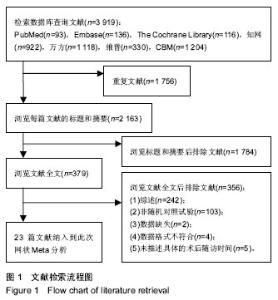
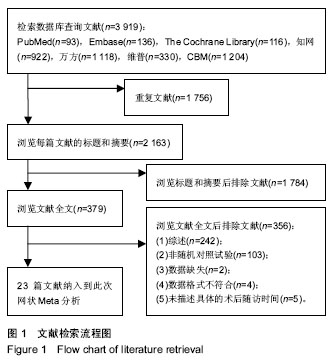
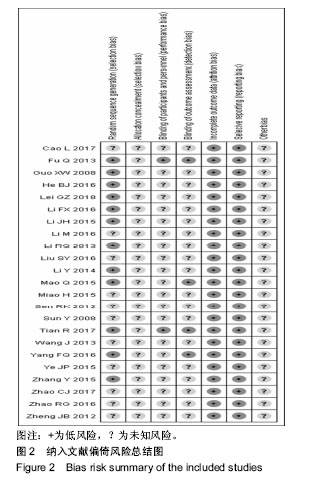
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (16): 2585-2593.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1215
Previous Articles Next Articles
Postoperative hip function of different hip joint preserving surgeries for osteonecrosis of femoral head: a network meta-analysis
Zhang Chi1, Lü Haoyuan2, Zhang Xiaoyun3, Lin Zonghan3, Chen Yueping3, Zhu Jianglong3, Long Feipan3, Huang Junli1, Mei Pengfei1
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Clinical School of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2019-06-08Published:2019-06-08 -
Contact:Lin Zonghan, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Chi, Master candidate, Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760796 (to CYP)| the Orthopedics Construction Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 04B2017082 (to CYP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Chi, Lü Haoyuan, Zhang Xiaoyun, Lin Zonghan, Chen Yueping, Zhu Jianglong, Long Feipan, Huang Junli, Mei Pengfei . Postoperative hip function of different hip joint preserving surgeries for osteonecrosis of femoral head: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2585-2593.
share this article
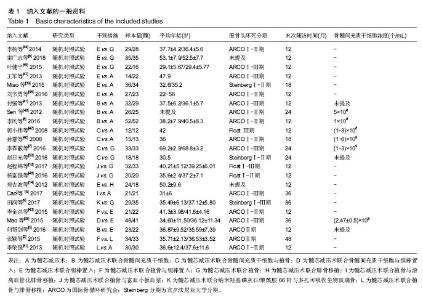
2.2 纳入研究基本特征 23篇文献共研究1 248髋,所有患者均被诊断为股骨头坏死,其中单独接受髓芯减压术有261髋,接受髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞有133髋,接受髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与植骨有78髋,接受髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与钽棒有48髋,接受髓芯减压术联合钽棒有272髋,接受髓芯减压术联合植骨与钽棒有55髋,接受髓芯减压术联合植骨有218髋,接受髓芯减压术联合腓骨移植有18髋,接受髓芯减压术联合植骨与游离血管化腓骨移植有21髋,接受髓芯减压术联合植骨与富血小板血浆有52髋,接受髓芯减压术联合纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66杆与多孔可吸收生物玻璃骨有29髋,接受髓芯减压术联合植骨与腓骨移植有63髋。纳入文献的一般资料如表1。"
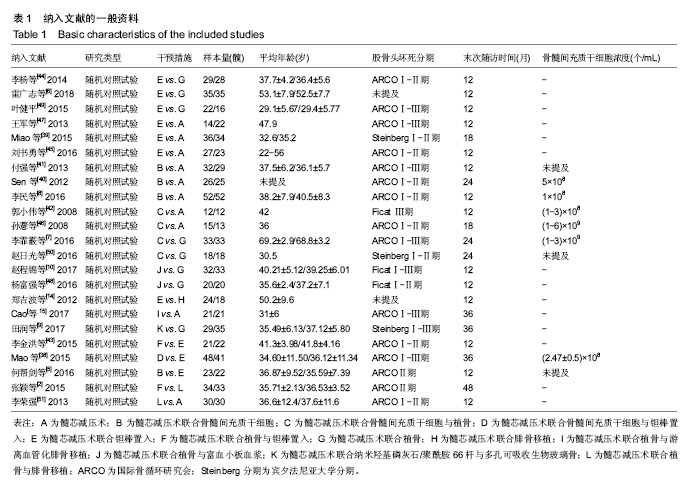

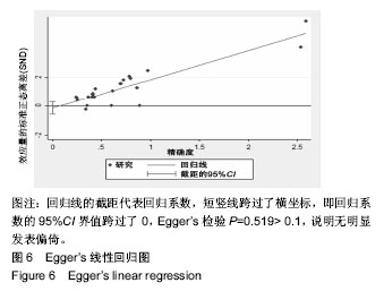
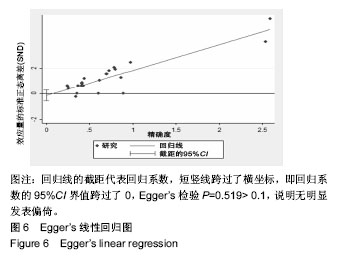
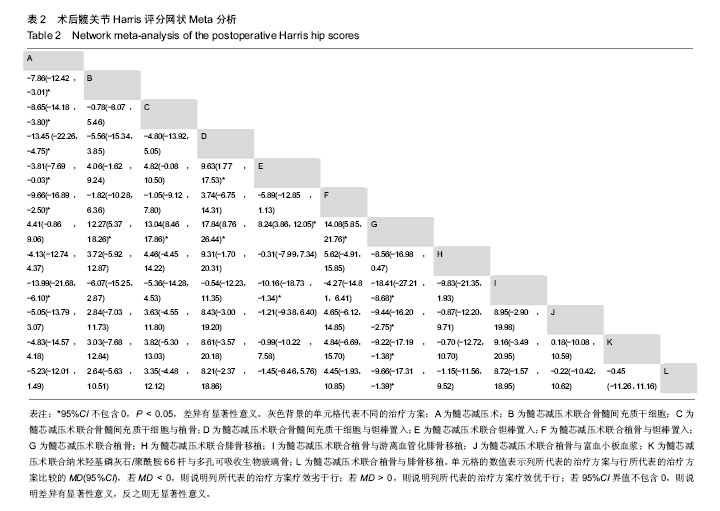
2.4 直接Meta分析 3篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入对比髓芯减压术联合植骨术后末次随访Harris评分[6,44,49],异质性较大(P=0.060,I2=64.5%),采用随机效应模型合并结果,髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合植骨(MD=9.15,95%CI[6.90,11.40])。3篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入对比髓芯减压术后末次随访Harris评分[39,45,47],异质性较大(P=0.022,I2=73.8%),采用随机效应模型合并结果,髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分与髓芯减压术相当(MD=1.63,95%CI[-2.33,5.59])。3篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞对比髓芯减压术后末次随访Harris评分[8,40-41],异质性较大(P=0.008,I2=79.4%),采用随机效应模型合并结果,髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术(MD=9.23,95%CI[2.02,16.44])。2篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与植骨对比髓芯减压术后末次随访Harris评分[42,46],异质性较大(P=0.131,I2=56.2%),采用随机效应模型合并结果,髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与植骨的术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术(MD=10.43,95%CI[3.49,17.36])。2篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与植骨对比髓芯减压术联合植骨的术后末次随访Harris评分[7,50],异质性小(P=0.912,I2=0.0%),采用固定效应模型合并结果,髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与植骨的术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合植骨(MD=12.23,95%CI[10.62,13.85])。 2篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合植骨与富血小板血浆与植骨对比髓芯减压术联合植骨术后末次随访Harris评分[10,48],异质性小(P=0.582,I2=0.0%),采用固定效应模型合并结果,髓芯减压术联合植骨与富血小板血浆术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合植骨(MD=9.08,95%CI[5.03,13.13])。1篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入对比髓芯减压术联合腓骨移植术后末次随访Harris评分[14],结果显示髓芯减压术联合植骨与富血小板血浆的术后末次随访Harris评分与髓芯减压术联合植骨相当(MD=-0.31,95%CI[-2.51,1.89])。1篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合植骨与游离血管化腓骨移植对比髓芯减压术后末次随访Harris评分[15],结果显示髓芯减压术联合植骨与游离血管化腓骨移植的术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术(MD=14.00,95%CI[11.51,16.49])。1篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66杆与多孔可吸收生物玻璃骨对比髓芯减压术联合植骨术后末次随访Harris评分[9],结果显示髓芯减压术联合纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66杆与多孔可吸收生物玻璃骨的术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合植骨(MD=9.28,95%CI[6.49,12.07])。1篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合植骨与钽棒置入对比髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分[43],结果显示髓芯减压术联合植骨与钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入(MD=5.10,95%CI[0.24,9.96])。1篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与钽棒置入对比髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分[38],结果显示髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入(MD=9.63,95%CI[6.82,12.44])。1篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞对比髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分[5],结果显示髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞的术后末次随访Harris评分与髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入相当(MD=-1.37,95%CI[-6.91,4.17])。1篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合植骨与钽棒置入对比髓芯减压术联合植骨与腓骨移植术后末次随访Harris评分[2],结果显示髓芯减压术联合植骨与钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合植骨与腓骨移植(MD=4.88,95%CI[4.11,5.65])。1篇文献涉及髓芯减压术联合植骨与腓骨移植对比髓芯减压术后末次随访Harris评分[51],结果显示髓芯减压术联合植骨与腓骨移植的术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术(MD=5.80,95%CI[2.61,8.99])。 2.5 网状Meta分析 2.5.1 网状证据图 总共纳入了23篇文献,12种治疗方案构成23对直接比较,有实线连接则证明2种治疗方案之间存在直接比较证据,无连线则证明未发现直接比较证据,见图3。 2.5.2 不一致性检测 23对直接比较构成了1个三角形闭环与2个四边形闭环,Z检验结果表明95%CI界值下限均为1,P > 0.05,表明各闭环具有一致性,见图4。 2.5.3 节点分裂模型 节点分裂分析结果显示各P值均> 0.05,说明各治疗方法的直接比较结果与间接比较结果具有一致性,可运用一致性模型实施网状Meta分析,见图5。 2.5.4 发表偏倚 作Egger’s检验P=0.519>0.1,说明无明显发表偏倚。Egger’s线性回归图见图6。"
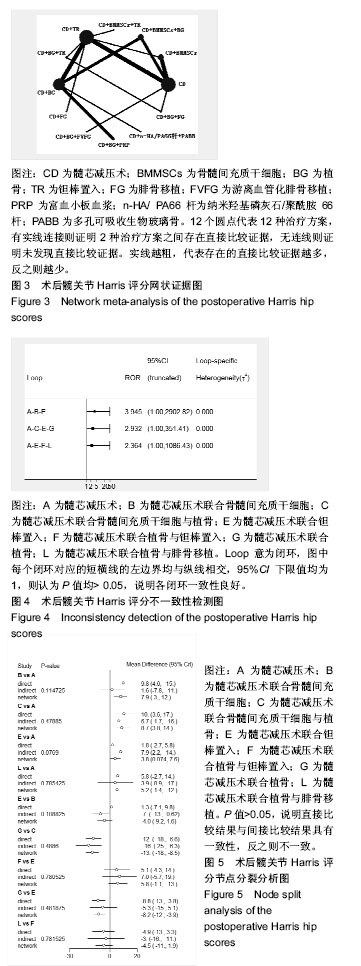
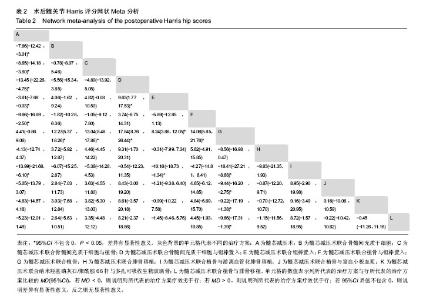
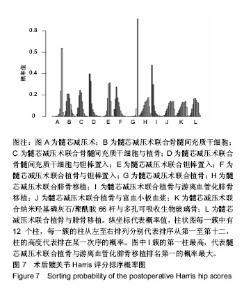
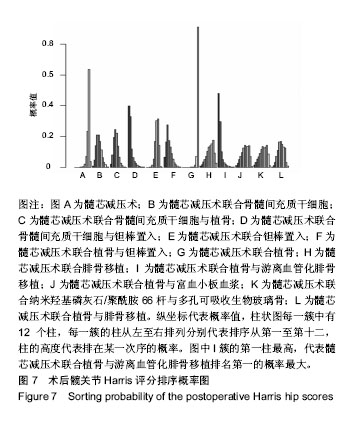
