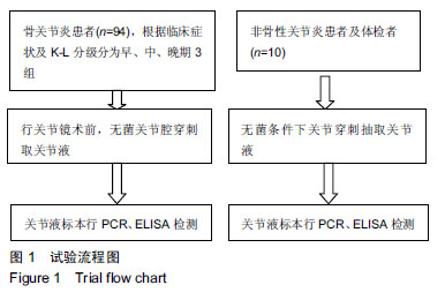
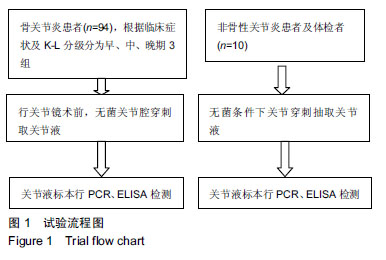
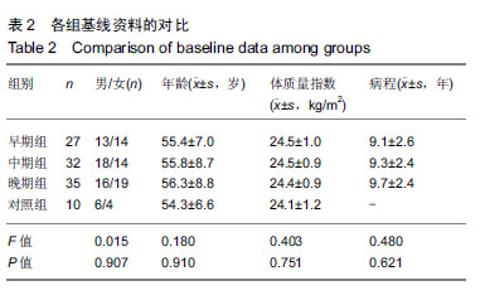
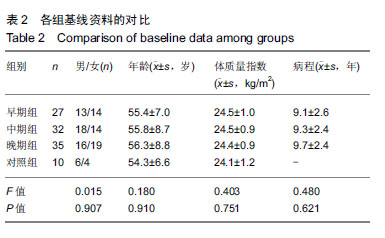
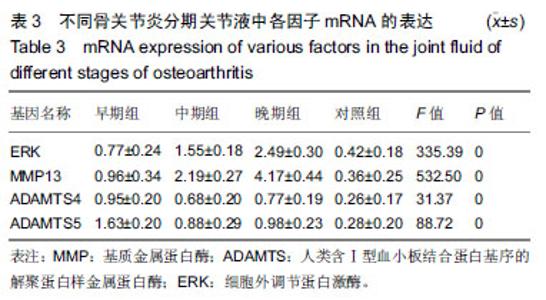
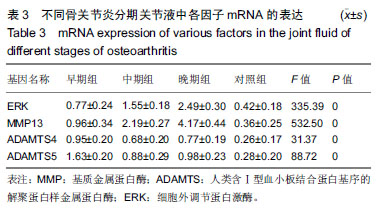
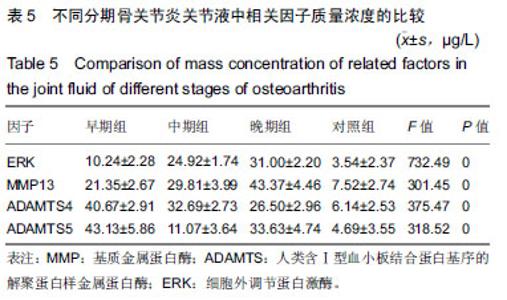
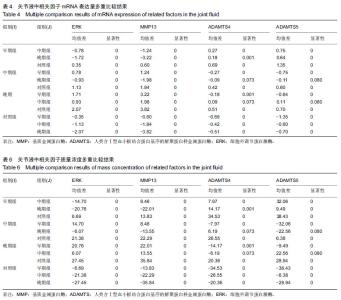
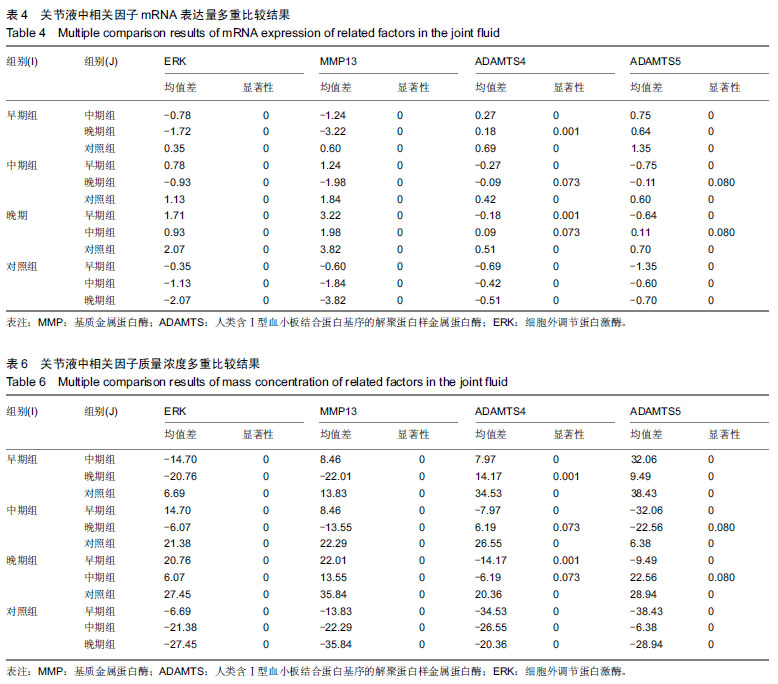
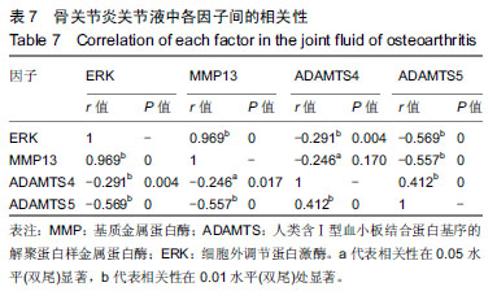
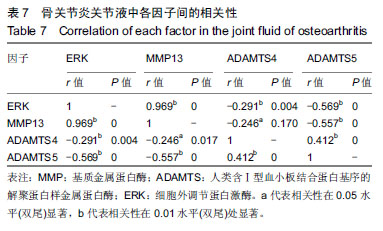
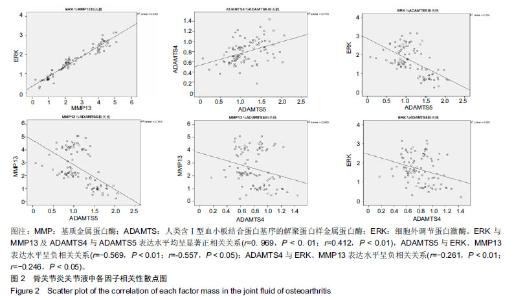
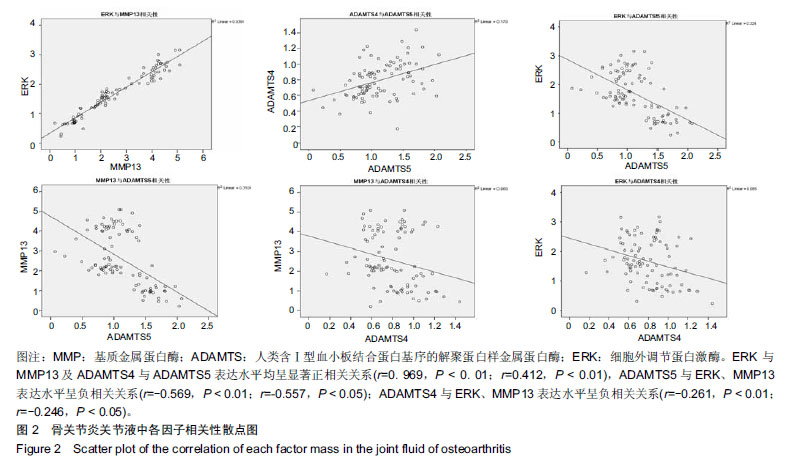
| [1]高世超,殷海波,刘宏潇,等.MAPK信号通路在骨关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(5):441-444. [2]Yang CY,Chanalaris A,Troeberg L.ADAMTS and ADAM metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis - looking beyond the 'usual suspects'.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(7):1000-1009.[3]赵昌盛,钟群杰,林剑浩.中国膝关节骨关节炎流行病学调查现状[J].广东医学,2016,37(13):2050-2052. [4]Tang X,Wang S,Zhan S,et al.The Prevalence of Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis in China: Results From the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(3):648-653.[5]Carr AJ,Robertsson O,Graves S,et al.Knee replacement. Lancet. 2012; 379(9823):1331-1340. [6]Pivec R,Johnson AJ,Mears SC,et al.Hip arthroplasty.Lancet. 2012; 380(9855):1768-1777.[7]Bijlsma JW,Berenbaum F,Lafeber FP.Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice.Lancet.2011;377(9783):2115-2126. [8]Glyn-Jones S,Palmer AJ,Agricola R,et al.Osteoarthritis. Lancet.2015; 386(9991):376-387.[9]Verma P,Dalal K.ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5: key enzymes in osteoarthritis.J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(12):3507-3514. [10]王利,王宪,孔炜.新型金属蛋白酶ADAMTS家族的研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2008,39(1):49-52.[11]Watanabe H.Aggrecan and its chondroitin sulfate in cartilage. Seikagaku.2008;80(1):28-32. [12]中华医学会骨科学分会.骨关节炎诊治指南(2007年版)[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(3):287-288.