Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (20): 3269-3274.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0231
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation of the signaling pathways of bone metabolism and lipid metabolism with bone metabolism related diseases: theoretical advance and research direction
Bo Mao-sheng1, Zhao Jian-ning1, Hong Ye2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Jinling Hospital Affiliated to Medical School of Nanjing University (Nanjing General Hospital), Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2017-12-23Online:2018-07-18Published:2018-07-18 -
Contact:Zhao Jian-ning, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Jinling Hospital Affiliated to Medical School of Nanjing University (Nanjing General Hospital), Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Bo Mao-sheng, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Jinling Hospital Affiliated to Medical School of Nanjing University (Nanjing General Hospital), Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bo Mao-sheng1, Zhao Jian-ning1, Hong Ye2. Correlation of the signaling pathways of bone metabolism and lipid metabolism with bone metabolism related diseases: theoretical advance and research direction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(20): 3269-3274.
share this article
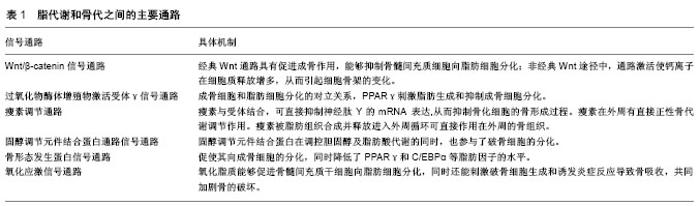
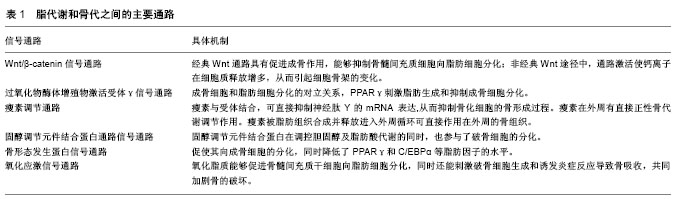
2.1 脂代谢与骨代谢的主要通路 脂代谢和骨代谢二者息息相关,由多条通路调控,包括无翼型MMTV整合位点通路(Wnt/β-catenin)、PPARγ、瘦素调节通路、骨形态发生蛋白通路、低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5通路、固醇调节元件结合蛋白通路、氧化应激通路等[11-15]。了解这些通路在调节脂代谢和骨代谢平衡的机制,可以为治疗骨代谢相关疾病提供新的靶点(表1)。 2.1.1 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 成骨细胞和脂肪细胞来源于骨髓间充质干细胞,骨髓间充质干细胞具有向这2种细胞分化的能力,调控两种细胞之间相互转化的有两条通路,其中一条通路为Wnt/β-catenin信号通路[16]。Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中存在一条经典途径和一条非经典途径。在经典途径中,Wnt蛋白(主要为Wnt-1,Wnt-3a,"
| [1] Derks TGJ, van Rijn M. Lipids in hepatic glycogen storage diseases: pathophysiology, monitoring of dietary management and future directions. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015;38(3):537-543.[2] Cao PQ, Pan HT, Xiao TC, et al. Advances in the study of the antiatherogenic function and novel therapies for HDL. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(8):17245-17272.[3] Kanis JA, Burlet N, Cooper C, et al. European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19(4): 399-428.[4] Yoo TK, Sung KK, Deok WK, et al. Osteoporosis risk prediction for bone mineral density assessment of postmenopausal women using machine learning. Yonsei Med J. 2013;54(6):1321-1330.[5] Liu HF, He HC, Yang L, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields for postmenopausal osteoporosis and concomitant lumbar osteoarthritis in southwest China using proximal femur bone mineral density as the primary endpoint: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16:265.[6] 张冰雨,曾瑞翔,雷涛.脂代谢与骨代谢相关机制的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,10:1263-1266.[7] Nishikawa A, Ishida T, Taketsuna M, et al. Safety and effectiveness of daily teriparatide in a prospective observational study in patients with osteoporosis at high risk of fracture in Japan: final report.Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11: 913-925.[8] Tian L, Yu XJ.Lipid metabolism disorders and bone dysfunction-interrelated and mutually regulated (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2015; 12(1): 783-794.[9] Imai Y, Youn MY, Inoue K. Nuclear receptors in bone physiology and diseases. Physiol Rev. 2013; 93(2): 481-523.[10] Go GW. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) is a novel nutritional therapeutic target for hyperlipidemia, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and atherosclerosis. Nutrients. 2015; 7(6): 4453-4464.[11] Kojetin DJ, Matta-Camacho E, Hughes TS, et al.Structural mechanism for signal transduction in RXR nuclear receptor heterodimers. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:8013.[12] Liu LF, Shen WJ, Zhang ZH, et al. Adipocytes decrease Runx2 expression in osteoblastic cells: roles of PPARgamma and adiponectin. J Cell Physiol. 2010; 225(3):837-845.[13] Wu M, Chen G, Li YP. TGF-beta and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 2016; 4:16009.[14] Park JG, Lee DH, Moon YS, et al. Reversine increases the plasticity of lineage-committed preadipocytes to osteogenesis by inhibiting adipogenesis through induction of TGF-beta pathway in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014; 446(1):30-36.[15] Haasters F, Docheva D, Gassner C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from osteoporotic patients reveal reduced migration and invasion upon stimulation with BMP-2 or BMP-7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;452(1): 118-123.