Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (23): 6010-6020.doi: 10.12307/2026.316
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of patch-clamp technique in traditional Chinese medicine: a visual analysis of relevant literature
Yang Jun1, 2, Li Bin1, 2, Xing Guogang3, Cai Jie3, Liu Lu1, 2, Chen Peng1, 2, Zhang Tao1, 2, Fu Yuanbo1, 2, Liu Huilin1, 2
- 1Acupuncture Center, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100010, China; 2Beijing Key Laboratory of Neuroregulation of Acupuncture, Beijing 100010, China; 3Institute of Neuroscience, Peking University School of Medicine, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2025-04-12Accepted:2025-06-13Online:2026-08-18Published:2025-12-31 -
Contact:Liu Huilin, PhD, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Acupuncture Center, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100010, China; Beijing Key Laboratory of Neuroregulation of Acupuncture, Beijing 100010, China -
About author:Yang Jun, PhD, Acupuncture Center, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing 100010, China; Beijing Key Laboratory of Neuroregulation of Acupuncture, Beijing 100010, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81973925 (to LHL); “Yangfan 3.0” Diagnostic and Treatment Ability Improvement Project of Beijing Hospitals Authority, No. ZLRK202324 (to LHL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Jun, Li Bin, Xing Guogang, Cai Jie, Liu Lu, Chen Peng, Zhang Tao, Fu Yuanbo, Liu Huilin. Application of patch-clamp technique in traditional Chinese medicine: a visual analysis of relevant literature[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6010-6020.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
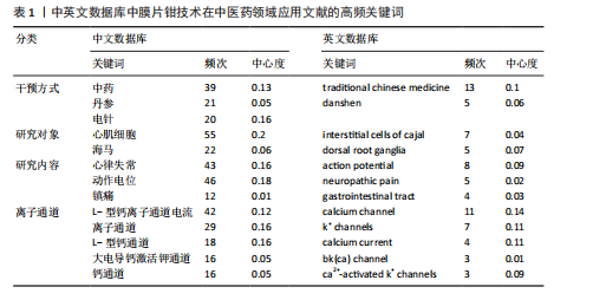
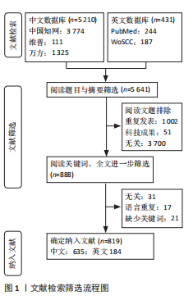
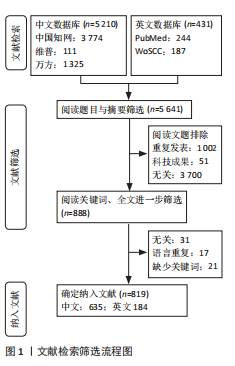
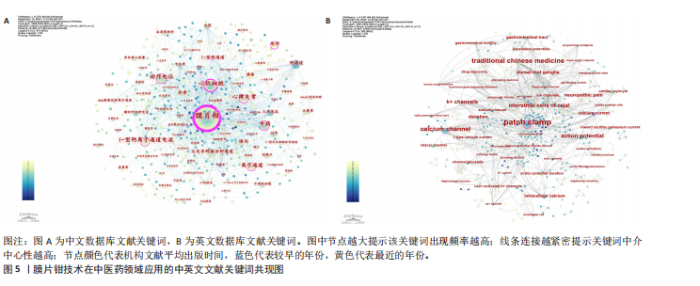
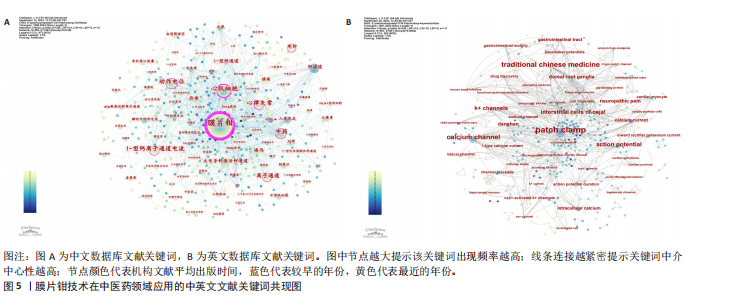
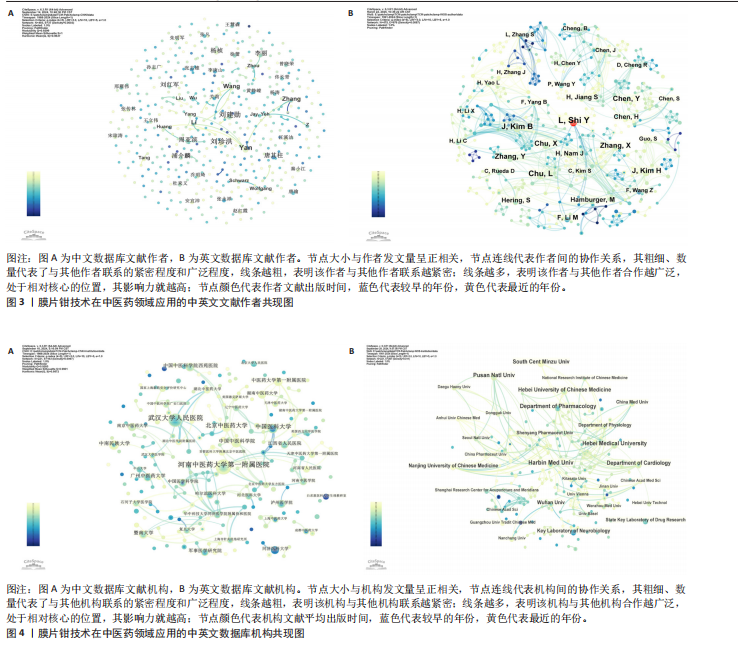
2.2 作者可视化分析 作者可视化分析可对研究领域内合作模式、学术影响力的深度解析,通过发节点大小(通常基于发文量或被引频次)和中介中心性,可快速定位领域内的高影响力学者。若某作者节点较大且中介中心性高,表明其不仅是高产作者,还可能是连接不同研究团队的桥梁。通过节点(作者)与连线(合作次数)的可视化,展示学术合作合作网络与团队结构。纳入此次研究的819篇文献中,共包含作者968名。依据普莱斯定律计算得出该领域研究的中英文核心作者的最低发文量约为2篇,核心作者共计129位(中文46,英文83)[9],发文量≥4篇的核心作者有17位(中文3,英文14)。将纳入文献绘制中英文文献作者共现图谱(图3),中文文献共计节点493个,37条网络连线,图谱的网络密度为0.000 3,作者之间未形成核心作者群及合作关系图中显示核心研究力量不足,研究作者较为分散,没有形成广泛合作的网络系统,整体结构分散。中文文献发文量最多为中国中医科学院西苑医院刘建勋、北京中医药大学刘洪珍。英文文献共计节点475个,976条网络连线,图谱的网络密度为0.008 7,发文量最高(7篇)为中国科学院上海生命科学研究院Shi Yu Liang。英文文献的个别核心作者在小范围构建了合作,河北医科大学Chu L与河北中医药大学Zhang Y,Zhang X合作较为紧密。 2.3 机构可视化分析 机构可视化分析可了解机构合作网络、发现核心机构、了解学科交叉情况,通过节点大小快速定位领域内高产机构,连线的粗细或颜色反映机构间合作频次。