Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2081-2090.doi: 10.12307/2026.070
Previous Articles Next Articles
Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy
Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing
- Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China
-
Received:2025-01-14Accepted:2025-04-27Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-28 -
Contact:Zhou Luxing, Lecturer, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
About author:Wang Zheng, MS, Experimentalist, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Exercise Physiology and Sports Medicine, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
Supported by:Young Teachers Scientific Research Support Project of Tianjin University of Sport, No. 24TYQZ009 (to ZLX); Tianjin Mental Health Education Research Special Project, No. 2024GX31 (to ZLX); Tianjin Sports Scientific Research “Preparation for Key Research Project”, No. 24BZ13 (to ZLX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

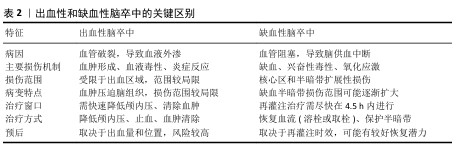
2.2.1 缺血性脑卒中的病理机制 缺血性脑卒中的核心病理机制是血流中断导致脑组织缺氧和能量代谢障碍。脑细胞对氧和葡萄糖需求极高,缺血几分钟内ATP迅速耗尽,诱发钙超载,最终导致细胞凋亡或坏死[40];同时,神经元大量释放谷氨酸,过度激活N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体,引发钙离子内流,加剧线粒体损伤和自由基生成,进一步恶化神经元损伤[41]。缺血再灌注后大量活性氧产生[42],对细胞膜、蛋白质和DNA造成氧化损伤,同时激活炎症信号通路,促使小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞释放炎症因子[43-44],破坏血脑屏障,导致水肿加重和损伤范围扩大[45]。血栓栓塞是缺血性脑卒中的重要特征[46]。血小板膜上糖蛋白高密度表达,激活后通过钙信号和CalDAG-GEFI途径促进血栓形成[47],血小板膜上糖蛋白在血小板聚集中发挥关键作用,它们缺失会损害整合素介导的血小板聚集,加速脑梗死[48]。因此,血栓不仅阻断血流,还通过细胞信号通路加剧脑损伤,进一步影响脑卒中的发展和预后。 2.2.2 出血性脑卒中的病理机制 出血性脑卒中由脑血管破裂引发,血液外渗至脑组织、脑室或蛛网膜下腔造成机械性损伤和毒性反应[49]。血肿形成后不仅压迫周围组织、阻碍局部血流,还引发继发性缺血损伤,导致颅内压升高,危及生命[50]。另外,血红蛋白及其降解产物(如血红素)会加剧氧化应激和神经元损伤,同时激活小胶质细胞和中性粒细胞,释放炎症因子,破坏血脑屏障并加重脑水肿[51]。红细胞在出血后24 h内溶解,它的降解产物进一步损伤脑组织。血红素通过Toll样受体4途径激活炎症反应,通过血红素加氧酶代谢产生铁、一氧化碳和胆红素,其中铁可通过芬顿反应生成自由基,加剧氧化应激和细胞损伤[52-53],因此,及时去除过量铁元素成为减轻二次损伤的关键策略。研究表明,去铁胺可有效减少血肿扩展,缓解脑水肿、降低神经损害[54]。总体而言,血红蛋白及其降解产物不仅具有直接的细胞毒性,还通过炎症和氧化应激加重出血性脑卒中的病理损伤。 "

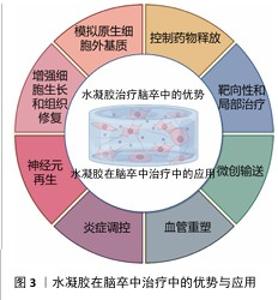
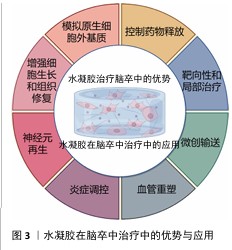
2.3 水凝胶在脑卒中治疗中的优势 2.3.1 水凝胶在脑卒中治疗的天然优势 水凝胶是一种水溶性聚合物的三维交联网络,通常由各种水溶性聚合物制成,具有多种化学组成[55]。通过如羟基和伯胺等化学残基形成物理或化学交联,水凝胶能够模拟原生细胞外基质,为神经修复提供结构支持[56]。 构成水凝胶骨架的材料包括胶原蛋白、透明质酸和明胶等,它们可以通过细胞黏附基序实现功能化,以促进细胞附着或内源性脑细胞的募集[56-58]; 此外,水凝胶的细胞外基质组成使它几乎不会引起免疫反应。WU等[59]的研究表明,细胞外基质水凝胶能减少病变体积、改善神经功能、调节促炎反应。在设计水凝胶时,可以通过动态可控的交联策略、多相结构优化降解动力学、结合力学性能调控优化组织适应性、降解产物安全性,在材料稳定性、降解速率和生物功能之间寻求最佳平衡[55-59]。 水凝胶具有优异的生物相容性,能够在植入部位逐渐降解,避免组织瘢痕和胶质瘢痕的形成。由透明质酸和纤维蛋白等生物材料制成的水凝胶已被用于增强脑卒中治疗,它的降解产物无毒,并且能减少巨噬细胞和小胶质细胞在损伤部位的浸润;此外,这些材料的弹性调节性能对细胞命运及水凝胶在损伤部位的分布具有重要影响[60]。由于脑组织具有特定的弹性模量(水凝胶可通过调节交联点或降解特性来匹配),水凝胶能够与脑组织融合而不引发排斥反应,并有利于细胞的分化。总体而言,水凝胶的可调力学性能在调节细胞行为和整合宿主组织方面至关重要。水凝胶可通过微创注射用于各种病理腔的填充,包括脑卒中的损伤区域,渗透性特性使得水凝胶能够以可控方式释放药物,延长药物在靶组织中的存在时间,减少药物剂量并避免全身不良反应。因此,基于水凝胶的生物材料在脑卒中治疗中的应用具有显著潜力[61]。 2.3.2 水凝胶在脑卒中治疗中的输送优势 水凝胶是一种在药物输送应用中得到广泛研究的生物材料。多糖基水凝胶因无毒性、生物相容性、可降解性和缓释性而受到广泛关注。目前可以用小分子药物、蛋白质、干细胞等治疗脑卒中。水凝胶在药物输送方面也有独特的优势。 (1)控制药物释放:一种具有吸引力的脑卒中治疗方法是输送生长因子,如成纤维生长因子和脑源性神经营养因子[62],然而这些生长因子在大脑中的滞留时间有限,导致疗效难以持续[63]。因此,如何延长生长因子的作用时间并提高其治疗效果,成为研究的重点。在这一背景下,水凝胶作为一种药物递送载体具有显著的优势,水凝胶可通过降解和扩散精确控制生长因子的持续释放,从而有效提高生长因子在大脑内的保留时间[64]。特别是,由细胞外基质成分构成的水凝胶,通过非共价相互作用能够调节生长因子的扩散和释放[65]。细胞外基质成分(如肝素和硫酸肝素)已被广泛应用于水凝胶的功能化设计[66]。NILASAROYA等[66]的研究表明,聚甲基丙烯酸2-羟乙基肝素功能化水凝胶能够有效保留成纤维生长因子2,并且水凝胶释放的生长因子能够持续渗透并作用于间充质基质细胞,促进组织修复。除此之外,细胞外基质中的其他成分(如胶原蛋白、纤维连接蛋白和玻璃体连接蛋白)也被探索用于增强水凝胶的功能,以促进生长因子的可持续释放。 通过在水凝胶中加载生长因子并控制生长因子释放,能够有效促进神经节细胞的定向神经突延伸。