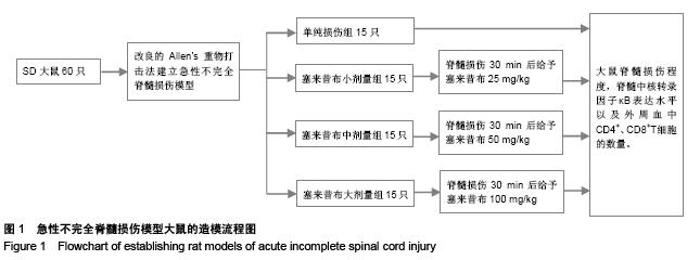
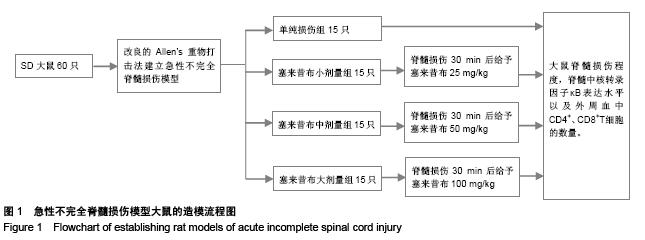
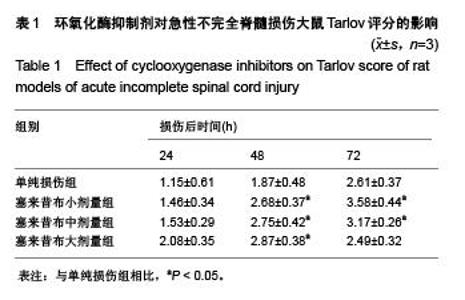
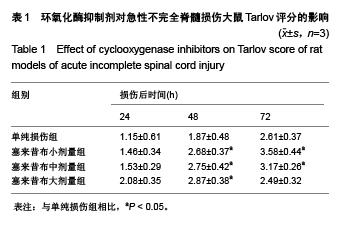
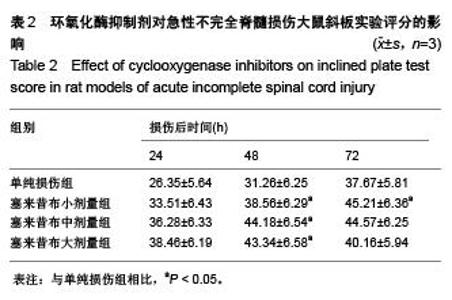
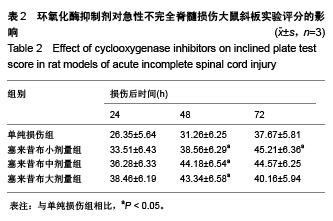
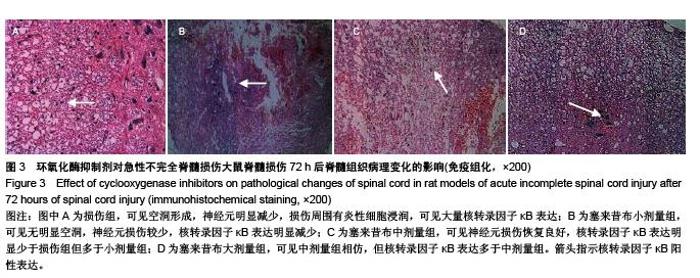
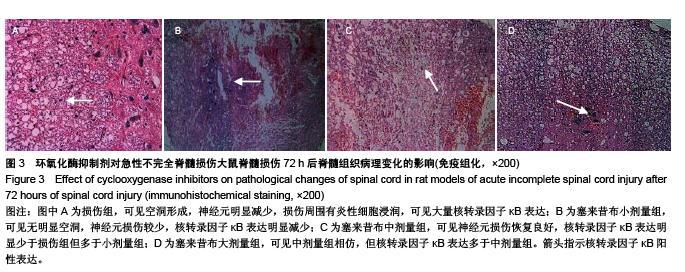
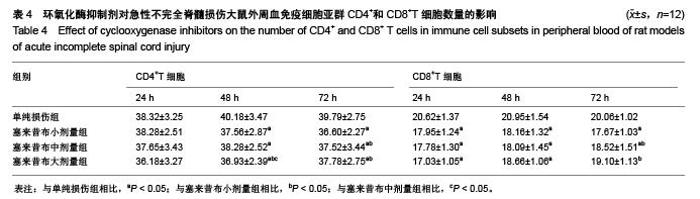
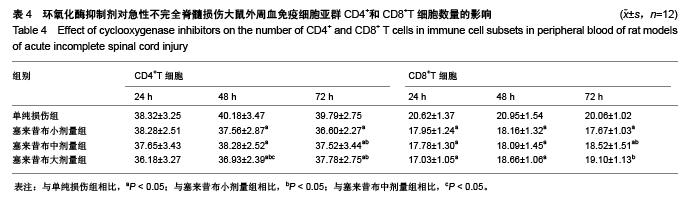
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 7908-7913.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on nuclear factor κB and CD4+/CD8+ expression in rat models of acute incomplete spinal cord injury
Xin Zhi-qiang, Pan Meng, Wang Jing-liang, Zheng Quan-xin, Xu Yi-dong, Pi An-ping
- Spine Disease Sickroom, Second Department of Orthopedics, Guangzhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guangzhou 510045, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-21Online:2015-11-30Published:2015-11-30 -
About author:Xin Zhi-qiang, Associate chief physician, Spine Disease Sickroom, Second Department of Orthopedics, Guangzhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guangzhou 510045, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province, China, No. 20120309
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xin Zhi-qiang, Pan Meng, Wang Jing-liang, Zheng Quan-xin, Xu Yi-dong, Pi An-ping. Effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on nuclear factor κB and CD4+/CD8+ expression in rat models of acute incomplete spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(49): 7908-7913.
