Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (23): 3694-3699.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.23.015
Previous Articles Next Articles
Diagnosis and prevention of deep vein thrombosis after spine surgery in the elderly
Yang Li-yong1, Ma Hai-gang2, Li Zhen1, Zao Dong-yang1, Zhang Ji1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, No. 1 People’s Hospital of Dali City, Dali 671000, Yunnan Province, China; 2Digestive Endoscopy Room, Naimanqi People’s Hospital, Tongliao 028300, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2017-08-18Published:2017-09-01 -
About author:Yang Li-yong, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, No. 1 People’s Hospital of Dali City, Dali 671000, Yunnan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Li-yong, Ma Hai-gang, Li Zhen, Zao Dong-yang, Zhang Ji. Diagnosis and prevention of deep vein thrombosis after spine surgery in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(23): 3694-3699.
share this article
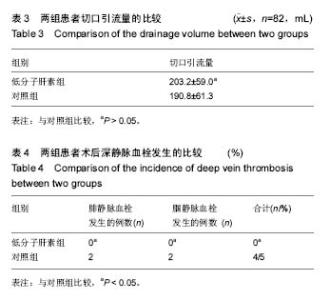
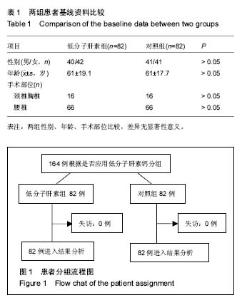
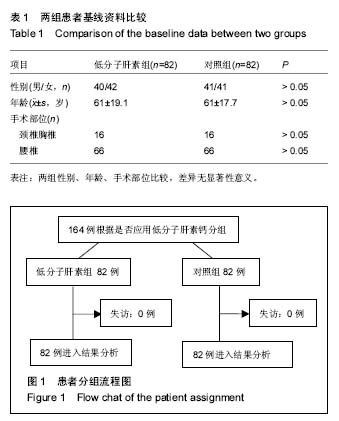
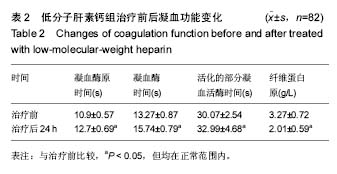
2.4 两组术后深静脉血栓发生的比较 对照组82例患者中,4例(5%)出现下肢肿胀,并在术后第1周行彩色多普勒超声检查发现有静脉血栓的形成,2例深静脉血栓形成患者血栓发生的部位在小腿腓静脉,2例深静脉血栓发生的部位是在腘静脉,血栓形成未在股静脉和髂静脉发现,这4例患者中,男性2例,女性2例,年龄范围67-88岁,平均年龄为71.7岁,只有1例有轻微的临床症状,无患者死亡。低分子肝素钙组患者中脊柱术后未出现肢体压痛及肿胀,彩色多普勒超声检查未发现下肢静脉血栓的形成。对照组与低分子肝素钙组相比,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,见表4)。 2.5 并发症 治疗组中无并发出现黑便、咯血、鼻出血及牙龈出血等并发症。"
| [1] Giuntini C, Di Ricco G, Marini C, et al. Pulmonaryembolism: epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management . Chest.1995;107(1 Suppl): 3-9.[2] Kiluk IE, Krajewska A, Kosacka U, et al. manifestations of pulmonary embolism in younger compared to older patients: Clinical presentation, prediction rules and long-term outcomes. Adv Med Sci.2017;62(2):254-258.[3] Sobreira ML, Rogatto SR, Dos Santos RM, et al.An Unexpectedly High rate of Thrombophilia Disorders in Patients with Superficial Vein Thrombosis of the Lower Extremities. Ann Vasc Surg. 2017;10(16)30897-30894.[4] Bahloul M, Chelly H, Regaieg K,et al. Pulmonary embolism following severe traumatic brain injury: incidence, risk factors and impact outcome.Intensive Care Med.2017;11(5):897-893.[5] Wang CJ, Wang JW,Chen LM,et,al. Deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. J Formos Med Assoc.2000;99:848-853.[6] Weinberg DS, Hedges BZ, Belding JE,et al.Risk factors for pulmonary complication following operative fixation of spine fractures.Spine J.2017;8(17):30199-30197.[7] Cook AD, Gross BW, Osler TM,et al.Vena Cava Filter Use in Trauma and Rates of Pulmonary Embolism, 2003-2015.JAMA Surg.2017;10(15):199-203.[8] Saigal D, Ganjoo P, Tetarway M,et al.Acute pulmonary edema and thrombocytopenia following venous air embolism during sitting position neurosurgery.Asian J Neurosurg.2017;12(2): 214-216. [9] Leon L, Rodriguez H, Tawk RG, et al. The prophylactic use of inferiorvena cava filters in patients undergoing high-risk spinal surgery. Ann Vasc Surg.2005;19(3):442-447.[10] Zaw HM,Osborne IC,Pettit PN, et al. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism in orthopedic surgery. Isr Med Assoc J. 2002; 4(11):1040-1042.[11] Chu JN, Maselli J, Auerbach AD,et al.The risk of venous thromboembolism with aspirin compared to anticoagulants after hip and knee arthroplasty.Thromb Res. 2017;12(10): 155:65-71. [12] Kim S, Ahn H, Shin SA,et al.Trends of thromboprophylaxis and complications after major lower limb orthopaedic surgeries in Korea: National Health Insurance Claim Data.Thromb Res.2017;26(4):48-52.