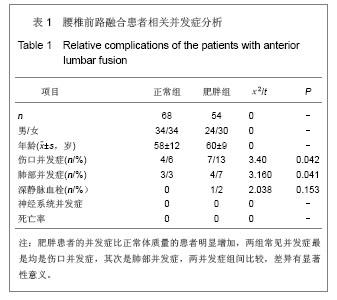
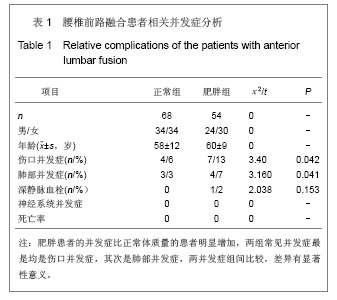
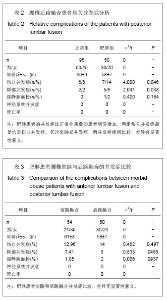
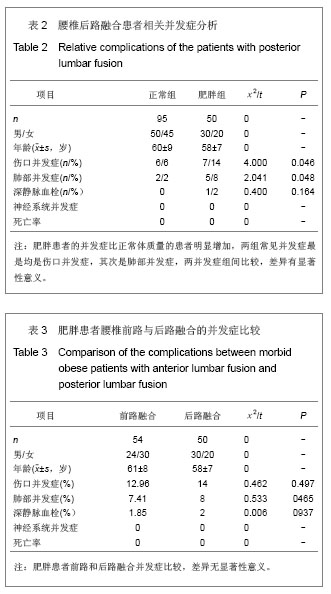
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (22): 4055-4061.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.22.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of complications between morbid obesity and normal weight patients with lumbar arthrodesis
Jiang Yu, Zhu Guo-xing, Yang Yu-sheng
- Department of Orthopedics, Wuxi No.2 People’s Hospital, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2013-05-28Published:2013-05-28 -
Contact:Zhu Guo-xing, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Wuxi No.2 People’s Hospital, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Jiang Yu★, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Wuxi No.2 People’s Hospital, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China jiangyu314@sohu.com -
Supported by:Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation, No.BK2012608*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Yu, Zhu Guo-xing, Yang Yu-sheng. Comparison of complications between morbid obesity and normal weight patients with lumbar arthrodesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(22): 4055-4061.
share this article
| [1]Hangai M, Kaneoka K, Kuno S, et al. Factors associated with lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in the elderly. Spine J. 2008;8(5):732-740.[2]Liuke M, Solovieva S, Lamminen A, et al. Disc degeneration of the lumbar spine in relation to overweight. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005;29(8):903-908.[3]Ji CJ, Gong LT, Zhang ST. Shandong Daxue Xuebao (Yixueban). 2007;45(5):520-523.汲长蛟,宫良泰,张寿涛.体重指数与腰椎间盘突出症发病的相关性临床研究[J].山东大学学报(医学版), 2007,45(5):520-523.[4]Hourigan JS. Impact of obesity on surgical site infection in colon and rectal surgery. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011;24(4): 283-290.[5]Geiger TM, Muldoon R. Complications following colon rectal surgery in the obese patient. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2011; 24(4):274-282.[6]Patel N, Bagan B, Vadera S, et al. Obesity and spine surgery: relation to perioperative complications. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007 ;6(4):291-297.[7]Djurasovic M, Bratcher KR, Glassman SD, et al. The effect of obesity on clinical outcomes after lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(16):1789-1792.[8]Gepstein R, Shabat S, Arinzon ZH, et al. Does obesity affect the results of lumbar decompressive spinal surgery in the elderly? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(426):138-144.[9]Pull ter Gunne AF, Cohen DB. Incidence, prevalence, and analysis of risk factors for surgical site infection following adult spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(13):1422-1428.[10]Patel N, Bagan B, Vadera S, Maltenfort MG, et al. Obesity and spine surgery: relation to perioperative complications. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(4):291-297.[11]Kalanithi PA, Arrigo R, Boakye M. Morbid obesity increases cost and complication rates in spinal arthrodesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(11):982-988.[12]Zheng XY, Hou SX. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2009;11: 873-876.郑晓勇,侯树勋. 腰椎后路经椎弓根螺钉动力内固定装置的临床应用及生物力学研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,11:873-876.[13]Yan LQ, Huan C, Sun Y, et al. Zhonghua Linchuang Yishi Zazhi(Dianziban). 2011;15:4432-4437.颜连启,宦诚,孙钰,等.腰椎融合固定和非融合固定生物力学分析[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2011,15:4432-4437.