Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1096-1105.doi: 10.12307/2026.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis
Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng
- Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, the Seventh Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen 518107, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-28Accepted:2025-01-09Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-20 -
Contact:Huang Dongfeng, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, the Seventh Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen 518107, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Qian, MD candidate, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, the Seventh Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen 518107, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Medical Research Fund, No. A2024023 (to ZQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
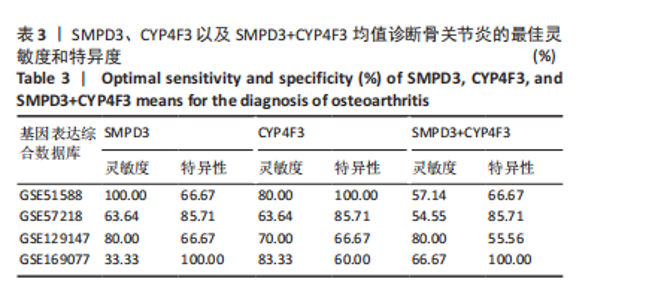
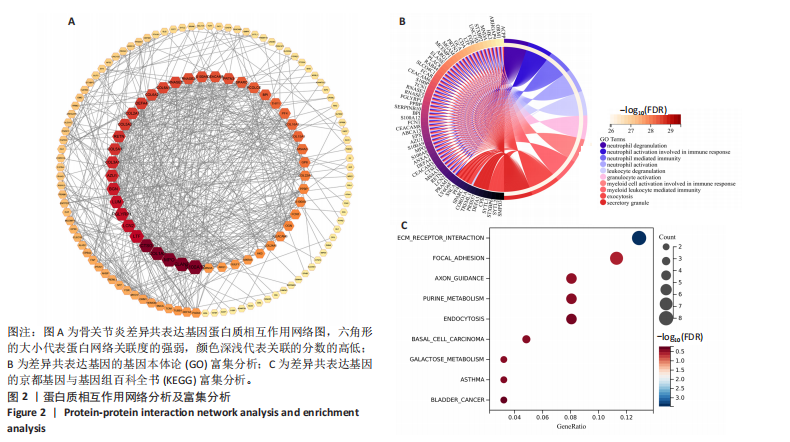
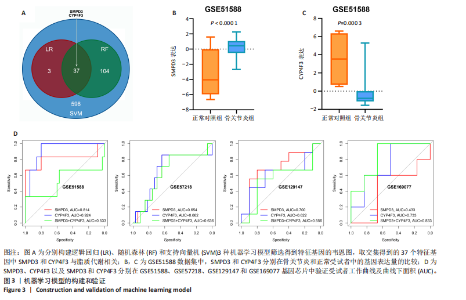
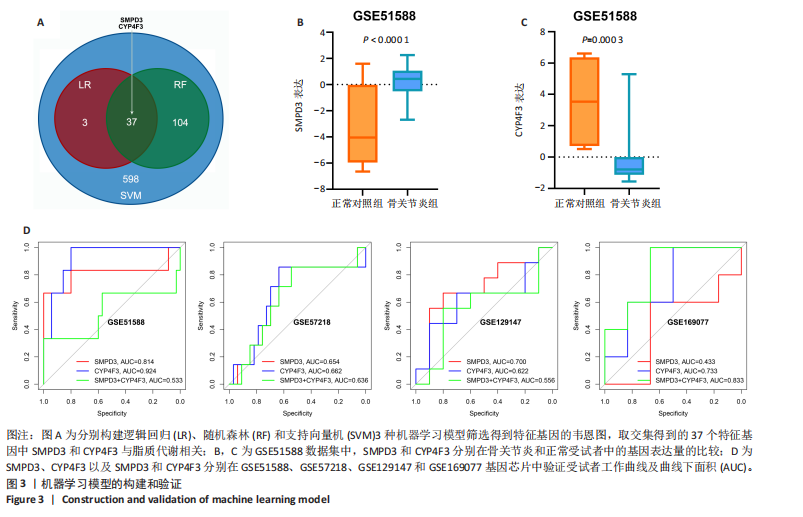
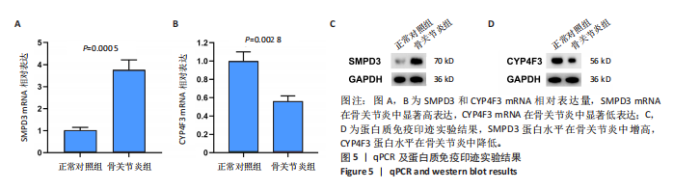
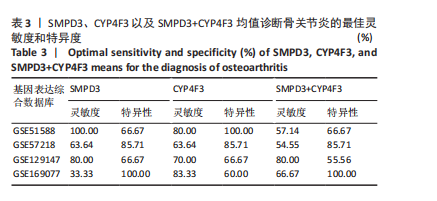
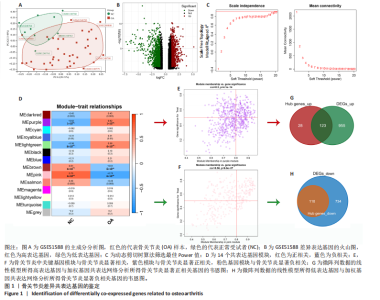
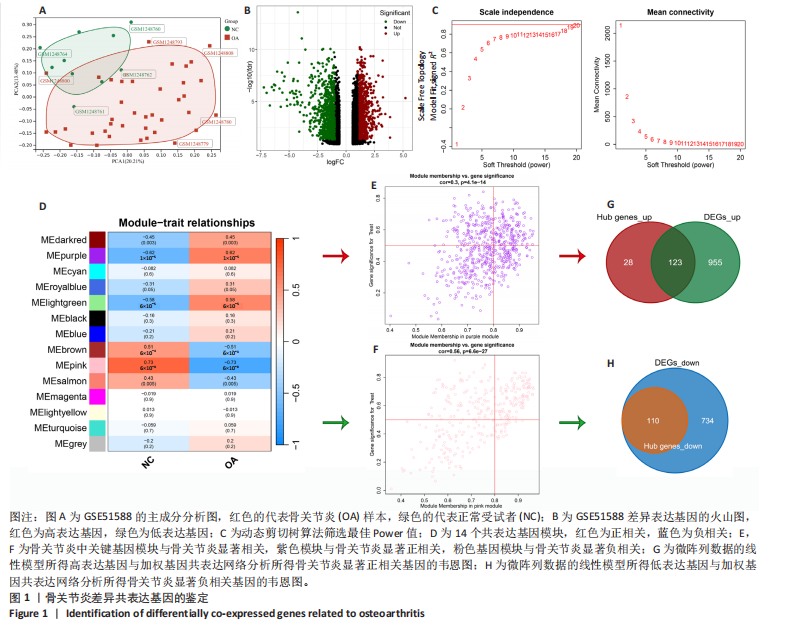
2.1 骨关节炎差异共表达基因筛选结果 通过LIMMA分析得到1 922个差异基因,其中高表达基因1 078个,低表达基因844个,绘制火山图(图1B)。同时,进行WGCNA分析,基于R2=0.9的无标度拓扑准则,选择20的软阈值(图1C),从而实现无标度网络的生成。最终产生14个模块(图1D)。其中,紫色模块与促进骨关节炎进展密切相关(r=0.62,P=1×10-5),而粉色模块与抑制骨关节炎密切相关(r=0.73,P=6×10-8)。最后,基于基因显著性> 0.5和模块隶属度 > 0.8,分别筛选得到促进和抑制骨关节炎的枢纽基因分别为151和110个(图1E,F)。进一步,骨关节炎中高表达基因和促进骨关节炎进展取交集,骨关节炎中低表达基因和抑制骨关节炎取交集,分别得到高/低表达的差异共表达基因123和110个(图1G,H)。 2.2 蛋白质相互作用网络分析结果 在STRING数据库中输入233个差异共表达基因,构建蛋白质相互作用网络。而后使用Cytoscape软件3.8.0版本cytoHubba插件的Degree算法进行排序并可视化(图2A),以探寻SMPD3和CYP4F3特征基因在蛋白网络中的贡献度,结果提示SMPD3和CYP4F3蛋白连接度均较低。 2.3 GO和KEGG富集分析结果 对差异共表达基因进行GO及KEGG富集分析。GO结果显示差异共表达基因主要富集在中性粒细胞脱颗粒、中性粒细胞免疫反应和应答、中性粒细胞激活和白细胞脱颗粒等(图2B)。KEGG富集分析结果提示差异共表达基因主要涉及细胞外基质受体的作用、黏附、轴突生长的调控以及嘌呤代谢等(图2C)。 2.4 机器学习模型的构建 选择差异共表达基因表达谱数据作为输入基因,运用R语言分别构建逻辑回归、随机森林和支持向量机模型并筛选获得特征基因。通过逻辑回归分析筛选得到40个基因;同时进行随机森林分析,随机选择并筛选最终得到141个基因;构建支持向量机模型,筛选得到154个基因;结合脂质代谢相关基因取交集,最终得到2个脂质代谢相关的特征基因,分别为SMPD3和CYP4F3(图3A-C)。 2.5 骨关节炎脂质代谢特征基因的验证 绘制ROC曲线并计算曲线下面积、灵敏度和特异性,从而验证SMPD3和CYP4F3作为骨关节炎特征基因的辨别效能。研究结果显示,训练集GSE51588的曲线下面积分别为0.814(SMPD3)、0.924(CYP4F3)和0.533 (SMPD3+CYP4F3),验证集GSE57218的曲线下面积分别为0.654(SMPD3)、0.662(CYP4F3)和0.636(SMPD3+CYP4F3),GSE129147的曲线下面积分别为:0.7(SMPD3)、0.622(CYP4F3)和0.556(SMPD3+CYP4F3),GSE169077的曲线下面积分别为0.433(SMPD3)、0.733(CYP4F3)和0.833(SMPD3+CYP4F3)(图3D),同时分别计算SMPD3、CYP4F3以及SMPD3+CYP4F3均值诊断骨关节炎的最佳灵敏度和特异性,见表3。总体来看SMPD3和CYP4F3作为骨关节炎特征基因具有一定的诊断效能。"
