Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (23): 6021-6029.doi: 10.12307/2026.364
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visual analysis of shear wave elastography in skeletal muscle research
Li Qian1, Li Zhenxing2, Qiao Pengyan3, Wang Pingzhi3
- 1Shanxi Bethune Hospital (Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences/Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University/Tongji Shanxi Hospital), Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China; 2First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 3Shanxi Bethune Hospital (Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences/Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University/Tongji Shanxi Hospital), Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2025-05-24Accepted:2025-09-11Online:2026-08-18Published:2025-12-31 -
Contact:Wang Pingzhi, PhD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Shanxi Bethune Hospital (Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences/Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University/Tongji Shanxi Hospital), Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Qian, MS, Shanxi Bethune Hospital (Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences/Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University/Tongji Shanxi Hospital), Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences , Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Shanxi Provincial Key Research and Development Program Project, No. 2023021305010142024 (to WPZ); Shanxi Provincial Medical Key Discipline in 2024; Shanxi Provincial Key Clinical Specialty in 2024
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Qian, Li Zhenxing, Qiao Pengyan, Wang Pingzhi. Visual analysis of shear wave elastography in skeletal muscle research[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6021-6029.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
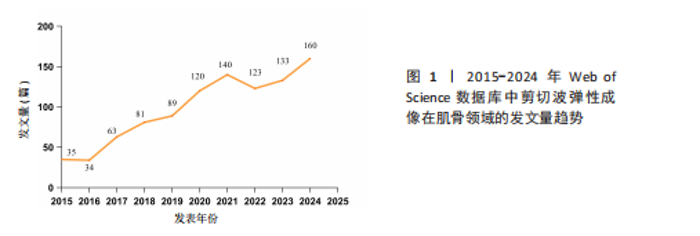
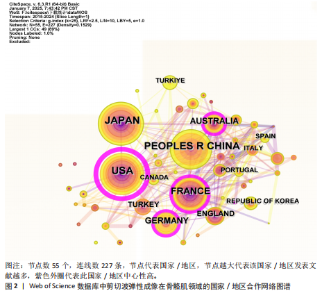
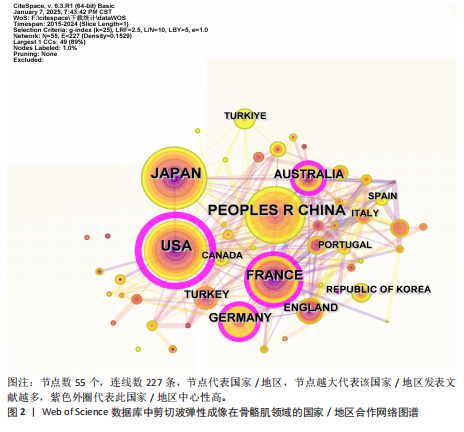
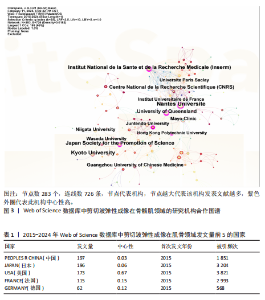
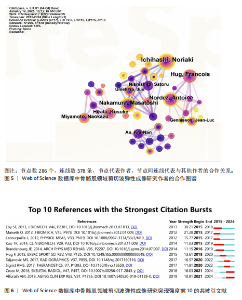
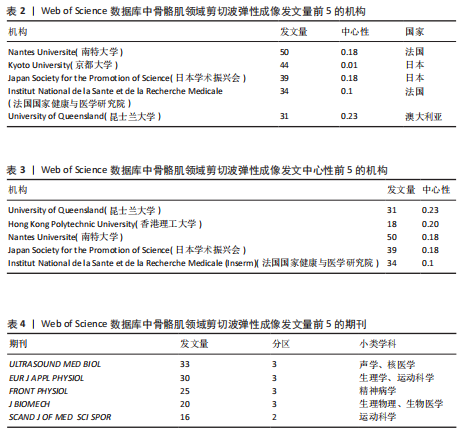