[16] TakadaI, Kouzmenko AP, Kato S.Molecular switching of osteoblastogenesis versus adipogenesis: implications for targeted therapies. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009;13(5): 593-603.[17] Liu Y, Huang L, Hao B, et al., Use of an osteoblast overload damage model to probe the effect of icariin on the proliferation, differentiation and mineralization of MC3T3-E1 cells through the Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.2017; 41(4): 1605-1615.[18] Zhao C, Li Y, Wang X, et al. The effect of uniaxial mechanical stretch on Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway in bone mesenchymal stem cells. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(1):113-117.[19] Zhou R, Yuan Z, Liu J, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide promotes the expression of osteoblastic genes and activates the WNT signal transduction pathway in bone marrow stromal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016; 13(6): 4689-4696.[20] Marques-Pinheiro A, Levasseur R, Cormier C, et al. Novel LRP5 gene mutation in a patient withosteoporosispseudoglioma syndrome. Joint Bone Spine, 2010;77(2):151-153.[21] Gong Y, Slee RB, Fukai N, et al. LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell. 2001; 107(4): 513-523.[22] Jiang XY, Chen Y, Xu L, et al. Association of LPR5 polymorphism with bone mass density and cholesterol level in population of Chinese Han. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2010; 118(6): 388-391.[23] Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, et al. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Wnt signaling. Science. 2000; 289(5481): 950-953.[24] MaedaK, Kobayashi Y, Udagawa N, et al. Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling between osteoblast-lineage cells and osteoclast precursors enhances osteoclastogenesis. Nat Med. 2012;18(3): 405-412.[25] Weivoda M, Ruan M, Hachfeld CM, et al. Wnt Signaling inhibits osteoclast differentiation by activating canonical and noncanonical cAMP/PKA pathways. J Bone Miner Res.2016;31(1):65-75.[26] Kim J, Lee YJ, Kim JM, et al. PPARgamma agonists induce adipocyte differentiation by modulating the expression of Lipin-1, which acts as a PPARgamma phosphatase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2016; 81: 57-66.[27] Mori H, Okada Y, Tanaka Y. The effects of pioglitazone on bone formation and resorption markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Intern Med. 2017;56(11):1301-1306.[28] AhmadianM, Suh JM, Hah N, et al. PPARgamma signaling and metabolism: the good, the bad and the future. Nat Med. 2013; 19(5): 557-566.[29] Brun J, Berthou F, Trajkovski M, et al. Bone regulates browning and energy metabolism through mature osteoblast/dsteocyte PPARgamma Expression. Diabetes. 2017.[30] Blair HC. Kalyvioti E, Papachristou NI, et al. Apolipoprotein A-1 regulates osteoblast and lipoblast precursor cells in mice. Lab Invest. 2016;96(7):763-772.[31] ZhangS, Feng P, Mo G, et al. Icariin influences adipogenic differentiation of stem cells affected by osteoblast-osteoclast co-culture and clinical research adipogenic. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017; 88: 436-442.[32] Farr OM, Gavrieli A, Mantzoros CS. Leptin applications in 2015: What have we learned about leptin and obesity? Metabolism. 2015; 22(5): 353-359.[33] Farooqi IS, Keogh JM, Kamath S, et al. Partial leptin deficiency and human adiposity. Nature. 2001;414(6859): 34-35.[34] Philbrick KA, Turner RT, Branscum AJ, et al. Paradoxical effects of partial leptin deficiency on bone in growing female mice. Anat Rec (Hoboken).2015; 298(12): 2018-2029.[35] Foo JP, Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD, et al.The effect of leptin replacement on parathyroid hormone, RANKL-osteoprotegerin axis, and Wnt inhibitors in young women with hythalamic amenorrhea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2014; 99(11):e2252-2258.[36] Hamrick MW, Pennington C, Newton D, et al. Leptin deficiency produces contrasting phenotypes in bones of the limb and spine. Bone. 2004 ;34(3):376-383.[37] Upadhyay J, Farr OM, Mantzoros CS. The role of leptin in regulating bone metabolism. Metabolism. 2015; 64(1): 105-113.[38] Xu JC, Wu GH, Zhou LL, et al. Leptin improves osteoblast differentiation of human bone marrow stroma stem cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2016; 20(16): 3507-3513.[39] Thomas T, Burguera B, Melton LJ , et al. Role of serum leptin, insulin, and estrogen levels as potential mediators of the relationship between fat mass and bone mineral density in men versus women. Bone. 2001; 29(2): 114-120.