这种持续的生长因子释放不仅有助于局部治疗,还能避免高浓度生长因子通过血脑屏障时产生的脱靶效应和潜在毒性问题,因此,水凝胶可以在损伤部位实现更精确的生长因子释放,避免全身不良反应[67]。另外,水凝胶的可调节力学性能使它能够优化生长因子的释放动力学,从而实现更加特异和精准的药物递送。这些特性使得水凝胶成为脑卒中治疗中的一种理想载体,具备提高治疗效果和减少不良反应的双重优势[68]。水凝胶在脑卒中治疗中通常需要负载不同类型的药物,如促血管生成因子、神经营养因子、抗炎因子和抗氧化剂,通过设计时序性释放策略,实现精准功能调控;采用层状水凝胶或纳米载体实现多药物协同释放;结合智能响应水凝胶,动态调节药物释放可在不同病理阶段精准释放药物,实现多种药物的最大功能发挥[62-69]。 (2)靶向性和局部治疗:水凝胶的一个显著优势是它能够在特定的病理环境中定向释放药物,这是因为水凝胶可以设计成对特定的生理或病理条件(pH值、温度变化或特定酶的存在)具有响应性。例如,在脑卒中的损伤区域,由于局部酸性环境的变化,水凝胶可通过改变其结构或溶胀性释放药物至目标区域[70],这种靶向输送显著提高了治疗的精确性,能够直接将药物输送到受损的脑组织区域,而无需通过全身循环。与传统的全身给药方式相比,水凝胶能够局部递送药物,减少了药物对其他组织的影响,显著降低了全身不良反应。因此,水凝胶为脑卒中患者提供了一种更为个性化和高效的治疗方案[71]。 (3)增强细胞生长和组织修复:水凝胶不仅可作为药物递送载体,还能通过模拟细胞外基质的功能提供支持细胞生长和组织修复的环境。在脑卒中治疗中,水凝胶能够为移植的细胞或内源性脑细胞提供支架,促进细胞的黏附、增殖和分化。水凝胶中的细胞黏附基序能够帮助细胞与基质相互作用,从而促进神经元的修复和再生[72]。通过为细胞提供类似细胞外基质的支持结构,水凝胶能够促进神经元、胶质细胞以及血管内皮细胞的迁移和组织重建;此外,水凝胶的降解性和力学性能可随着时间的推移调整,为修复过程提供动态支持。整体上,这种材料不仅能改善药物的输送效果,还能通过改善微环境增强细胞修复和再生功能[73]。 (4)微创输送:水凝胶的流动性使它能够通过微创方式直接输送到脑卒中的损伤区域。与传统的手术治疗相比,注射水凝胶不仅减少了创伤,还缩短了患者恢复时间,减少了发生并发症的风险[74-76]。水凝胶可以通过针头注射、局部灌注等方式进入脑组织,精准地填充到病变区域,尤其是脑卒中后形成的病理腔或脑水肿区域[77-78]。由于水凝胶能够适应复杂的形状和大小,它可以完美地填充不同类型的病变区域,确保药物或细胞能够被均匀地分布在整个损伤区域,这种微创治疗方法不仅提高了治疗的便捷性,也降低了传统手术治疗中可能出现的操作风险和技术难度[79]。水凝胶在脑卒中治疗中的优势有天然优势和输送优势,下面将介绍水凝胶在脑卒中治疗中的应用情况。水凝胶在脑卒中治疗中的优势与应用见图3。 2.4 水凝胶在脑卒中治疗中的应用 水凝胶作为一种多功能生物材料,在脑卒中治疗中展现出显著的应用潜力。水凝胶独特的三维交联网络结构和生物相容性,使它能够针对神经元再生、血管重塑和炎症调控三大关键病理过程提供有效的治疗支持。 "
2.4.1 神经元再生 脑卒中后受损神经元难以自然再生,这是功能恢复的主要障碍之一。水凝胶通过以下机制促进神经元再生:①模拟细胞外基质:水凝胶可以模仿天然的细胞外基质,为神经元的再生提供类似于体内环境的支架。水凝胶的柔性和弹性特性与脑组织的力学性能相匹配,能够为神经元的黏附、增殖和分化提供理想的物理支持[65-73]。②递送神经营养因子:水凝胶能够以可控方式递送脑源性神经营养因子、成纤维生长因子等神经保护和修复因子[62]。通过持续释放这些因子,水凝胶能够激活神经元的再生信号通路,促进神经突的延伸和突触的重建。③支持移植细胞:水凝胶为干细胞提供了良好的存活微环境。通过将这些细胞嵌入水凝胶中,可增强移植细胞在脑组织中的存活率和分化潜力,从而促进损伤区域的神经修复[80]。 JIAN等[81]开发了一种由巯基糖胺聚糖聚电解质复合物纳米颗粒组成的纳米杂化水凝胶,可通过静电相互作用控制碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和基质衍生因子1α的释放;在缺血性脑卒中模型中,该水凝胶通过募集内源性神经干细胞并增强神经发生与血管生成,显著改善神经功能。另一方面,水凝胶的形状可塑性使其能够填充复杂的病理腔体。WANG等[82]设计的碳纳米管掺杂丝胶支架表现出良好的适形性,可完全填充脑卒中后形成的空腔。 自组装水凝胶因与细胞外基质类似的纳米纤维结构而备受关注,这些水凝胶通过氨基酸为交联体实现高水合性和生物相容性,避免免疫反应并融入病理区域,创造了理想的微环境[83]。功能化自组装肽水凝胶通过结合生物活性配体(如IKVAV和RGD肽)增强了细胞黏附和移植效果。例如,FARRUKH 等[84]开发的自组装肽纳米纤维水凝胶能够在适宜的pH值条件下自组装,载体兼具递送神经生长因子和包裹神经干细胞的能力,为神经再生提供了高效的支持。 水凝胶作为干细胞递送载体是脑卒中治疗中最有前景的策略之一,它不仅提高了干细胞移植的存活率,还通过优化细胞与微环境的相互作用促进神经发生和功能恢复。然而,从实验到临床应用仍存在诸多挑战,需要进一步深入研究。 针对不同患者的损伤程度和部位,个性化水凝胶的开发主要涉及以下几个方面:①针对不同损伤程度:轻度脑损伤可采用降解较快、负载低浓度神经营养因子的水凝胶,而严重脑损伤则需使用更稳定、可长时间释放神经营养因子和抗炎分子的水凝胶,如自修复水凝胶或双网络水凝胶,以提供长期支持[28]。②针对不同损伤部位:不同脑区的微环境(pH值、炎症程度、机械特性)不同,可设计响应性水凝胶。缺血性损伤区域可使用pH值响应型水凝胶,在低氧低pH值环境下释放血管生成因子,而炎症反应较强的区域可使用抗炎水凝胶,以调节免疫微环境[35-40]。③水凝胶材料的选择:生物来源水凝胶(如透明质酸、胶原蛋白、海藻酸盐)适用于需要高生物相容性、促进细胞黏附和组织修复的情况[50-55]。合成水凝胶适用于需要精确控制降解速率和药物释放的场景,可结合纳米技术优化递送效率。结合纳米颗粒、导电聚合物或基因的复合水凝胶,可适应更复杂的治疗需求,促进神经突生长或血管再生。④个性化制备策略:采用3D生物打印技术,根据患者影像学数据(如MRI)精确制备水凝胶支架,使它匹配个体损伤区域的形态和微环境。结合患者来源细胞体外模型,测试水凝胶对不同患者细胞的适应性,优化水凝胶的机械性能和生物活性[70-79]。 2.4.2 血管重塑 新生血管生成是指血管生成、动脉生成和血管形成的综合过程,对缺血性脑卒中的神经修复和减少继发性损伤具有重要作用[85]。新生血管不仅为病变区域提供足够的血液和氧气支持,还为细胞的能量代谢和功能恢复提供基础,因此,血管重塑是促进神经再生的关键途径[86]。现有研究表明,输送血管内皮生长因子或血管生成激素能够有效刺激新生血管生成,促进神经功能恢复。然而,如何在复杂的病理微环境中实现血管内皮生长因子的精准输送仍是主要挑战[87-88]。 基于透明质酸的水凝胶在血管内皮生长因子递送方面显示出显著优势。GAO等[89]设计了一种可生物降解的透明质酸水凝胶,其中含有负载血管内皮生长因子和血管生成素1的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸复合物微球,该水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性,能够在植入部位促进血管新生,在动物模型中显著促进运动功能恢复。NIH等[90]研究发现,肝素纳米颗粒可有效结合血管内皮生长因子,同时避免影响凝血功能;在中大脑动脉闭塞模型中,负载肝素纳米颗粒、血管内皮生长因子的透明质酸凝胶不仅促进了血管生成,还减少了小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞的数量,进一步验证了该水凝胶抗炎和血管修复的双重作用。 