2.1 文献量的时间分布情况 年发文量由2015年35篇增至2024年160篇(年均增长率16.2%),表明该领域研究活跃度持续上升(图1)。 2.2 国家/地区合作可视化 国家合作分析旨在揭示SWE研究的全球合作模式。尽管过去10年间中国在这一领域发文量较多(197篇),但合作网络影响力较低且篇均被引频次低,表明其独立研究性强但国际协同不足且文献质量仍有提升空间。中心性排名前5的国家为美国(0.67)、法国(0.15)、澳大利亚(0.15)、德国(0.12)和韩国(0.07),显示美国节点辐射范围最广,与欧盟亚太地区形成多边合作集群,证明其具有学术影响力(表1,图2)。中国学者2022年发文量突破35篇,被引最多的文献为FENG等[5]用SWE和手持式MyotonPRO测量20名健康受试者的腓肠肌肌腹及跟腱,发现两种技术在骨骼肌中测得的硬度呈显著正相关。 2.3 机构可视化分析 共涉及236个机构,其中南特大学发文量居首。该机构在动态弹性成像技术开发方面处于领先地位,统计纳入的最新发表成果为GACHON等[6]进行的前瞻性研究,该团队用SWE评估不同妊娠阶段孕妇盆底肌弹性特征变化,发现阴道分娩时未发生撕裂的妇女在妊娠晚期Valsalva动作中肛门外括约肌硬度增加。中国发文量最多的机构为广州中医药大学(25篇)。研究机构大多来自高校,中心性排名前3的机构为昆士兰大学(0.23)、香港理工大学(0.20)及南特大学(0.18)。昆士兰大学在康复医学与运动生物力学交叉研究中表现突出,其合作网络涵盖多个国家/地区(表2,表3,图3)。"
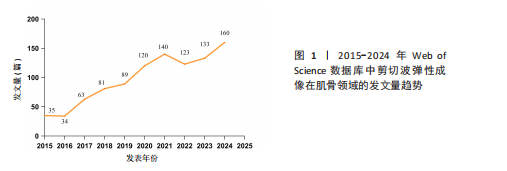
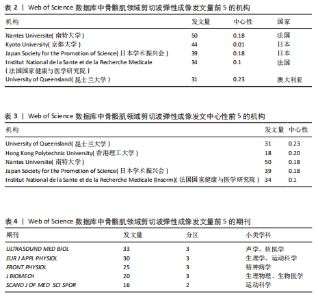
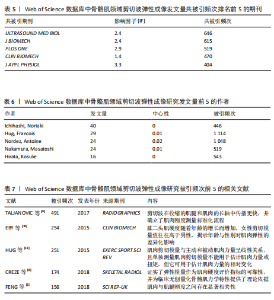
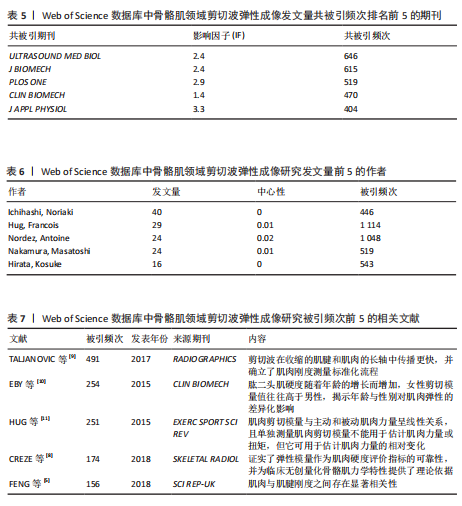
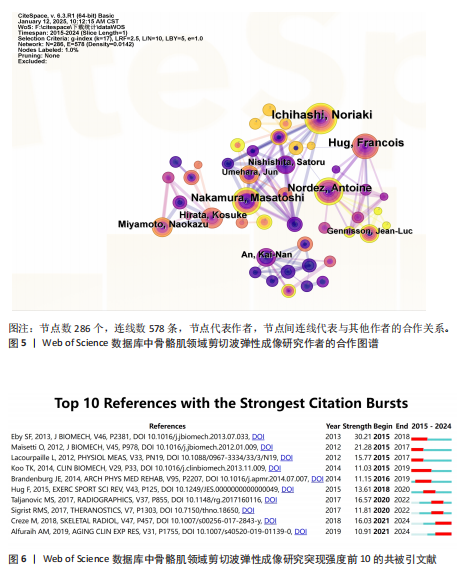
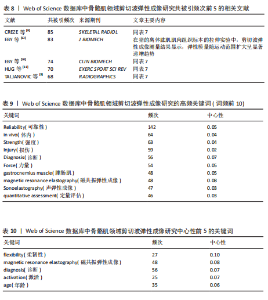
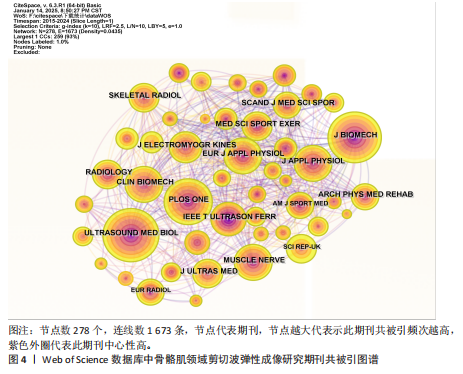
2.4 期刊分析 在2015-2024年,共346个期刊发表了SWE相关文章,研究领域涉及运动科学、生理物理、生物医学等。发文量最高的期刊是《ULTRASOUND MED BIOL》,说明该期刊是SWE技术研发与肌肉应用研究的首选发表平台,同时该期刊共被引频次最高,说明在此领域影响力较高(表4,表5,图4)。 2.5 作者可视化分析 对Web of Science数据库文献进行分析,此领域发文量前3的作者是京都大学医学物理治疗系的Ichihashi,Noriaki(40篇)、昆士兰大学健康与康复科学学院的Hug,Francois(29篇)及南特大学超声与生物力学实验室的Nordez,Antoine(24篇)。Ichihashi教授是神经康复领域SWE应用的权威学者,尤其在儿科肌肉痉挛评估方面具有较高影响力。合作网络最具影响力的作者是Nordez,Antoine教授,其在动态弹性成像技术开发与各向异性校正方面具有开创性贡献(表6,图5)。 2.6 纳入文献的被引分析和参考文献共被引分析 被引次数超过200次的文献有3篇(表7)。2024年共有2篇共被引文献突现(图6),其中ALFURAIH等[7]通过SWE技术测量了不同年龄范围受试者的股四头肌、腘绳肌和肱二头肌,结果显示老年参与者肌肉刚度下降与肌肉力量降低的相关性强于与肌肉质量的相关性。CREZE等[8]研究发现使用声辐射脉冲技术可定量测量骨骼肌硬度获得弹性模量值,值越大代表肌肉越硬,再次证实弹性模量值与剪切波速度呈正相关(表8)。 2.7 关键词分析 文献的关键词具有突出重点、快速导引的作用,因此分析关键词可快速了解文献的核心内容。 2.7.1 高频关键词分析 去除其中与SWE及肌骨有关的词,包括shear wave elastography、skeletal muscle、ultrasound elastography、elasticity、muscle等。关键词频次越高则代表研究主题热度越高,高频关键词显示:SWE的研究已从离体组织实验逐步转变为临床诊疗应用。SWE在"
腓肠肌中的研究成果最多,包括评估帕金森病、脑瘫等[13-16](表9)。有研究表明,SWE可评估肉毒毒素治疗后痉挛性脑瘫患儿内侧腓肠肌的肌肉硬度改变情况[17]。中心性前5位分别为flexibility(柔韧性)、Magnetic Resonance Elastography(磁共振弹性成像,MRE)、diagnosis(诊断)、activation(激活)、age(年龄)(表10)。SWE与MRE具有互补性和差异性,MRE对深层肌肉(如髂腰肌)成像的效果优于SWE,并可清晰显示脂肪浸润与水肿范围,但其动态成像能力差且成本高。研究表明,SWE与MRE评估肩袖等肌腱病变(包括撕裂)均具有敏感性[18-19]。撕裂的肩袖肌腱逐渐向近端回缩,可引发冈上肌等肌肉的退行性改变(如萎缩、脂肪浸润或纤维化)。这些病理性改变会导致肌肉刚度异常,因此可通过SWE技术量化冈上肌等肌肉的弹性模量变化,辅助评估肩袖损伤程度。近期研究热点为肌肉硬度与性别年龄的相关性,意味着设计神经肌肉疾病个体的骨骼肌干预措施时,性别和年龄是SWE需要考虑的重要因素,但目前此类研究仍缺乏共识[20]。已知衰老过程中肌肉会发生结构变化,有学者用SWE测腓肠肌厚度和硬度,发现老年人收缩状态下肌肉硬度的下降速度明显快于肌肉厚度[21]。 2.7.2 关键词聚类分析 分析结果显示,SWE在运动医学领域、物理治疗学和康复医学领域应用广泛(表11,图7)。 在运动中肌肉弹性是肌肉表现的关键决定因素,正常人或运动损伤患者在训练前后的肌肉硬度常会发生变化,肌肉硬度增加会限制关节活动范围,而肌肉硬度降低易导致关节部分脱位。通过SWE技术对肌肉硬度进行动态评估可识别异常模式(如局部纤维化或松弛),进而预防运动损伤并提高训练和肌肉表现。SWE凭借实时动态可视化优势,可实时监测肌肉主被动或阻力运动下的形态变化,通过量化肌肉组织弹性模量,实现了对运动状态下肌肉形态-功能偶联机"
