Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 643-649.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1046
Previous Articles Next Articles
Tranexamic acid plus drain-clamping reduces blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
Zhang Yan1, Kan Quan2, Zhang Junwei1, Wang Baohua1, Ping Shaohua1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 2School of Basic Medicine, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
-
Online:2019-02-08Published:2019-02-08 -
Contact:Zhang Yan, Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yan, Master, Attending physician, Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Research Project of Hebei Provincial Universities, No. QN2018123
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yan, Kan Quan, Zhang Junwei, Wang Baohua, Ping Shaohua. Tranexamic acid plus drain-clamping reduces blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 643-649.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
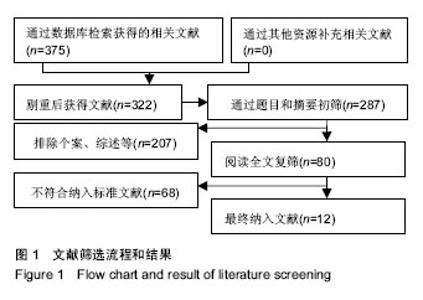
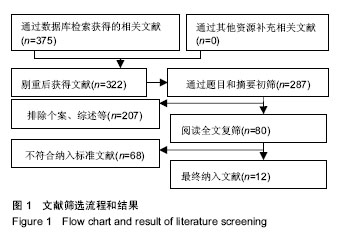
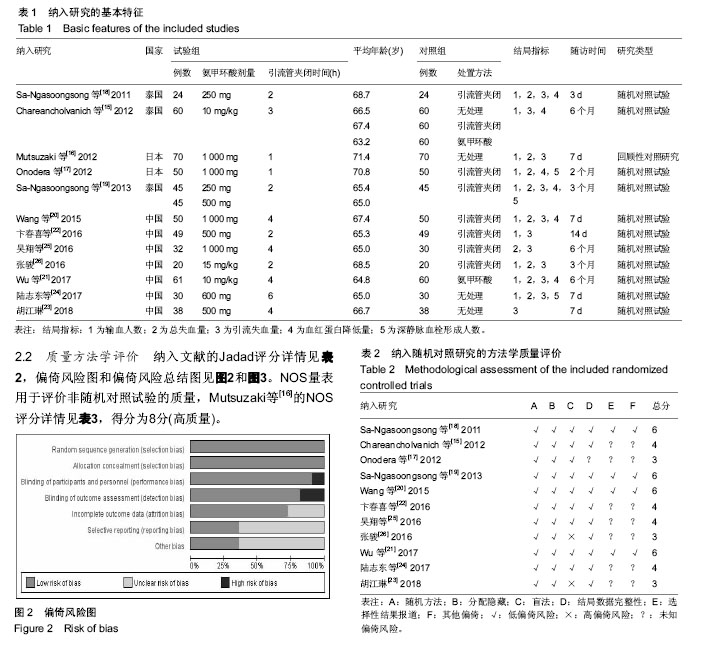
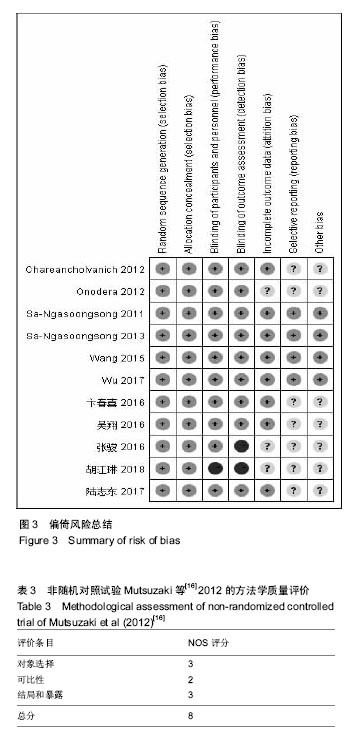
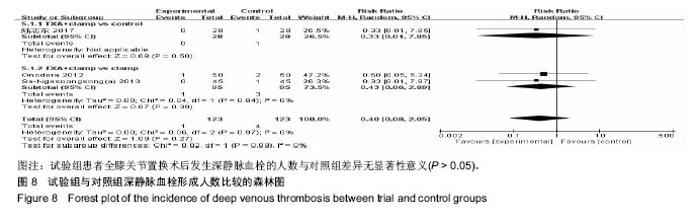
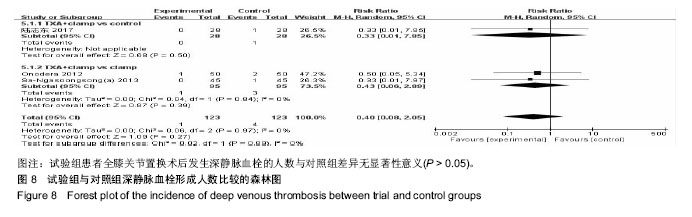
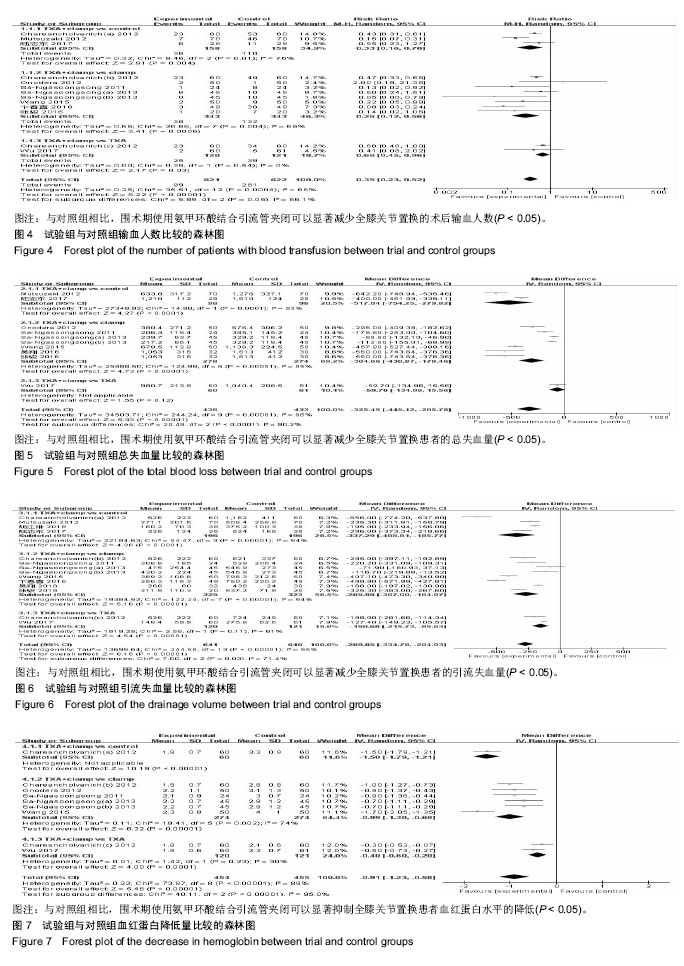
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 输血人数 试验组与对照组输血人数比较见图4,共纳入10个研究[15-22,24,26]。根据随机效应模型Meta分析结果显示,围术期使用氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭治疗的患者术后输血人数显著少于对照组,且差异有显著性意义[RR=0.35,95%CI(0.23,0.52),P < 0.05]。亚组分析结果显示,氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭组术后输血人数显著少于无处理组[RR=0.33,95%CI(0.16,0.70),P < 0.05]、单独引流管夹闭组[RR=0.26,95%CI(0.12,0.56),P < 0.05]及单独氨甲环酸组[RR=0.66,95%CI(0.45,0.96),P < 0.05]。总体结果表明,与对照组治疗方法相比,围手术期使用氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭可以显著减少全膝关节置换的术后输血人数。 2.3.2 总失血量 试验组与对照组总失血量比较见图5,共纳入9个研究[16-21,24-26]。根据随机效应模型Meta分析结果显示,围手术期使用氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭治疗的患者总失血量显著低于对照组,且差异有显著性意义[MD=-325.45,95%CI(-445.12,-205.78),P < 0.05]。亚组分析结果显示,氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭组总失血量显著低于无处理组[MD=-517.04,95%CI(-754.25,-279.82),P < 0.05]及单独引流管夹闭组[MD=-304.66,95%CI(-430.87,-178.46),P < 0.05],单独氨甲环酸组与试验组相比差异无显著性意义[MD=-59.70,95%CI(-134.96,-15.56),P > 0.05]。总体结果表明,跟对照组治疗方法相比,围手术期使用氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭可以显著减少全膝关节置换患者的总失血量。 2.3.3 引流失血量 试验组与对照组引流失血量比较见图6,共纳入11个研究[15-16,18-26]。根据随机效应模型Meta分析结果显示,围手术期使用氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭治疗的患者引流失血量显著低于对照组,且差异有显著性意义[MD=-269.85,95%CI(-334.78,-204.93),P < 0.05]。