对纳入研究的机构进行可视化分析如图4所示,中文文献发文排名前5分别为河南中医药大学第一附属医院(19篇)、武汉大学人民医院(17篇)、中国医科大学(11篇)、北京中医药大学(11篇)、中南民族大学(8篇)、中国中医科学院(8篇)。英文文献发文排名前3为哈尔滨医科大学(8篇)、河北医科大学(7篇)、釜山大学(7篇)。涉及膜片钳在中医药领域研究的机构较多,且机构之间联系较为广泛。中文文献中北京中医药大学的研究机构中具有广泛的合作关系,拥有10个连接点,显示了其显著的影响力和学术网络中的核心地位;其次为中国中医科学院(7个连接点)、武汉大学人民医院(7个连接点)。英文文献中机构影响力排名前3为南京中医药大学(10个连接点)、釜山大学(9个连接点)、河北医科大学(8个连接点)。 2.4 关键词可视化分析 关键词共现图谱可直观显示该领域研究热点,图谱中节点的大小反映关键词出现的频率,连线的紧密程度反映节点中介中心性大小,关键词的中介中心性越大提示其在共现网络中的影响力越大。研究纳入819篇国内外相关文献提取关键词,将同义词合并,绘制关键词共现图谱(图5),中文文献共计506个节点,1 383条连线,网络密度为0.010 8,英文文献共计467个节点,891条线,网络密度为0.008 2。将关键词归纳为干预方式、研究对象、研究内容、离子通道4类,以出现频次为据分类排序,见表1。中文文献以“中药”及“电针”为热点治疗措施,“丹参”在中药研究中尤为关注。“心律失常” “动作电位”及“镇痛”为主要研究内容,关注对象集中为“心肌细胞” “海马”,关注离子通道主要涉及“L-型钙离子通道电流” “大电导钙激活钾通道”及“钾通道”。英文文献与中文文献治疗措施大体相似,以“中药” “丹参”为主。研究对象存在差异,英文文献主要关注对象为“Cajal间质"
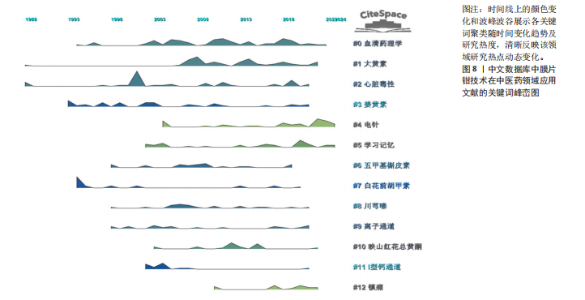
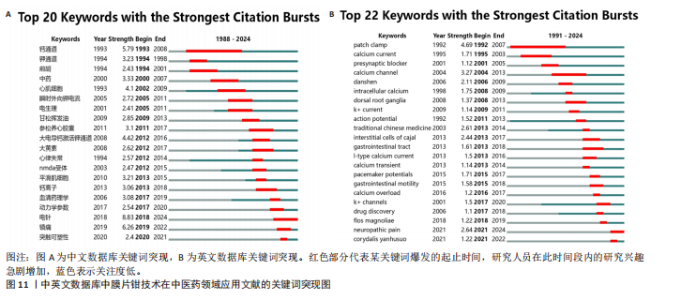
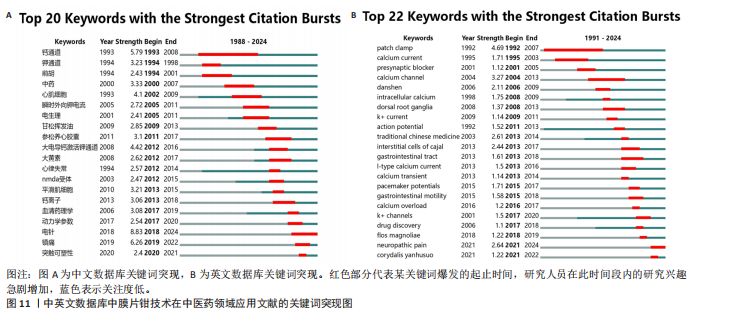
细胞” “背根神经节”,研究热点集中于“动作电位” “神经病理痛”及“胃肠道”,离子通道主要围绕“钙通道”及“钾通道”展开。 关键词聚类分析将具有相似研究主题的文献进行聚类,形成不同的研究主题群,从而帮助研究者了解某一领域的研究动态和发展趋势。在图5的基础上,选择对数似然比算法对聚类的关键词进行标记,得到关键词的聚类图谱(图6),中文数据库共形成506个节点,1 383条连线,12个聚类模块,聚类模块Q值=0.619 6> 0.3,S=0.880 7> 0.5,英文数据库共形成467个节点,891条连线,12个聚类模块,聚类模块Q值=0.845 2> 0.3,S=0.957 5> 0.5,中英文数据库聚类结构合理,具有高度可信性。中文数据库聚类:#0、#2、#5、#12为研究内容;#1、#3、#4、#6、#8、#10为干预措施;#9、#11为研究离子通道,研究主要涉及中医药效应的体液调节及中药安全性,电针镇痛机制及调节突触可塑性的效应机制。英文数据库关键词聚类归纳:#0、#1、#2、#10为干预措施, #6、#8、#9、#11为研究内容,#3、#4为研究对象,#5、#7为离子通道,研究关注中药单体或复方心脑血管保护中的作用,电针神经调节机制,提示钙通道及钠离子调节是各种效应机制发挥的靶点。 时线图展示研究主题的时间演变,峰峦图可识别研究热点的突变,将两者结合可有助于研究者了解某一领域的研究动态和发展趋势。将中英文数据库的关键词聚类标签绘制时间线图及峰峦图,图7,8显示膜片钳技术在中医药领域发展过程中#0、#1、#2 持续受到学者关注,自2008-2024年,#6、#7、#10的关注逐渐降低,近10来年(2014-2024)更多的研究聚焦于#4、#5、#12也是日后发展的趋势。图9,10显示英文数据库的文献中关于#1、#2、#3研究自2000年持续至今,近10年#0、#4、#5、#6、#7、#8、#9热度下降,#10新近研究方向。 2.5 关键词突现分析 突现分析是指分析某一时间段内关键词使用频次的显著增加,从而识别研究领域的热点、前沿和动态变化。将纳入中英文数据库文献绘制关键词突线图谱,见图11。中文数据库自1990-2009年,“钙通道”和“心肌细胞”是研究的热点;2010年至现阶段,“电针”和“镇痛”成为了新的研究焦点。自2018年来,对电针关注持续升温,同时间段“镇痛”研究尤为突出。2020年后突现的“突触可塑性”持续时间短,有一定的发展空间。英文数据库关键词如“patch clamp”(1992年)、“calcium current”(1995年)和“calcium channel”(2004年)等,在特定年份开始出现突现,持续时间近20年(1992-2013年),研究者对该领域拥有持续的兴趣,2021年以来,“neuropathic pain”为新的关注热点。"
| [1] 刘振伟. 实用膜片钳技术[M].2版.北京:北京科学技术出版社,2016. [2] NEHER E, SAKMANN B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976;260(5554):799-802. [3] COSTE B, MATHUR J, SCHMIDT M, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science. 2010;330(6000):55-60. [4] WANG P, GU YY, LU JP, et al. Endothelial TRPV4 channel mediates the vasodilation induced by Tanshinone IIA. Chem Biol Interact. 