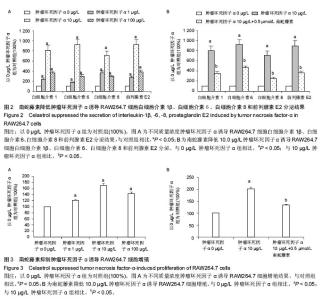
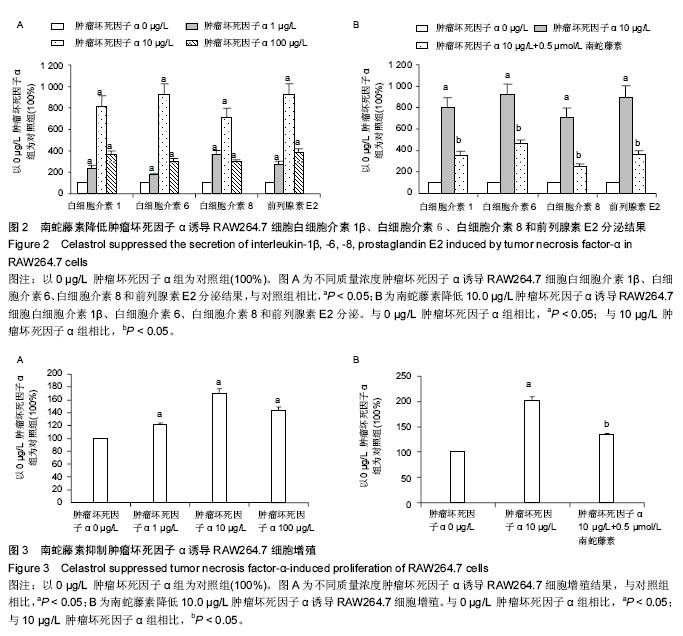
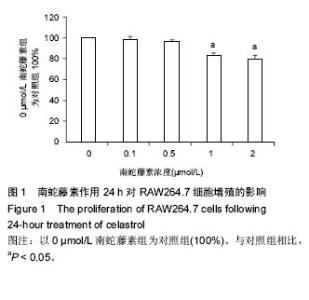
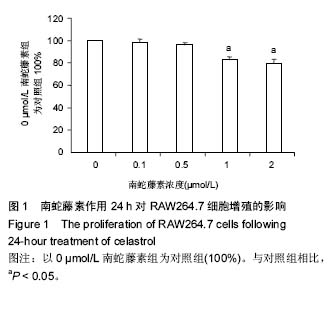
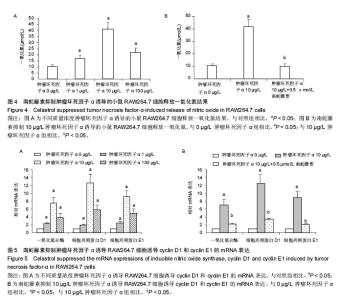
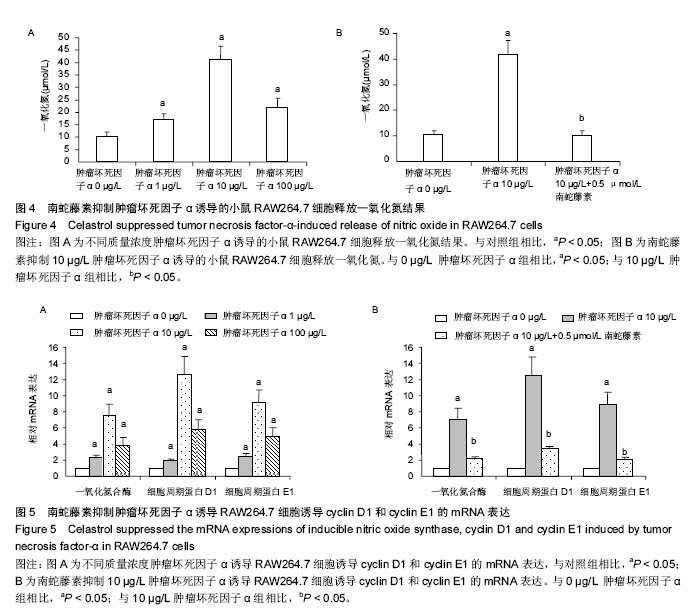
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (37): 5552-5559.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.37.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Celastrol inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced proliferation and inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cells
Chen Guang-fu1, Guo Yuan-qing2, Wu Yu-tian3
- 1Department of Spine Surgery, the Affiliated Foshan Chancheng District Center Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Foshan 528031, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Sun Yat-sen University No.5 Hospital, Zhuhai 519000, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Pharmacy, the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2016-09-09Published:2016-09-09 -
About author:Chen Guang-fu, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Spine Surgery, the Affiliated Foshan Chancheng District Center Hospital, Guangdong Medical University, Foshan 528031, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Planning Project of Zhuhai, China, No. 2014D0401990016
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Guang-fu, Guo Yuan-qing, Wu Yu-tian. Celastrol inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced proliferation and inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(37): 5552-5559.
