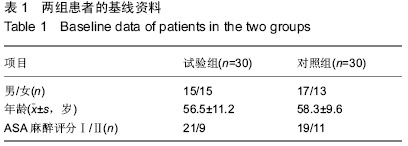
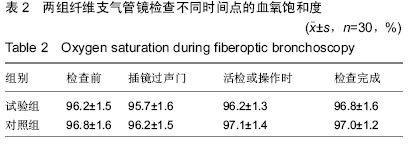
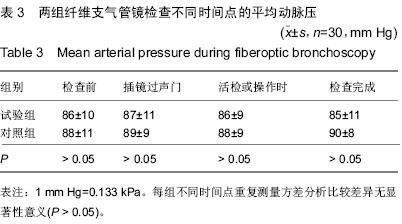
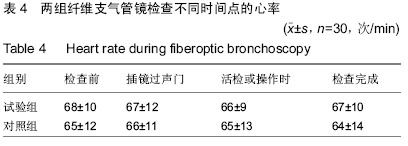
| [1] |
Li An’an, Chen Jiayun, Chen Jin, Song Min, Li Congcong, Ye Guozhu, Wu Gaoyi, Lin Wenzheng, Cai Yuning, Liu Wengang.
Efficacy of arthroscopy combined with sodium hyaluronate for knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2437-2444.
|
| [2] |
Zhang Yicen, Wang Peixin, Liu Zhicheng.
Ultrasound-guided injection of hyaluronic acid and corticosteroid for treating plantar fasciitis: evaluation of pain, fascia thickness and ankle-foot function
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1670-1674.
|
| [3] |
Shang Qingqing, Zhou Jianye.
Combination of hyaluronic acid hydrogel and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes cardiac function after myocardial infarction in rats (II)
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5559-5563.
|
| [4] |
Guo Enhui, Xu Zitong, Liang Yize, Zhou Liang, Lu Zhaoxiang, You Liang, Xia Yujun.
Properties of a novel photocrosslinked fish collagen peptide-hyaluronic acid hydrogel
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4518-4525.
|
| [5] |
Wang Yangfa, Liu Jun, Pan Jianke, Gao Shihua, Huang Junhan, Li Huiwen, He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun.
Therapeutic effects of platelet-rich plasma versus hyaluronic acid for knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4421-4428.
|
| [6] |
Li Jingjing, Guo Xuan, Xie Jun, Huang Lei, Suo Jinrong, Fu Songtao.
Preparation of agarose/gelatin/hyaluronic acid/extracellular matrix hydrogel and its property characterization
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2900-2908.
|
| [7] |
Liu Zhicheng1, Song Jian2, Zhang Qiliang3 .
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy versus intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate for knee osteoarthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2297-2302.
|
| [8] |
He Zhijiang, Zhu Lei, Cheng Shixiang, Huang Kui, Chen Cao, Sun Minglin.
Neurotrophin-3 modified hyaluronan-methylcellulose hydrogel promotes neurological function in rats with spinal cord injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2202-2207.
|
| [9] |
Shang Qing-qing, Zhou Jian-ye, Li Kai, Sun Jia-kang, Meng Jian, Li Jun.
Combination of hyaluronic acid and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes cardiac function after myocardial infarction
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(5): 675-679.
|
| [10] |
Jin Shao-feng, Qi Hui, Shu Xiong, Jie Yong-sheng, Zheng Rui, Chen Lei, Sun Lei .
In vivo and in vitro hemostatic effects of composite collagen sponge
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(2): 216-221.
|
| [11] |
Zhang Xiao-ou, Lv Yang, Mao Hua, Fan Xin-yi, Huang Si-ling, Guo Xue-ping.
Hyaluronic acid scaffolds: application research and product prospects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(2): 294-302.
|
| [12] |
Di Jia-wei, Li Xiang, Xie Rui-min, Wang Yong-ping.
Effect of hyaluronic acid and its derivatives on osteoblast function: molecular mechanisms and clinical values
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(18): 2927-2932.
|
| [13] |
Lou Min-ming, Wang Hong-wei, Ma Jie.
Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium combined with hyaluronic acid for mouse skin repair
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(1): 20-25.
|
| [14] |
Zhao Feng, He Wei, Liu Shao-jun, Wang Hui, Lv Ya-jun, Kang Kai, Zhang Guo-ping.
Injectable hyaluronic acid carrying autologous chondrocytes repairs cartilage defects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(30): 4787-4792.
|
| [15] |
Hao De-feng, Zhang Lu-qing, Liu Yu-dong.
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound combined with intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate in the repair of articular cartilage defects
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(30): 4775-4780.
|