2024:402:111181. [5] QI JY, KANG DY, YU J, et al. Suxiao Jiuxin Pills Prevent Ventricular Fibrillation from Inhibiting L-type Calcium Currents CaV1.2 in vivo and in vitro. Chin J Integr Med. 2023; 29(2):108-118. [6] 朱传安,谢彦颖.电针对抑郁样小鼠内侧前额叶锥体神经元E/I平衡的影响[J].中医药通报,2023;22(3):32-34,54. [7] 李冀,付强,胡晓阳,等. 中药研究中膜片钳技术的应用[J].中医药学报,2018; 46(2):129-130,封3. [8] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1): 5303-5310. [9] 郭海珍,丛紫东,赵玉珂,等. 膜片钳技术10年发展:基于CiteSpace和VOSviewer的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(31):6717-6726. [10] PRICE DDS. A general theory of bibliometric and other cumulative advantage processes. J Am Soc Inf Sci. 1976;27(5):292-306. [11] 孟红旭,郭浩,姚明江,等.采用膜片钳技术观察3种中药复方含药血清对大鼠心室肌细胞L-型钙通道的作用[J].中药药理与临床,2017,33(3):127-131. [12] 刘甜甜,赵红霞,高蔚,等.细辛醇提物对瞬时感受器电位香草素受体1的干预作用及改善小鼠神经性疼痛的机制研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(8):4998-5001. [13] 陈香云,佟海英,王坦,等.香薷醇提物对热敏通道瞬时受体电位香草酸亚型1的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(1):518-522. [14] LI MF, SHI YL. Toosendanin interferes with pore formation of botulinum toxin type A in PC12 cell membrane. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27(1):66-70. [15] LI MF, SHI YL. The long-term effect of toosendanin on current through nifedipine-sensitive Ca2+ channels in NG108-15 cells. Toxicon. 2005;45(1):53-60. [16] SONG Q, CHU X, ZHANG X, et al. Mechanisms underlying the cardioprotective effect of Salvianic acid A against isoproterenol-induced myocardial ischemia injury in rats: Possible involvement of L-type calcium channels and myocardial contractility. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;189:157-164. [17] GAO Y, ZHANG K, ZHU F, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) inhibits L-type calcium current and attenuates calcium transient and contractility in rat ventricular myocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;158: 397-403. [18] TU WZ, CHENG RD, CHENG B, et al. Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on chronic neuropathic pain mediated by P2X3 receptors in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurochem Int. 2012;60(4):379-386. [19] ZHENG YY, JIA CQ, JIANG X, et al. Electroacupuncture effects on the P2X4R pathway in microglia regulating the excitability of neurons in the substantia gelatinosa region of rats with spinal nerve ligation. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(3):175. [20] 刘俊红,邢作英,宋欢欢,等.桂枝甘草汤含药血清对豚鼠心室肌细胞钠通道的影响[J].中医学报,2020,35(4):837-839. [21] 邢作英,王永霞,朱明军,等.桂枝甘草汤及其拆方含药血清对豚鼠心室肌细胞L-型钙通道的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2018,38(3)331-335. [22] 王永霞,邹志暖,刘红军,等.交泰丸浸膏粉溶液对豚鼠心室肌细胞膜电位的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2010,16(8): 157-160. [23] 王腾,唐其柱,江洪李,等.