Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2091-2100.doi: 10.12307/2026.598
Previous Articles Next Articles
Quaternized chitosan hemostatic materials: synthesis, mechanism, and application
Guo Yuchao1, Ni Qianwei2, Yin Chen1, Jigeer·Saiyilihan1, Gao Zhan2
- 1Graduate School of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, General Hospital of Xinjiang Military Command, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-12-31Accepted:2025-03-21Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-29 -
Contact:Gao Zhan, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, General Hospital of Xinjiang Military Command, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Guo Yuchao, Master candidate, Physician, Graduate School of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Xinjiang Military Region General Hospital “Karakoram” Talent Fund Project, No. 2023JC05 (to NQW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Yuchao, Ni Qianwei, Yin Chen, Jigeer·Saiyilihan, Gao Zhan . Quaternized chitosan hemostatic materials: synthesis, mechanism, and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
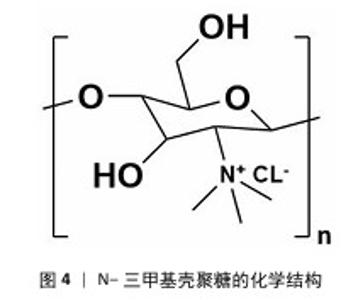
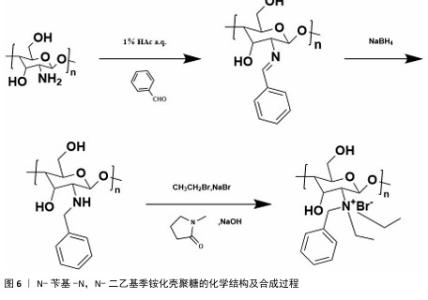
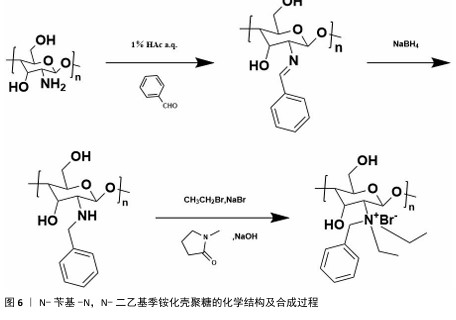
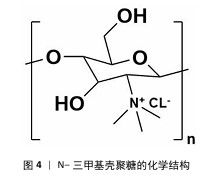
2.1 季铵化壳聚糖的制备与改性 季铵化壳聚糖存在众多种类,包括N-三甲基壳聚糖和N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖等,制备方式也不尽相同。 2.1.1 N-三甲基壳聚糖 季铵化壳聚糖衍生物中研究最多、形式最简单的是N-三甲基壳聚糖(图4)。相比于壳聚糖,N-三甲基壳聚糖在水溶液中具有更好的溶解性,能够与阴离子凝胶或大分子形成复合物,作为吸收促进剂、抗菌剂和基因载体被广泛研究,因此,N-三甲基壳聚糖比壳聚糖具有更多的应用前景和价值。KANG等[13]采用改良两步法合成可控摩尔质量的N-三甲基壳聚糖,季铵化程度可达70%-82%,第一步反应是通过Eschweiler-Clarke甲基化反应将壳聚糖制备N,N-二甲基壳聚糖;第二步是将N,N-二甲基壳聚糖与碘化甲酯在N-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮中反应一定时间,然后在N-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮中加入等体积的二甲基亚砜作为反应介质,延长反应时间后得到N-三甲基壳聚糖。MAHAJANA等[14]开发了一种高效、环保、安全的N-三甲基壳聚糖合成方法,以脂肪酶为生物催化剂、碳酸二甲酯为绿色甲基化剂,在三元深共晶溶剂组成的反应介质中,采用绿色方法合成N-三甲基壳聚糖,避免使用氢氧化钠和碘化甲酯等危险化学品,使合成过程完全绿色环保。 "
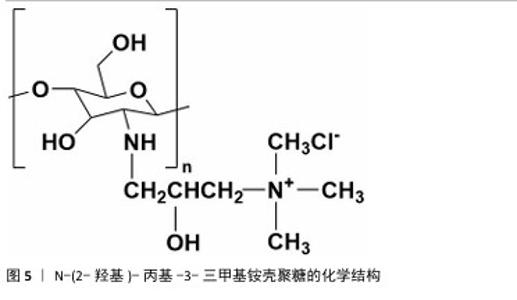
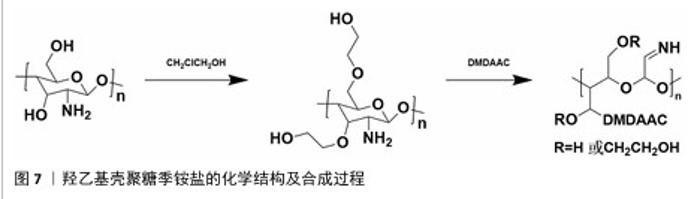
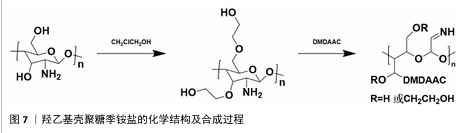
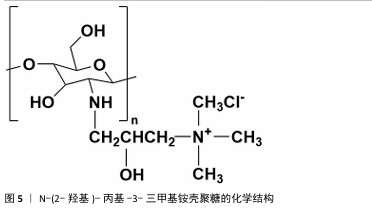
2.1.2 N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖 N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖拥有优秀的抗菌性、保湿性和吸湿性[15],同时具备良好的水溶性(图5),因而在紧急止血应用方面具有更大优势。N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖的合成已较成熟,DHLAMINI等[16]调整以往方法,在不断搅拌的壳聚糖醋酸溶液中加入缩水甘油基三甲基氯化铵,产物在过量的丙酮中沉淀,离心后洗涤干燥得到白色泡沫N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖;还有以1-烯丙基3-甲基咪唑氯化物为均相绿色反应介质制备取代度高的N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖的方法[17]。通过上述方法合成的N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖具有优异的生物活性。"
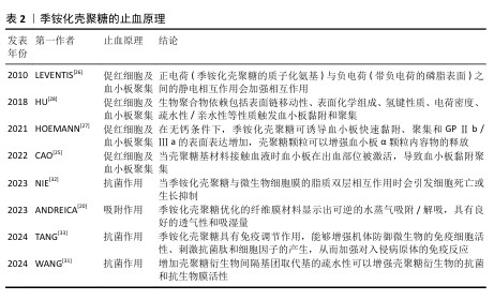
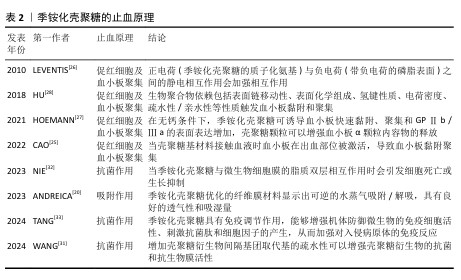