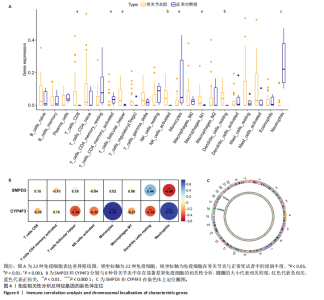
2.6 免疫浸润分析结果 使用CIBERSORT算法计算22种免疫细胞的丰度(图4A),结果显示8种免疫细胞在骨关节炎中具有显著差异。CD8 T细胞、T细胞滤泡辅助细胞、激活的自然杀伤细胞、巨噬细胞M1及静息态的树突状细胞在骨关节炎中显著升高,而激活的CD4记忆T细胞、单核细胞和中性粒细胞显著降低,其中中性粒细胞的差异是最显著的,这也与GO富集分析结果相一致。 2.7 特征基因相关性分析及染色体定位 基于以上结果,对骨关节炎中脂质相关特征基因SMPD3和CYP4F3与具有显著差异的8种免疫细胞进行相关性分析,结果显示SMPD3与静息态树突状细胞呈显著正相关(r=0.44,P=3.6×10-3),与中性粒细胞呈显著负相关(r=-0.48,P=1.7×10-3);而CYP4F3与单核细胞和中性粒细胞呈显著正相关(r=0.76,P=7.6×10-9;r=0.73,P=6.0×10-8),与T细胞滤泡辅助细胞和静息态树突状细胞呈显著负相关(r=-0.38,P=0.01;r=-0.38,P=0.01)(图4B)。染色体分布图显示高表达的"
| [1] CISTERNAS MG, MURPHY L, SACKS JJ, et al. Alternative Methods for Defining Osteoarthritis and the Impact on Estimating Prevalence in a US Population-Based Survey. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016;68(5):574-580. [2] JIANG Y. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):207-215. [3] ALLEN KD, THOMA LM, GOLIGHTLY YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):184-195. [4] 王成岩,安静楠,刘畅,等.1990至2019年中国不同部位骨关节炎疾病负担的年龄-时期-队列分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2024,13(8):614-620. [5] GIORGINO R, ALBANO D, FUSCO S, et al. Knee Osteoarthritis: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Mesenchymal Stem Cells: What Else Is New? An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6405. [6] 刘勇,蒋联建,梁功强,等.关节腔内注射药物治疗膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J].牡丹江医学院学报,2023,44(4):146-149. [7] 陈志安,段培押,普进兵,等.骨关节炎基因组学研究进展[J].武警医学,2024,35(5):443-447. [8] ROOS EM, ARDEN NK. Strategies for the prevention of knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(2):92-101. [9] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [10] CHIRICHELLA PS, JOW S, IACONO S, et al. Treatment of Knee Meniscus Pathology: Rehabilitation, Surgery, and Orthobiologics. PM R. 2019;11(3):292-308. [11] GELBER AC. Knee Osteoarthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2024;177(9):ITC129-ITC144. [12] FRANCISCO V, PÉREZ T, PINO J, et al. Biomechanics, obesity, and osteoarthritis. The role of adipokines: when the levee breaks. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(2):594-604. [13] XIONG J, LONG J, CHEN X, et al. Dyslipidemia Might Be Associated with an Increased Risk of Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:3105248. [14] BAKER KR, MATTHAN NR, LICHTENSTEIN AH, et al. Association of plasma n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with synovitis in the knee: the MOST study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(5):382-387. [15] EBRAHIM HA, ALZAMIL NM, AL-ANI B, et al. Suppression of knee joint osteoarthritis induced secondary to type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats by resveratrol: role of glycated haemoglobin and hyperlipidaemia and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(5):1375-1382. [16] CHOU CH, WU CC, SONG IW, et al. Genome-wide expression profiles of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R190. [17] AŞıK MD, GÜRSOY S, AKKAYA M, et al. Microarray analysis of cartilage: comparison between damaged and non-weight-bearing healthy cartilage. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(5):456-464. [18] RAMOS YF, DEN HOLLANDER W, BOVÉE JV, et al. Genes involved in the osteoarthritis process identified through genome wide expression analysis in articular cartilage; the RAAK study. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e103056. [19] DEN HOLLANDER W, RAMOS YF, BOS SD, et al. Knee and hip articular cartilage have distinct epigenomic landscapes: implications for future cartilage regeneration approaches. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(12):2208-2212. [20] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559. [21] WANG J, PENG X, PENG W, et al. Dynamic protein interaction network construction and applications. Proteomics. 2014;14(4-5):338-352. [22] HU X, NI S, ZHAO K, et al. Bioinformatics-Led Discovery of Osteoarthritis Biomarkers and Inflammatory Infiltrates. Front Immunol. 2022;13:871008. [23] NEWMAN AM, LIU CL, GREEN MR, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods. 2015;12(5):453-457. [24] SCHOBER P, VETTER TR. Logistic Regression in Medical Research. Anesth Analg. 2021;132(2):365-366. [25] HU J, SZYMCZAK S. A review on longitudinal data analysis with random forest. Brief Bioinform. 2023;24(2):bbad002. [26] VALKENBORG D, ROUSSEAU AJ, GEUBBELMANS M, et al. Support vector machines. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2023;164(5):754-757. [27] WANG XG, GAO LX, ZHAO MW, et al. Relationship between quantitative magnetic resonance imaging and clinical symptoms in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(14):1741-1743. [28] WEINHAGE T, KÖLSCHE T, RIEGER-FACKELDEY E, et al. Cord Blood Low-Density Granulocytes Correspond to an Immature Granulocytic Subset with Low Expression of S100A12. J Immunol. 2020;205(1):56-66. [29] 孙思东,黄群.右归丸联合中药熏蒸治疗肾阳虚型老年膝骨关节炎及其对关节液中OPN、S100A12及MMP-3的影响研究[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2023,50(11):113-116. [30] XU M, TU J, YANG Y, et al. Study on the relationship between the expression of S100A12, CaSR, and IL-7R in the synovium of knee osteoarthritis and angiogenesis. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(12):12775-12781. [31] 代凤雷,尹宏,张斌,等.大鼠滑膜组织中S100A12、IL-1β、Galectin-3与早期膝骨关节炎相关性研究[J].四川医学,2020,41(6):570-574. [32] 康麟,曹磊,赵秋鹤,等.过表达骨形态发生蛋白2对骨折大鼠的骨愈合和成骨能力的影响及其可能机制[J].广西医学,2021,43(8):966-971. [33] STOFFEL W, HAMMELS I, JENKE B, et al. Neutral sphingomyelinase (SMPD3) deficiency disrupts the Golgi secretory pathway and causes growth inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(11):e2488. [34] LUAN T, YANG X, KUANG G, et al. Identification and Analysis of Neutrophil Extracellular Trap-Related Genes in Osteoarthritis by Bioinformatics and Experimental Verification. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:3837-3852. [35] KANEVA MK. Neutrophil elastase and its inhibitors-overlooked players in osteoarthritis. FEBS J. 2022;289(1):113-116. [36] LUO Y, WANG L, PENG A, et al. Metabolic profiling of human plasma reveals the activation of 5-lipoxygenase in the acute attack of gouty arthritis. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2019;58(2):345-351. [37] NI KD, LIU JY. The Functions of Cytochrome P450 ω-hydroxylases and the Associated Eicosanoids in Inflammation-Related Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:716801. [38] MONTFORT A, BERTRAND F, ROCHOTTE J, et al. Neutral Sphingomyelinase 2 Heightens Anti-Melanoma Immune Responses and Anti-PD-1 Therapy Efficacy. Cancer Immunol Res. 2021;9(5):568-582. [39] XU Z, XU C, LU J, et al. Cytochrome P450 F3 promotes colorectal cancer via inhibiting NRF2-mediated ferroptosis. Transl Oncol. 