亚组分析结果显示,氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭组引流失血量显著低于无处理组[MD=-337.29,95%CI(-488.81,-185.77),P < 0.05]、单独引流管夹闭组[MD=-265.98,95%CI(-367.00,-164.97),P < 0.05]及单独氨甲环酸组[MD=-150.68,95%CI(-215.73,-85.63),P < 0.05]。总体结果表明,与对照组治疗方法相比,围手术期使用氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭可以显著减少全膝关节置换患者的引流失血量。 2.3.4 血红蛋白降低量 试验组与对照组血红蛋白降低量比较见图7,共纳入6个研究[15,17-21]。根据随机效应模型Meta分析结果显示,围手术期使用氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭治疗的患者血红蛋白降低量显著低于对照组,且差异有显著性意义[MD=-0.91,95%CI(-1.23,-0.58),P < 0.05]。亚组分析结果显示,氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭组血红蛋白降低量显著低于无处理组[MD=-1.50,95%CI(-1.79,-1.21),P < 0.05]、单独引流管夹闭组[MD=-0.99,95%CI(-1.30,-0.69),P < 0.05]及单独氨甲环酸组[MD=-0.40,95%CI(-0.60,-0.20),P < 0.05]。总体结果表明,与对照组治疗方法相比,围手术期使用氨甲环酸结合引流管夹闭可以显著抑制全膝关节置换患者血红蛋白水平的降低。"
| [1] Schilling CG, Dowsey MM, Petrie DJ, et al. Predicting the long-term gains in health-related quality of life after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(2):395-401. [2] Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785. [3] 郭斌斌,张华.人工全膝关节表面置换术的临床应用浅析[J].甘肃医药, 2017,36(11):913-916.[4] Numkanisorn S, Chareancholvanich K, Pornrattanamaneewong C. Intravenous tranexamic acid before and after tourniquet use can reduce blood loss and blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016;99(11):1220-1225. [5] Good L, Peterson E, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth. 2003;90(5):596-599. [6] Li J, Li HB, Zhai XC, et al. Topical use of topical fibrin sealant can reduce the need for transfusion, total blood loss and the volume of drainage in total knee and hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 1489 patients. Int J Surg. 2016;36:127-137. [7] Li JF, Li H, Zhao H, et al. Combined use of intravenous and topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Oorthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):12-22. [8] Li B, Liu ZT, Shen P, et al. Comparison of therapeutic effects between drainage blood reinfusion and temporary clamping drainage after total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clinics. 2015 ; 70(3):202-206. [9] Fillingham YA, Ramkumar DB, Jevsevar DS, et al. The efficacy of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a network meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;5(18):425-430. [10] Gianakos AL, Hurley ET, Haring RS, et al. Reduction of blood loss by tranexamic acid following total hip and knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. JBJS Rev. 2018;6(5):e1. [11] Kiely N, Hockings M, Gambhir A. Does temporary clamping of drains following knee arthroplasty reduce blood loss? A randomised controlled trial. Knee. 2001;8(4):325-327. [12] Mccormick F, Cvetanovich GL, Kim JM, et al. An assessment of the quality of rotator cuff randomized controlled trials: utilizing the Jadad score and CONSORT criteria. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(9): 1180-1185. [13] Oremus M, Oremus C, Hall GB, et al. Inter-rater and test-retest reliability of quality assessments by novice student raters using the Jadad and Newcastle-Ottawa Scales. BMJ Open. 2012;2(4):136-138. [14] 罗杰,冷卫东.系统评价/Meta分析理论与实践[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2013,5(2):115.[15] Chareancholvanich K, Siriwattanasakul P, Narkbunnam R, et al. Temporary clamping of drain combined with tranexamic acid reduce blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:124. [16] Mutsuzaki H, Ikeda K. Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid via a drain plus drain-clamping to reduce blood loss in cementless total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2012;7:32.[17] Onodera T, Majima T, Sawaguchi N, et al. Risk of deep venous thrombosis in drain clamping with tranexamic acid and carbazochrome sodium sulfonate hydrate in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(1):105-108. [18] Sa-Ngasoongsong P, Channoom T, Kawinwonggowit V, et al. Postoperative blood loss reduction in computer-assisted surgery total knee replacement by low dose intra-articular tranexamic acid injection together with 2-hour clamp drain: a prospective triple-blinded randomized controlled trial. Orthop Rev. 2011;3(2):12. [19] Sa-Ngasoongsong P, Wongsak S, Chanplakorn P, et al. Efficacy of low-dose intra-articular tranexamic acid in total knee replacement; a prospective triple-blinded randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:340. [20] Wang G, Wang D, Wang B, et al. Efficacy and safety evaluation of intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty operation with temporarily drainage close. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(8):14328-14334. [21] Wu Y, Yang T, Zeng Y, et al. Clamping drainage is unnecessary after minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty in patients with tranexamic acid: A randomized, controlled trial. Medicine. 2017;96(7):5804. [22] 卞春喜,耿秋丽,马永成,等.氨甲环酸关节腔内灌注联合2小时引流管夹闭在初次单侧全膝关节置换术后失血量的临床研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2016,13(1):10-12.[23] 胡江琳.全膝关节置换术患者局部应用氨甲环酸以及引流管夹闭的护理及对患者出血量的影响[J].世界最新医学信息文摘, 2018,18(37): 250-251.[24] 陆志东,谭希鹏,李鹏,等.局部使用氨甲环酸联合夹闭引流管6 h减少人工全膝关节置换术后失血量[J].宁夏医学杂志, 2017,39(9):778-781.[25] 吴翔,朱光勇,陈杰.局部使用氨甲环酸结合临时夹闭引流管减少全膝关节置换术后出血效果观察[J].浙江创伤外科, 2016,21(2):355-356.[26] 张骏.静脉和局部联合应用氨甲环酸配合夹闭引流管在膝关节置换中的疗效分析[J].