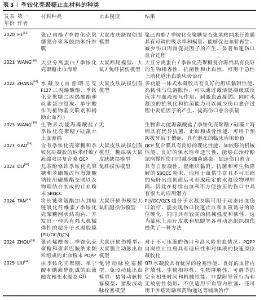
2.2 季铵化壳聚糖在紧急止血中的机制 季铵化壳聚糖的阳离子特性、黏附能力和生物活性共同驱动多维度止血机制,在紧急止血领域展现出独特的材料优势。季铵化壳聚糖的效能不仅依赖于物理性吸附血液水分、浓缩凝血因子以加速血块形成(吸附作用),还通过电荷诱导红细胞聚集、激活血小板黏附与活化通路协同增强凝血级联反应。另外,季铵基团赋予壳聚糖的抗菌性能进一步降低了感染风险,为创伤愈合提供双重保障,凸显季铵化壳聚糖在复杂创伤急救中的综合应用潜力。 2.2.1 季铵化壳聚糖的止血原理 (1) 吸附作用:由于季铵基的引入,季铵化壳聚糖表面带正电荷,使得它在水溶液中具有较好的稳定性,这种稳定性有助于保持突出的吸附性能,能够与带负电荷的离子发生静电吸引,从而实现离子的吸附和去除。ANDREICA等[20]将壳聚糖与N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖静电纺丝后按不同比例混合,发现N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖含量越高,材料的吸湿性能越好;同时比较了溶菌酶培养基与伤口渗出液的pH值,发现二者的变换相似,纤维在第16天后完全降解,证明材料具有作为生物可吸收敷料的潜力。WANG等[21]在棉制创面材料中添加季铵化壳聚糖后显著提升了棉制创面材料的吸湿性能,表现出较高的亲水性和压力下的保液率,相比原棉制材料及壳聚糖涂层棉制材料更适合作为创面材料。 (2) 促进红细胞聚集:红细胞是血液中血细胞的主要成员,通过有效增加血液黏度促进血小板向血管壁转运,在生理性止血中发挥重要作用。在自然生理条件下,红细胞表面带负电荷的糖脂之间的静电斥力抑制了红细胞的聚集[22]。壳聚糖链上的正电荷可以与带负电荷的红细胞静电相互作用,导致红细胞在出血点周围聚集形成血凝块,季铵化壳聚糖经季铵化改性后的溶解性显著增强,所携带的正电荷数量增多,增强了静电作用,使得红细胞更多的聚集。 FANG等[23]研制了一种由季铵化壳聚糖和儿茶酚修饰的海藻酸盐组成的双组分止血粉末,该粉末中的亲水性颗粒能迅速吸收界面血液转化为可溶性链,使红细胞和血小板聚集,在静电相互作用和氢键作用下这些可溶性多糖链相互交联并编织成一个网络,捕获聚集的红细胞和血小板,形成稳定有力的血凝块。SINGH等[24]将季铵化壳聚糖、磷酸化壳聚糖和单宁酸混合配置成新型止血水凝胶,通过季铵化壳聚糖聚集血细胞加速凝血级联反应的启动,而磷酸化壳聚糖模拟多磷酸盐,通过与血小板、因子Ⅴ和因子Ⅺ结合来激活凝血级联反应,加速纤维蛋白网络的形成以凝固血液,从而减少凝血时间。 (3) 促进血小板黏附和聚集:在自然生理状态下,血小板处于静止状态,不黏附在内皮细胞上。当壳聚糖基材料接触血液时血小板在出血部位被激活,导致血小板黏附聚集,在生理止血过程中起着至关重要的作用[25]。季铵化壳聚糖料相关止血机制主要涉及以下方面:正电荷(季铵化壳聚糖的质子化氨基)与负电荷(带负电荷的磷脂表面)之间的静电相互作用[26];糖蛋白Ⅱb-Ⅲa的表达升高,刺激血小板在血管壁上的活化、黏附和聚集[27];显著增加血小板中的Ca2+浓度、增强血小板膜GPⅡ b/ Ⅲ a复合物表达,阻止Ca2+进入血小板胞浆,大量Ca2+加速血小板活化,增强黏附性和聚集性[28]。由于带正电的季铵化壳聚糖与带负电的血细胞(包括红细胞和血小板)之间的静电相互作用,季铵化壳聚糖材料的主要止血机制建立在血细胞聚集的基础上。事实上,没有必要严格区分两种止血机制(红细胞聚集和血小板黏附/聚集),因为它们通常是协同作用的,同时血细胞在出血部位的聚集和集中也促进了多种凝血因子的集中和活化,进一步促进了血凝块的快速形成。 一旦动脉血管受损和破裂,基于聚乙烯亚胺/聚丙烯酸/季铵化壳聚糖的止血粉末在原位水化后迅速转化为粘接水凝胶,形成物理屏障[29],黏附的水凝胶还聚集血小板和血细胞,增强止血性能。LI等[30]使用季铵化壳聚糖和聚多巴胺制备的组织粘接冷冻剂具有相互连接的大孔结构,在吸收血液的膨胀过程中可为血细胞和血小板提供过滤功能,通过血细胞和血小板在血液吸收过程中的黏附、富集和活化促进血液凝固。 季铵化壳聚糖的止血原理见表2[20,25-28,31-33]。 "

2.2.2 季铵化壳聚糖抗菌性能在止血中的辅助作用 分子结构中的氨基使季铵化壳聚糖在酸性环境中带有正电荷,许多微生物,尤其是细菌和真菌细胞表面通常带有负电荷,这种电荷差异导致季铵化壳聚糖与微生物细胞表面之间产生静电吸引,从而影响细胞膜或细胞壁的完整性,发挥抗菌性能。当季铵化壳聚糖与微生物细胞膜的脂质双层相互作用时会引发细胞死亡或生长抑制[31-32],具体而言,季铵化壳聚糖能够插入脂质分子之间导致细胞膜的不稳定性,从而引起细胞成分的泄漏、重要功能的丧失,最终导致微生物的死亡。除此以外,季铵化壳聚糖能够直接与细菌、真菌和病毒等微生物细胞结合,这种结合阻碍了微生物在表面上的附着,从而降低了它们的定植能力和感染风险。通过与微生物的相互作用,季铵化壳聚糖还可以干扰微生物与宿主细胞的结合,防止疾病的发生。另外,季铵化壳聚糖具有免疫调节作用,能够增强机体防御微生物的免疫细胞活性、刺激抗菌肽和细胞因子的产生,从而加强对入侵病原体的免疫反应[33]。季铵化壳聚糖能够在止血过程中有效抑制细菌的生长、避免伤口感染,显著提升伤口愈合质量和效率。 KIM等[34]通过氯化缩水甘油三甲基铵和壳聚糖之间的反应制备了N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖,并将它用作棉花的抗菌添加剂,结果表明低浓度N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖能够有效抑制微生物的生长。SEONG等[35]对壳寡糖和N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖的抗菌效果进行研究,发现壳寡糖和N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖的最低抑菌浓度(取代度为1.04)分别为400,50 mg/mL,低浓度的N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖(0.2%)能够完全抑制细菌的生长(100%),而壳寡糖则需要达到1.8%的浓度才能实现完全的抑制效果;通过模拟洗涤实验评估材料的耐洗性,并在一定的洗涤周期后进行抗菌测试,结果显示0.30%的N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖能够完全抑制细菌生长,而2.4%壳寡糖在经过50次洗涤循环后仅能杀死96%的细菌,证实N-(2-羟基)-丙基-3-三甲基铵壳聚糖对受试微生物表现出更强的抑制作用。LUO等[36]将季铵化壳聚糖与光敏剂二氢卟吩e6共轭设计新型抗菌纳米胶束,通过激光照射和静电作用联合应用实现了快速且有效的靶向抗菌,在抑制生物膜形成及根除成熟生物膜方面展现出卓越效果,又能促进胶原蛋白沉积和上皮再生,显著加速感染伤口愈合,而不会对主要器官造成损害。 "

