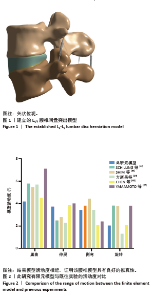
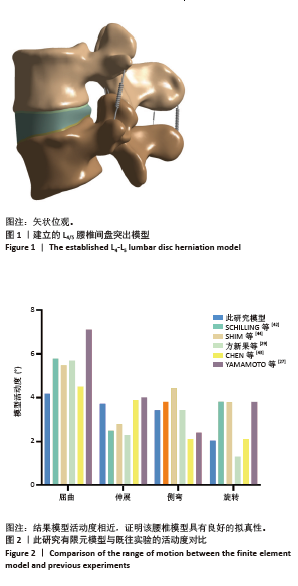
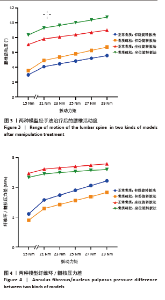
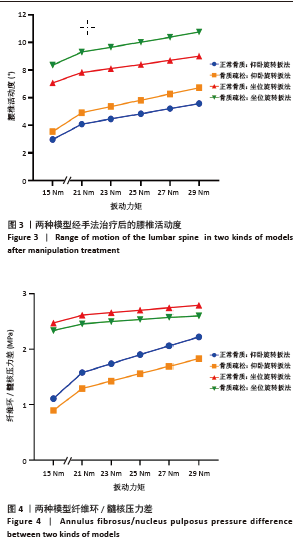
[1] 崔学军, 梁倩倩. 腰椎间盘突出症中西医结合诊疗专家共识[J]. 世界中医药,2023,18(7):945-952.
[2] 秦晓宽, 孙凯, 冯天笑, 等. 腰椎间盘突出症临床实践指南和专家共识的方法学质量评价与综合分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2024,27(31): 3857-3864.
[3] LEE JS, LEE S, KANG K, et al. Review of Recent Treatment Strategies for Lumbar Disc Herniation (LDH) Focusing on Nonsurgical and Regenerative Therapies. J Clin Med. 2025;14(4):1196.
[4] HARTVIGSEN J, HANCOCK MJ, KONGSTED A, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018;391(10137): 2356-2367.
[5] 饶筱荣, 马迎春. 腰夹脊穴深刺配合斜扳法治疗腰椎间盘突出症58例[J]. 中国针灸,2013,33(3):253-254.
[6] 张燕, 栾国瑞, 吴雯, 等. 李业甫定位腰椎旋转扳法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床研究[J]. 陕西中医药大学学报,2024,47(4):102-106.
[7] 吕立江, 王晓东, 陆森伟, 等. 仰卧旋转法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的病例对照研究[J]. 中国骨伤,2012,25(8):674-677.
[8] 徐曼琪, 吴自强, 朱如意, 等. 仰卧旋转扳法治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效的临床观察[J]. 中医临床研究,2012,4(20):81-82.
[9] 毕胜, 李义凯, 赵卫东,等. 推拿手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的机制[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2001,25(1):8-10.
[10] 王多多, 张延海, 郭潘靖, 等. 不同腰椎退变程度下两种腰椎推拿斜扳法作用效果的比较研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(1):59-64.
[11] 何芳芳, 吕立江, 牛红社, 等. 仰卧旋转扳法联合电针治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床效果观察[J]. 中国现代医生,2020,58(36):12-15.
[12] 杨学平, 欧泽锋, 李展鹏, 等. 身痛逐瘀汤配合坐位旋扳法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床观察[J]. 光明中医,2024,39(20):4142-4144.
[13] XIE R, LIANG L, LI K, et al. Effects of seated lumbar rotation manipulation in treating degenerative lumbar instability: a protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2021;22(1):398.
[14] 叶建东, 程哲, 王剑龙. 腰椎融合术3种内固定方式的生物力学特点[J]. 医用生物力学,2021,36(2):208-215.
[15] 程莹莹, 梁畅, 许鹏, 等. 不同固定方案的腰椎后路椎间融合术生物力学有限元分析[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版),2024, 51(3):88-97.
[16] DEMIR E, ELTES P, CASTRO AP, et al. Finite element modelling of hybrid stabilization systems for the human lumbar spine.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2020;234(12):1409-1420.
[17] LI S, XU B, LIU Y, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Spinal Column after Percutaneous Cement Discoplasty: A Finite Element Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(8):1853-1863.
[18] 肖永川, 许泽川, 梁川东, 等. 腰1椎体应力的有限元分析及分区[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2020,30(11):1016-1026.
[19] YANG S, SUN T, ZHANG L, et al. Stress Distribution of Different Pedicle Screw Insertion Techniques Following Single-Segment TLIF:A Finite Element Analysis Study. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(4):1153-1164.
[20] 张敏, 彭婧, 张强, 等. 有限元法分析老年骨质疏松患者L3/4椎板减压椎间融合的力学性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(6):847-851.
[21] 唐亮, 郑佳佳, 李文熙, 等. 人体腰椎生物力学模型及损伤参数敏感性分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(9):94-106.