与此同时,干细胞递送系统的发展也为血管再生提供了新途径。MCCRARY等[91]将神经祖细胞包裹于含碱性成纤维生长因子结合硫酸软骨素A的水凝胶中,成功改善了小鼠脑卒中模型的损伤。总体而言,基于水凝胶的多功能输送系统为血管生成和神经再生提供了重要支持,为脑卒中治疗带来了新的可能性。 新生血管的稳定性对于持续改善损伤脑组织的微循环至关重要[86]。为确保新生血管的长期稳定,可联合递送促血管生成和血管成熟因子:血管内皮生长因子主要促进内皮细胞增殖和血管生成,但单独作用可能导致血管结构不稳定[10,40-42];血管生成素1可增强血管周细胞的募集,提高新生血管的稳定性;研究表明,血管内皮生长因子和血管生成素1的协同作用可改善血管完整性,减少病理性血管渗漏。优化水凝胶的递送模式以匹配血管生成动态,采用双相递送系统,先快速释放血管内皮生长因子以促进血管生成,再缓释血管生成素1以增强血管稳定性[12-15]。设计可降解微球或纳米载体实现时序控制释放,确保血管生成与成熟的平衡;调控局部微环境促进血管稳定,优化水凝胶的机械性能;载抗炎因子或免疫调节因子可改善血管稳定性;结合细胞疗法促进血管长期存活,采用间充质干细胞或内皮祖细胞结合水凝胶提高血管修复能力,促进新生血管与宿主循环整合[22,54-59]。 2.4.3 炎症调控 炎症反应是脑卒中后神经胶质细胞活化、外周免疫细胞募集以及炎症因子(如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6)释放的综合结果[91],这些炎症因子在病理过程中具有双重作用——早期加剧神经损伤,后期促进组织修复,因此治疗时机至关重要。炎症反应通过诱导神经细胞死亡、增强兴奋性毒性和氧化应激、破坏血脑屏障完整性以及扩大脑水肿,进一步加重脑损伤。调节小胶质细胞从M1表型向M2表型极化被认为是抑制炎症并促进脑修复的重要策略[92]。 脑卒中后的炎症反应具有时间依赖性,在急性期(损伤后0-3 d)主要表现为促炎反应,而在亚急性期(4-7 d)和恢复期(> 7 d)则需要促修复调控,因此,精准调控水凝胶在不同阶段的炎症调节作用,对于实现最佳治疗效果至关重要。在急性期时,主要是抑制过度促炎反应,水凝胶材料可通过负载抗炎因子和纳米载体减少小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞的M1型极化,防止炎症失控导致继发性损伤,缓释促血管生成因子(如血管内皮生长因子),防止缺血环境恶化。在亚急性期,水凝胶可通过缓释血管生成素1和神经营养因子(脑源性神经营养因子)增强血管和神经修复能力,以减少炎症损伤并促进组织修复。在恢复期,主要是促进组织重塑与神经功能恢复,水凝胶逐步降解并释放干细胞或外泌体,增强损伤组织的再生能力。另外,通过结合环境响应型水凝胶和细胞治疗与免疫微环境调节,可实现动态炎症调控。 水凝胶因优异的生物相容性和抗炎特性为脑卒中治疗提供了新的思路。例如,LIU等[93]设计了一种工程化透明质酸水凝胶,通过负载糖原合成酶激酶3β抑制剂和血管内皮生长因子实现双重药物递送,初期释放糖原合成酶激酶3β抑制剂抑制炎症,后期释放血管内皮生长因子促进血管生成。自组装丝素蛋白水凝胶能够减少小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞的活化,为病变区域提供修复性微环境。注射型水凝胶也因能够特异性结合细胞受体以调控免疫细胞极化而受到关注。水凝胶作为中药载体在脑卒中治疗中显示出潜力,多种中药被证实可通过抑制NLRP3炎性体激活发挥神经保护作用。研究表明神经干细胞具有显著的抗炎能力,结合水凝胶载体可进一步增强治疗效果[94]。总体而言,水凝胶在抗炎、神经保护和微环境调控方面展现出广阔的应用前景,为脑卒中治疗提供了新的策略。 "
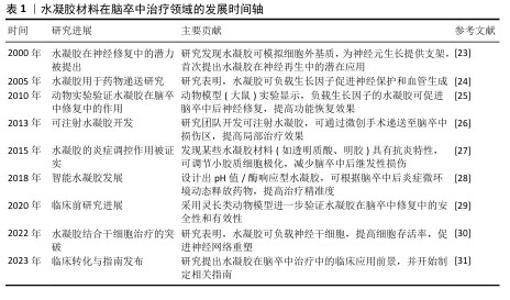
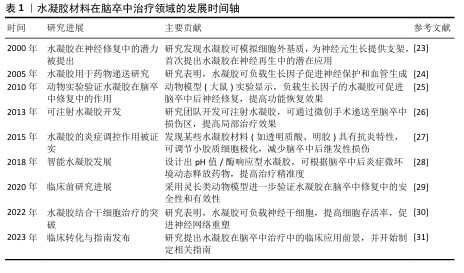
| [1] 张楠,孟庆华,鲍春雨,等.脑卒中患者运动过程中动力学特征的智能预测[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(3):489-496. [2] 周鲁星,孟庆华,刘文红,等.偏瘫患者下台阶过程下肢生物力学特征分析[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(1):125-131. [3] 周鲁星,孟庆华,刘文红,等.偏瘫患者以不同步态模式通过障碍物的生物力学特征对比分析[J].医用生物力学,2022, 37(5):805-811. [4] 符荷琯,沈栩轩,徐佳丽,等.青年烟雾病患者的卒中类型及危险因素分析[J].中国卒中杂志,2022,17(9):937-943. [5] RUST R, NIH LR, LIBERALE L. Brain repair mechanisms after cell therapy for stroke. Brain. 2024;147(10):3286-3305. [6] MIAO ZW, WANG Z, ZHENG SL, et al. Anti-stroke biologics: from recombinant proteins to stem cells and organoids. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2024;9(5):467-480. [7] PERERA KS, SHARMA MA, EIKELBOOM JW, et al. Combination Antithrombotic Therapy for Reduction of Recurrent Ischemic Stroke in Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease. Stroke. 2025; 56(2):380-389. [8] MCCABE JJ, WALSH C, GOREY S, et al. Interleukin-6, C-Reactive Protein, and Recurrence After Stroke: A Time-Course Analysis of Individual-Participant Data. Stroke. 2024;55(12):2825-2834. [9] SAFOURIS A, MAGOUFIS G, TSIVGOULIS G, et al. Emerging agents for the treatment and prevention of stroke: progress in clinical trials. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2021;30(10):1025-1035. [10] WANG Y, WANG Z, GUO W, et al. An injectable extracellular matrix-mimicking conductive hydrogel for sequential treatment of ischemic stroke. Chem Eng J. 2024;502:158039. [11] JIANG S, GENG R, WANG R, et al. The potential of hydrogels as a niche for promoting neurogenesis and regulating neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke. Mater Design. 