[14]Zhou BF. Zhonghua Liuxing Bingxue Zazhi. 2002;23(1):5-10.周北凡. 我国成人体重指数和腰围对相关疾病危险因素异常的预测价值:适宜体重指数和腰围切点的研究[J].中华流行病学杂志,2002,23(1):5-10.[15]Pull ter Gunne AF, van Laarhoven CJ, Cohen DB. Incidence of surgical site infection following adult spinal deformity surgery: an analysis of patient risk. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(6): 982-988.[16]Linam WM, Margolis PA, Staat MA, et al. Risk factors associated with surgical site infection after pediatric posterior spinal fusion procedure. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009; 30(2):109-116.[17]Roders WB, Cox CS, Gerber EJ. Early complications of extreme lateral interbody fusion in the obese. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(6):393-397.[18]Xu JW, Ji J, Zhong YM, et al. Guangxi Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao. 2011;14(3):38-39.许建文,冀晶,钟远鸣,等. 肥胖女性腰椎间盘突出症椎间盘退变的病例对照研究[J]. 广西中医学院学报,2011,14(3):38-39.[19]Gu HL, Wang H, Liu L, et al. ZHonghua Guke Zazhi. 2003; 23(9):523-526.顾海伦,王欢,刘莉,等.体质指数与腰椎间盘突出症术后疗效的关系[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(9):523-526.[20]Li MP. Jibing Jiance yu Kongzhi Zazhi. 2010;9:546-547.李明平.肥胖症与腰椎间盘突出症的相关联系[J].疾病监测与控制杂志,2010,9:546-547.[21]Chrastil J, Patel AA. Complications associated with posterior and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(5):283-291.[22]Bose B. Delayed infection after instrumented spine surgery: case reports and review of the literature. Spine J.2003; 3(5): 394-395. [23]Jackson TD, Hutter MM. Morbidity and effectiveness of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, adjustable gastric band, and gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Adv Surg. 2012; 46:255-268.[24]Stiefelhagen P. Pulmonary embolism after spinal operation: what lies in the pulmonary artery?. MMW Fortschr Med. 2012;154(4):34-35.[25]McClendon J Jr, O shaughnessy BA, Smith TR, et al. Comprehensive assessment of prophylactic preoperative inferior vena cava filters for major spinal reconstruction in adults. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(13):1122-1129. [26]Al-Dujaili TM, Majer CN, Madhoun TE, et al. Deep venous thrombosis in spine surgery patients: incidence and hematoma formation. Int Surg. 2012;97(2):150-154.[27]Ludwig KP, Simons HJ, Mone M,et al. Implementation of an enoxaparin protocol for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in obese surgical intensive care unit patients. Ann Pharmacother. 2011;45(11):1356-1362.[28]Al-Benna S. Perioperative management of morbid obesity. J Perioper Pract. 2011;21(7):225-233.[29]Bird ST, Hartzema AG, Brophy JM, et al. Risk of venous thromboembolism in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a population-based matched cohort analysis. CMAJ. 2012 Dec 3.[30]Freeman AL, Pendleton RC, Rondina MT. Prevention of venous thromboembolism in obesity. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010;8(12):1711-1721. [31]Yan GL, Ji ZG, Gao HR, et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2013;23(3):244-250.闫国良,纪振钢,高浩然,等.微创经椎间孔减压腰椎融合内固定术与传统后路开放手术治疗腰椎退变性疾病的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(3):244-250.[32]Ni WF, Xu GJ. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu Yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(30):5949-5952.倪伟峰,徐建广.有限元法在脊柱结构和腰椎融合生物力学评价中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(30): 5949-5952.[33]Zheng ZY, Qin L, Tang SP, et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2005;l5(7):440-443.郑振耀,秦岭,唐盛平,等. 实验性脊柱融合术骨与植入物界面融合的评估方法[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2005,l5(7):440-443.