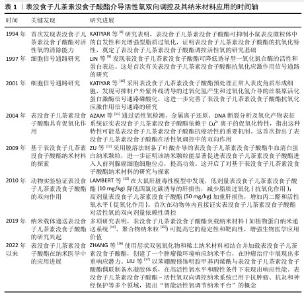
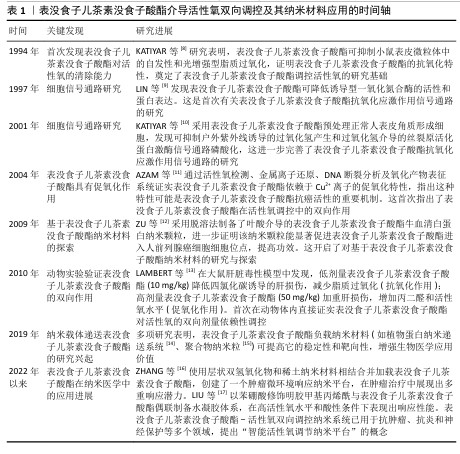
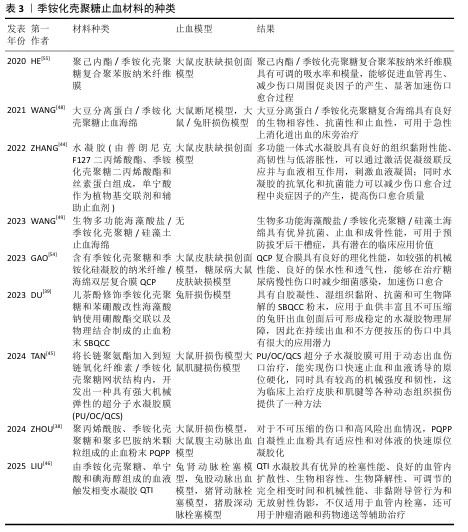
2.3 季铵化壳聚糖止血材料的研发与应用 随着对季铵化壳聚糖独特性能的深入认识,研究人员开发了多种不同形态的季铵化壳聚糖止血材料,包括季铵化壳聚糖粉末、季铵化壳聚糖水凝胶、季铵化壳聚糖海绵和季铵化壳聚糖纳米材料。当前研究聚焦于材料形态-性能的协同优化,以期突破传统止血剂的局限。 2.3.1 季铵化壳聚糖粉末 形状灵活的止血粉末适合用于复杂内出血的治疗,因为它们能够轻松进入深部伤口,有效接触隐藏的出血部位,填补复杂形状的空隙,并完全覆盖不规则伤口[37]。目前,基于多糖的止血粉末备受关注,特别是带正电荷的壳聚糖能够静电吸引带负电荷的红细胞和血小板,从而促进凝血。然而,值得注意的是,这类多糖粉末的止血机制主要依赖于物理堵塞,而非激活患者自身的凝血级联反应。另外,现有的止血粉通常存在凝胶化速度缓慢、机械强度不足以及黏附性不够的问题,这些因素增加了在高压血流下再次出血的风险。 为了解决止血粉机械强度和黏附力等问题,ZHOU等[38]使用微流控技术将聚丙烯酰胺、季铵化壳聚糖和聚多巴胺纳米颗粒组成复合材料,再通过冷冻干燥和机械研磨得到胶粘剂复合粉末材料PQPP,PQPP止血粉在吸收血液后自凝形成高度多孔的PQPP水凝胶,增强了材料的机械强度并抑制过度肿胀,同时促进血细胞和血红蛋白的黏附,达到有效止血的目的,这些优势使得PQPP止血粉能够应对心肌出血、动脉大出血等创伤性大出血;DU等[39]研制了能应用在非压迫止血和持续出血环境下的自凝胶粉末,他们将儿茶酚修饰季铵化壳聚糖和苯硼酸改性海藻酸钠使用硼酸酯交联以及物理结合制成止血粉末SBQCC,SBQCC能够迅速吸收渗出血液中的大量液体,导致凝血因子的浓缩,形成水凝胶型血凝块,随后凝血级联反应被启动并持续进行,促使纤维蛋白网络的生成和稳定的血凝块形成,同时SBQCC水凝胶优异的组织黏附性使血凝块能够牢固地附着在出血部位,实现稳定的止血效果。尽管季铵化壳聚糖止血粉末具有优异性能,面对紧急伤口也能早期进行止血,但在复杂伤口的长期稳定性方面仍需进一步探索[40]。 2.3.2 季铵化壳聚糖水凝胶 水凝胶具有独特的性能,包括适应生理条件的能力、亲水性、与软组织相似的含水量以及良好的柔韧性,这使得水凝胶成为一种高度通用的材料[41]。水凝胶能够通过吸水或失水而可逆地膨胀和收缩,表现出对环境刺激的特定响应能力,能够通过维持有助于伤口愈合的湿润环境来促进皮肤组织的愈合。水凝胶材料的结构与细胞外基质相似,为细胞生长提供了良好的支持;此外,水凝胶可以嵌入活细胞,细胞分泌的各种生物标志物能够扩散至伤口区域,从而促进愈合过程[42]。水凝胶的优越弹性也显著降低了因撕裂造成的二次损伤风险,进而提高了患者舒适度和愈合效率。 尽管用于伤口的水凝胶黏合剂已取得显著进展,但在潮湿条件下这些黏合剂容易与伤口分离,这种分离现象主要由于水凝胶溶胀后的机械黏附性和组织黏附性显著降低,给伤口护理带来了挑战[43]。为了解决传统水凝胶胶粘剂的局限性,ZHANG等[44]开发了一种新型低溶胀增韧黏合剂敷料,这种水凝胶由普朗尼克F127二丙烯酸酯、季铵化壳聚糖二丙烯酸酯和丝素蛋白组成,单宁酸则作为植物基交联剂和辅助止血剂,单宁酸与季铵化壳聚糖之间的协同作用使得水凝胶胶粘剂具备显著的抗菌特性,单宁酸的抗氧化特性有效降低了受伤部位炎症分子的释放,从而加速了伤口愈合过程。TAN等[45]通过酰腙键将长链聚氨酯加入到希夫碱反应获得的短链氧化纤维素/季铵化壳聚糖网状结构内,开发出一种具有强大机械弹性的超分子水凝胶膜(PU/OC/QCS)作为流动出血伤口治疗的生物黏附性伤口敷料,可实现快速伤口止血并经历血液诱导的原位硬化,同时呈现高机械强度和韧性。LIU等[46]研制一种由季铵化壳聚糖、单宁酸和碘海醇组成的血液触发相变水凝胶,该水凝胶接触血液时会从柔软的水凝胶转变为稳定的水凝胶,从而实现血管内栓塞,这种水凝胶在大动脉出血治疗中表现出良好的应用前景,能够根据不同病灶定制栓塞剂。 2.3.3 季铵化壳聚糖海绵 海绵因致密的多孔结构而具有优异的吸水性能,这一特性可增加血小板浓度和凝血因子,促进血小板的黏附和聚集,形成止血血凝块。然而,海绵止血材料的机械性能较差,容易破损,特别是在接触血液时更为明显,因此不适合治疗深部和不规则的伤口[47],严重者可能会引起疼痛并对神经造成局部压力。尽管如此,海绵止血材料的应用仍然十分广泛,治疗急性上消化道出血的复合海绵便是其中之一[48]。使用乙二醇二缩水甘油醚交联季铵化壳聚糖和大豆分离蛋白再冷冻干燥后得到多孔复合海绵,该复合海绵不仅能够向出血部位施加外部压力、密封血管破损末端,还能快速吸收大量血浆、浓缩红细胞和凝血因子与激活凝血途径,从而促进血液凝固;在止血的同时能抵抗消化酶保持材料的稳定及光谱的抗菌活性,应用于消化道急性出血中够快速止血,防止损伤进一步恶化。WANG等[49]将海藻酸盐、硅藻土、季铵化壳聚糖作为原材料,通过静电作用、Ca2+交联以及冷冻干燥制备CQD止血复合海绵用于临床拔牙后止血和预防干槽症的发生,CQD止血海绵可促进红细胞黏附与纤维蛋白网的产生,具有出色的止血性能;季铵化壳聚糖优异的抗菌性能合并硅藻土释放的硅离子介导成骨细胞分化,这些优点共同增强牙槽伤口的愈合。 2.3.4 季铵化壳聚糖纳米材料 近年来,纳米纤维材料在止血领域的应用逐渐增多。纳米材料具有独特特性,例如高纵横比、大表面积、良好的柔韧性,故能用于不同类型的伤口[50]。纳米纤维材料与天然纤维蛋白纤维相似的结构有助于包裹血细胞、血小板和其他凝血因子,从而提高止血效果[51];此外,纳米纤维在形态上与细胞外基质相似,可将成纤维细胞吸引到真皮层使它们分泌细胞质基质成分,如生长因子和胶原蛋白,加速受损组织的修复[52]。 在用于伤口的敷料中,季铵化壳聚糖基纤维是目前研究热点之一[53]。GAO等[54]采用静电纺丝和冷冻干燥相结合的方法成功制备了含有季铵化壳聚糖和季铵化硅凝胶的纳米纤维/海绵双层复合膜QCP,QCP表现出优异的物理化学性能,如强大的机械性能、良好的保水性和透气性,可促进血液凝固、减少细菌感染并加速糖尿病伤口闭合、抑制和去除病理瘢痕。为了解决伤口愈合过程中自由基导致组织感染并延长伤口愈合时间的问题,HE等[55]合成了季铵化壳聚糖复合聚苯胺材料,该材料具有更好的细胞相容性、抗菌活性与良好的电活性,可以减少伤口部位产生的过多自由基;随后,将聚己内酯的良好机械性能与季铵化壳聚糖复合聚苯胺材料的多功能行结合制备了纳米纤维膜,用于促进伤口愈合。 季铵化壳聚糖止血材料的种类,见表3。 "