2023;229:111916. [12] SHI T, LU H, ZHU J, et al. Naturally derived dual dynamic crosslinked multifunctional hydrogel for diabetic wound healing. Compos Part B-Eng. 2023;257:110687. [13] LEE JS, KIM HS, NAH H, et al. Bioinspired semi-flexible hydrogel with anti-inflammatory potential for natural tissue-mimicking bone regeneration. Compos Part B Eng. 2024;273:111223. [14] LIU Y, ZHANG W, HU C, et al. A composite hydrogel improves the survival and differentiation of human iPSC-derived neural stem cells after ischemic stroke. Compos Part B Eng. 2023;259: 110711. [15] WANG Y, LI G, YANG L, et al. Development of innovative biomaterials and devices for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Adv Mater. 2022;34(46):2201971. [16] WANG Z, HU C, ZHANG W, et al. An injectable ECM-like hydrogel with bioactive peptides and RepSox nanoparticles for myocardial infarction treatment. Chem Eng J. 2023;474:145878. [17] OVERMAN JJ, CLARKSON AN, WANNER IB, et al. A role for ephrin-A5 in axonal sprouting,recovery, and activity-dependent plasticity after stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(33):E2230-2239. [18] SHI Y, ZHOU M, ZHAO S, et al. Janus amphiphilic nanofiber membranes synergistically drive antibacterial and anti-inflammatory strategies for skin wound healing. Mater Design. 2023;227:111778. [19] SHAZEEB MS, CORAZZINI R, KONOWICZ PA, et al. Assessment of in vivo degradation profiles of hyaluronic acid hydrogels using temporal evolution of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI. Biomaterials. 2018;178:326-338. [20] LI C, WANG JT, LIU K, et al. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory synergistic effects of double-layer hydrogel promoting bacterial wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2024;493:152513. [21] DUAN H, LI S, HAO P, et al. Activation of endogenous neurogenesis and angiogenesis by basic fibroblast growth factor-chitosan gel in an adult rat model of ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(2):409-415. [22] ZHENG W, YAO SY, HU H, et al. Hypoxia-responsive calixarene-grafted self-assembled peptide hydrogel for inflammation suppression in ischemic stroke. Nano Today. 2024;54:102064. [23] O’CONNOR SM, ANDREADIS JD, SHAFFER KM, et al. Immobilization of neural cells in three-dimensional matrices for biosensor applications. Biosens Bioelectron. 2000; 14(10-11):871-881. [24] TIAN WM, ZHANG CL, HOU SP, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel as Nogo-66 receptor antibody delivery system for the repairing of injured rat brain: in vitro. J Control Release. 2005;102(1):13-22. [25] EMERICH DF, SILVA E, ALI O, et al. Injectable VEGF hydrogels produce near complete neurological and anatomical protection following cerebral ischemia in rats. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(9):1063-1071. [26] ZHANG Y, GAO C, LI X, et al. Thermosensitive methyl cellulose-based injectable hydrogels for post-operation anti-adhesion. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;101:171-178. [27] ZHANG S, ERMANN J, SUCCI MD, et al. An inflammation-targeting hydrogel for local drug delivery in inflammatory bowel disease. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(300): 300ra128. [28] GORENKOVA N, OSAMA I, SEIB FP, et al. In Vivo Evaluation of Engineered Self-Assembling Silk Fibroin Hydrogels after Intracerebral Injection in a Rat Stroke Model. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(2):859-869. [29] BATES NM, HEIDENREICH HE, FALLON ME, et al. Bioconjugation of a Collagen-Mimicking Peptide Onto Poly(vinyl alcohol) Encourages Endothelialization While Minimizing Thrombosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:621768. [30] LIU H, FENG Y, CHE S, et al. An Electroconductive Hydrogel Scaffold with Injectability and Biodegradability to Manipulate Neural Stem Cells for Enhancing Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(1):86-97. [31] JIANG S. The potential of hydrogels as a niche for promoting neurogenesis and regulating neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke. Mater Design. 2023;229:111916. [32] WARDLAW JM, William M. Feinberg Award for Excellence in Clinical Stroke: Small Vessel Disease; a Big Problem, But Fixable. Stroke. 2018;49(7):1770-1775. [33] FASTNER C, LESCH H, KRUSKA M, et al. Cardiac troponin elevation in intracerebral hemorrhage patients may rather reflect acute myocardial damage than acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2024;45(Supplement_1):Supplement_1.doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehae666.3019. [34] IZQUIERDO JM. Blood platelet factor 4: the elixir of brain rejuvenation. Mol Neurodegener. 2024;19(1):3. [35] 刘艺,肖凌勇,王璨,等.针刺介入时机对急性缺血性脑卒中患者肢体运动功能障碍的影响[J].中医杂志,2024, 65(19):2002-2009. [36] 曹克勇,王颍,黄昭鸣,等.语言认知评估训练与沟通仪治疗脑卒中患者复述障碍[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2021, 29(4):411-414. [37] 张梦妍,田苗苗,姚金玉,等.基于疾病特征的内养功训练对脑卒中患者焦虑抑郁及认知功能的影响[J].护理学杂志, 2024,39(23):44-47. [38] 仲思潼,曹馨元,梁吉,等.功能磁共振成像技术诠释针刺治疗缺血性中风机制的进展[J].磁共振成像,2024,15(11): 174-179. [39] 王雪,王立平,宋宁,等.脑卒中后眼球运动障碍行为视觉训练的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2024,30(6):726-730. [40] WEILINGER N, MASLIEIEVA V, BIALECKI J, et al. Ionotropic receptors and ion channels in ischemic neuronal death and dysfunction. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34:39-48. [41] MAYOR D, TYMIANSKI M. Neurotransmitters in the mediation of cerebral ischemic injury. Neuropharmacology. 2018;134:178-188. [42] BOCK FJ, TAIT SWG. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:85-100. [43] SHAKERI R, KHEIROLLAHI A, DAVOODI J. Apaf-1: Regulation and function in cell death. Biochimie. 2017;135:111-125. [44] LOU Y, MA M, JIANG Y, et al. Ferroptosis: A new strategy for traditional Chinese medicine treatment of stroke. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156:113806. [45] CHAI Z, ZHENG J, SHEN J. Mechanism of ferroptosis regulating ischemic stroke and pharmacologically inhibiting ferroptosis in treatment of ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024;30(7):e14865. [46] CHAN PH. Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001; 21(1):2-14. [47] JI C, YU X, XU W, et al. The role of glymphatic system in the cerebral edema formation after ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol. 2021;340:113685. [48] ZHOU X, LI Y, LENAHAN C, et al. Glymphatic System in the Central Nervous System, a Novel Therapeutic Direction Against Brain Edema After Stroke. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:698036. [49] 张宇,任倩玉,姜文慧,等.老年缺血性脑卒中伴脑微出血患者脂代谢特征及调脂药物应用特点与预后的相关性[J].中国老年学杂志,2025,45(1):20-24. [50] LI Z, HAN H, MA L, et al. Registry of Multimodality Treatment for Brain Arteriovenous Malformation in Mainland China (MATCH). Venous aneurysms in unruptured supratentorial brain arteriovenous malformations: a protective factor against hemorrhagic stroke and insights into hemodynamic mechanisms. Eur Radiol. 