丹参注射液对模拟缺血预适应引起兔心室肌细胞动作电位和ATP敏感性钾电流变化的影响[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2005, 26(6):696-699. [24] 唐其柱,黄峥嵘,史锡腾,等.甘松提取物对家兔心室肌细胞钠、钙通道的影响[J].中华心血管病杂志,2004,32(z2):267-270. [25] 韩雪珍,佟海英,高蔚,等.基于热敏通道TRPV1探讨中药甘遂止痛机理[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(7):126-130. [26] 刘珍洪,高琳,汪文来,等.羌活提取物对热敏通道TRPV1的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2017,23(4):553-557. [27] SONG JA, JIANG MY, JIN YC, et al. Phytol from Faeces Bombycis alleviated migraine pain by inhibiting Nav1.7 sodium channels. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;306:116161. [28] ZHANG SY, LI GL, XU XW, et al. Acupuncture to point Baihui prevents ischemia-induced functional impairment of cortical GABAergic neurons. J Neurol Sci. 2011;307(1-2):139-143. [29] DING R, WANG Y, ZHU JP, et al. Danggui Sini decoction protects against oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats. J Integr Neurosci. 2020;19(4):663-671. [30] CHEN YG, XU EJ, SANG M, et al. Makatoxin-3, a thermostable Nav1.7 agonist from Buthus martensii Karsch (BmK) scorpion elicits non-narcotic analgesia in inflammatory pain models. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;288:114998. [31] CHEN YL, WU MH. Aitongping patch could alleviate cancer pain via suppressing microglia activation and modulating the miR-150-5p/CXCL12 signaling. Postgrad Med J. 2024;100(1180):96-105. [32] LEE S, GIM H, SHIM JH, et al. The traditional herbal medicine, Ge-Gen-Tang, inhibits pacemaker potentials by nitric oxide/cGMP dependent ATP-sensitive K+ channels in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from mouse small intestine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;170:201-209. [33] KIM HJ, HAN T, KIM YT, et al. Magnolia Officinalis Bark Extract Induces Depolarization of Pacemaker Potentials Through M2 and M3 Muscarinic Receptors in Cultured Murine Small Intestine Interstitial Cells of Cajal. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(5):1790-1802. [34] KIM D, KIM JN, NAM JH, et al. Modulation of Pacemaker Potentials in Murine Small Intestinal Interstitial Cells of Cajal by Gamisoyo-San, a Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicine. Digestion. 2018;98(1): 56-68. [35] 杨唯. 野黄芩素结构修饰与抗心律失常活性研究[D].昆明:云南中医药大学, 2023. [36] 郭晟,周承志,杨波,等.炙甘草汤对大鼠心房肌细胞L型钙电流及其动力学特征的影响[J].世界中医药,2022,17(10): 1385-1389. [37] 于婷婷.基于人源心肌细胞探索丹红注射液治疗乌头碱诱导心律失常的研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2023. [38] 宋琼涛.基于钙离子浓度调节、抗氧化应激、抗炎症反应的丹参酸A对心血管保护作用的研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2018. [39] 宋琼涛.