2.5.5 网状Meta分析结果 各治疗方法对比的潜在规模缩减因子值均为1,说明模型具有良好的收敛性。髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞、髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与植骨、髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与钽棒置入、髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入、髓芯减压术联合植骨与钽棒置入、髓芯减压术联合植骨与游离血管化腓骨移植的术后末次随访Harris评分均高于髓芯减压术;髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞、髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与植骨、髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与钽棒置入、髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入、髓芯减压术联合植骨与钽棒置入、髓芯减压术联合植骨与游离血管化腓骨移植、髓芯减压术联合植骨与富血小板血浆、髓芯减压术联合纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66杆与多孔可吸收生物玻璃骨、髓芯减压术联合植骨与腓骨移植的术后末次随访Harris评分均高于髓芯减压术联合植骨;髓芯减压术联合骨髓间充质干细胞与钽棒置入术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入;髓芯减压术联合植骨与游离血管化腓骨移植的术后末次随访Harris评分高于髓芯减压术联合钽棒置入。其他两两比较结果差异均无显著性意义,见表2。"
| [1] Ando W, Yamamoto K, Koyama T, et al. Radiologic and clinical features of misdiagnosed idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics. 2017; 40(1): e117-e123.[2] 张颖,刘又文,冯立志,等. 非创伤性早期股骨头坏死患者保髋术中钽棒和异体腓骨支撑股骨头的效果比较[J]. 山东医药, 2015, 55(48): 5-8.[3] Swarup I, Lee YY, Movilla P, et al. Common factors associated with osteonecrosis of the femoral head in young patients requiring total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2015;25(3): 232-236.[4] Chotivichit A, Korwutthikulrangsri E, Pornrattanamaneewong C, et al. Core decompression with bone marrow injection for the treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis. J Med Assoc Thai.2014;97 Suppl 9: S139-S143.[5] 何帮剑,厉驹,吕一,等. 髓芯减压联合干细胞移植与钽棒植入术治疗Ⅱ期非创伤性股骨头坏死的临床研究[J]. 中国骨伤, 2016, 29(12): 1119-1124.[6] 雷广志. 研究髓芯减压联合钽金属棒植入治疗股骨头坏死的效果[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2018, 12(2): 16-17.[7] 李霏霰,吴齐英,李新志,等. 髓心减压术联合自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗老年缺血性股骨头坏死的疗效[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2016, 36(22): 5671-5672.[8] 李民,李书奎,陈汉文,等. 髓芯减压后自体Mcs移植治疗早期股骨头坏死效果[J]. 齐鲁医学杂志, 2016, 31(3): 340-341+343.[9] 田润,李越,王坤正,等. 髓芯减压联合纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66杆治疗股骨头坏死的前瞻性研究[J]. 中华解剖与临床杂志, 2017, 22(3): 201-207.[10] 赵程锦,冯阳阳,周煜虎. 髓芯减压植骨术结合富血小板血浆治疗股骨头缺血性坏死的疗效及术后并发症临床观察[J]. 中国临床研究, 2017, 30(7): 878-882.[11] Arbeloa-Gutierrez L, Dean CS, Chahla J, et al. Core decompression augmented with autologous bone marrow aspiration concentrate for early avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Arthrosc Tech. 2016;5(3): e615-e620.[12] 王谦,黄国鑫,陈磊,等. 髓芯减压联合自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗股骨头坏死:安全和有效性的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(17): 2733-2739.[13] Gao YS, Chen SB, Jin DX, et al. Modified surgical techniques of free vascularized fibular grafting for treatment of the osteonecrosis of femoral head: results from a series of 407 cases. Microsurgery. 2013;33(8): 646-651.[14] 郑吉波. 