2025;35(5):2660-2669. [51] SLOANE KL, GOTTESMAN RF, JOHANSEN MC, et al. Stroke Subtype and Risk of Subsequent Hospitalization: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Neurology. 2024;102(3):e208035. [52] CHEN CH, SHOAMANESH A, COLORADO P, et al. Hemorrhagic Transformation in Noncardioembolic Acute Ischemic Stroke: MRI Analysis From PACIFIC-STROKE. Stroke. 2024;55(6):1477-1488. [53] EDWARDSON MA, MITSUHASHI M, VAN EPPS D. Elevation of astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles over the first month post-stroke in humans. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):5272. [54] CHENG Y, VALDÉS HERNÁNDEZ MDC, XU M, et al. Differential risk factor profile and neuroimaging markers of small vessel disease between lacunar ischemic stroke and deep intracerebral hemorrhage. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024;17:17562864241253901. [55] DONOFRIO CA, ARNAUTOVIC K, RICCIO L, et al. Neurological and functional outcomes of 32 patients with hemorrhagic brainstem cavernous malformations: a practical guide for surgical planning. J Neurosurg. 2025;142(5):1465-1475. [56] RIMMER J, LUND VJ. Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Rhinology. 2015;53(3):195-203. [57] AGUILAR BJ. All-cause mortality among veterans with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s dementia who have Intracerebral hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Alzheimer Dementia. 2024; 20(S4):e089735. [58] SANJANWALA D, LONDHE V, TRIVEDI R, et al. Polysaccharide-based hydrogels for drug delivery and wound management: a review. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022; 19(12):1664-1695. [59] WU Y, WANG J, SHI Y, et al. Implantation of Brain-Derived Extracellular Matrix Enhances Neurological Recovery after Traumatic Brain Injury. Cell Transplant. 2017;26(7): 1224-1234. [60] SAHA K, KEUNG AJ, IRWIN EF, et al. Substrate Modulus Directs Neural Stem Cell Behavior. Biophys J. 2008;95(9):4426-4438. [61] ENGLER AJ, SEN S, SWEENEY HL, et al. Matrix Elasticity Directs Stem Cell Lineage Specification. Cell. 2006;126(4):677-689. [62] CHAN SJ, LOVE C, SPECTOR M, et al. Endogenous regeneration: Engineering growth factors for stroke. Neurochem Int. 2017;107:57-65. [63] CORREA S, GROSSKOPF AK, LOPEZ HERNANDEZ H, et al. Translational Applications of Hydrogels. Chem Rev. 2021;121(18):11385-11457. [64] CAI L, HEILSHORN SC. Designing ECM-mimetic materials using protein engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(4): 1751-1760. [65] FU L, SUFLITA M, LINHARDT RJ. Bioengineered heparins and heparan sulfates. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;97: 237-249. [66] NILASAROYA A, KOP AM, MORRISON DA. Heparin-functionalized hydrogels as growth factor-signaling substrates. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(3):374-384. [67] YIN S, CAO Y. Hydrogels for Large-Scale Expansion of Stem Cells. Acta Biomater. 2021;128: 1-20. [68] VERNEREY FJ, LALITHA SRIDHAR S, MURALIDHARAN A,et al. Mechanics of 3D Cell-Hydrogel Interactions: Experiments, Models, and Mechanisms. Chem Rev. 2021; 121(18):11085-11148. [69] LI J, TIAN Q, SUN H, et al. A novel, liposome-loaded, injectable hydrogel for enhanced treatment of choroidal neovascularization by sub-tenon’s injection. Mater Today Nano. 2022;20:100264. [70] LIU C, ZHANG Q, ZHU S, et al. Preparation and applications of peptide-based injectable hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2019;9(48):28299-28311. [71] JIN T, NICHOLLS FJ, CRUM WR, et al. Diamagnetic chemical exchange saturation transfer (diaCEST) affords magnetic resonance imaging of extracellular matrix hydrogel implantation in a rat model of stroke. Biomaterials. 