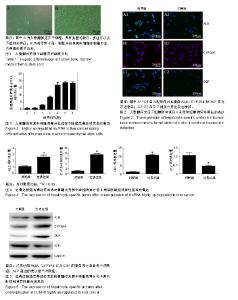
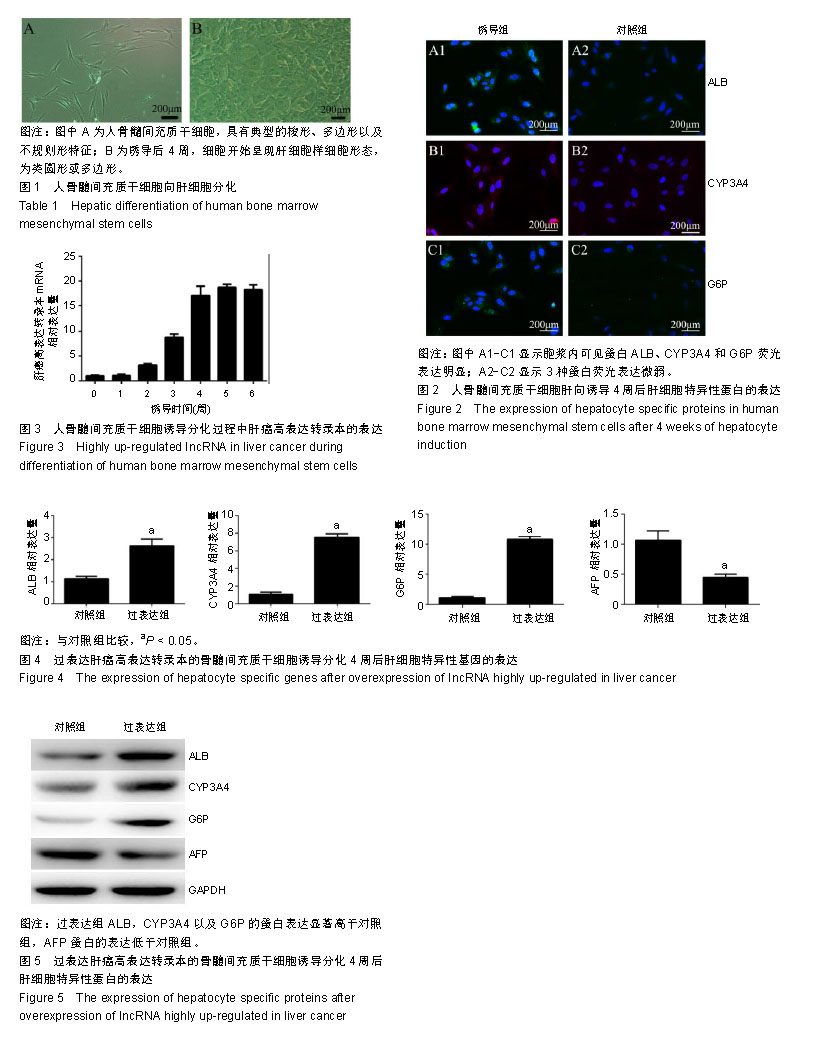
| [1]Ishibashi H, Nakamura M, Komori A, et al. Liver architecture, cell function, and disease. Semin Immunopathol. 2009;31(3): 399-409.[2]Wang H, Liang X, Gravot G, et al. Visualizing liver anatomy, physiology and pharmacology using multiphoton microscopy. J Biophotonics. 2017;10(1):46-60.[3]Åberg F, Isoniemi H, Höckerstedt K. Long-term results of liver transplantation. Scand J Surg. 2011;100(1):14-21.[4]Locke JE, Shamblott MJ, Cameron AM. Stem cells and the liver: clinical applications in transplantation. Adv Surg. 2009; 43:35-51.[5]Meirelles Júnior RF, Salvalaggio P, Rezende MB, et al. Liver transplantation: history, outcomes and perspectives. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2015;13(1):149-152.[6]Lin H, Xu R, Zhang Z, et al. Implications of the immunoregulatory functions of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of human liver diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2011; 8(1):19-22.[7]Chew JRJ, Chuah SJ, Teo KYW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance periodontal ligament cell functions and promote periodontal regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2019 Mar 13. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.03.021. [Epub ahead of print] [8]Zhou X, Yang J, Liu Y, et al. Observation of the effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation by different interventions on cirrhotic rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019; 52(3):e7879.[9]Lee KD, Kuo TK, Whang-Peng J, et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275-1284.[10]Stock P, Brückner S, Winkler S, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived hepatocytes improve the mouse liver after acute acetaminophen intoxication by preventing progress of injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4): 7004-7028.[11]He H, Liu X, Peng L, et al. Promotion of hepatic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on decellularized cell-deposited extracellular matrix. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:406871.[12]Chen S, Jia L, Zhang S, et al. DEPTOR regulates osteogenic differentiation via inhibiting MEG3-mediated activation of BMP4 signaling and is involved in osteoporosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):185.[13]Huang Y, Zheng Y, Jin C, et al. Long Non-coding RNA H19 Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Epigenetic Modulation of Histone Deacetylases. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28897.[14]Zhang W, Dong R, Diao S, et al. Differential long noncoding RNA/mRNA expression profiling and functional network analysis during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):30.[15]Cao Z, Huang S, Li J, et al. Long noncoding RNA expression profiles in chondrogenic and hypertrophic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017;17(6):739-749.[16]Yang Q, Jia L, Li X, et al. Long Noncoding RNAs: New Players in the Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow- and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2018;14(3):297-308.[17]Xie Z, Li J, Wang P, et al. Differential Expression Profiles of Long Noncoding RNA and mRNA of Osteogenically Differentiated Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Ankylosing Spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 2016;43(8):1523-1531.[18]Huo S, Zhou Y, He X, et al. Insight into the Role of Long Non-coding RNAs During Osteogenesis in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(1):52-59.[19]Panzitt K, Tschernatsch MM, Guelly C, et al. Characterization of HULC, a novel gene with striking up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma, as noncoding RNA. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(1):330-342.[20]Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, et al. CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010; 38(16):5366-5383.[21]Mu N, Liu HB, Meng QH, et al. The differentiation of human multipotent adult progenitor cells into hepatocyte-like cells induced by coculture with human hepatocyte line L02. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015;88(1):1-7.[22]Xu C, Zhang Y, Wang Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 controls human embryonic stem cell self-renewal by maintaining NODAL signalling. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13287.[23]Wang L, Zhao Y, Bao X, et al. LncRNA Dum interacts with Dnmts to regulate Dppa2 expression during myogenic differentiation and muscle regeneration. Cell Res. 2015; 25(3):335-350.[24]Kalwa M, Hänzelmann S, Otto S, et al. The lncRNA HOTAIR impacts on mesenchymal stem cells via triple helix formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(22):10631-10643.[25]Cui Y, Lu S, Tan H, et al. Silencing of Long Non-Coding RNA NONHSAT009968 Ameliorates the Staphylococcal Protein A-Inhibited Osteogenic Differentiation in Human Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016; 39(4):1347-1359.[26]Cui M, Xiao Z, Wang Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA HULC modulates abnormal lipid metabolism in hepatoma cells through an miR-9-mediated RXRA signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2015;75(5):846-857.[27]Li J, Wang X, Tang J, et al. HULC and Linc00152 Act as Novel Biomarkers in Predicting Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(2):687-696.[28]Du Y, Kong G, You X, et al. Elevation of highly up-regulated in liver cancer (HULC) by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell proliferation via down-regulating p18. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(31):26302-26311.[29]Li SP, Xu HX, Yu Y, et al. LncRNA HULC enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-200a-3p/ZEB1 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2016; 7(27):42431-42446.[30]Liu Y, Pan S, Liu L, et al. A genetic variant in long non-coding RNA HULC contributes to risk of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population. PLoS One. 2012;7(4): e35145.[31]Lu Z, Xiao Z, Liu F, et al. Long non-coding RNA HULC promotes tumor angiogenesis in liver cancer by up-regulating sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1). Oncotarget. 2016;7(1): 241-254.[32]Zhou C, Wu H, Liu Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HULC affects downstream-related targets to regulate migration and invasion of hepatoma cells. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018;26(7):513-518.[33]Feng H, Wei B, Zhang Y. Long non-coding RNA HULC promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by down-regulating microRNA-15a. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;126:891-898.[34]Yan H, Tian R, Zhang M, et al. High expression of long noncoding RNA HULC is a poor predictor of prognosis and regulates cell proliferation in glioma. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;10:113-120.[35]Yu X, Zheng H, Chan MT, et al. HULC: an oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(2): 410-417.[36]Zhang Y, Song X, Wang X, et al. Silencing of LncRNA HULC Enhances Chemotherapy Induced Apoptosis in Human Gastric Cancer. J Med Biochem. 2016;35(2):137-143.[37]Zhao Y, Guo Q, Chen J, et al. Role of long non-coding RNA HULC in cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumor metastasis of gastric cancer: a clinical and in vitro investigation. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(1):358-364.[38]Uzan VR, Lengert Av, Boldrini É, et al. High Expression of HULC Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Osteosarcoma Patients. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0156774.[39]Wang J, Ma W, Liu Y. Long non-coding RNA HULC promotes bladder cancer cells proliferation but inhibits apoptosis via regulation of ZIC2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Biomark. 2017;20(4):425-434.[40]Wang YF, Zhang S, Li XQ, et al. Expression of lncRNA HULC in cervical cancer and its correlation with tumor progression and patient survival. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016; 20(19):3987-3991. |