丹参酸A对心肌细胞离子通道以及收缩力的调控作用[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2015. [40] 郁蕾.丹参酮衍生物DS-201脂质体的制备及其促进细胞内BK_(Ca)通道激活和增强血管舒张作用的研究[D].泸州:西南医科大学,2016. [41] LIU ZL, SHAN ZM, YANG HY, et al. Quercetin, Main Active Ingredient of Moutan Cortex, Alleviates Chronic Orofacial Pain via Block of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel. Anesth Analg. 2024;138(6):1324-1336. [42] LI ZY, GAN Y, KANG T, et al. Camphor Attenuates Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Pain Models in Mice. J Pain Res. 2023;16:785-795. [43] WANG H, LIU WJ, WANG XY, et al. A central amygdala input to the dorsal vagal complex controls gastric motility in mice under restraint stress. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1074979. [44] 陈思雨,杨海红,巩固.重复电针抑制前扣带回皮层腺苷酸环化酶1治疗神经病理性痛的研究[J].成都医学院学报,2024, 19(3):405-410. [45] 刘玲.电针激活α2肾上腺素受体缓解小鼠炎性痛的研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2023. [46] ZHU X, ZHANG C, HU Y, et al. Modulation of Comorbid Chronic Neuropathic Pain and Anxiety-Like Behaviors by Glutamatergic Neurons in the Ventrolateral Periaqueductal Gray and the Analgesic and Anxiolytic Effects of Electroacupuncture. eNeuro. 2024;11(8):ENEURO.0454-23.2024. [47] 李旻.华蟾素注射液及其单体成分蟾毒灵心脏毒性及其机制研究[D]. 上海:中国医药工业研究总院,2020. [48] 张艺哲,邢红艳,王美婷,等.基于膜片钳技术的中药单体体外心脏毒性评价研究[G]. 第九届药物毒理学年会:新时代·新技术·新策略·新健康论文集,2019. [49] 刘昕彦,邵瑞,贺爽,等.类器官和立体细胞模型在中药心脏毒性评价中的应用前景[J].药学学报,2019,54(11):1888-1894. [50] 刘雨露.电针调控血管性认知障碍大鼠海马CA3-CA1神经环路时间模式依赖突触可塑性的机制研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2022. [51] 李顺.槲皮素对中枢神经系统囊泡循环动力学调控及突触可塑性的机制研究[D].南昌:江西中医药大学,2023. [52] 左燕,刘永斌,袁子焉,等.电针耳甲区耳穴对创伤后应激障碍小鼠前扣带回皮层谷氨酸能神经元兴奋性水平的影响[J].针刺研究,2024,49(11):1121-1128. [53] LI L, WU XR, GONG JL, et al. Activation of GABA type A receptor is involved in the anti-insomnia effect of Huanglian Wendan Decoction. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15: 1389768. [54] CHEN Q, KANG L, LI YH, et al. Effect of Shenfu Injection on Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Pacemaker-Like Cells and Improvement of Pacing Function of Sinoatrial Node. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:4299892. [55] YANG HJ, KONG B, SHUAI W, et al. Shensong Yangxin Protects Against Metabolic Syndrome-Induced Ventricular Arrhythmias by Inhibiting Electrical Remodeling. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:993. [56] 戴雅玲. 电针调控miR-219a促进血管性认知障碍大鼠内嗅-海马CA1神经环路突触可塑性的机制[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2021. [57] 朱贺. 电针镇痛与vlPAG下行镇痛环路机制的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2020. [58] SIMONNET J, RICHEVAUX L, FRICKER D. Single or Double Patch-Clamp Recordings In Ex Vivo Slice Preparation: Functional Connectivity, Synapse Dynamics, and Optogenetics. Methods Mol Biol. 2021; 2188:285-309. