANG B, et al. Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging to Evaluate Immediate Response to Irreversible Electroporation in a Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumor Model. J Vasc Interv Radiol.2019;5(30):1863-1869.
[14] MASADA T, TANAKA T, NISHIOFUKU H, et al. Use of a Glass Membrane Pumping Emulsification Device Improves Systemic and Tumor Pharmacokinetics in Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumor in Transarterial Chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol.2019;s1051-0443(19):30577-30799.
[15] LI SY, HUANG PT, FANG Y, et al. Ultrasonic Cavitation Ameliorates Antitumor Efficacy of Residual Cancer After Incomplete Radiofrequency Ablation in Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumor Model. Transl Oncol.2019;12(8):1113-1121.
[16] XING J, HE W, DING Y W, et al. Correlation between Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and Microvessel Density via CD31 and CD34 in a rabbit VX2 lung peripheral tumor model. Med Ultrason.2018;1(1):37-42.
[17] KIM TH, CHOI HI, KIM BR, et al. No-Touch Radiofrequency Ablation of VX2 Hepatic Tumors In Vivo in Rabbits: A Proof of Concept Study. Korean J Radiol.2018; 19(6):1099-1109.
[18] BING C, PATEL P, STARUCH RM, et al. Longer heating duration increases localized doxorubicin deposition and therapeutic index in Vx2 tumors using MR-HIFU mild hyperthermia and thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin. Int J Hyperthermia.2019;36(1):196-203.
[19] 高斌,贺克武,李嘉嘉.剪碎法及匀浆法制备兔肌肉VX2肿瘤单细胞悬液的方法比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(41):8315-8317.
[20] 郑林丰,王悍,李康安,等.介绍一种兔VX2肿瘤的传代和接种方法及其应用经验和体会[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(16): 3010-3012.
[21] 李文军,朱红,孙业全,等.兔VX2乳腺癌淋巴转移模型的建立及超声对其诊断的价值[J].精准医学杂志,2019,34(3):245-248.
[22] 米金霞,方肇勤.兔VX2肿瘤模型的研究进展[J].实验动物与比较医学, 2019,39(2):163-168.
[23] 阮亚超.制作兔VX2肝癌模型的改良[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2018.
[24] NITTA-SEKO A, NITTA N, SONODA A, et al. Anti-tumour effects of transcatheter arterial embolisation administered in combination with thalidomide in a rabbit VX2 liver tumour model. Br J Radiol. 2011;84(998):179-183.
[25] GUO Y, ZHANG Y, JIN N, et al. Electroporation-mediated transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the rabbit VX2 liver tumor model. Invest Radiol.2012,47(2):116-120.
[26] 陈松旺,周云,孟凡荣,等.超声引导下穿刺注射VX2组织块或其悬液制作兔VX2肝癌模型[J].江苏医药,2011,37(2):145-147.
[27] 王崇文.超声引导下建立兔VX2肢体软组织肿瘤模型及应用VMAT-SIB技术制作外科边界的实验研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2015.
[28] 王东东,彭金钊,李云芳,等. 兔脊柱旁肌肉VX2种植瘤模型建立及生物学特性[J].介入放射学杂志,2019,28(6):561-565.
[29] 金光鑫,王军,仇晓霞,等. MR导引经皮穿刺瘤块种植法构建兔VX2肝癌模型[J].介入放射学杂志,2016,25(11):980-983.
[30] SUN Y, XIONG X, PANDYA D, et al. Enhancing tissue permeability with MRI guided preclinical focused ultrasound system in rabbit muscle: From normal tissue to VX2 tumor. J Control Release.2017;256(1):1-8.
[31] LIU X, DENG L, GUO R, et al. [Evaluation of total liver perfusion imaging of CT for efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with apatinib on rabbit VX2 liver tumors]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.2019; 44(5):477-484. [32] LEE J H, MOON H, HAN H, et al. Antitumor Effects of Intra-Arterial Delivery of Albumin-Doxorubicin Nanoparticle Conjugated Microbubbles Combined with Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Activation on VX2 Rabbit Liver Tumors. Cancers (Basel).2019;11(4):581.
[33] HU J, DONG Y, DING L, et al. Localized Chemotherapy Prevents Lung Metastasis After Incomplete Microwave Ablation of Hepatic VX2 Tumor. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019; 15(2):261-271.
[34] FU X, LUO R G, QIU W, et al. Sustained release of arsenic trioxide benefits interventional therapy on rabbit VX2 liver tumor. Nanomedicine. 2019;24(1):102-118.