临床医药文献电子杂志, 2016,3(31):6165-6166.[27] Steinhaus ME, Christ AB, Cross MB. Total knee arthroplasty for knee osteoarthritis: support for a foregone conclusion? HSS J. 2017;13(2): 207-210. [28] Carling MS, Jeppsson A, Eriksson BI, et al. Transfusions and blood loss in total hip and knee arthroplasty: a prospective observational study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:48. [29] Wang JW, Chen B, Lin PC, et al. The efficacy of combined use of rivaroxaban and tranexamic acid on blood conservation in minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty a double-blind randomized, controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(3):801-806. [30] Song EK, Seon JK, Prakash J, et al. Combined administration of iv and topical tranexamic acid is not superior to either individually in primary navigated tka. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(1):37-42. [31] Zekcer A, Priori RD, Tieppo C, et al. Comparative study of topical vs. intravenous tranexamic acid regarding blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Rev Bras Ortop. 2017;52(5):589-595. [32] Napolitano LM, Cohen MJ, Cotton BA, et al. Tranexamic acid in trauma: how should we use it? J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;74(6): 1575-1586. [33] Prasad N, Padmanabhan V, Mullaji A. Comparison between two methods of drain clamping after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(6):381-384. [34] Keska R, Paradowski TP, Witonski D. Outcome in primary cemented total knee arthroplasty with or without drain: A prospective comparative study. Indian J Orthop. 2014;48(4):404-409. [35] Kim YH, Cho SH, Kim RS. Drainage verus no ndrainage in simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop. 1998;347: 188-193. [36] 荆鑫,滕红林,吴海山,等.全关节置换术后关节腔引流问题的探讨[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,20(13):1295-1297.[37] Huang Z, Ma J, Pei F, et al. Meta-analysis of temporary versus no clamping in TKA. Orthopedics. 2013;36(7):543-550. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [5] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [6] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [7] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [8] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [9] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [10] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [11] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [12] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [13] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [14] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||