2017;113:176-190. [72] GHUMAN H, GERWIG M, NICHOLLS FJ, et al. Long-term retention of ECM hydrogel after implantation into a sub-acute stroke cavity reduces lesion volume. Acta Biomater. 2017;63:50-63. [73] BUDRIENĖ S, KOCHANĖ T, ŽURAUSKAITĖ N, et al. Synthesis and characterization of UV curable biocompatible hydrophilic copolymers containing siloxane units. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2023;34(11): 1539-1558. [74] GU C, LI Y, LIU J, et al. Neural stem cell-derived exosomes-loaded adhesive hydrogel controlled-release promotes cerebral angiogenesis and neurological function in ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol. 2023;370:114547. [75] POWERS WJ, RABINSTEIN AA, ACKERSON T. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019; 50(12):e344-e418. [76] ALLAN SM, ROTHWELL NJ. Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2(10):734-744. [77] BARTLETT RD, ELEFTHERIADOU D, EVANS R. Mechanical properties of the spinal cord and brain: Comparison with clinical-grade biomaterials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120303. [78] BOESE AC, LE QE, PHAM D, et al. Neural stem cell therapy for subacute and chronic ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018; 9(1):154. [79] CONTRERAS E, BOLÍVAR S, NAVARRO X, et al. New insights into peripheral nerve regeneration: The role of secretomes. Exp Neurol. 2022;354:114069. [80] ZHANG Y, ZHANG M, ZHANG R, et al. Conductive GelMA/PEDOT: PSS Hybrid Hydrogel as a Neural Stem Cell Niche for Treating Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front Mater. 2022;9:914994. [81] JIAN WH, WANG HC, KUAN CH, et al. Glycosaminoglycan-based hybrid hydrogel encapsulated with polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles for endogenous stem cell regulation in central nervous system regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018;174: 17-30. [82] WANG J, LI X, SONG Y, et al. Injectable silk sericin scaffolds with programmable shape-memory property and neuro-differentiation-promoting activity for individualized brain repair of severe ischemic stroke. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(7):1988-1999. [83] FU K, WU H, SU Z. Self-assembling peptide-based hydrogels: Fabrication, properties, and applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2021; 49:107752. [84] FARRUKH A, ORTEGA F, FAN W, et al. Bifunctional Hydrogels Containing the Laminin Motif IKVAV Promote Neurogenesis. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;9(5):1432-1440. [85] CARMICHAEL ST. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of neural repair after stroke: making waves. Ann Neurol. 2006;59(5): 735-742. [86] GUO F, LI J, CHEN Z, et al. An Injectable Black Phosphorus Hydrogel for Rapid Tooth Extraction Socket Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(20): 25799-25812. [87] CHEN J, LUO J, FENG J, et al. Spatiotemporal controlled released hydrogels for multi-system regulated bone regeneration. J Control Release. 2024;372:846-861. [88] OGLE ME, KRIEGER JR, TELLIER LE, et al. Dual Affinity Heparin-Based Hydrogels Achieve Pro-Regenerative Immunomodulation and Microvascular Remodeling. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(4):1241-1250. [89] GAO G, PARK JY, KIM BS, et al. Coaxial Cell Printing of Freestanding, Perfusable, and Functional In Vitro Vascular Models for Recapitulation of Native Vascular Endothelium Pathophysiology. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(23):e1801102. [90] NIH LR, GOJGINI S, CARMICHAEL ST, et al. Dual-function injectable angiogenic biomaterial for the repair of brain tissue following stroke. Nature Mater. 2018;17: 642-651. [91] MCCRARY MR, JESSON K, WEI ZZ, et al. Cortical Transplantation of Brain-Mimetic Glycosaminoglycan Scaffolds and Neural Progenitor Cells Promotes Vascular Regeneration and Functional Recovery after Ischemic Stroke in Mice. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(5):e1900285. [92] ZHENG W, YAO SY, HU H, et al. Hypoxia-responsive calixarene-grafted self-assembled peptide hydrogel for inflammation suppression in ischemic stroke. Nano Today. 2024;54:102064. [93] LIU Y, ZHANG F, LONG L. Dual-function hydrogels with sequential release of GSK3β inhibitor and VEGF inhibit inflammation and promote angiogenesis after stroke. Chem Eng J. 2022;433: 133671. [94] ANG H, HUANG W, MA J, et al. SWOT analysis and revelation in traditional Chinese medicine internationalization. Chin Med. 2018;13:5. [95] BECKER ML, BURDICK JA. Introduction: Polymeric Biomaterials. Chem Rev. 2021; 121(18):10789-10791. [96] POURAZARIYAN A, SHAHGHOLI M, KARIMIPOUR A. The effect of initial temperature and ZnO nanoparticle volume fractions on the stability of sodium alginate hydrogel nanocomposite using molecular dynamics simulation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer. 2025; 162:108641. [97] LIU RR, MAO LB, YU SH. Strong and tough chitin hydrogel constructed by dehydration and rehydration strategy. Nano Res. 2024; 17(9):8192-8199. [98] BORDINI EAF, FERREIRA JA, DUBEY N, et al. Injectable Multifunctional Drug Delivery System for Hard Tissue Regeneration under Inflammatory Microenvironments. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(9):6993-7006. [99] CHEN M, WANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Stimuli-responsive DNA-based hydrogels for biosensing applications. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):40. [100] LIU J, WANG K, LUAN J, et al. Visualization of in situ hydrogels by MRI in vivo. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(7): 1343-1353. |
| [1] | Liu Yang, Liu Donghui , Xu Lei, Zhan Xu, Sun Haobo, Kang Kai. Role and trend of stimuli-responsive injectable hydrogels in precise myocardial infarction therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [2] | Guo Yuchao, Ni Qianwei, Yin Chen, Jigeer·Saiyilihan, Gao Zhan . Quaternized chitosan hemostatic materials: synthesis, mechanism, and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [3] | Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei. Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| [4] | Liu Xiaohong, Zhao Tian, Mu Yunping, Feng Wenjin, Lyu Cunsheng, Zhang Zhiyong, Zhao Zijian, Li Fanghong. Acellular dermal matrix hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [5] | Huang Xinxu, Zhang Xin, Wang Jian. Living microecological hydrogels promote skin wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 489-498. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||