[35] SUN Y, XIONG X, PANDYA D, et al. Enhancing tissue permeability with MRI guided preclinical focused ultrasound system in rabbit muscle: From normal tissue to VX2 tumor. J Control Release.2017;256(1):1-8.
[36] 姚青,陈江浩,凌瑞,等.组织块悬液注射法制作兔VX_2乳腺癌模型[J].中国癌症杂志,2004,14(1):22-23.
[37] 李宁,刘海生,孙楚东,等.肿瘤细胞悬液注射法制作兔食管癌移植瘤模型[J].中国肿瘤临床,2008,35(12):707-710.
[38] DU YN, XING W, YU S N, et al. [Feasibility study of blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging in evaluating the response of metastatic lymph nodes of rabbit VX2 tumor to radiotherapy]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019, 99(13):1028-1033.
[39] WANG B, TAN HN, LIANG P, et al. [Relationship between one-stop CT spectral perfusion imaging parameters and expression of lymphatic microvessel density and vascular endothelial growth factor-C in axillary lymph nodes of rabbit VX2 breast cancer]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;99(13): 1024-1027.
[40] WANG L,CHANG J,QU Y,et al. Combination therapy comprising irreversible electroporation and hydroxycamptothecin loaded electrospun membranes to treat rabbit VX2 subcutaneous cancer. Biomed Microdevices. 2018;20(4):88.
[41] TONG H, DUAN LG, ZHOU HY, et al. Modification of the method to establish a hepatic VX2 carcinoma model in rabbits. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(4):5333-5338.
[42] GUAN L. Angiogenesis dependent characteristics of tumor observed on rabbit VX2 hepatic carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.2015;8(10):12014-12027. |
| [1] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [2] | Zeng Zhen, Hu Jingwei, Li Xuan, Tang Linmei, Huang Zhiqiang, Li Mingxing. Quantitative analysis of renal blood flow perfusion using contrast-enhanced ultrasound in rats with hemorrhagic shock during resuscitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1201-1206. |
| [3] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [4] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [5] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [6] | Liu Xing, Wei Xiaohan, Deng Jie, Li Zhongming . Preparing a blunt contusion model of rabbit skeletal muscle under different blow strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 196-200. |
| [7] | Mu Yufeng, Wei Lina, Wu Yong, Shao Anliang, Chen Liang, Qu Shuxin, Xu Liming. Development and evaluation of alpha-galactosyl antigen-deficient rabbit model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 281-285. |
| [8] | Cao Yang, Zhang Junping, Peng Li, Ding Yi, Li Guanghui. Isolation and culture of rabbit aortic endothelial cells and biological characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3000-3003. |
| [9] | Chen Pu, Ruan Anmin, Zhou Jun, Zhang Xiaozhe, Ma Yufeng, Zong Chenzhong, Wang Qingpu. Effect of Tongluo Analgesic Gel on cartilage inflammation and degeneration in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2670-2675. |
| [10] | Wang Renxian, Cao Jingjing, Wang Honggang, Wan Ben, Liu Weifeng. Effects of dispersants on aggregation, intracellular distribution and cell proliferation of nano-hydroxyapatite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2500-2505. |
| [11] | Xia Sijie, Liao Qi. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in treatment of fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1944-1950. |
| [12] | Ren Jun, Zhao Yan, Xiao Bin, Ma Chao, Wang Xinke, Hao Yabin, Cheng Jie. Platelet-rich plasma promotes the healing of tibial fracture in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5595-5599. |
| [13] | Lei Senlin, Liu Hongyuan, Yang Hongsheng, Xiong Yan, Duan Hong. In vivo biosafety and histocompatibility of absorbable poly-D,L-lactic acid screws implanted with ultrasound-assisted technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5454-5460. |
| [14] | Li Xuewei, Hu Beibei, Zhang Dawei, Quan Lulu, Liang Yongqiang. Calcium hydrogen phosphate dehydrate combined with gelatin and recombinant human bone morphologic protein 2/7 for repair of bone defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4533-4539. |
| [15] | Yang Zhen, Li Hao, Gao Cangjian, Fu Liwei, Tian Guangzhao, Zha Kangkang, Sun Zhiqiang, Li Xu, Guo Weimin, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Liu Shuyun, Lu Shibi, Guo Quanyi . Regulation of stem cells by transforming growth factor β3/polylactic acid-glycolic acid microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4540-4546. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||