Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (18): 4663-4674.doi: 10.12307/2026.772
Previous Articles Next Articles
Electroacupuncture improves inflammatory pathology and intestinal integrity in mice with ulcerative colitis
Zhang Jiahao1, Liu Jidong1, Qu Yi2, Wang Jianbo2, Li Yang3, Xue Yanan1
- 1College of Acupuncture and Tuina, 2Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Education for the Theory and Application of Chinese Organisms, 3Medical College of Laboratory Animal Medicine, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2025-09-02Accepted:2025-10-22Online:2026-06-28Published:2025-12-06 -
Contact:Liu Jidong, MD, Professor, College of Acupuncture and Tuina, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jiahao, MS, College of Acupuncture and Tuina, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:The National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82474634 (to LJD); Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Plan Joint Program, No. 2024JH2/102600199 (to LJD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jiahao, Liu Jidong, Qu Yi, Wang Jianbo, Li Yang, Xue Yanan. Electroacupuncture improves inflammatory pathology and intestinal integrity in mice with ulcerative colitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4663-4674.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
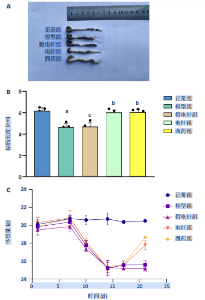
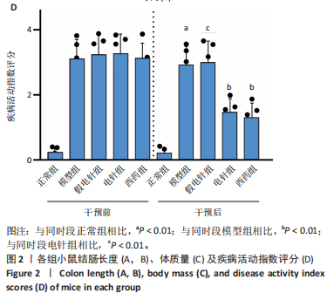
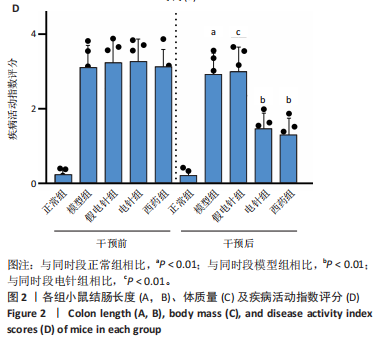
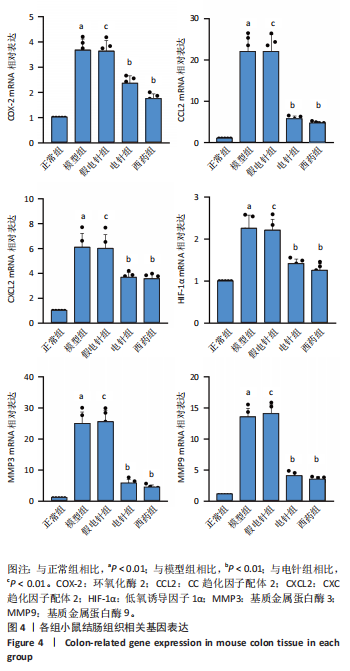
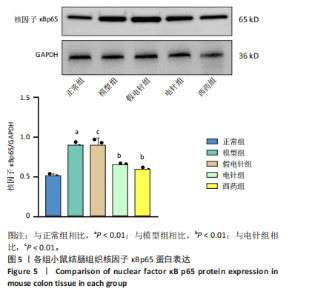
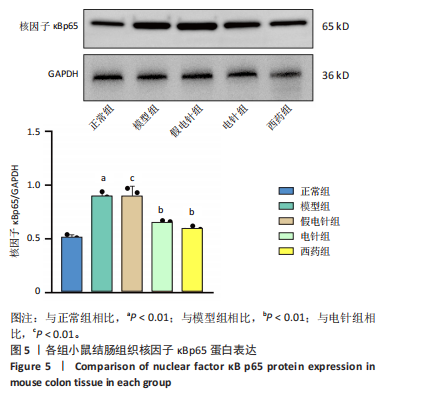
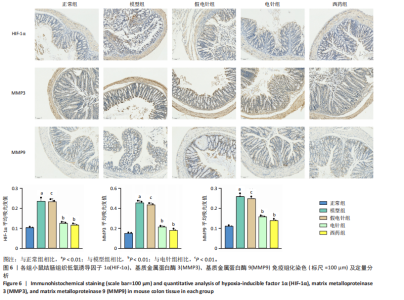
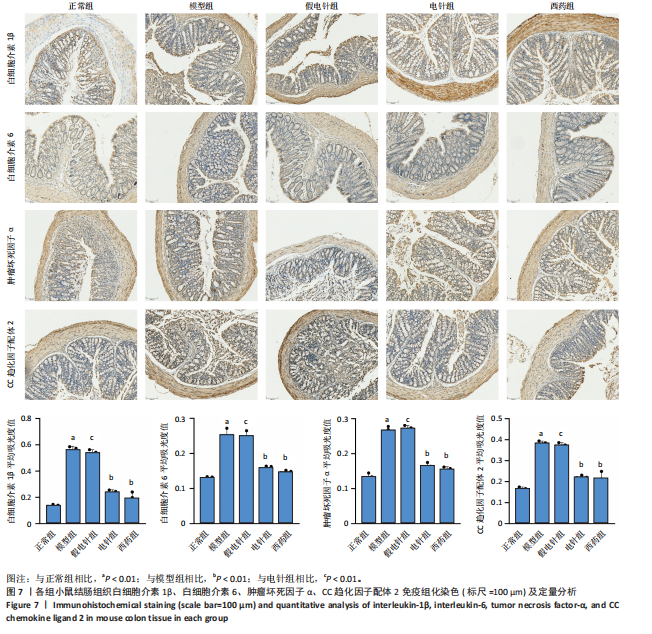
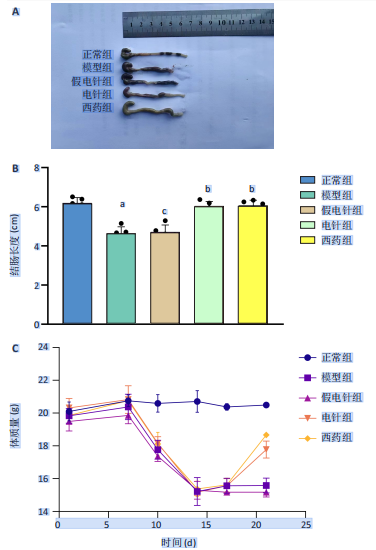
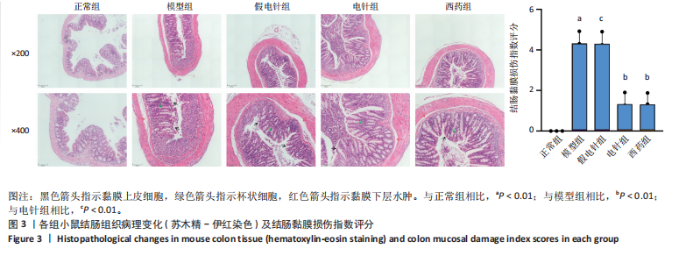
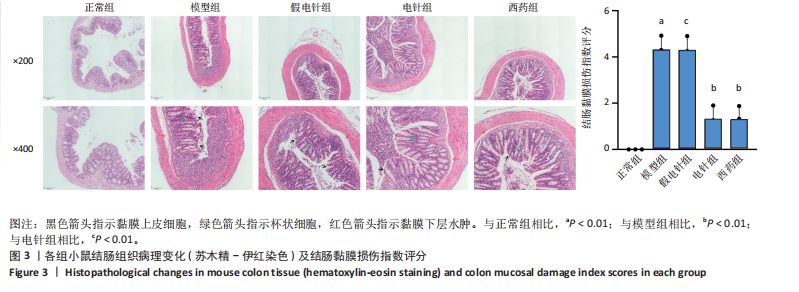
2.1 实验动物数量分析 参加实验的60只小鼠均无脱失,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 各组小鼠一般情况 正常组结肠长度最长,模型组及假电针组结肠长度最短,电针组及西药组结肠长度得到一定改善(P < 0.01),见图2A,B。正常组小鼠体质量呈自然增长,模型组小鼠随着时间增长,体质量持续下降,针刺组与西药组曲线介于模型组与正常组之间,且数值与模型组均有显著性差异(P < 0.01),见图2C。