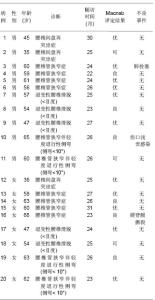
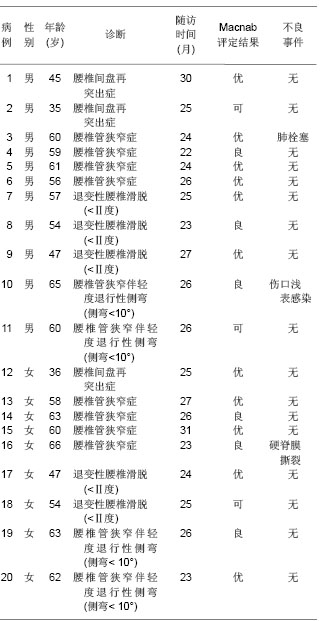
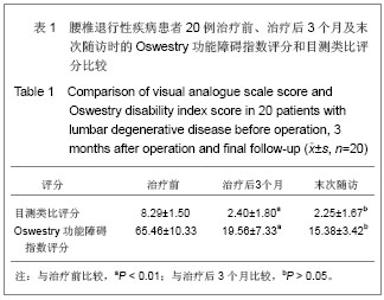
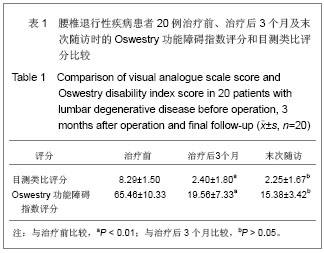
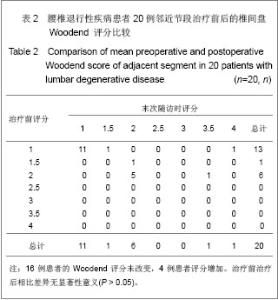
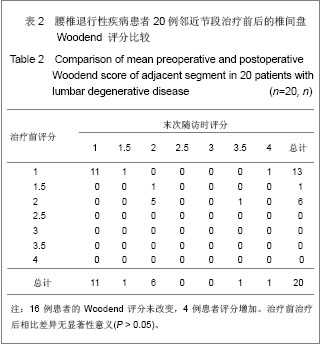
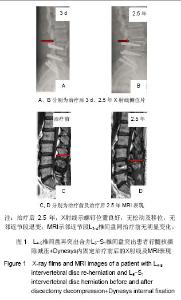
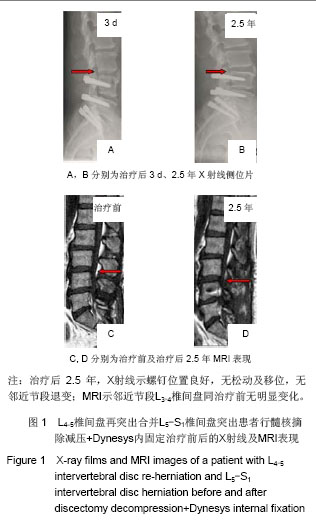
| [1] Chou WY, Hsu CJ, Chang WN, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar spinal posterolateral fusion with instrumentation in elderly patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002;122(1):39-43.[2] Markwalder TM, Wenger M. Adjacent-segment morbidity. J Neurosurg Spine. 2002;96(1):139-140. [3] Highsmith JM, Tumialán LM, Rodts GE Jr. Flexible rods and the case for dynamic stabilization. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 22(1):E11.[4] Askar Z, Wardlaw D, Muthukumar T, et al. Correlation between intervertebral disc morphology and the results in patients undergoing graf ligament stabilization. Eur Spine J. 2004;13(8):714-718.[5] Macnab I. Negative disc exploration:an analysis of nerve root involvement in sixty eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 1971;53(5):891-903.[6] Stoll TM, Dubois G, Schwarzenbach O. The dynamic neutralization system for the spine: a multi-center study of a novel non-fusion system. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(suppl 2): S170-S178. [7] Putzier M, Schneider SV, Funk JF, et al. The surgical treatment of the lumbar disc prolapse:nucleotomy with additional transpedicular dynamic stabilization versus nucleotomy alone.Spine. 2005;30(5):E109-E114. [8] Di Silvestre M, Lolli F, Bakaloudis G, et al. Dynamic Stabilization for Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis in Elderly Patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(2):227-234. [9] Grob D, Benini A, Junge A, et al. Clinical experience with the dynesys semirigid fixation system for the lumbar spine:surgical and patient-oriented outcome in 50 cases after an average of 2 years. Spine. 2005;30(3):324-331. [10] Schnake KJ, Schaeren S, Jeanneret B, et al. Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2006; 31(4):442-449. [11] Schaeren S, Broger I, Jeanneret B, et al.Minimum four-years follow-up of spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and dynamic stabilization. Spine. 2008;33(18):636-642. [12] Vaga S, Brayda-Bruno M, Perona F, et al. Molecular MR imaging for the evaluation of the effect of dynamic stabilization on lumbar intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(Suppl 1):40-48.[13] Chen BL, Wei FX, Ueyama K, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after single-segment PLIF:the risk factor for degeneration and its impact on clinical outcomes. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(11):1946-1950.[14] Ekman P, Moller H, Shalabi A, et al. prospective randomised study on the long-term effect of lumbar fusion on adjacent disc degeneration. Eur spine J. 2009;18(8):1175-1186.[15] Sears WR , Sergides IG , Kazemi N, et al. Incidence and prevalence of surgery at segments adjacent to a previous posterior lumbar arthrodesis. Spine J. 2011;11(1):11-20.[16] Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, et al. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine. 2004;29(2):1938-1934.[17] Kumar MN, Jacquot F, Hall H, et al.Long-term follow-up of functional outcomes and radiographic changes at adjacent levels following lumbar Spine fusion for degenerative disc disease. Eur Spine J. 2001;10(4):309-313.[18] Schmoelz W, Huber JF, Nydegger T, et al. Dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine and its effects on adjacent segments: an in vitro experiment. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003; 16(4):418-423.[19] Schmoelz W, Huber JF, Nydegger T, et al. Influence of a dynamic stabilization system on load bearing of a bridged disc :in vitro study of intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(8):1276-1285.[20] Liu CL, Zhong ZC, Shih SL, et al. Influence of Dynesys system screw profile on adjacent segment and screw. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(6):410-417.[21] Liu CL, Zhong ZC, Hsu HW, et al. Effect of the cord pretension of the Dynesys dynamic stabilisation system on the biomechanics of the lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(11):1850-1858. [22] Cunningham BW, Dawson JM, Hu N, et al. Preclinical evaluation of the Dynesys posterior spinal stabilization system, a nonhuman primate model. Spine. 2010;10(9): 775-783. [23] Niosi CA, Wilson DC, Zhu Q, et al. The effect of dynamic posterior stabilization on facet joint contact forces: an in vitro investigation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(1):19-26.[24] Niosi CA, Zhu QA, Wilson DC, et al. Biomechanical characterization of the three-dimensional kinematic behaviour of the Dynesys dynamic stabilization system: an in vitro study. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(6):913-922.[25] Ko CC, Tsai HW, Huang WC, et al. Screw loosening in the Dynesys stabilization system: radiographic evidence and effect on outcomes. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28(6):E10.[26] Bothmann M, Kast E, Boldt GJ, et al. Dynesys fixation for lumbar spine degeneration. Neurosurg Rev. 2008;31(2): 189-196.[27] Sapkas G, Mavrogenis AF, Starantzis KA, et al. Outcome of a dynamic neutralization system for the spine. Orthopedics. 2012;35(10):e1497-1502. |