share this article
| [1] Ma Y, Pope RM. The role of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(5): 569-580. [2] McCaulley ME, Grush KA. Alzheimer's Disease: Exploring the Role of Inflammation and Implications for Treatment. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;2015: 515248. [3] Wang Y, Chen J, Luo X, et al. Ginsenoside metabolite compound K exerts joint-protective effect by interfering with synoviocyte function mediated by TNF-alpha and Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;771:48-55. [4] Siebert S, Tsoukas A, Robertson J,et al. Cytokines as therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(2): 280-309. [5] Nabika T, Terashima M, Momose I, et al. Synergistic effect of ubiquitin on lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-alpha production in murine macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. 1450(1): 25-34. [6] Crisafulli C, Galuppo M, Cuzzocrea S. Effects of genetic and pharmacological inhibition of TNF-alpha in the regulation of inflammation in macrophages. Pharmacol Res. 2009,60(4): 332-340. [7] 李杰,阎伟.炎症因子与血管损伤的相关性研究进展[J]. 实用医药杂志,2009, 26(11): 78-80. [8] 范精华,刘康,刘保林. NO在炎症及免疫应答中的调节作用[J].中外医疗,2009,28(25): 163,166. [9] Yang H, Chen D, Cui QC,et al. Celastrol, a triterpene extracted from the Chinese "Thunder of God Vine," is a potent proteasome inhibitor and suppresses human prostate cancer growth in nude mice. Cancer Res. 2006; 66(9): 47584765. [10] Huang S, Tang Y, Cai X, et al. Celastrol inhibits vasculogenesis by suppressing the VEGF-induced functional activity of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 423(3): 467-472. [11] Allison AC, Cacabelos R, Lombardi VR, et al. Celastrol, a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory drug, as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2001;25(7): 1341-1357. [12] Trott A, West JD, Klaic L, et al. Activation of heat shock and antioxidant responses by the natural product celastrol: transcriptional signatures of a thiol-targeted molecule. Mol Biol Cell.2008;19(3):1104-1112. [13] Ji GQ, Chen RQ, Wang L.Anti-inflammatory activity of atractylenolide III through inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in mouse macrophages. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2015:1-5. [14] Ichikawa N,Yamashita K,Funakoshi T,et al.Novel anti-inflammatory agent 3-[(dodecylthiocarbonyl)- methyl]-glutarimide ameliorates murine models of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Res. 2016; 65(3):245-260. [15] Huang S, He P, Peng X, et al. Pristimerin Inhibits Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis by Targeting PC-3 Stem Cell Characteristics and VEGF-Induced Vasculogenesis of BM-EPCs. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(1): 253-268. [16] Zuo J,Guo Y,Peng X,et al.Inhibitory action of pristimerin on hypoxiamediated metastasis involves stem cell characteristics and EMT in PC-3 prostate cancer cells.Oncol Rep.2015; 33(3): 1388-1394. [17] Tang Y, Vater C, Jacobi A, et al. Salidroside exerts angiogenic and cytoprotective effects on human bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells via Akt/mTOR/p70S6K and MAPK signalling pathways. Br J Pharmacol. 2014; 171(9): 2440-2456. [18] Tang Y, Huang B, Sun L, et al. Ginkgolide B promotes proliferation and functional activities of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells: involvement of Akt/eNOS and MAPK/p38 signaling pathways. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;21: 459-469. [19] De Rycke L, Baeten D, Foell D, et al. Differential expression and response to anti-TNFalpha treatment of infiltrating versus resident tissue macrophage subsets in autoimmune arthritis. J Pathol.2005;206(1): 17-27. [20] Peng L, Wang H, Song K, et al. Lentivirus-mediated TNF-alpha gene silencing and overexpression of osteoprotegerin inhibit titanium particle-induced inflammatory response and osteoclastogenesis in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(1):1010-1018. [21] Cheng XL, Liu XG, Wang Q, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects of Guge Fengtong Formula: in vitro and in vivo studies.Chin J Nat Med. 2015;13(11): 842-853. [22] Olejnik A,Kowalska K, Kidon M, et al. Purple carrot anthocyanins suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the co-culture of intestinal Caco-2 and macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Food Funct. 2016;7(1): 557-564. [23] Di CL, Movia D, Bianchi MG, et al. Pro-inflammatory effects of pyrogenic and precipitated amorphous silica nanoparticles in innate immunity cells. Toxicol Sci. 2016; 150(1):40-53. [24] Cai R, Jiang Y, Yang W, et al. Surface-displayed IL-10 by Recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum Reduces Th1 Responses of RAW264.7 Cells Stimulated with Poly(I:C) or LPS. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;26(2): 421-431. [25] Kim KJ, Yoon KY, Yoon HS, et al. Brazilein Suppresses Inflammation through Inactivation of IRAK4-NF-kappaB Pathway in LPS-Induced Raw264.7 Macrophage Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11): 27589-27598. [26] Chen L, Shen X, Chen G, et al. A Comparative Study of the Effects upon LPS Induced Macrophage RAW264.7 Inflammation in vitro of the Lipids of Hippocampus trimaculatus Leach. J Oleo Sci. 2015;64(12): 1273-1281. [27] Bao G, Xu L, Xu X, et al. SGTB Promotes the Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in Chondrocytes of Osteoarthritis. Inflammation. 