[13] Hwang HG, Koo SM, Uh ST,et al.The Perioperative Management of Antithrombotic Therapies Using Enoxaparin.J Korean Med Sci.2017; 32(6):942-947.[14] Marrochi LCR. Prophylaxis of Venous Thromboembolism in Home Care: An Integrative Review.Home Healthc Now.2017; 35(5):268-276.[15] Cheng JS, Arnold PM, Anderson PA, et al. Anticoagulation risk in spine surgery. Spine. 2010;35(9 Suppl):117-124.[16] Audibert G, Faillot T, Vergnes MC, et al. Thromboprohylaxis in elective spinal and spinal cord surgery. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2005;24(8): 928-934.[17] 许建强,张庆俊.脊髓损伤后的高凝状态[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2002,12(6):422- 423.[18] Nagamalesh UM, Prakash VS, Naidu KC, et al. Acute pulmonary thromboembolism: Epidemiology, predictors, and long-term outcome-A single center experience.Indian Heart J. 2017;69(2):160-164.[19] Barco S, Corti M, Trinchero A, et al. Survival and recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with first proximal or isolated distal deep vein thrombosis and no pulmonary embolism.J Thromb Haemost.2017;25(5)145-157. [20] Landisch RM, Hanson SJ, Cassidy LD,et al. Evaluation of guidelines for injured children at high risk for venous thromboembolism: A prospective observational study.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2017;82(5):836-844.[21] Ahmad J, Lynch MK, Maltenfort M,et al.Incidence and Risk Factors of Venous Thromboembolism After Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgery.Foot Ankle Spec.2017;17(4):834-841.[22] Velmahos GC, Arroyo H, Ramicone E, et al. Timing of fracture fixation in blunt trauna patients with severe head injures.Am J Surg.1998;176(4):324-329.[23] Roberts SH, Lawrence SM.CE: Venous Thromboembolism: Updated Management Guidelines.Am J Nurs.2017;117(5):38-47. [24] Mitsunaga MM, Kogachi S, Yoon HC,et al.Risk of Venous Thromboembolism after a Single Normal Proximal Lower Extremity Venous Ultrasound. Perm J. 2017;21(5):38-47.[25] 王学文,王振义.抗凝治疗的进展[J].国外医学输血及血液学分册, 1993,16(1):4.[26] Lim S, Edelstein AI, Patel AA, et al. Risk factors for postoperative infections following single level lumbar fusion surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;40:1022-1032.[27] Chahoud J, Kanafani Z, Kanj SS. Surgical site infections following spine surgery: eliminating the controversies in the diagnosis. Front Med(Lausanne). 2014;1:7.[28] Chiang HY, Herwaldt LA, Blevins AE, et al. Effectiveness of local vancomycin powder to decrease surgical site infections: a meta-analysis. Spine J. 2014;14:397-407.[29] Srinivasan D, La Marca F, Than KD, et al. Perioperative characteristics and complications in obese patients undergoing anterior cervical fusion surgery. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21:1159-1162.[30] Tetreault L, Nouri A, Singh A, et al. An assessment of the key predictors of perioperative complications in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy undergoing surgical treatment: results from a survey of 916 AO Spine International Members. World Neurosurg. 2015;83:679-690.[31] Rihn JA, Lee JY, Ward WT. Infection after the surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: evaluation of the diagnosis, treatment, and impact on clinical outcomes. Spine. 2008;33: 289-294. [32] Kanafani ZA, Dakdouki GK, El-Dbouni O, et al. Surgical site infections following spinal surgery at a tertiary care center in Lebanon: incidence, microbiology, and risk factors. Scand J Infect Dis. 2006;38:589-592. [33] Sasso RC, Garrido BJ. Postoperative spinal wound infections. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16:330-337.[34] An HS, Seldomridge JA. Spinal infections: diagnostic tests and imaging studies. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;444:27-33.