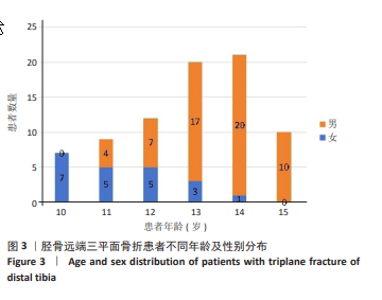
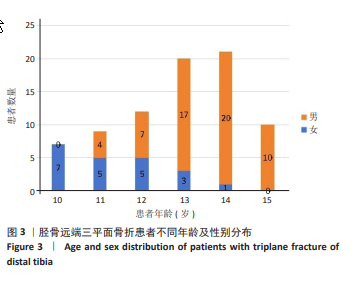
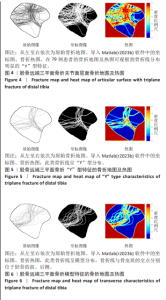
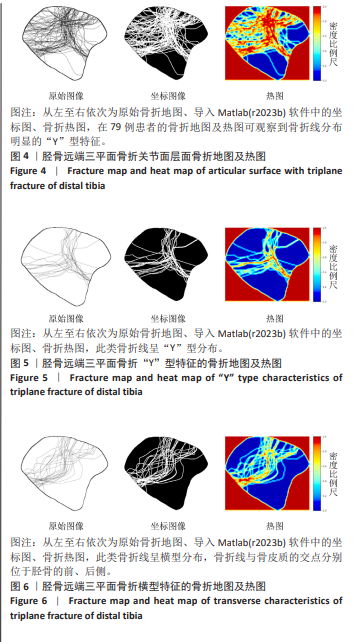
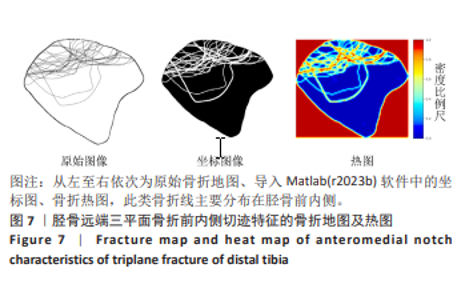
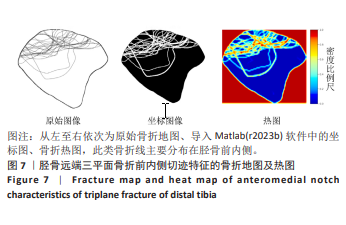
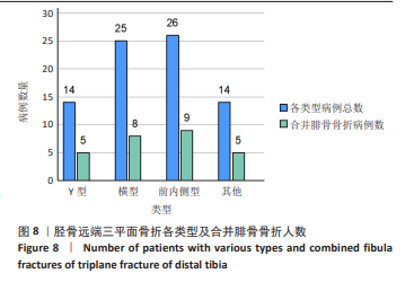
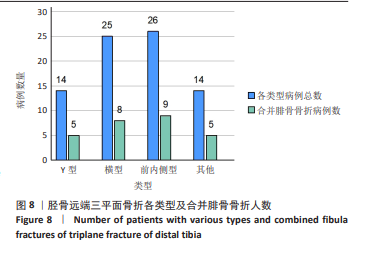
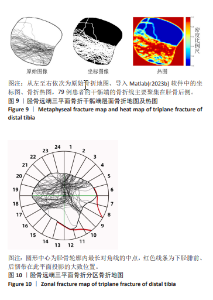
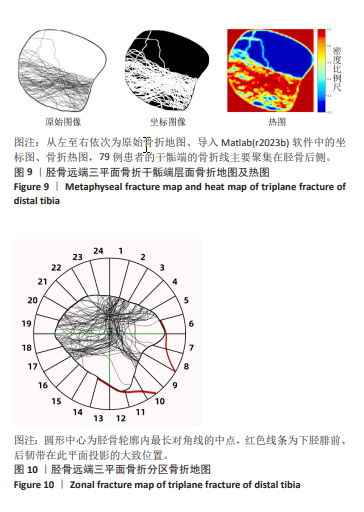
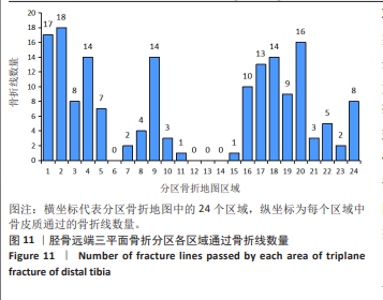
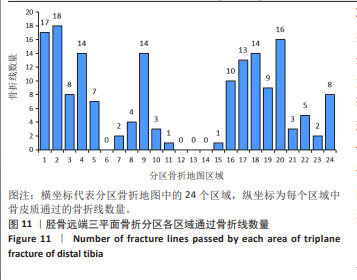
[1] LYNN MD. The triplane distal tibial epiphyseal fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972;86:187-190.
[2] PRIJS J, RAWAT J, TEN DUIS K, et al. Triplane ankle fracture patterns in paediatric patients. Bone Joint J. 2023;105-b(11):1226-1232.
[3] COLE PA, MEHRLE RK, BHANDARI M, et al. The pilon map: fracture lines and comminution zones in OTA/AO type 43C3 pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(7):e152-e156.
[4] 车健. 下胫腓韧带损伤解剖重建的研究[D].北京: 解放军医学院, 2015.
[5] 沈国栋, 杨康勇, 赖志斌, 等. 新鲜标本的下胫腓联合韧带解剖特点及临床意义[J]. 解剖学杂志,2021,44(1):49-52.
[6] 董伟强, 余斌, 白波. 下胫腓联合断裂对踝关节生物力学影响的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(6):532-535.
