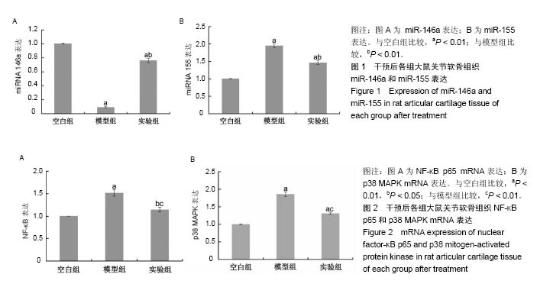
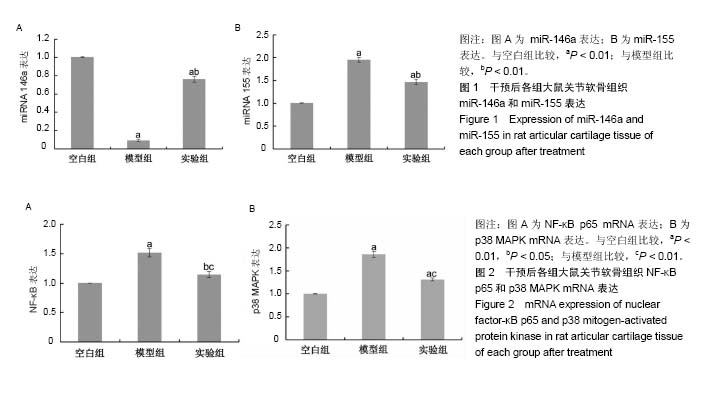
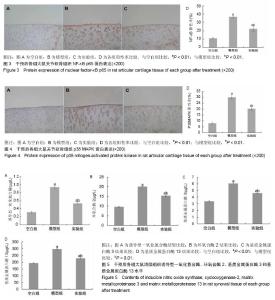
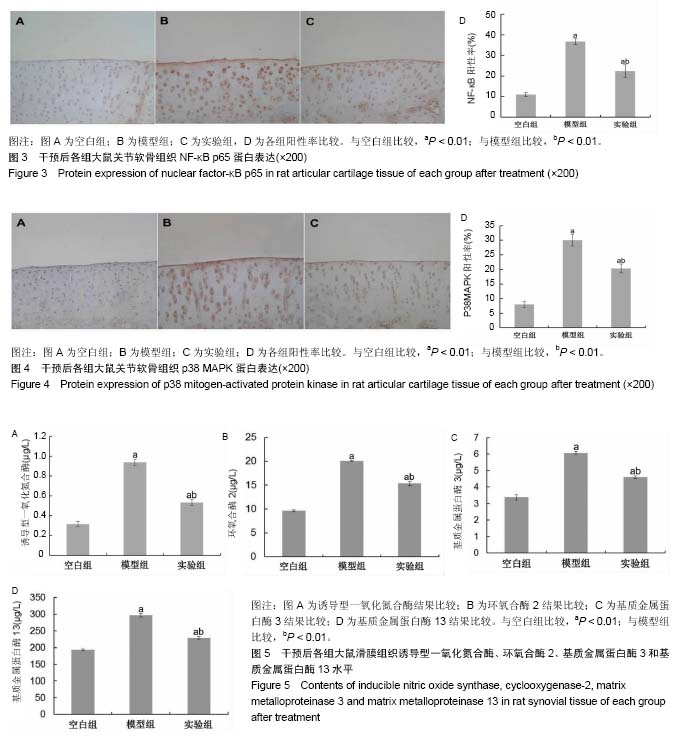
| [1] Roush JK,Cross AR,Renberg WC,et al.Evaluation of the effects of dietary supplementation with fish oil omega-3 fatty acids on weight bearing in dogs with osteoarthritis.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2010;236(1):67-73.[2] Ceppi M,Pereira PM,Dunand-Sauthier I,et al.MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(8):2735-2740.[3] Gu SX,Li X,Hamilton JL,et al.MicroRNA-146a reduces IL-1 dependent inflammatory responses in the intervertebral disc. Gene.2015;555(2):80-87.[4] Taganov KD,Boldin MP,Chang KJ,et al. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(33): 12481-12486.48[5] 王武炼,叶锦霞,刘献祥,等.独活寄生汤加减内服外洗治疗膝骨性关节炎66例临床观察[J].福建中医药大学学报, 2011,21(2): 44-46.[6] 胡慧丽.独活寄生汤加减方治疗膝骨性关节炎临床效果分析[J].临床与实践,2018,16(23):28-30.[7] 郑春松,叶蕻芝,李西海,等.分子对接法预测独活寄生汤对TNF-法和IL-1法作用的活性成分[J].福建中医药大学学报, 2012, 22(4):28-30.[8] Zheng CS, Xu XJ, Ye HZ, et al. Computational approaches for exploring the potential synergy and polypharmacology of Duhuo Jisheng Decoction in the therapy of osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(6):1812-1818. [9] 陈巧玉,周鑫,扶世杰.独活寄生汤干预食蟹猴自发性膝骨关节炎模型炎症的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(12): 1866-1871.[10] 吴广文,王武炼,潘彩彬,等.独活寄生汤含药血清对大鼠退变软骨细胞线粒体凋亡通路的影响[J].风湿病与关节炎, 2014, 3(10):5-9.[11] 刘献祥,李西海,周江涛.改良Hulth造模法复制膝骨性关节炎的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2005,25(12):1104-1108.[12] 黄继汗,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2004,9(9): 1069-1072.[13] Soslow RA, Dannenberg AJ, Rush D, et al. Cox-2 is expressed in human pulmonary, colonic, and mammary tumors. Cancer.2000;89:2637-2645.[14] Smeriqlio P,Dhulipala L,Lai JH,et al.Collagen VI Enhances Cartilage Tissue Generation by Stimulating Chondrocyte Proliferation. Tissue Enq Part A. 2015;21(3-4):840-849.[15] 高世超,殷海波,刘宏潇,等.MAPK信号通路在骨关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(5):441-444.[16] Chen F, Castranova V, Shi X. New insights into the role of nuclear factor-kappaB in cell growth regulation. Am J Pathol. 2001;159(2):387-397.