[13]Martel-Pelletier J,Boileau C,Pelletier JP,et al.Cartilage in normal and osteoarthritis conditions.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008;22(2): 351-384. [14]Braun HJ,Gold GE.Diagnosis of osteoarthritis:imaging.Bone. 2012; 51(2):278-288. [15]曾明珠,段戡,袁长深,等.不同分期骨关节炎滑膜细胞中COX-2 mRNA表达的差异[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(7):1003-1008. [16]王维山,史晨辉,何仁豪,等. MicroRNAs、uPA及MMP-3在骨关节炎患者滑膜组织中的表达及相关性[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014,34(4):871-873. [17]胡毅,任云萍,张勇,等.持续被动运动条件下骨关节炎软骨细胞Erk活性及增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(42):6265-6270. [18]邓小兰,晋贞超,王健,等.ERK途径可能参与抗坏血酸诱导的神经干细胞向多巴胺能细胞分化[J].第三军医大学学报,2013,35(22):2430-2434. [19]KELLGREN JH,LAWRENCE JS.Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis.Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16(4):494-502. [20]Joshi S,Platanias LC.Mnk kinase pathway: Cellular functions and biological outcomes.World J Biol Chem.2014;5(3):321-333. [21]Fecher LA,Amaravadi RK,Flaherty KT.The MAPK pathway in melanoma.Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20(2):183-189. [22]王涛,殷红,廖江龙,等.骨关节炎与MAPK信号通路关系的研究概况[J].中国民族民间医药,2017,26(19):27-29,33. [23]陈泽华,李楠.ERK1/2信号通路与骨关节炎软骨细胞活性及其治疗的相关性研究[J].风湿病与关节炎,2015,4(1):63-65,71.[24]Prasadam I,Crawford R,Xiao Y.Aggravation of ADAMTS and matrix metalloproteinase production and role of ERK1/2 pathway in the interaction of osteoarthritic subchondral bone osteoblasts and articular cartilage chondrocytes -- possible pathogenic role in osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2012;39(3):621-634. [25]付长龙,林洁,赵忠胜,等.电针抑制Ras/Raf/MEK1/2/ERK1/2信号通路介导骨关节炎软骨超微结构退变[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(32): 5134-5139. [26]黄媛霞,徐海斌,郭春.IL-1β和MMP-13在兔骨关节炎模型软骨和滑液中的表达[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2017,38(4):507-511,528. [27]Fukui N,Miyamoto Y,Nakajima M,et al.Zonal gene expression of chondrocytes in osteoarthritic cartilage.Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(12): 3843-3853. [28]魏凡华,张玉颖,于修平.基质金属蛋白酶ADAMTS的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2014,36(8):1186-1192.[29]王维山,史晨辉,李长俊,等.OA 患者关节液 uPA 和 MMP-3,9,13,14的表达水平与关节功能的相关性研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(6): 602-605,610.[30]Dreier R,Grässel S,Fuchs S,et al.Pro-MMP-9 is a specific macrophage product and is activated by osteoarthritic chondrocytes via MMP-3 or a MT1-MMP/MMP-13 cascade.Exp Cell Res. 2004;297(2):303-312. [31]Jiang TJ. Detection of levels of serum and knee synovial fluid MMP-9 and TNF-α in patients with osteoarthritis and its clinical significance. Medical Journal of National Defending Forces in Southwest China. 2009;19(4):380-382.[32]兰平文,刘跃洪,刘树平,等.不同病变阶段OA软骨细胞中TGF-β信号通路相关分子的表达规律[J].四川医学,2017,38(10):1128-1132. [33]祁雷,姚运峰,李子煜,等.大鼠骨关节炎模型的建立及软骨组织中MMP-13和ADAMTS-5的表达[J].局解手术学杂志, 2018,27(3):157-163. [34]Malfait AM,Liu RQ,Ijiri K,et al.Inhibition of ADAM-TS4 and ADAM-TS5 prevents aggrecan degradation in osteoarthritic cartilage.J Biol Chem. 2002;277(25):22201-22208.[35]Song RH,Tortorella MD,Malfait AM,et al.Aggrecan degradation in human articular cartilage explants is mediated by both ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5.Arthritis Rheum.2007;56(2):575-585.[36]Tortorella MD,Malfait AM,Deccico C,et al.The role of ADAM-TS4 (aggrecanase-1) and ADAM-TS5 (aggrecanase-2) in a model of cartilage degradation.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9(6):539-552. [37]Stanton H,Rogerson FM,East CJ,et al.ADAMTS5 is the major aggrecanase in mouse cartilage in vivo and in vitro. Nature. 2005; 434(7033):648-652.[38]Gendron C,Kashiwagi M,Lim NH,et al.Proteolytic activities of human ADAMTS-5: comparative studies with ADAMTS-4.J Biol Chem. 2007;282(25):18294-18306. [39]李保驰,王维山,董金波,等.MMP-3、MMP-13在骨性关节炎患者滑膜中的表达及意义[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(6):593-596,697.[40]陈临新.膝关节骨关节炎的诊疗[J].中国全科医学, 2009,12(4):297-298. |