2015 Nov 20. [Epub ahead of print] [28] Veronesi F, Fini M, Giavaresi G, et al. Experimentally induced cartilage degeneration treated by pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation; an in vitro study on bovine cartilage. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16: 308. [29] Sandy JD, Chan DD, Trevino RL, et al. Human genome-wide expression analysis reorients the study of inflammatory mediators and biomechanics in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015;23(11): 1939-1945. [30] Maeda T, Miura Y, Fukuda K, et al. Decoy receptor 3 regulates the expression of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2015; 12(4): 5191-5196. [31] Sun J, Xu P, Du X, et al. Piperlongumine attenuates collagen-induced arthritis via expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and inhibition of the activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(4): 2689-2694. [32] Shafia S, Dilafroze, Sofi FA, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and genetic variations in cytokine genes: a population-based study in Kashmir Valley. Immunol Invest. 2014;43(4): 349-59. [33] Hreggvidsdottir HS, Noordenbos T, Baeten DL. Inflammatory pathways in spondyloarthritis. Mol Immunol. 2014;57(1): 28-37. [34] McInnes IB, Buckley CD, Isaacs JD. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis - shaping the immunological landscape. Nat Rev Rheumatol.2016;12(1):63-68. [35] Chimenti MS, Triggianese P, Conigliaro P, et al. The interplay between inflammation and metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1887. [36] Perpetuo IP, Raposeiro R, Caetano-Lopes J, et al. Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Therapy on Osteoclasts Precursors in Ankylosing Spondylitis. PLOS ONE. 2015;10(12): e0144655. [37] Maxwell LJ, Zochling J, Boonen A, et al. TNF-alpha inhibitors for ankylosing spondylitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; 4: CD005468. [38] Tam LS, Kitas GD, Gonzalez-Gay MA. Can suppression of inflammation by anti-TNF prevent progression of subclinical atherosclerosis in inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014; 53(6):1108-1119. [39] Pallebage-Gamarallage M, Takechi R, Lam V,et al. Pharmacological modulation of dietary lipid-induced cerebral capillary dysfunction: Considerations for reducing risk for Alzheimer's disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015: 1-18. [40] Gerin F, Sener U, Erman H, et al. The Effects of Quercetin on Acute Lung Injury and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Rat Model of Sepsis. Inflammation. 2015 Dec 15. [Epub ahead of print]. [41] Wang L, Xu ML, Liu J, et al. Sonchus asper extract inhibits LPS-induced oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in RAW264.7 macrophages. Nutr Res Pract. 2015;9(6): 579-585. [42] Shin S, Na S, Kim OS,et al. Effect of Pneumoperitoneum on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via the Arginase Pathway in Rats. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(1): 238-246. [43] Butt AJ, Caldon CE, McNeil CM, et al. Cell cycle machinery: links with genesis and treatment of breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;630: 189-205. [44] Dragnev KH, Feng Q, Ma Y, et al. Uncovering novel targets for cancer chemoprevention. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2007; 174: 235-243. [45] Cheng J, Bawa T, Lee P, et al. Role of desumoylation in the development of prostate cancer. Neoplasia. 2006; 8(8): 667-676. [46] Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA. Cyclins and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2004;9(1): 95-104. |
| [1] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [2] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [3] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [4] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [6] | Yang Yang, Yao Yu, Shen Xiaotian, Liu Jiajia, Xue Jianhua. Expression and significance of interleukin-21 in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 690-694. |
| [7] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [8] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [9] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [10] | Xu Xiaoming, Chen Yan, Song Qian, Yuan Lu, Gu Jiaming, Zhang Lijuan, Geng Jie, Dong Jian. Human placenta derived mesenchymal stem cell gel promotes the healing of radiation skin damage in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3976-3980. |
| [11] | Bi Qingwei, Liu Chengpu, Li Yan, Zhao Wenwen, Han Mei. Structure analysis of platelet-rich fibrin derived from two centrifugation procedures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3534-3539. |
| [12] | Cui Tiantian, Yi Lan, Ouyang Hougan, Wu Huiting, Ouyang Yanchu, Chen Chu. Effect of thermosensitive moxibustion in a rat model of pelvic inflammation based on trifocal focal membrane theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3168-3172. |
| [13] | Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi. Potential molecular mechanism of Wuling powder in treating osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3185-3193. |
| [14] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [15] | Cong Renyuan, Yuan Jing, Xia Jinchan, Sun Ying . Effects of baicalin on oxidative stress in BEAS-2B cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide combined with adenosine triphosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 286-291. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||