[40] Chen XX, Yang T. Roles of leptin in bone metabolism and bone diseases. J Bone Miner Metab.2015;33(5): 474-485.[41] Inoue K, Imai Y. Fatostatin, an SREBP inhibitor, prevented RANKL-induced bone loss by suppression of osteoclast differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015; 1852(11): 2432-2441.[42] Wu M, Chen G, Li YP. TGF-beta and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res.2016;4:16009.[43] Park JG, Lee DH, Moon YS, et al. Reversine increases the plasticity of lineage-committed preadipocytes to osteogenesis by inhibiting adipogenesis through induction of TGF-beta pathway in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2014;446(1): 30-36.[44] Wu Q, Zhong ZM, Pan Y, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel marker of oxidative stress in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Med Sci Monit. 2015; 21: 2428-2432.[45] Xiao Y, Cui J, Li YX, et al. Dyslipidemic high-fat diet affects adversely bone metabolism in mice associated with impaired antioxidant capacity. 2011;27(2): 214-220.[46] Hyeon S, Lee H, Yang Y, et al. Nrf2 deficiency induces oxidative stress and promotes RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;65:789-799.[47] Corwin RL, Hartman TJ, Maczuga SA, et al. Dietary saturated fat intake is inversely associated with bone density in humans: analysis of NHANES III. J Nutr. 2006;136(1):159-165.[48] Fehrendt H, Linn T, Hartmann S, et al. Negative influence of a long-term high-fat diet on murine bone architecture. Int J Endocrinol. 2014; 2014:1-9.[49] Park SW, Nam GE, Jung DW,et al. Association of lipid parameters and insulin resistance with bone health in South Korean adolescents. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(2): 635-642.[50] 陈劲松,栾晓军,许雪娟,等.中老年男性骨密度与脂代谢关系研究[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2012,23: 95-98.[51] 王自力.左卡尼汀对肥胖骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折患者术后恢复及脂代谢影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,5:542-546.[52] Di CC, Tommaselli GA, Gargano V, et al. Effects of estrogen-progestin therapy on serum levels of RANKL, osteoprotegerin, osteocalcin, leptin, and ghrelin in postmenopausal women. Menopause, 2007. 14(1): p. 38-44.[53] Tanna N, Patel K, Moore AE, et al. The relationship between circulating adiponectin, leptin and vaspin with bone mineral density (BMD), arterial calcification and stiffness: a cross-sectional study in post-menopausal women. J Endocrinol Invest. 2017.[54] Ajeganova S, Andersson ML, Hafstrom I. Association of obesity with worse disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis as well as with comorbidities: a long-term followup from disease onset. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013;65(1): 78-87.[55] Halade GV, Jamali AEl, Williams PJ, et al. Obesity-mediated inflammatory microenvironment stimulates osteoclastogenesis and bone loss in mice. Exp Gerontol.2011;46(1): 43-52.[56] Loredo-Pérez AA, Montalvo-Blanco CE, Hernández-González LI, et al. High-fat diet exacerbates pain-like behaviors and periarticular bone loss in mice with CFA-induced knee arthritis. Obesity. 2016; 24(5): 1106-1115.[57] Hu Y, Lin H, Dib B, et al. Cholesterol crystals induce inflammatory cytokines expression in a human retinal pigment epithelium cell line by activating the NF-kappaB pathway. Discov Med. 2014;18(97): 7-14.[58] Monika P, Geetha A. The modulating effect of Persea americana fruit extract on the level of expression of fatty acid synthase complex, lipoprotein lipase, fibroblast growth factor-21 and leptin--A biochemical study in rats subjected to experimental hyperlipidemia and obesity. Phytomedicine. 2015. 22(10):939-945. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [4] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [5] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [6] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [7] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [8] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [9] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [10] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [11] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [12] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [13] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [14] | Xiao Fangjun, Chen Shudong, Luan Jiyao, Hou Yu, He Kun, Lin Dingkun. An insight into the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza intervention on osteoporosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 772-778. |
| [15] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||