[35] Pull ter Gunne AF, Mohamed AS, Skolasky RL,et al. The presentation, incidence, etiology, and treatmentof surgical site infections after spinal surgery. Spine. 2010;35:1323-1328.[36] Enoch DA,Cargill JS, Laing R.Value of CT-guided biopsy in the diagnosis of septic discitis. J Clin Pathol. 2008;6:750-753.[37] Chaudhary SB, Vives MJ, Basra SK. Postoperative spinal wound infections and postprocedural discitis. J Spinal Cord Med. 2007;30:441-451.[38] Mok JM, Guillaume TJ, Talu U, et al. Clinical outcome of deep wound infection after instrumented posterior spinal fusion: a matched cohort analysis. Spine. 2009;34:578-583.[39] Collins I, Wilson-MacDonald J, Chami G, et al. The diagnosis and management of infection following instrumented spinal fusion. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:445-450.[40] Mehbod AA, Ogilvie JW, Pinto MR,et al. Postoperative deep infections in adults after spinal fusion: management with vacuum-assisted wound closure.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005; 18:14-17.[41] Akins PT, Harris J, Alvarez JL, et al. Risk factors associated with 30-day readmissions after instrumented spine surgery in 14,939 patients. Spine (PhilaPa 1976). 2015;40:1022-1032.[42] Bydon M, Macki M, De la Garza-Ramos R, et al. Smoking as an independent predictor of reoperation after lumbar laminectomy: a study of 500 cases. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015; 22:288-293.[43] Lim S, Edelstein AI, Patel AA, et al. Risk factors for postoperative infections following single level lumbar fusion surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;40:1022-1032.[44] GREEN D, IEE M Y, IIM A C, et al. Prevention of thromboembolism after spinal cord injury using low molecular weight heparin. Ann Internal Med.1990; 113(8):571-574.[45] Hill BW, Emohare O, Song B, et al. The use of vancomycin powder reduces surgical reoperation in posterior instrumented and noninstrumented spinal surgery. Acta neurochirurgica. 2014;156:749-754. [46] Theologis AA, Demirkiran G, Callahan M, et al. Local intrawound vancomycin powder decreases the risk of surgical site infections in complex adult deformity reconstruction: a cost analysis. Spine. 2014;39:1875-1880. [47] Martin JR, Adogwa O, Brown CR, et al. Experience with intrawound vancomycin powder for spinal deformity surgery. Spine. 2014;39:177-184. [48] Armaghani SJ, Menge TJ, Lovejoy SA, et al. Safety of topical vancomycin for pediatric spinal deformity: nontoxic serum levels with supratherapeutic drain levels. Spine. 2014,39: 1683-1687.[49] Rayes M, Colen CB, Bahqat DA, et al. Safety of instrumentation in patients with spinal infection. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;12: 647-659.[50] Sierra-Hoffman M, Jinadatha C, Carpenter JL, et al. MD-Postoperative Instrumented Spine Infections:A Retrospective Review. South Med J. 2010;1(103):25-30.[51] Turnbull F. Postoperative in?ammatory disease of lumbar discs.J Neurosurg.1953;10:469-473.[52] Liu X, Wang Y, Qiu G, et al. A systematic review with meta-analysis of posterior interbody fusion versus posterolateral fusion in lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2014;23:43-56.[53] Maruo K, Berven SH. Outcome and treatment of postoperative spine surgical site infections: predictors of treatment success and failure. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19: 398-404.[54] Calvert G, May LA, Theiss S. Use of permanently placed metal expandable cages for vertebral body reconstruction in the surgical treatment of spondylodiscitis. Orthopedics. 2014;37:e536-542.[55] Deep K, Jigajinni MV, McLean AN, et al.Prophylaxis of thromboembolism in spinal injuries-results of enoxaparin used in 276 patients. Spinal Cord. 2001;39(2):88-91.