| [1] CHENG F, LIU C, WEI X, et al. Preparation and Characterization of 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO)-Oxidized Cellulose Nanocrystal/Alginate Biodegradable Composite Dressing for Hemostasis Applications. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2017;5(5):3819-3828. [2] WANG C, ZHOU H, NIU H, et al. Tannic acid-loaded mesoporous silica for rapid hemostasis and antibacterial activity. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(12):3318-3331. [3] Watts SA, Smith JE, Woolley T, et al. Resuscitation with whole blood or blood components improves survival and lessens the pathophysiological burden of trauma and haemorrhagic shock in a pre-clinical porcine model. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023;49(1):227-239. [4] MALIK A, REHMAN FU, SHAH KU, et al. Hemostatic strategies for uncontrolled bleeding: A comprehensive update. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021; 109(10):1465-1477. [5] FORCILLO J, PERRAULT LP. Armentarium of topical hemostatic products in cardiovascular surgery: An update. Transfus Apher Sci. 2014;50(1):26-31. [6] SEIDI F, KHODADADI YAZDI M, JOUYANDEH M, et al. Chitosan-based blends for biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;183:1818-1850. [7] LÓPEZ-MALDONADO EA, MAVAEI M, DAN S, et al. Diverse applications of versatile quaternized chitosan salts: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;281:136276. [8] ANDREICA BI, ANISIEI A, ROSCA I, et al. Quaternized chitosan-based nanofibers with strong antibacterial and antioxidant activity designed as ecological active food packaging. Food Packaging Shelf. 2023;39: 101157. [9] BAN W, YANG Q, HUANG W, et al. Mussel-Inspired Catechol-Grafted Quaternized Chitosan Flocculant for Efficiently Treating Suspended Particles and Refractory Soluble Organic Pollutants. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2023;62(2):1099-1111. [10] BEJAN A, ANISIEI A, ANDREICA BI, et al. Chitosan nanofibers encapsulating copper oxide nanoparticles: A new approach towards multifunctional ecological membranes with high antimicrobial and antioxidant efficiency. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;260:129377. [11] PATHAK K, MISRA SK, SEHGAL A, et al. Biomedical Applications of Quaternized Chitosan. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(15): 2514. [12] PIRAS AM, ESIN S, BENEDETTI A, et al. Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Antiadhesive Properties of Different Quaternized Chitosan Derivatives. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6297. [13] KANG Y, LIU Z, LONG Y, et al. Synthesis and structural characterization of N , N, N ‐trimethyl chitosan. J Appl Polym Sci. 2021; 138(48):51811. [14] MAHAJAN T, BANGDE P, DANDEKAR P, et al. Greener approach for synthesis of N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan (TMC) using ternary deep eutectic solvents (TDESs). Carbohydr Res. 2020;493:108033. [15] WANG C, FAN J, XU R, et al. Quaternary ammonium chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composites prepared by electrospinning with high antibacterial properties and filtration efficiency. J Mater Sci. 2019;54(19): 12522-12532. [16] DHLAMINI KS, SELEPE CT, RAMALAPA B, et al. Dual Antimicrobial Activity of HTCC and Its Nanoparticles: A Synergistic Approach for Antibacterial and Antiviral Applications Through Combined In Silico and In Vitro Studies. Polymers (Basel). 2024; 16(21):2999. [17] ZHAO J, LI J, JIANG Z, et al. Chitosan, N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan (TMC) and 2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan (HTCC): The potential immune adjuvants and nano carriers. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;154:339-348. [18] CHEN Q, XIAO S, SHI SQ, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of N-substituted quaternized chitosan and its cellulose-based composite film. BioResources. 2019;15(1):415-428. [19] 郭睿,郭煜,马兰,等.羟乙基壳聚糖季铵盐的合成及絮凝性能[J].现代化工, 2018,38(3):147-150. [20] ANDREICA BI, ANISIEI A, ROSCA I, et al. Quaternized chitosan/chitosan nanofibrous mats: An approach toward bioactive materials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Carbohydr Res. 2023;302:120431. [21] WANG Y, ZHANG M, HOU H, et al. Synthesis of quaternized chitosan and its application in cotton as wound-dressing material. Surf Innov. 2023;11(4):213-222. [22] NAVEED M, PHIL L, SOHAIL M, et al. Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS): An overview. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;129:827-843. [23] FANG Y, LIN Y, WANG L, et al. Gluing blood into adhesive gel by oppositely charged polysaccharide dry powder inspired by fibrin fibers coagulation mediator. Carbohydr Res. 2024;333:121998. [24] SINGH G, NAYAL A, MALHOTRA S, et al. Dual functionalized chitosan based composite hydrogel for haemostatic efficacy and adhesive property. Carbohydr Res. 2020;247:116757. [25] CAO S, XU G, LI Q, et al. Double crosslinking chitosan sponge with antibacterial and hemostatic properties for accelerating wound repair. Compos Part B-Eng. 2022; 234:109746. [26] LEVENTIS PA, GRINSTEIN S. The Distribution and Function of Phosphatidylserine in Cellular Membranes. Annu Rev Biophys. 