髓心减压钽棒假体植入治疗股骨头坏死的临床疗效[J]. 中国医药导报, 2012, 9(16):187-188.[15] Cao L, Guo C, Chen J, et al. Free vascularized fibular grafting improves vascularity compared with core decompression in femoral head osteonecrosis: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(9): 2230-2240.[16] JW G. ARCO Intronational stage of osteonecrosis. ARCO Newsl. 1993;5:79-82.[17] 康鹏德,裴福兴,王坤正. 股骨头坏死的宾夕法尼亚大学分期[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2004, 12(Z3): 136-137.[18] Ficat RP. Idiopathic bone necrosis of the femoral head. early diagnosis and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985; 67(1): 3-9.[19] Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. an end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg. 1969;51(4): 737-755.[20] 吴婷婷,刘丹璐,黄娇,等. 偏倚风险评估工具在针刺Cochrane系统评价中的应用[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2014, 14(3): 361-364.[21] 张天嵩,钟文昭,李博. 实用循证医学方法学.2版[M]. 长沙:中南大学出版社, 2014.[22] 赵坤,陈凌霄,田金徽,等. 使用R、GeMTC和STATA软件实现连续变量的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2015, 15(7): 861-868.[23] 汪徐林,秦正积,陆益花,等. Stata软件在网状Meta分析中的应用[J]. 现代预防医学, 2016, 43(19): 3461-3464+3482.[24] 石修权,王增珍. Egger’s test与Begg’s test的功效差异比较与原因分析[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2009, 38(1): 91-93+102.[25] 易跃雄,张蔚,刘小媛,等. 网状Meta分析图形结果解读[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2015,15(1): 103-109.[26] 田金徽,李伦. 网状Mate分析方法与实践[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2017.[27] 韦标方,孙丙银. 髓芯减压加钽棒植入治疗老年非创伤性股骨头坏死疗效及塌陷预测安全性[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2015, 35(19): 5572-5573.[28] 徐鸿尧,赵建宁,郭亭. 纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66骨支撑材料与钽棒置入修复早期股骨头坏死:近期效果比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(39): 6292-6297.[29] Pepke W, Kasten P, Beckmann NA, et al. Core decompression and autologous bone marrow concentrate for treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis: a randomized prospective study. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2016;8(1): 6162.[30] Zhao D, Cui D, Wang B, et al. Treatment of early stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head with autologous implantation of bone marrow-derived and cultured mesenchymal stem cells. Bone. 2012;50(1): 325-330.[31] 韩继成. 髓心减压植骨、钽棒植入治疗股骨头缺血性坏死的疗效[J]. 吉林医学,2013,34(15): 2898.[32] 喜占荣,彭鹏,布林. 带血管的腓骨移植联合红骨髓与碳棒植入在治疗Onfh中的疗效比较[J]. 医药前沿, 2017, 7(26): 72-73.[33] 李宗洲. 髓芯减压联合钽棒植入治疗早期股骨头坏死的疗效观察[J]. 基层医学论坛, 2016, 20(26): 3658-3659.[34] 穆杰. 钽棒与髓芯减压植骨治疗早中期股骨头坏死的效果对比[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2016, 7(17): 71-72.[35] 强廷会,周新立,牟欢,等. 髓芯减压并钽金属棒植入、髓芯减压并植骨术在股骨头坏死保头治疗中的短期疗效比较[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2018, 35(4): 513-517.[36] 吴刚. 髓芯减压加钽棒植入治疗早期股骨头坏死的临床效果观察[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2015, 28(23): 3227-3228.[37] 姜良斌,刘松,岳永彬,等. 