[17] Ghosh S, May M J, Kopp E B. NF-κS and Rel ptoteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16(1):225-260.[18] Baldwin A.The NF-κa and Ian ptoteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;(14):649-681.[19] Karin M,Ben-Neriah Y.Phosphorlation meets ubiquition: The control of NF-κB activity. Annu Rev Immunol.2000;18(1): 621-623. [20] May MJ, Ghosh S. Signal transduction through NF-κB. Immunol Today. 1998;19(2):80-88.[21] Musikacharoen T, Matsuguchi T, Kikuchi T, et al.NF—kappa B and STAT5 play important roles in the regulation of mouse Toll-like receptor 2 gene expression. J Immunol.2001;166(7): 4516.[22] 陈宁,叶静,汤特,等.共有序列寡核苷酸竞争结合NF-κF以减少TNF产生的实验研究[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2003,19(5): 619-621. [23] Rigoglou S,Papavassiliou AG.The NF-κA signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2013;45(11): 2580-2584.[24] Brinckerhoff CE, Matrisian LM. Matrix meatlloproetinases:a tail of frog that became a prince. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002; 3(3):207-214.[25] Iliopoulos D,Malizos KN,Oikonomou P,et al.Integrative microRNA and proteomic approaches identify novel osteoarthritis genes and their collaborative metabolic and inflammatory networks.PLoS One. 2008;3(11):e3740.[26] 冯知涛.RA患者外周血miR-146a、miR-16表达与疾病活动、中医证型相关性及青藤碱制剂对其干预的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.[27] Boldin MP, Taganov KD, Rao D S, et al.miR-146α is a significant brake on autoimmunity, myeloproliferation, and cancer in mice. J Exp Med.2011;208(6):1189-1201.[28] Bluml S, Bonelli M, Niederreiter B, et al.Essential role of micro RNA-155 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum.2011;63(5):1281-1288.[29] 张烈,马歆,谢渭根. 全身炎症反应患者miR-146a的表达与病情发展相关性研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2013,23(22): 5404-5406.[30] Kurowska-Stolarska M, Alivernini S, Ballantine LE, et al. MicroRNA-155 as aproinflammatory regulator in clinical and experimental arthritis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108(27):11193-11198.[31] O'Connell RM, Kahn D, Gibson WS, et al.MicroRNA-155 promotes autoimmune inflammation by enhancing inflammatory T cell development. Immunity. 2010;33(4): 607-619. |