[56] Chiang HY, Herwaldt LA, Blevins AE, et al. Effectiveness of local vancomycin powder to decrease surgical site infections: a meta-analysis. Spine J. 2014;14(3):397-407. [57] Tomov M, Mitsunaga L, Durbin-Johnson B, et al. Reducing surgical site infection in spinal surgery with betadine irrigation and intrawound vancomycin powder. Spine. 2015;40:491-499. [58] Ghobrial GM, Thakkar V, Andrews E, et al. Intraoperative vancomycin use in spinal surgery: single institution experience and microbial trends. Spine. 2014;39:550-555. [59] Bakhsheshian J, Dahdaleh NS, Lam SK, et al. The use of vancomycin powder in modern spine surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical evidence. World Neurosurgery. 2015;83:816-823. [60] Hill BW, Emohare O, Song B, et al. The use of vancomycin powder reduces surgical reoperation in posterior instrumented and noninstrumented spinal surgery. Acta Neurochirurgica. 2014;156:749-754. [61] Theologis AA, Demirkiran G, Callahan M, et al. Local intrawound vancomycin powder decreases the risk of surgical site infections in complex adult deformity reconstruction: a cost analysis. Spine. 2014;39:1875-1880. [62] Martin JR, Adogwa O, Brown CR, et al. Experience with intrawound vancomycin powder for spinal deformity surgery. Spine. 2014;39:177-184. [63] Armaghani SJ, Menge TJ, Lovejoy SA, et al. Safety of topical vancomycin for pediatric spinal deformity: nontoxic serum levels with supratherapeutic drain levels. Spine. 2014,39: 1683-1687.[64] Eder C, Schenk S, Trifinopoulos J, et al. Does intrawound application of vancomycin influence bone healing in spinal surgery? Eur Spine J. 2016;25(4):1021-1028.[65] Zebala LP, Chuntarapas T, Kelly MP, et al. Intrawound vancomycin powder eradicates surgical wound contamination: an in vivo rabbit study. J Bone Joint Surg. 2014;96:46-51. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Yu Chengxiang, Liu Lehong, Li Wenbo, Chen Jinshi, Ran Chunlei, Wang Zhongping. Correlation between spine-pelvic sagittal parameters and prognosis of vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1412-1417. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [5] | Liu Yuhang, Zhou Jianqiang, Xu Xuebin, Qu Xingyue, Li Ziyu, Li Kun, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Zhang Shaojie. Establishment and validation of finite element model of lower cervical spine in 6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 870-874. |
| [6] | Li Yuqiao, Sun Tianwei, Ma Bin, Zhou Zhaohong, Dong Runbei, Wu Haiyang. A comparative study of imaging parameters and quality of life scores between subtypes of lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 943-948. |
| [7] | Li Jian, Bao Zhengqi, Zhou Pinghui, Zhu Ruizhi, Li Zhixiang, Wang Jinzi. Effects of posterior single open-door laminoplasty and anterior cervical corpectomy fusion on cervical sagittal balance parameters in the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 949-953. |
| [8] | Yi Xinrong, Jia Fuquan, He Xin, Zhang Shaojie, Ren Xiaoyan, Li Zhijun. Establishment of cervical bone age equation for male adolescents aged 8-16 years old in Hohhot based on thin-slice CT [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 954-958. |
| [9] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [10] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [11] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [12] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [13] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [14] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [15] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||