富血小板血浆联合钻孔减压、同种异体腓骨支撑治疗早期股骨头坏死的研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2018, 36(1): 93-97.[38] Mao Q, Wang W, Xu T, et al. Combination treatment of biomechanical support and targeted intra-arterial infusion of peripheral blood stem cells mobilized by granulocyte-colony stimulating factor for the osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(4): 647-656.[39] Miao H, Ye D, Liang W, et al. Effect of osteonecrosis intervention rod versus core decompression using multiple small drill holes on early stages of necrosis of the femoral head: a prospective study on a series of 60 patients with a minimum 1-year-follow-up. Open Orthop J.2015;9: 179-184.[40] Sen RK, Tripathy SK, Aggarwal S, et al. Early results of core decompression and autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells instillation in femoral head osteonecrosis: a randomized control study. J Arthroplasty. 2012; 27(5): 679-686.[41] 付强,闫世杰,王江泳,等. 髓芯减压联合自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗45例股骨头无菌性坏死的临床疗效分析[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2013, 13(25): 4925-4928.[42] 郭小伟,吴卫新,洪云飞,等. 髓芯减压并自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗股骨头缺血性坏死[J]. 医药论坛杂志, 2008,29(5): 19-21.[43] 李金洪,邓盛江,杜全印,等. 多孔钽棒联合植骨治疗成年股骨头坏死的临床研究[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2015, 30(5): 630-632, 640.[44] 李杨,冯世庆. 早期股骨头缺血性坏死治疗:髓芯减压并钽棒优于并植骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(5): 815-820.[45] 刘书勇,马晓燕. 多孔钽棒置入联合髓芯减压对早期股骨头坏死的近期疗效[J]. 临床医学, 2016, 36(7): 58-59.[46] 孙薏,张文华,姚一民,等. 中心减压植骨联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗股骨头缺血坏死[J]. 西南国防医药, 2008, 18(6): 800-802.[47] 王军,刘刚,张定伟,等. 髓芯减压与钽棒植入治疗早期股骨头坏死的比较[J]. 现代临床医学, 2013, 39(4): 258-259+262.[48] 杨富强,杨晓明,葛建健,等. 髓芯减压植骨联合富血小板血浆治疗股骨头缺血性坏死的前瞻随机对照研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志•电子版, 2016, 10(2): 140-144.[49] 叶健平. 髓芯减压加钽棒植入治疗早期股骨头坏死的临床效果观察[J]. 河南医学研究, 2015, 24(9): 39-41.[50] 赵日光,刘宏滨,韩冰,等. 髓芯减压联合自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的疗效观察[J]. 人民军医, 2016, 59(4): 372-373.[51] 李荣强. 腓骨柱钻孔支撑结合髂骨泥骨诱导治疗早期股骨头坏死26例[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2013, 2(11): 29-31.[52] Sadile F, Bernasconi A, Russo S, et al. Core decompression versus other joint preserving treatments for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a meta-analysis. Br Med Bull. 2016; 118(1): 33-49.[53] Silva LL, Castelar M, Matos MA. Quality of life in pediatric patients with avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2016; 18(5): 445-449.[54] 李子荣. 股骨头坏死:早期诊断与个体化治疗[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(19): 1909-1911.[55] Kubo Y, Yamamoto T, Motomura G, et al. Patient-reported outcomes of femoral osteotomy and total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a prospective case series study. Springer Plus. 2016;5(1): 1880.