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [3] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [4] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [5] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [6] | Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Cai Tianyuan, Wang Zicheng, Meng Zhuo, Zhan Xiaoqian, Chen Guoqian . Pain after total knee arthroplasty: current status and trend analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [7] | Li Qian, Li Zhenxing, Qiao Pengyan, Wang Pingzhi. Visual analysis of shear wave elastography in skeletal muscle research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6021-6029. |
| [8] | Qu Bolin, Ciren Lunzhu, Guo Jinyang, Meng Hanlu, Ding Guanxiang, Sang Hongpeng. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a visual analysis of current status and emerging trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6040-6050. |
| [9] | Li Yiguang, Guo Haonan, Ding Xiaotao, Yuan Mengyao, Jiang Lijin, Fan Xinfeng, Feng Yan. Visual analysis of research hotspots in the field of gut microbiota in the elderly at home and abroad [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6071-6080. |
| [10] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [11] | Zhang Jiahao, Liu Jidong, Qu Yi, Wang Jianbo, Li Yang, Xue Yanan. Electroacupuncture improves inflammatory pathology and intestinal integrity in mice with ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4663-4674. |
| [12] | Yang Jiangxi, Li Huangyan, Zhang Yeting, Yu Zuoyin . Research hotspots and thematic evolution in the field of exercise interventions for multiple sclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4771-4781. |
| [13] | Chen Yuanyue, Shen Junfan, Yu Cui, Lu Jianxia, Hu Wenxuan, Zhu Jun, Guo Chuan. Knowledge structure and evolutionary trends in the application of surface electromyography in musculoskeletal pain rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4791-4801. |
| [14] | Meng Zhuo, Zhao Renghao, Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Wang Zicheng, Xu Yingtian, Tong Peijian. Literature visualization analysis of brain-computer interface applications in stroke rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4802-4813. |
| [15] | Li Ruiying, Xia Hong. Visual analysis of cuproptosis research: global landscape of hotspots and frontiers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4529-4541. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||