[7] 李中华, 杨茂伟, 王旭东, 等. 下胫腓韧带的断层解剖学研究[J]. 中国医药导报,2009,6(28):29-30.
[8] AHMED A, MISHRA P, PATRA B, et al. Lateral Ankle Ligaments: An Insight Into Their Functional Anatomy, Variations, and Surgical Importance. Cureus. 2024;16(2):e53826.
[9] CLANTON TO, WILLIAMS BT, BACKUS JD, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of the Individual Ligament Contributions to Syndesmotic Stability. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(1):66-75.
[10] KIKUCHI S, TAJIMA G, SUGAWARA A, et al. Characteristic features of the insertions of the distal tibiofibular ligaments on three-dimensional computed tomography- cadaveric study. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):3.
[11] WILLIAMS BT, AHRBERG AB, GOLDSMITH MT, et al. Ankle syndesmosis: a qualitative and quantitative anatomic analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(1):88-97.
[12] TAN AC, CHONG RW, MAHADEV A. Triplane fractures of the distal tibia in children. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2013;21(1):55-59.
[13] 王恩波, 郑振耀, 吴健华. 胫骨远端三平面骨折分析与致伤机制探讨[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,2004,25(1):51-54.
[14] RAHLF SH, ERICHSEN JL, BALLE U, et al. Fractures in the lower leg in children. Ugeskr Laeger. 2023;185(4):V01220040.
[15] DENG Y, CHEN Y, HE Q, et al. Bone age assessment from articular surface and epiphysis using deep neural networks. Math Biosci Eng. 2023;20(7):13133-13148.
[16] CHO JH, JUNG HW, SHIM KS. Growth plate closure and therapeutic interventions. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):553-559.
[17] BROWN SD, KASSER JR, ZURAKOWSKI D, et al. Analysis of 51 tibial triplane fractures using CT with multiplanar reconstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(5):1489-1495.
[18] DIAS LS, GIEGERICH CR. Fractures of the distal tibial epiphysis in adolescence. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983;65(4):438-444.
[19] 黎路根, 林浩, 黄东, 等. 三角韧带与下胫腓联合韧带对踝关节稳定的生物力学影响[J]. 实用手外科杂志,2020,34(1):78-82.
[20] NGUYEN CV, GREENE JD, COOPERMAN DR, et al. An Anatomic and Radiographic Study of the Distal Tibial Epiphysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2020;40(1):23-28.
[21] CLEMENT DA, WORLOCK PH. Triplane fracture of the distal tibia. A variant in cases with an open growth plate. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987; 69(3):412-415.
[22] KLEIGER B, MANKIN HJ. Fracture of the lateral portion of the distal tibial epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964;46:25-32.
[23] 霍力为, 黄崇博, 庾伟中, 等. 正骨手法治疗青少年胫骨远端三平面骨折临床研究 [J]. 新中医,2014,46(8):94-95.
[24] RIZZOLI R, CHEVALLEY T. Bone health: biology and nutrition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2024;27(1):24-30.
[25] GOLSHTEYN G, KATSMAN A. Pediatric Trauma. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2022;39(1):57-71.
[26] D’ANGELI V, BELVEDERE C, ORTOLANI M, et al. Load along the tibial shaft during activities of daily living. J Biomech. 2014;47(5):1198-1205.
[27] JARVIS JG, MIYANJI F. The complex triplane fracture: ipsilateral tibial shaft and distal triplane fracture. J Trauma. 2001;51(4):714-716.
[28] DENTON JR, FISCHER SJ. The medial triplane fracture: report of an unusual injury. J Trauma. 1981;21(11):991-995.
[29] VON LAER L. Classification, diagnosis, and treatment of transitional fractures of the distal part of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67(5):687-698.
[30] ARMITAGE BM, WIJDICKS CA, TARKIN IS, et al. Mapping of scapular fractures with three-dimensional computed tomography. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(9):2222-2228.
[31] 诸葛英杰, 罗从风. 骨折地图在膝关节创伤中的应用[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2022,24(6):548-552.
[32] 邓朝阳, 杨朝晖. 胫骨平台骨折线的三维模型分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):334-339.
[33] YAO X, HU M, LIU H, et al. Classification and morphology of hyperextension tibial plateau fracture. Int Orthop. 2022;46(10): 2373-2383.
[34] KERSCHBAUM M, TYCZKA M, KLUTE L, et al. The Tibial Plateau Map: Fracture Line Morphology of Intra-Articular Proximal Tibial Fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:9920189.
[35] 蒋代翔, 鲁辉, 马玲, 等. 基于三维骨折地图技术的跟骨骨折线分布研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18):2842-2847.
[36] SHI G, LIN Z, LIAO X, et al. Two and three-dimensional CT mapping of the sustentacular fragment in intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):20424.
[37] CHO JW, YANG Z, LIM EJ, et al. Multifragmentary patellar fracture has a distinct fracture pattern which makes coronal split, inferior pole, or satellite fragments. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):22836.
[38] WANG X, ZI S, WEI W, et al. A study of fracture lines distribution characteristics in complete articular fractures of the patella. Front Surg. 2023;10:1284479.
[39] KAHMANN SL, RAUSCH V, PLÜMER J, et al. The automized fracture edge detection and generation of three-dimensional fracture probability heat maps. Med Eng Phys. 2022;110:103913.
[40] MA Z, QIANG Z, ZENG K, et al. Prediction of cross section fracture path of cortical bone through nanoindentation array. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;116:104303.
[41] SCHNEIDMUELLER D, SANDER AL, WERTENBROEK M, et al. Triplane fractures: do we need cross-sectional imaging? Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2014;40(1):37-43. |