[56] Tripathy SK, Goyal T, Sen RK. Management of femoral head osteonecrosis: current concepts. Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(1): 28-45.[57] 赵德伟,谢辉.成人股骨头坏死保髋手术治疗的策略及探讨[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018, 32(7): 792-797.[58] Pierce TP, Elmallah RK, Jauregui JJ, et al. A Current Review of Non-Vascularized Bone Grafting in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8(3): 240-245.[59] Zhao D, Liu B, Wang B, et al. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells associated with tantalum rod implantation and vascularized iliac grafting for the treatment of end-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015: 240506.[60] Jin H, Xu T, Chen Q, et al. The fate and distribution of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with intra-arterial infusion in osteonecrosis of the femoral head in dogs. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016: 8616143.[61] 曾宪涛,熊期,沈可. Meta分析系列之十三:盲法的评价[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2013, 5(4): 331-333.[62] 曾宪涛,沈可,罗杰. Meta分析系列之十二:分配隐藏的评价[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2013, 5(3): 219-221.[63] 李康,贺佳. 医学统计学.6版[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2013.[64] Hungerford DS, Jones LC. Asymptomatic osteonecrosis: should it be treated? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; 429(429): 124-130.[65] Morita D, Hasegawa Y, Okura T, et al. Long-term outcomes of transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone Joint J. 2017; 99-B(2): 175-183.[66] Marker DR, Seyler TM, Ulrich SD, et al. Do modern techniques improve core decompression outcomes for hip osteonecrosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(5): 1093-1103.[67] Hernigou P, Poignard A, Manicom O, et al. The use of percutaneous autologous bone marrow transplantation in nonunion and avascular necrosis of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7): 896-902.[68] Hernigou P, Manicom O, Poignard A, et al. Core decompression with marrow stem cells. Oper Tech Orthop. 2004;14(2): 68-74. |
| [1] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [2] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [5] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [6] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [7] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [8] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [9] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [10] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [11] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [12] | Zeng Xianghong, Liang Bowei. A new strategy for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 431-437. |
| [13] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [14] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [15] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||