[34]Schnake KJ, Schaeren S, Jeanneret B. Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis.Spine.2006;31(4):442-449.[35]Bordes-Monmeneu M,Bordes-Garcia V,Rodrigo-Baeza F, et al.System of dynamic neutralization in the lumbar spine: experience on 94 cases.Neurocirugia (Astur).2005; 16(6): 499-506.[36]Zhang JD, Zhang TL, Xia Q, et al. Guoji Gukexue Zazhi. 2008;29(6):375-377.张继东,张铁良,夏群,等. 前路腰椎椎体间融合术的生物力学研究[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2008,29(6):375-377.[37]Yu Q, Ma JX, Ma XL, et al. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Waike. 2011;4(2):151-157.于琦,马剑雄,马信龙,等. 腰椎融合术后邻近节段小关节应力变化及椎间盘退变研究[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2011,4(2):151-157.[38]Gu GF, Zhang HL, He SS, et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2012;22(4):313-317.顾广飞,张海龙,贺石生,等.体重指数对微创手术治疗单节段腰椎管狭窄症并腰椎不稳疗效的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012, 22(4):313-317.[39]Yin JC, Liu N, Sun YD, et al. Meizhong Guoji Chuangshang Zazhi. 2012;11(5):19-19.殷继超,刘娜,孙银娣,等.开链-闭链康复运动对腰椎间盘突出症腰背肌生物力学变化临床观察[J].美中国际创伤杂志,2012, 11(5):19-19.[40]Tomasino A, Parikh K, Steinberger J, et al. Tubular microsurgery for lumbar discectomies and laminectomies in obese patients: operative results and outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(18):E664-672.[41]Yadla S, Malone J, Campbell PG, et al. Early complications in spine surgery and relation to preoperative diagnosis: a single-center prospective study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010; 13(3): 360-366. [42]Campbell PG, Malone J, Yadla S, et al. Early complications related to approach in thoracic and lumbar spine surgery: a single center prospective study. World Neurosurg. 2010; 73(4):395-401. [43]Rosen DS, Ferguson SD, Ogden AT, et al. esity and self-reported outcome after minimally invasive lumbar spinal fusion surgery. Neurosurgery. 2008;63(5):956-960.[44]Peng CW, Bendo JA, Goldstein JA, et al. Perioperative outcomes of anterior lumbar surgery in obese versus non-obese patients. Spine J. 2009;9(9):715-720.[45]Campbell PG, Malone J, Yadla S, et al. Comparison of ICD-9-based, retrospective, and prospective assessments of perioperative complications: assessment of accuracy in reporting. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;14(1):16-22.[46]Shunwu F,Xing Z,Fengdong Z,et al.Minimally invasivetransforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of de-generative lumbar diseases.Spine. 2010; 35(17):1615-1620. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [4] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [5] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [6] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [7] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [8] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [9] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [10] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [11] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [12] | Yuan Xinping, Shao Yanbo, Wu Chao, Wang Jianling, Tong Liangcheng, Li Ying. Accuracy of target bone segments in personalized differential modeling and simulation of CT scanning parameters at fracture end [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 912-916. |
| [13] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [14] | Kong Lingbao, Lü Xin. Effect of implant selection and approach on support in the operation of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 942-947. |
| [15] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||