2024;48:102077. [40] TANG XL, XU ZY, GUAN J, et al. Establishment of a neutrophil extracellular trap-related prognostic signature for colorectal cancer liver metastasis and expression validation of CYP4F3. Clin Exp Med. 2024;24(1):112. [41] ZHAO Z, HE X, BI Y, et al. Induction of CYP4F3 by benzene metabolites in human white blood cells in vivo in human promyelocytic leukemic cell lines and ex vivo in human blood neutrophils. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37(2):282-291. [42] KIKUTA Y, YAMASHITA Y, KASHIWAGI S, et al. Expression and induction of CYP4F subfamily in human leukocytes and HL60 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1683(1-3):7-15. |
| [1] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [2] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [3] | Gu Fucheng, Yang Meixin, Wu Weixin, Cai Weijun, Qin Yangyi, Sun Mingyi, Sun Jian, Geng Qiudong, Li Nan. Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| [4] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [5] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [6] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [7] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [8] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [9] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [10] | Chen Ying, Guo Xiaojing, Mo Xueni, Ma Wei, Wu Shangzhi, Li Xiangling, Xie Tingting. Analysis of diagnostic biomarkers for ischemic stroke and experimental validation of targeted cuproptosis related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7562-7570. |
| [11] | Ji Long, Chen Ziyang, , Jin Pan, Kong Xiangkui, Pu Rui, . Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7611-7619. |
| [12] | Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| [13] | Wu Qingyun, Su Qiang. Antioxidant nanomedicine-mediated targeted therapy for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7431-7438. |
| [14] | Li Jing, Lu Guangqi, Zhuang Minghui, Cui Ying, Yu Zhangjingze, Sun Xinyue, Ma Mingming, Zhu Liguo, Yu Jie. Development of a clinical prediction model for cervical instability in young and middle-aged adults based on machine learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7203-7210. |
| [15] | Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||