[22] 廖运钱, 周宇, 王政伦, 等. 双头螺钉对三柱截骨术后多棒结构稳定性的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2024,39(3):407-412.
[23] DU CF, CAI XY, GUI W, et al. Does oblique lumbar interbody fusion promote adjacent degeneration in degenerative disc disease: A finite element analysis.Comput Biol Med. 2021;128:104122. .
[24] 代云磊, 魏亚, 吴昌兵, 等. 有限元模拟脊柱内镜下椎间孔成形对腰椎生物力学的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2022,43(1):127-132.
[25] 刘江, 张晗硕, 丁逸苇, 等. 棘突间固定辅助内镜下椎间融合治疗重度腰椎管狭窄症的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(24):3789-3795.
[26] 文鹏飞, 李亚宁, 路玉峰, 等. 腰椎—骨盆—髋关节有限元模型建立及生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(36): 5741-5746.
[27] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[28] 王宏卫, 刘新宇, 万熠. 人体腰椎L4~L5段有限元模型建立及力学有效性验证[J]. 医学与哲学,2017,38(10):50-53.
[29] 方新果, 赵改平, 王晨曦, 等. 基于CT图像腰椎L4~L5节段有限元模型建立与分析[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2014,33(4):487-492.
[30] ZHANG G, LI J, ZHANG L, et al. Biomechanical Effect of Different Posterior Fixation Techniques on Stability and Adjacent Segment Degeneration in Treating Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture With Osteoporosis: A Finite Element Analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2024; 49(15):E229-E238.
[31] 潘泓宇, 李红桃, 肖常明, 等. 个体化精准穿刺椎体强化治疗不同类型骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(27):5773-5784.
[32] LIU C, ZHAO M, ZHANG W, et al. Biomechanical assessment of different transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion constructs in normal and osteoporotic condition: a finite element analysis. Spine J. 2024;24(6):1121-1131.
[33] 吴周统, 周红海, 苏少亭, 等. 腰椎定点旋转手法治疗L4~S1双节段腰椎间盘突出症力学效应的三维有限元分析[J]. 中医正骨, 2024,36(10):1-9+38.
[34] 田强, 钟侨霖, 赵家友, 等. 提拉旋转斜扳法操作时腰椎椎间盘应力及应变的有限元研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2019,37(1):83-86.
[35] 苏少亭, 周红海, 侯召猛. 腰椎定点旋转手法对L4~5不同退变程度椎间盘的生物力学影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2023,38(10): 4964-4967.
[36] 丘明旺, 孙玫瑶, 吴耿佳, 等. 腰椎立体定位斜扳法与传统腰椎斜扳法对椎间盘及关节突关节软骨影响的有限元分析[J]. 中医正骨, 2024,36(1):14-22.
[37] LI L, SHEN T, LI Y. A Finite Element Analysis of Stress Distribution and Disk Displacement in Response to Lumbar Rotation Manipulation in the Sitting and Side-Lying Positions.J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017;40(8):580-586.
[38] 毕胜, 李义凯, 赵卫东, 等. 腰部推拿手法生物力学和有限元比较研究[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2002,24(9):16-19.
[39] 田强, 钟侨霖, 郭汝松, 等. 两种腰椎脊柱推拿手法推扳力的研究[J]. 广州中医药大学学报,2016,33(3):324-326.
[40] 范志勇, 黄淑云, 李黎, 等. 基于“法从手出”分析提拉旋转斜扳手法的数字化特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(27):4354-4359.
[41] 张德盛, 宋跃明. L3-L5三维非线性有限元模型的建立及其临床意义[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,2006,23(6):1250-1252.
[42] SCHILLING C, KRÜGER S, GRUPP TM, et al. The effect of design parameters of dynamic pedicle screw systems on kinematics and load bearing: an in vitro study. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(2):297-307.
[43] CHEN CS, CHENG CK, LIU CL, et al. Stress analysis of the disc adjacent to interbody fusion in lumbar spine. Med Eng Phys.2001;23(7):483-491.
[44] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;3 3(22):E820-E827.
[45] 丁立军, 吕杰, 廖跃华, 等. 中医推拿手法生物力学研究进展[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(5):1051-1056.
[46] 张玉璞, 吉登军, 张炎, 等. 推拿手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的作用机制进展[J]. 中国医药导报,2022,19(25):51-54.
[47] 彭思琪, 何添艺, 曾雯慧, 等. 腰椎斜扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的研究进展[J]. 中医正骨,2022,34(4):38-41, 45.
[48] 张锦平, 罗家良, 李义凯, 等. 牵扳手法对腰椎髓核内压力影响的实验研究[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2001,9(2):23-25.
[49] 徐海涛, 徐达传, 李云贵, 等. 坐位旋转手法时退变腰椎间盘内在应力和位移的有限元分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2007,22(9):769-771.
[50] 卢钰, 向俊宜, 尹本敬, 等. 斜扳手法和拔伸按压斜扳复合手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的有限元对比分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023,27(13):2011-2015.
[51] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会, 章振林. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691. |