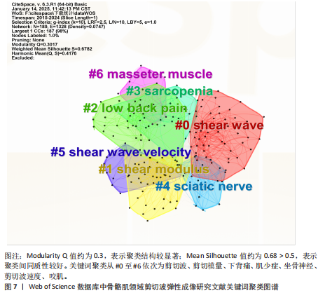
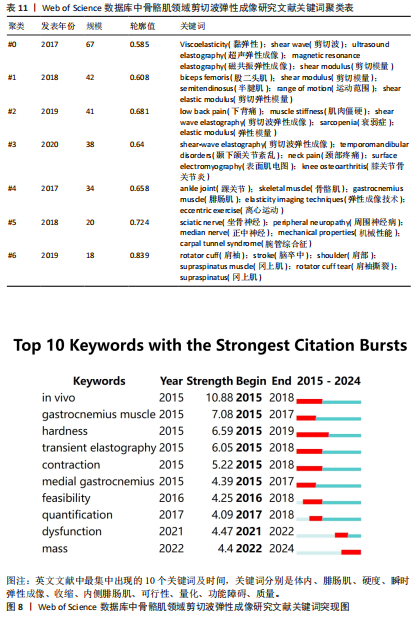
制的动态解析[22]。在运动损伤诊疗体系中,SWE不仅可精准区分急性期水肿与纤维化愈合阶段,更能有效识别肌肉疝等延迟性并发症。YOSHIDA等[23]的前瞻性队列研究证实,腓肠肌损伤患者肌肉肌腱交界处的剪切波弹性值在12周时与4周和8周相比显著升高,这一弹性模量动态演变规律为肌腱愈合质量评估提供了客观量化标准。 SWE技术的生物力学检测特性在物理治疗学和康复医学领域也获得了突破性应用。针对慢性非特异性腰痛患者可使用SWE监测多裂肌、腹横肌等核心肌群的弹性模量,同时量化康复训练中腰部肌的收缩功能,从而为个性化康复方案的制定与疗效评估提供创新性工具[24]。此外,在中枢神经损伤康复领域,SWE推动了对痉挛性瘫痪病理机制的认知。肌肉痉挛会导致严重的运动限制和功能受损,通常表现为肌肉力学特性的改变,脑卒中后偏瘫患者肱二头肌等肌肉的弹性模量升高时,其痉挛发生风险显著增加,这为临床早期干预提供了客观依据[25]。 肩关节生物力学研究的最新进展进一步拓展了SWE的临床应用边界。由于水含量以及血运改变,在受伤的肌腱中通常观察到肌肉解剖横截面积改变,意味着与肌肉活动和关节活动度相关的肌肉硬度可能与肌腱病有关。在肩袖损伤的病理机制研究中,除冈上肌的经典改变外,SWE首次揭示了斜方肌与三角肌弹性模量的代偿性变化规律,为理解肩关节力学失衡机制提供了新视角。针对传统评估手段的局限性,SWE在冈上肌肌腱炎疗效评价中表现出独特优势,其通过动态监测肌腱弹性模量的时空演变规律,有效解决了传统主观评估导致的治疗不足与复发难题[26]。如今在肌少症的诊疗中,SWE通过腓肠肌、股直肌等靶肌群的弹性特征分析,已被确立为监测肌肉质量变化的重要方法[27]。 2.7.3 关键词突现分析 关键词突现分析用于识别SWE研究热点的动态"
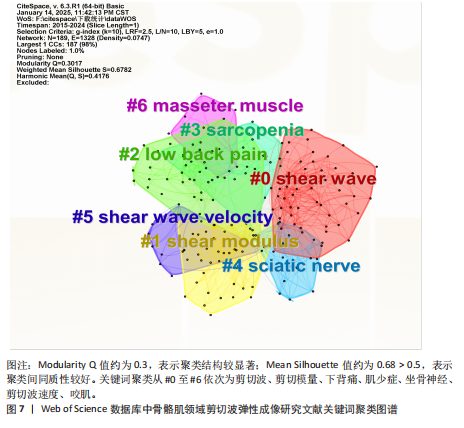
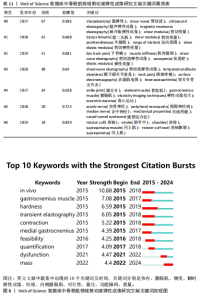
演变。2015年热点为利用SWE测量腓肠肌内侧的剪切模量作为肌肉硬度的指标。相比外侧腓肠肌,内侧肌纤维更短且超声图像更清晰。由于快速离心运动对短纤维的损伤效应更为显著,因此在涉及内侧腓肠肌快速离心收缩的短跑、跳跃等运动中,基于SWE技术开展肌肉组织力学特性及损伤程度的精准评估呈现提升态势[28]。2016年,随着实时SWE技术的发展,其逐渐用于评估神经系统或软组织损伤等患者的肌肉硬度[29]。2017年,剪切模量的量化特性成为诊断疾病的研究热点,这可能有助于更好地理解运动医学和临床中肌肉的力学行为,为康复医师及治疗师将SWE用于临床诊疗提供了可能[30-31]。2021年,“功能障碍”成为研究热点[32-34]。2022年至今,研究者验证了SWE评估肌肉质量的可行性,并提出SWE在肌少症筛查中的临床阈值,此技术作为评估肌少症的有效工具持续受到关注[35-36](图8)。"
| [1] ALBANO D, BASILE M, GITTO S, et al. Shear-wave elastography for the evaluation of tendinopathies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiol Med. 2024; 129(1):107-117. [2] CIUFFREDA G, ESTÉBANEZ-DE-MIGUEL E, ALBAROVA-CORRAL I, et al. Median nerve stiffness with three movement sequences of the upper limb neurodynamic test 1: An ultrasound shear-wave elastography study. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2025;75: 103221. [3] INNES S, JACKSON J. Musculoskeletal ultrasound imaging - An exploration of physiotherapists’ interests and use in practice. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2019; 44:102068. [4] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究, 2015,33(2):242-253. [5] FENG YN, LI YP, LIU CL, et al. Assessing the elastic properties of skeletal muscle and tendon using shearwave ultrasound elastography and MyotonPRO. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17064. [6] GACHON B, FRITEL X, PIERRE F, et al. In vivo measurement of the elastic properties of pelvic floor muscles in pregnancy using shear wave elastography. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024;309(6):2623-2631. [7] ALFURAIH AM, TAN AL, O’CONNOR P, et al. The effect of ageing on shear wave elastography muscle stiffness in adults. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019;31(12):1755-1763. [8] CREZE M, NORDEZ A, SOUBEYRAND M, et al. Shear wave sonoelastography of skeletal muscle: basic principles, biomechanical concepts, clinical applications, and future perspectives. Skeletal Radiol. 2018;47(4): 457-471. [9] TALJANOVIC MS, GIMBER LH, BECKER GW, et al. Shear-Wave Elastography: Basic Physics and Musculoskeletal Applications. Radiographics. 2017;37(3):855-870. [10] EBY SF, CLOUD BA, BRANDENBURG JE, et al. Shear wave elastography of passive skeletal muscle stiffness: influences of sex and age throughout adulthood. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2015;30(1):22-27. [11] HUG F, TUCKER K, GENNISSON JL, et al. Elastography for Muscle Biomechanics: Toward the Estimation of Individual Muscle Force. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2015;43(3):125-133. [12] EBY SF, SONG P, CHEN S, et al. Validation of shear wave elastography in skeletal muscle. J Biomech. 2013;46(14):2381-2387. [13] DEVIS M, LECOUVET F, LEJEUNE T, et al. Shear wave elastography in the assessment of gastrocnemius spastic muscle elasticity: influences of ankle position and muscle contraction. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2025; 61(1):52-60. [14] DING CW, WANG CS, ZHAO P, et al. Shear wave elastography characteristics of the gastrocnemius muscle in postural instability gait disorder vs tremor dominant Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neurol Belg. 2024;124(6):1875-1884. [15] BOULARD C, MATHEVON L, ARNAUDEAU LF, et al. Reliability of Shear Wave Elastography and Ultrasound Measurement in Children with Unilateral Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021;47(5):1204-1211. [16] LALL PS, ALSUBIHEEN AM, ALDAIHAN MM, et al. Differences in Medial and Lateral Gastrocnemius Stiffness after Exercise-Induced Muscle Fatigue. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(21):13891. [17] CEYHAN BILGICI M, BEKCI T, ULUS Y, et al. Quantitative assessment of muscle stiffness with acoustic radiation force impulse elastography after botulinum toxin A injection in children with cerebral palsy. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2018;45(1):137-141. [18] LI R, XUE H, ZHU Z, et al. The effect of shear wave elastography in the diagnosis of delaminated partial-thickness rotator cuff tears. Med Ultrason. 2023;25(4):390-397. [19] NASR AJ, PIERSON CJ, TZEN YT, et al. Emerging Role of Quantitative Ultrasound-Based Imaging Techniques for Characterizing Rotator Cuff Tears: A Scoping Review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13(12):2011. [20] ZHANG Z, WANG W, LI F, et al. Age and sex-related differences in elastic properties of the gastrocnemius muscle-tendon unit: an observational prospective study. Front Aging. 2024;5:1455404. [21] PANG J, WU M, LIU X, et al. Age-Related Changes in Shear Wave Elastography Parameters of the Gastrocnemius Muscle in Association with Physical Performance in Healthy Adults. Gerontology. 2021;67(3): 306-313. [22] KAWAMA R, YANASE K, HOJO T, et al. Acute changes in passive stiffness of the individual hamstring muscles induced by resistance exercise: effects of contraction mode and range of motion. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022;122(9):2085-2086. [23] YOSHIDA K, ITOIGAWA Y, MARUYAMA Y, et al. Healing Process of Gastrocnemius Muscle Injury on Ultrasonography Using B-Mode Imaging, Power Doppler Imaging, and Shear Wave Elastography. J Ultrasound Med. 2019;38(12):3239-3246. [24] LIU K, ZHAO T, ZHANG Y, et al. Shear wave elastography based analysis of changes in fascial and muscle stiffness in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1476396. [25] LEHOUX MC, SOBCZAK S, CLOUTIER F, et al. Shear wave elastography potential to characterize spastic muscles in stroke survivors: Literature review. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2020;72:84-93. [26] ZHOU J, YANG DB, WANG J, et al. Role of shear wave elastography in the evaluation of the treatment and prognosis of supraspinatus tendinitis. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(14):2977-2987. [27] WANG Z, XU Z, ZHONG H, et al. Establishment and Validation of a Predictive Model for Sarcopenia Based on 2-D Ultrasound and Shear Wave Elastography in the Medial Gastrocnemius Muscle. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2024;50(9):1299-1307. [28] ANDO R, SATO S, HIRATA N, et al. Relationship between resting medial gastrocnemius stiffness and drop jump performance. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2021;58:102549. [29] LI X, SUN H, ZHANG Z, et al. Shear Wave Elastography in the Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:899822. [30] ZIMMER M, STRAUB LF, ATEŞ F. Shear wave elastography reveals passive and active mechanics of triceps surae muscles in vivo: from shear modulus-ankle angle to stress-strain characteristics. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025;138(2):577-591. [31] HAYASHI D, ROEMER FW, TOL JL, et al. Emerging Quantitative Imaging Techniques in Sports Medicine. Radiology. 2023;308(2): e221531. [32] CHEN Y, LI J, DONG B, et al. Two-dimensional shear wave elastography: a new tool for evaluating respiratory muscle stiffness in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. BMC Pulm Med. 2022;22(1):441. [33] LIN LZ, YU YN, FAN JC, et al. Increased Stiffness of the Superficial Cervical Extensor Muscles in Patients With Cervicogenic Headache: A Study Using Shear Wave Elastography. Front Neurol. 2022;13:874643. [34] PINTO SM, CHEUNG JPY, SAMARTZIS D, et al. Are Morphometric and Biomechanical Characteristics of Lumbar Multifidus Related to Pain Intensity or Disability in People With Chronic Low Back Pain After Considering Psychological Factors or Insomnia. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:809891. [35] WANG Z, LYU G, ZHONG H, et al. Shear Wave Elastography for Detecting Calf Muscle Stiffness: An Effective Tool for Assessing Sarcopenia. J Ultrasound Med. 2023;42(4):891-900. [36] HAN X, LI Q, ZHANG G, et al. Application value of two-dimensional ultrasound and shear-wave elastography parameters in evaluating sarcopenia with essential hypertension. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025;15(1):831-842. [37] ZHU J, QIU L, TA D, et al. Chinese Ultrasound Doctors Association Guideline on Operational Standards for 2-D Shear Wave Elastography Examination of Musculoskeletal Tissues. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2024;50(2):175-183. [38] ROMANO A, STABER D, GRIMM A, et al. Limitations of Muscle Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography for Clinical Routine-Positioning and Muscle Selection. Sensors (Basel). 2021;21(24):8490. [39] HAYWARD S, CARDINAEL C, TAIT C, et al. Exploring the adoption of diaphragm and lung ultrasound (DLUS) by physiotherapists, physical therapists, and respiratory therapists: an updated scoping review. Ultrasound J. 2025;17(1):9. [40] ELLIS R, HELSBY J, NAUS J, et al. Exploring the use of ultrasound imaging by physiotherapists: An international survey. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;49:102213. [41] BOISSONNAULT È, JEON A, MUNIN MC, et al. Assessing muscle architecture with ultrasound: implications for spasticity. Eur J Transl Myol. 2024;34(2):12397. [42] UZUN AKKAYA K, AKKAYA HE, BEZGIN S, et al. Long-Term Effects of Different Number of Botulinum Toxin Injections Into the Gastrocnemius Muscle on Function and Muscle Morphology in Children With Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 2025;162: 97-104. [43] YIN S, ZHENG S, LI J, et al. Assessing Intensive Care Unit Acquired Weakness: An Observational Study Using Quantitative Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography of the Rectus Femoris and Vastus Intermedius. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2025;51(2):235-241. [44] YAGIZ G, FREDIANTO M, ULFA M, et al. A retrospective comparison of the biceps femoris long head muscle structure in athletes with and without hamstring strain injury history. PLoS One. 2024;19(2):e0298146. [45] GRANSEE H, SMITH J, JOHNSTON J, et al. Comparison of shear-wave elastography to state-of-the-art respiratory function testing to measure the range of forces generated by the diaphragm muscle. Physiology. 2023; 38(S1):5731374. [46] FOSSÉ Q, POULARD T, NIÉRAT MC, et al. Ultrasound shear wave elastography for assessing diaphragm function in mechanically ventilated patients: a breath-by-breath analysis. Crit Care. 2020;24(1): 669. [47] LEE J, MYRIE NO, JEONG GJ, et al. In vivo shear wave elasticity imaging for assessment of diaphragm function in muscular dystrophy. Acta Biomater. 2023;168:277-285. [48] PADUA L, CUCCAGNA C, GIOVANNINI S, et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome: updated evidence and new questions. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(3):255-267. [49] GURUN E, OZTURK M, CAKIR IM, et al. The Efficacy of Shear Wave Elastography in Evaluating Treatment Response to US-Guided Steroid Injection in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Acad Radiol. 2025; 32(5):2815-2821. [50] FAN Y, ZHENG H, FENG L, et al. Elasticity and cross-sectional thickness of paraspinal muscles in progressive adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Front Pediatr. 2024; 12:1323756. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Cao Yong, Teng Hongliang, Tai Pengfei, Li Junda, Zhu Tengqi, Li Zhaojin. Interactions between cytokines and satellite cells in muscle regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [3] | Pan Dong, Yang Jialing, Tian Wei, Wang Dongji, Zhu Zheng, Ma Wenchao, Liu Na, Fu Changxi. Resistance exercise activates skeletal muscle satellite cells in aged rats: role of adiponectin receptor 1 pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1736-1746. |
| [4] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [5] | Hou Chaowen, Li Zhaojin, Kong Jianda, Zhang Shuli. Main physiological changes in skeletal muscle aging and the multimechanism regulatory role of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [6] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [7] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [8] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [9] | Huang Liuyan, Zhang Wenxi, Chen Shuwen, Yu Shimei, Dai Zhong, Zuo Changqing. Forskolin promotes C2C12 myoblast differentiation via regulating the ERK and Akt signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1114-1121. |
| [10] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [11] | Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Cai Tianyuan, Wang Zicheng, Meng Zhuo, Zhan Xiaoqian, Chen Guoqian . Pain after total knee arthroplasty: current status and trend analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [12] | Yang Jun, Li Bin, Xing Guogang, Cai Jie, Liu Lu, Chen Peng, Zhang Tao, Fu Yuanbo, Liu Huilin. Application of patch-clamp technique in traditional Chinese medicine: a visual analysis of relevant literature [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6010-6020. |
| [13] | Qu Bolin, Ciren Lunzhu, Guo Jinyang, Meng Hanlu, Ding Guanxiang, Sang Hongpeng. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a visual analysis of current status and emerging trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6040-6050. |
| [14] | Li Yiguang, Guo Haonan, Ding Xiaotao, Yuan Mengyao, Jiang Lijin, Fan Xinfeng, Feng Yan. Visual analysis of research hotspots in the field of gut microbiota in the elderly at home and abroad [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6071-6080. |
| [15] | Yang Zijiang, Guo Chenggen, Deng Ziao, Xue Xinxuan. Postbiotic targeting muscle aging: mechanistic insights and application prospects of urolithin A [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5804-5813. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||