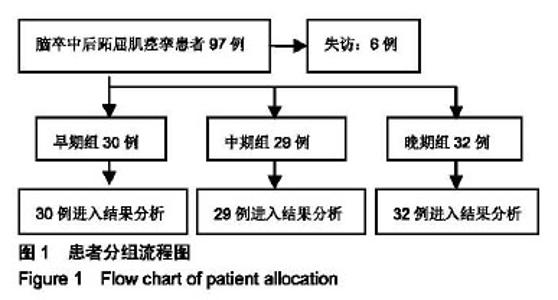
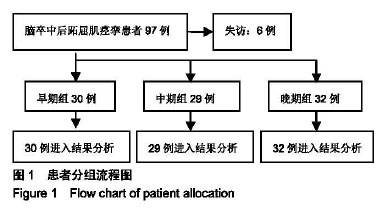
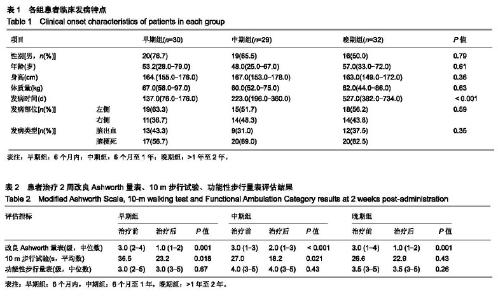
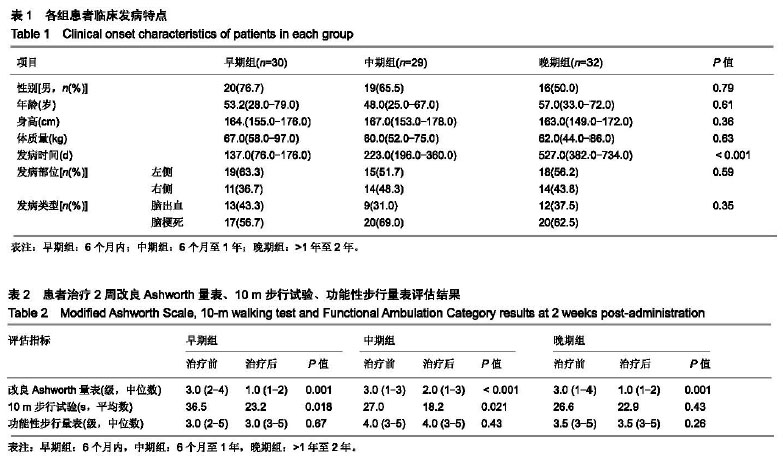
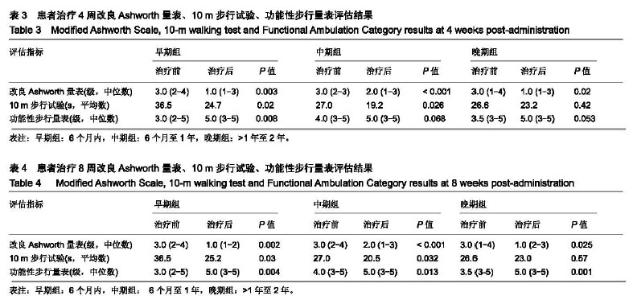
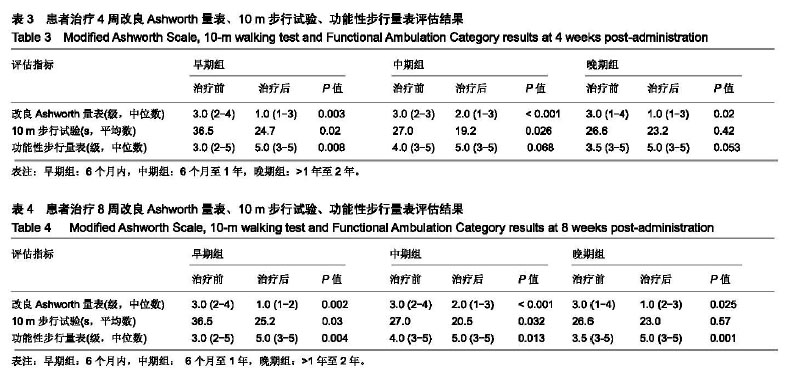
| [1]Teasell R, Foley N, Pereira S,et al.Evidence to practice: botulinum toxin in the treatment of spasticity post stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil.2012;19(2): 115-121.[2]Rosales RL, Efendy F, Teleg ES, et al.Botulinum toxin as early intervention for spasticity after stroke or non-progressive brain lesion: A meta-analysis.J Neurol Sci.2016;371(371): 6-14.[3]李亚斌,冯海霞,白佳佳,等.A型肉毒素局部注射结合强化运动治疗对脑卒中后下肢痉挛患者步行能力的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2017, 20(6): 5-9.[4]Tao W, Yan D, Li JH, et al.Gait improvement by low-dose botulinum toxin A injection treatment of the lower limbs in subacute stroke patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(3): 759-762.[5]Fock J, Galea MP, Stillman BC, et al.Functional outcome following Botulinum toxin A injection to reduce spastic equinus in adults with traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury.2004;18(1): 57-63.[6]中华神经科学会.中华神经外科学会.各类脑血管病诊断要点[J].中华神经科杂志,1996,29(6):379-380.[7]肉毒毒素治疗成人肢体痉挛状态中国指南(2015),中国康复医学杂志,2015,1(30),81-110.[8]Oh HM,Park GY,Choi YM, et al.The effects of botulinum toxin injections on plantar flexor spasticity in different phases after stroke. A secondary analysis from a double-blind, randomized trial. PM R. 2018 Aug;10(8):789-797.[9]洪永锋,徐军,沈显山,等.肌电引导A型肉毒毒素早期精准注射对脑卒中偏瘫侧上肢功能恢复的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2018,7(40):499-502.[10]Holden MK, Gill KM, Magliozzi MR, et al.Clinical gait assessment in the neurologically impaired. Reliability and meaningfulness.Phys Ther 1984;64:35-40.[11]Dong Y, Wu T, Hu X, et al.Efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A for upper limb spasticity after stroke or traumatic brain injury: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med.2017;(2): 256-267.[12]Fheodoroff K,Dressler D,Woldag H,et al.Treatment goals in patients with post-stroke upper limb spasticity following injection of botulinum toxin A : Results of the German-Austrian subgroup of the ULIS-II study, Nervenarzt.2018;(8): 245-256.