2010;39(1):407-427. [27] HOEMANN CD, RIVARD GE. Chitosan–Platelet Interactions. JAYAKUMAR R, PRABAHARAN M, eds.//Chitosan for Biomaterials III. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021:319-342. [28] HU Z, ZHANG DY, LU ST, et al. Chitosan-Based Composite Materials for Prospective Hemostatic Applications. Mar Drugs. 2018; 16(8):273. [29] PENG X, XU X, DENG Y, et al. Ultrafast Self‐Gelling and Wet Adhesive Powder for Acute Hemostasis and Wound Healing. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(33):2102583. [30] LI M, ZHANG Z, LIANG Y, et al. Multifunctional Tissue-Adhesive Cryogel Wound Dressing for Rapid Nonpressing Surface Hemorrhage and Wound Repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(32): 35856-35872. [31] WANG L, PANG Y, XIN M, et al. Effect of the structure of chitosan quaternary ammonium salts with different spacer groups on antibacterial and antibiofilm activities. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;276:133777. [32] NIE L, WEI Q, SUN M, et al. Injectable, self-healing, transparent, and antibacterial hydrogels based on chitosan and dextran for wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;233:123494. [33] TANG X, ZHANG Q, AIKELAMU K, et al. Effect of quaternized chitosan magnetic nanoparticles carrying indocyanine green phototherapy on cervical cancer cells. J Nanopart Res. 2024;26(5): 89. [34] KIM YH, YOON KS, LEE SJ, et al. Synthesis of Fully Deacetylated Quaternized Chitosan with Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity and Low Cytotoxicity. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022;11(11):1644. [35] SEONG HS, WHANG HS, KO SW. Synthesis of a quaternary ammonium derivative of chito-oligosaccharide as antimicrobial agent for cellulosic fibers. J Appl Polym Sci. 2000; 76(14):2009-2015. [36] LUO H, XU H, ZHANG H, et al. Photodynamic therapy combined with quaternized chitosan antibacterial strategy for instant and prolonged bacterial infection treatment. Carbohydr Res. 2025;352:123147. [37] FANG Y, ZHANG L, CHEN Y, et al. Polysaccharides based rapid self-crosslinking and wet tissue adhesive hemostatic powders for effective hemostasis. Carbohydr Res. 2023;312:120819. [38] ZHOU H, KONG B, CHENG Y, et al. Ultrafast Self‐Gelling, Adhesive, Anti‐Bacterial Coacervate‐Based Powders for Enhanced Hemostasis and Wound Healing. Small. 2024;21(3):2409164. [39] DU Y, CHEN X, LI L, et al. Benzeneboronic-alginate/quaternized chitosan-catechol powder with rapid self-gelation, wet adhesion, biodegradation and antibacterial activity for non-compressible hemorrhage control. Carbohydr Res. 2023;318:121049. [40] FANG Y, LIN Y, WANG L, et al. Cohering Plasma into Adhesive Gel by Natural Biopolymer–Nanoparticle Hybrid Powder for Efficient Hemostasis and Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(9): 11263-11274. [41] YAZDI MK, VATANPOUR V, TAGHIZADEH A, et al. Hydrogel membranes: A review. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;114:111023. [42] NILFOROUSHZADEH MA, KHODADADI YAZDI M, BARADARAN GHAVAMI S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids Embedded in an Injectable Thermosensitive Hydrogel: An In Situ Drug Formation Platform for Accelerated Wound Healing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(9):5096-5109. [43] PEAK CW, WILKER JJ, SCHMIDT G. A review on tough and sticky hydrogels. Colloid Polym Sci. 2013;291(9):2031-2047. [44] ZHANG L, ZHANG Y, MA F, et al. A low-swelling and toughened adhesive hydrogel with anti-microbial and hemostatic capacities for wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(6):915-926. [45] TAN L, HUYAN C, WANG Y, et al. Mechanically Robust Hemostatic Hydrogel Membranes with Programmable Strain-Adaptive Microdomain Entanglement for Wound Treatment in Dynamic Tissues. ACS Nano. 2024;18(11):8360-8382. [46] LIU M, SUN Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Blood‐Triggering Phase Transformational Hydrogel for Endovascular Embolization. Adv Funct Mater. 2025:2420440.doi:10.1002/adfm.202420440 [47] GUO Y, WANG M, LIU Q, et al. Recent advances in the medical applications of hemostatic materials. Theranostics. 2023;13(1):161-196. [48] WANG Z, KE M, HE L, et al. Biocompatible and antibacterial soy protein isolate/quaternized chitosan composite sponges for acute upper gastrointestinal hemostasis. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(4):rbab034. [49] WANG D, SUN Y, ZHANG D, et al. Root-shaped antibacterial alginate sponges with enhanced hemostasis and osteogenesis for the prevention of dry socket. Carbohydr Res. 2023;299:120184. [50] LI Y, LI M, ZHANG J, et al. Adsorption properties of the double-imprinted electrospun crosslinked chitosan nanofibers. Chin Chem Lett. 2019;30(3):762-766. [51] LU X, SI Y, ZHANG S, et al. In Situ Synthesis of Mechanically Robust, Transparent Nanofiber‐Reinforced Hydrogels for Highly Sensitive Multiple Sensing. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(30):2103117. [52] AHN S, CHANTRE CO, GANNON AR, et al. Soy Protein/Cellulose Nanofiber Scaffolds Mimicking Skin Extracellular Matrix for Enhanced Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(9):1701175. [53] MARIN L, ANDREICA BI, ANISIEI A, et al. Quaternized chitosan (nano)fibers: A journey from preparation to high performance applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;242:125136. [54] GAO Z, QI Q, LI R, et al. A nanofiber/sponge double-layered composite membrane capable of inhibiting infection and promoting blood coagulation during wound healing. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023; 224:113209. [55] HE J, LIANG Y, SHI M, et al. Anti-oxidant electroactive and antibacterial nanofibrous wound dressings based on poly(ε-caprolactone)/quaternized chitosan-graft-polyaniline for full-thickness skin wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2020;385:123464. [56] LI M, PAN G, YANG Y, et al. Smart aligned multi-layered conductive cryogels with hemostasis and breathability for coagulopathy epistaxis, nasal mucosal repair and bleeding monitoring. Nano Today. 2023;48:101720. [57] XU J, FANG H, SU Y, et al. A 3D bioprinted decellularized extracellular matrix/gelatin/quaternized chitosan scaffold assembling with poly(ionic liquid)s for skin tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;220:1253-1266. [58] SAYLAN Y, DENIZLI A. Supermacroporous Composite Cryogels in Biomedical Applications. Gels. 2019;5(2):20. [59] CHEN J, ZHAO L, LING J, et al. A quaternized chitosan and carboxylated cellulose nanofiber-based sponge with a microchannel structure for rapid hemostasis and wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;233:123631. [60] SASMAL P, DATTA P. Tranexamic acid-loaded chitosan electrospun nanofibers as drug delivery system for hemorrhage control applications. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 2019;52:559-567. [61] LIU A, HUANG Z, CUI S, et al. Ionically assembled hemostatic powders with rapid self-gelation, strong acid resistance, and on-demand removability for upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Mater Horiz. 2024;11(23):5983-5996. [62] MOTTAGHITALAB F, KHODADADI YAZDI M, REZA SAEB M, et al. Green and sustainable hydrogels based on quaternized chitosan to enhance wound healing. Chem Eng J. 2024;492:152288. |
| [1] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [2] | Bai Xiangyu, Huo Feng, Hao Yan, Wang Zecheng, Guo Xiaoyu. Platelet-derived growth factor BB-loaded chitosan/reduced graphene oxide scaffold for repairing alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 329-337. |
| [3] | Liu Xiaohong, Zhao Tian, Mu Yunping, Feng Wenjin, Lyu Cunsheng, Zhang Zhiyong, Zhao Zijian, Li Fanghong. Acellular dermal matrix hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [4] | Yuan Qian, Zhang Hao, Pang Jie. Characterization and biological properties of naringin-loaded chitosan/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [5] | Wang Zhuo, Sun Panpan, Cheng Huanzhi, Cao Tingting. Application of chitosan in repair and regeneration of oral hard and soft tissues [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 459-468. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||