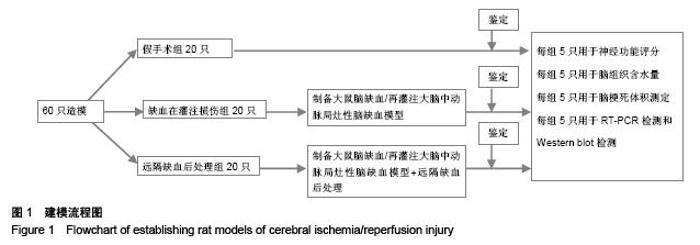
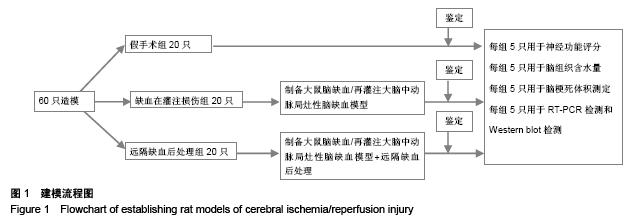
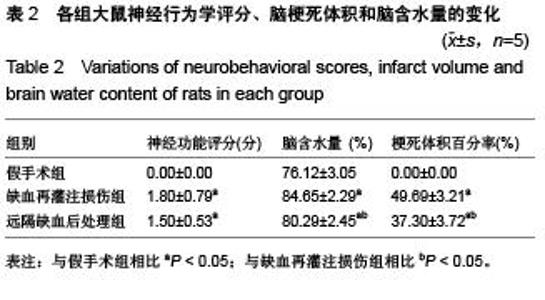
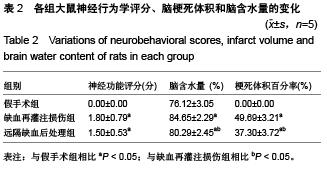
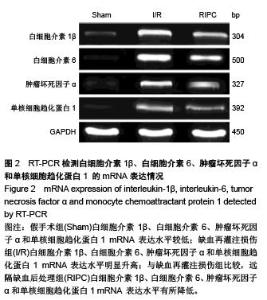
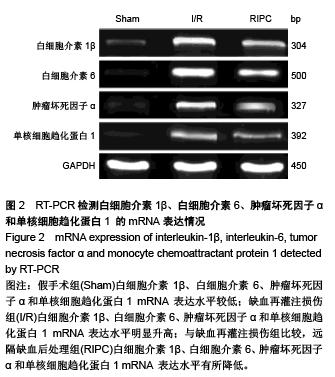
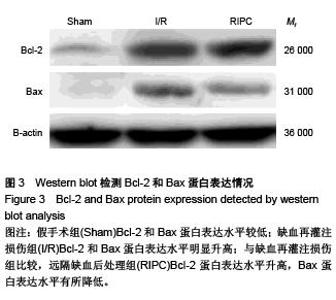
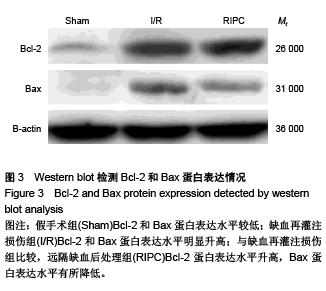
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 7902-7907.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of remote ischemic postconditioning on inflammation related factors of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
Wang Ning1, Li Xiao-ou1, Ba Xiao-hong2
- 1Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, First Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-10Online:2015-11-30Published:2015-11-30 -
Contact:Ba Xiao-hong, Master, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, First Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Ning, Studying for master’s degree, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:a grant from Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Department of China, No. 2014022006
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Ning, Li Xiao-ou, Ba Xiao-hong. Effects of remote ischemic postconditioning on inflammation related factors of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(49): 7902-7907.
share this article
| [1] Durukan A, Tatlisumak T. Preconditioning-induced ischemictolerance: a window into endogenous gearing for cerebroprotection. Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2010;2(1):2.[2] Yannopoulos FS, Mkel T, Niemel E, et al. Improved cerebral recovery from hypothermic circulatory arrest after remote ischemic preconditioning. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90(1): 182-188.[3] Ren C, Gao M, Dornbos D, et al. Remote ischemic post-conditioning reduced brain damage in experimental ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurol Res. 2011;33(5): 514-519.[4] Ren C, Yan Z, Wei D, et al. Limb remote ischemic postconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2009;1288:88-94.[5] Peng B, Guo QL, He ZJ, et al. Remote ischemic postconditioning protects the brain from global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by up-regulating endothelial nitric oxide synthase through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Brain Res. 2012;1445:92-102. [6] Zhou Y, Fathali N, Lekic T, et al. Remote limb ischemic postconditioning protects against neonatal hypoxic- ischemic brain injury in rat pups by the opioid receptor/Akt pathway. Stroke. 2011;42(2):439-444.[7] 严利,周文胜.脑缺血/再灌注损伤与高尔基体破裂的研究进展[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2015,3:70-72. [8] Liu Q, Zhou S, Wang Y, et al. A feasible strategy for focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: remote ischemic postconditioning. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(15): 1460-1463.[9] Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlotn S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery oclusion without craniotomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.[10] Carty M, Bowie AG. Evaluating the role of Toll-like receptors in diseases of the central nervous system. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;81:825-837. [11] Pignataro G, Cuomo O, Vinciguerra A, et al. NCX as a key player in the neuroprotection exerted by ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:223-240.[12] Oppenheim JJ, Tewary P, de la Rosa G, et al. Alarmins initiate host defense. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;601:185-194.[13] Qiu J, Xu J, Zheng Y, et al. High-mobility group box 1 promotes metalloproteinase-9 upregulation through Toll-like receptor 4 after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2010;41: 2077-2082. [14] Facci L, Barbierato M, Marinelli C, et al. Toll-like receptors 2, -3 and -4 prime microglia but not astrocytes across central nervous system regions for ATP-dependent interleukin-1β release. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6824.[15] Kim JH, Hong KW, Bae SS, et al. Probucol plus cilostazol attenuate ercholesterolemia induced exacerbation in ischemic brain injury via anti-inflammatory effects. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(3):687-694.[16] Luheshi NM, Kovacs KJ, Lopez-Castejon G, et al. Interleukin-1alpha expression precedes IL-1beta after ischemic brain injury and is localised to areas of focal neuronal loss and penumbral tissues. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:186. [17] Emsley HC, Smith CJ, Georgiu RF, et al. Interleukin-6 and acute ischaemic stroke. Acta Neurol Scand. 2005;112:273-274.[18] Buttini M, Appel K, Sauter A, et al. Expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha after focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. Neuroscience. 1996;71(1):1-16.[19] Del Zoppo GJ. The neurovascular unit, matrix proteases, and innate inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1207: 46-49.[20] Kong Y, Rogers MR, Qin X. Effective neuroprotection by ischemic postconditioning is associated with a decreased expression of RGMa and inflammation mediators in ischemic rats. Neurochem Res. 2013;38(4):815-825. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||