[13]Li J, Zhang R, Cui BL, et al.Therapeutic efficacy and safety of various botulinum toxin A doses and concentrations in spastic foot after stroke: a randomized controlled trial.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(9):1451-1457.[14]Ivanhoe CB, Reistetter TA. Spasticity: the misunderstood part of the upper motor neuron syndrome.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;83(10 Suppl): S3-S9.[15]Im S, Park JH, Son SK, et al. Does botulinum toxin injection site determine outcome in post-stroke plantarflexion spasticity? Comparison study of two injection sites in the gastrocnemius muscle: a randomized double-blind controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2014;(28): 604-613.[16]Wu T, Li JH, Song HX, et al.Effectiveness of botulinum toxin for lower limbs spasticity after stroke:a systematic review and Meta-Analysis. Top Stroke Rehabil.2016;(23): 217-223.[17]Nair KP, Marsden J. The management of spasticity in adults. BmJ.2014;349:g4737.[18]Mehrholz J, Wagner K, Rutte K,et al.Predictive validity and responsiveness of the Functional Ambulation Category in hemiparetic patients after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88(10): 1314-1319.[19]Hara T, Abo M, Hara H, et al. The Effect of Repeated Botulinum Toxin A Therapy Combined with Intensive Rehabilitation on Lower Limb Spasticity in Post-Stroke Patients.Toxins.2018;10 (9):2-12.[20]Chan J, Winter A, Palit M, et al.Are gait and mobility measures responsive to change following botulinum toxin injections in adults with lower limb spasticity? Disabil Rehabil. 2013;35:959-967. [21]Mohammadi R, Talebian S, Phadke CP, et al.Effects of treadmill incline and speed on ankle muscle activity in subjects after a stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.2016;97(3): 445-453.[22]Fietzek UM, Kossmehl P, Schelosky L, et al.Early botulinum toxin treatment for spastic pes equinovarus--a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Eur J Neurol. 2014; 21(8):1089-1095.[23]Suh YW, Uhm CS, Cho YA. Ultrastructural changes in myotendinous nerve endings induced by injection of botulinum toxin into the extraocular muscle. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;248(12):1795-801..[24]Longino D, Frank C, Leonard TR, et al.Proposed model of botulinum toxin-induced muscle weakness in the rabbit. J Orthop Res.2005;(23): 1411-1418. |