share this article
| [1] 刘秉锐,马玉林.脊髓损伤后免疫炎症反应机制及治疗的研究进展[J].宁夏医学杂志,2008,30(8):760-762.[2] 宗少晖,方晔,彭金珍,等.急性不完全脊髓损伤模型大鼠相关炎症因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18): 2806-2811.[3] Zhou X, He X, Ren Y. Function of microglia and macrophages in secondary damage after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(20):1787-1795. [4] 王开友,王颖,陈德喜,等.选择性COX-2抑制剂对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后运动诱发电位和后肢运动功能的影响[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2009,45(6):532-533.[5] 杨森,王海龙,盛伟斌,等.骨折合并脊髓损伤患者血清中转化生长因子β1变化:有利于促进骨折愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(2):165-169.[6] 李基民,权正学,刘渤.核转录因子-κB信号途径与急性脊髓损伤继发伤的研究进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2009,11(1):85-87.[7] 王慧,郭俊,赵宇,等.DO11.10转基因小鼠脊髓损伤后的运动功能恢复[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2010,36(3):231-234.[8] 张大威,李一帆,朱丹,等.急性大鼠脊髓损伤模型的建立与评估[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2015,32(4):325-327.[9] 陈刚,段惠君.不同剂量塞来昔布对人肺癌裸鼠移植瘤的治疗作用及机制研究[J].肿瘤,2008,28(10):837-841.[10] 秦江,侯树勋,石秀秀,等.2012年版“脊髓损伤后残存自主神经功能国际记录标准”简要介绍[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2014(9): 702-704.[11] 陈科,吕小华.参芎葡萄糖注射液对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后后肢功能及NF-kB表达的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2008,17(19): 2939-2940.[12] 卢旻鹏,权正学,刘渤,等.小鼠脊髓损伤标准化重物打击模型的制备及评价[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(8):933-938.[13] Nishi RA, Liu H, Chu Y, et al. Behavioral, histological, and ex vivo magnetic resonance imaging assessment of graded contusion spinal cord injury in mice. J Neurotrauma. 2007; 24(4):674-689.[14] Caughey GE, Cleland LG, Penglis PS, et al. Roles of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 in prostanoid production by human endothelial cells: selective up-regulation of prostacyclin synthesis by COX-2. J Immunol. 2001;167(5): 2831-2838.[15] Dai ZJ, Ma XB, Kang HF, et al. Antitumor activity of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, on breast cancer in Vitro and in Vivo. Cancer Cell Int. 2012;12(1):53. [16] El-Ghazaly MA, Nada AS, El-Hazek RM, et al. Effect of selective COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib on adjuvant-induced arthritis model in irradiated rats. Int J Radiat Biol. 2010;86(12): 1079-1087.[17] 吴亚楠,赵鹏翔,马雪梅.NF-κB研究进展及其与炎症的关系[J].安徽农业科学,2012,40(34):16533-16535. [18] 霍岩,沈兆亮,王冬,等.重组人促红细胞生成素对大鼠脊髓损伤后NF-κB表达的影响[J].解剖科学进展,2012,18(2):109-112. [19] Yune TY, Lee SM, Kim SJ, et al. Manganese superoxide dismutase induced by TNF-beta is regulated transcriptionally by NF-kappaB after spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21(12):1778-1794.[20] 陆相前,李晓,沈方臻,等.不同剂量的塞来昔布对C57BL/6小鼠移植瘤微淋巴管密度抑制作用的研究[J].现代生物医学进展. 2014, 29(13):5629-5632.[21] Cafferty WB, Duffy P, Huebner E, et al. MAG and OMgp synergize with Nogo-A to restrict axonal growth and neurological recovery after spinal cord trauma. J Neurosci. 2010;30(20):6825-6837.[22] Ankeny DP, Popovich PG. Mechanisms and implications of adaptive immune responses after traumatic spinal cord injury. Neuroscience. 2009;158(3):1112-1121.[23] 陈开廷,王永堂,舒亚海,等.以髓磷脂相关抑制因子及其受体为靶点的脊髓损伤免疫治疗策略研究[J].生命科学,2015,27(2): 191-197.[24] 蒋昌宇,刘德明.微囊化异种坐骨神经组织移植对脊髓损伤大鼠T淋巴细胞亚群的影响及行为学观察[J].解剖科学进展, 2008, 14(3):252-255.[25] Schäfers M, Marziniak M, Sorkin LS, et al. Cyclooxygenase inhibition in nerve-injury- and TNF-induced hyperalgesia in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2004;185(1):160-168.[26] Oatway MA, Chen Y, Bruce JC, et al. Anti-CD11d integrin antibody treatment restores normal serotonergic projections to the dorsal, intermediate, and ventral horns of the injured spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2005;25(3):637-647.[27] Shih VF, Tsui R, Caldwell A, A single NFκB system for both canonical and non-canonical signaling. Cell Res. 2011;21(1): 86-102. [28] Beni SM, Tsenter J, Alexandrovich AG, et al. CuZn-SOD deficiency, rather than overexpression, is associated with enhanced recovery and attenuated activation of NF-kappaB after brain trauma in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006; 26(4):478-490.[29] 骆二红,胡建国,吕合作.SD大鼠脊髓损伤前后外周血T淋巴细胞亚群的变化[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2012,37(6):621-623. [30] 朱海涛,周治宇,张烽.T细胞在小鼠脊髓损伤与修复中的作用[J].江苏医药,2011,37(20):2372-2374.[31] 张帆,郭风劲,蒋伟,等.COX-2抑制剂塞来昔布对大鼠脊髓损伤的保护作用[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2007,36(3):366-369. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||