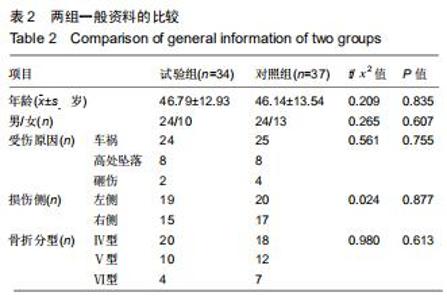
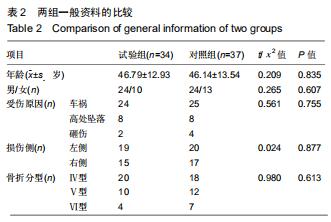
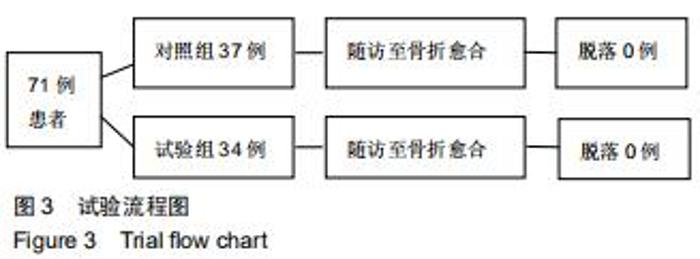
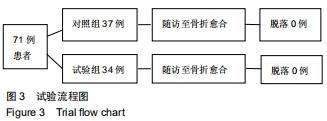
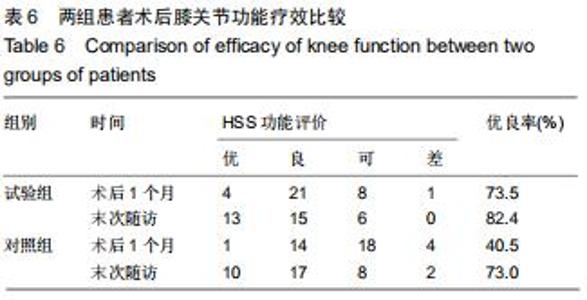
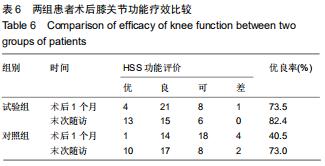
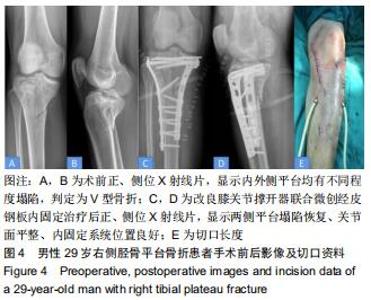
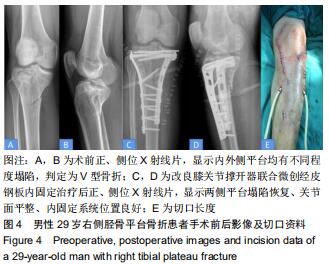
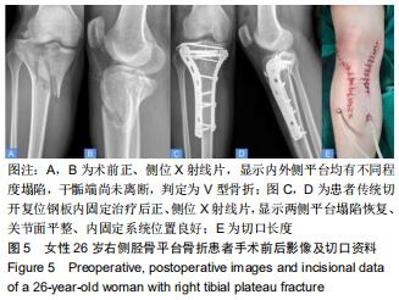
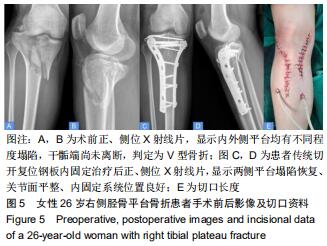
|
[1] SAGLAM Y, DIKMEN G, BADEMLER S, et al. Analysis of the cause, classification,treatment,outcome and associated injuries of pediatric pelvic ring fractures.Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2015;21(5):392-396.
[2] XU YQ, LI Q, SHEN TG, et al. An efficacy analysis of surgical timing and procedures for high-energy complex tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Surg.2013;5(3):188-195.
[3] XU Y, LI Q, SU P, et al. MDCT and MRI for the diagnosis of complex fractures of the tibial plateau: A case control study.Exp Ther Med. 2014;7(1):199-203.
[4] SCHATZKER J, MCBROOM R, BRUCE D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968-1975.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1979; (138): 94-104.
[5] BATTA V, SINHA S, TROMPETER A. Temporary Fixation Using a Long Femoral-tibial Nail to Treat a Displaced Medial Tibial Plateau Fracture in a 90-year-old Patient: A Case Report.J Orthop Case Rep. 2017;7(4): 36-38.
[6] 曾智敏,罗从风.胫骨平台骨折手术治疗的并发症[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2009,30(4):244-246.
[7] 傅俊伟,陈卓,吴俊彪,等.关节镜辅助下微创手术治疗胫骨平台骨折48例[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(12):1271-1272.
[8] 姜新峰,陈华.股骨撑开器辅助复位治疗不稳定型胫骨平台骨折疗效分析[J].江苏医药,2016, 42(13):1511-1512.
[9] 张志伟.长骨撑开器于胫骨平台骨折手术中的应用[J].中国医学工程, 2015,23(11):71-71.
[10] 罗从风,胡承方,高洪,等.基于CT的胫骨平台骨折的三柱分型[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009, 11(3):201-205.
[11] DUWELIUS PJ, CONNOLLY JF. Closed reduction of tibial plateau fractures. A comparison of functional and roentgenographic end results.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1988;(230):116-126.
[12] DAVIS AM, MACKAY C. Osteoarthritis year in review: outcome of rehabilitation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2013;21(10):1414-1424.
[13] REAHL GB, MARINOS D, OʼHARA NN, et al. Risk Factors for Knee Stiffness Surgery After Tibial Plateau Fracture Fixation.J Orthop Trauma.2018;32(9):e339-e343.
[14] LI J, ZHU Y, LIU B, et al. Incidence and risk factors for surgical site infection following open reduction and internal fixation of adult tibial plateau fractures.Int Orthop. 2018;42(6):1397-1403.
[15] BIGGI F, DI FABIO S, D'ANTIMO C, et al. Tibial plateau fractures: internal fixation with locking plates and the MIPO technique.Injury.2010; 41(11):1178-1182.
|