正常组小鼠疾病活动指数评分最低,模型组及假电针组最高,针刺组与西药组疾病活动指数评分与模型组相比显著下调(P < 0.01),见图2D。 2.3 各组小鼠结肠组织病理变化 正常组小鼠黏膜上皮完整,排列紧密,杯状细胞丰富,无炎性浸润;模型组及假电针组黏膜上皮、杯状细胞丢失,有较多炎性细胞浸润,黏膜下层出现水肿;电针组和西药组小鼠结肠组织炎性细胞浸润减少,组织损伤程度减轻,见图3。正常组结肠黏膜损伤指数评分最低,模型组最高。与模型组及假电针组相比,电针组和西药组结肠黏膜损伤指数评分均下降(P < 0.01)。 2.4 各组小鼠结肠相关基因表达 与正常组相比,模型组环氧化酶2、CC趋化因子配体2、CXC趋化因子配体2、低氧诱导因子1α、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9 mRNA表达显著升高(P < 0.01);与模型组和假电针组比较,电针组和西药组环氧化酶2、CC趋化因子配体2、CXC趋化因子配体2、低氧诱导因子1α、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.01),见图4。 2.5 各组小鼠结肠核因子κBp65蛋白表达 与正常组相比,模型组小鼠结肠组织中核因子κBp65蛋白表达水平明显升高(P < 0.01),与模型组及假电针组相比,电针组和西药组小鼠结肠组织中核因子κBp65蛋白表达水平有所降低(P < 0.01),见图5。 2.6 各组小鼠结肠组织中相关蛋白表达 与正常组比较,模型组结肠组织中低氧诱导因子1α、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、CC趋化因子配体2免疫组化阳性表达升高(P < 0.01);与模型组及假电"
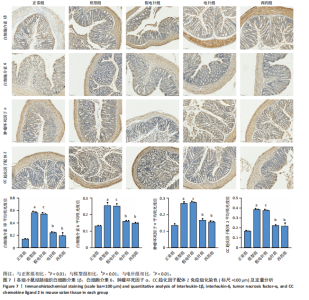
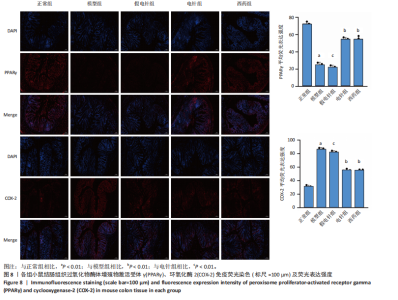
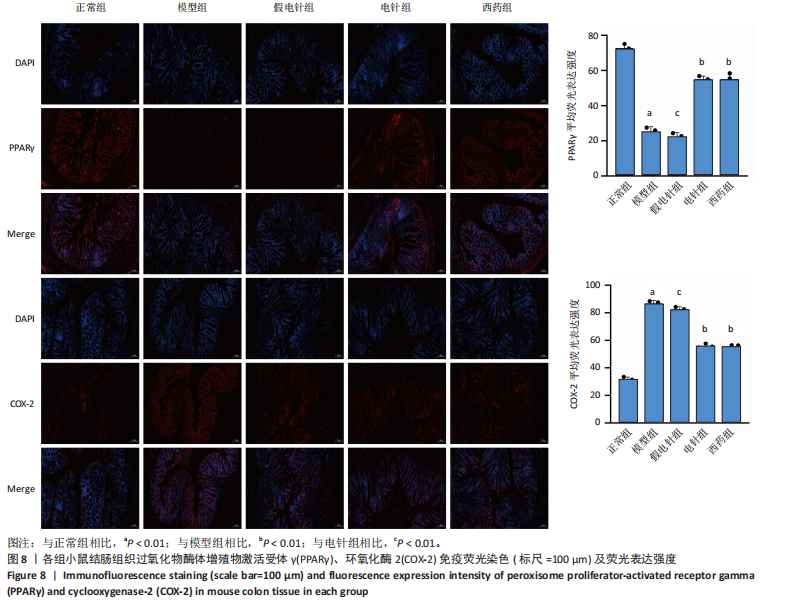
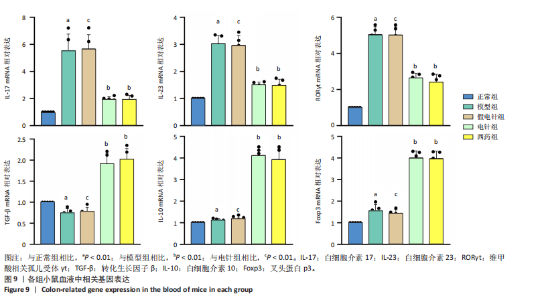
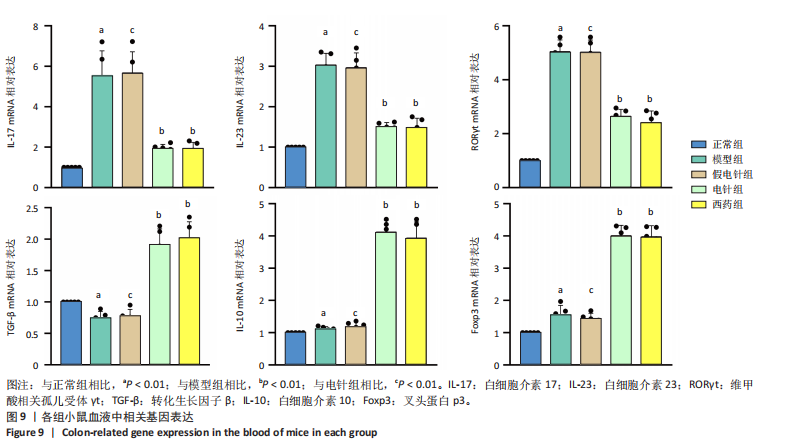
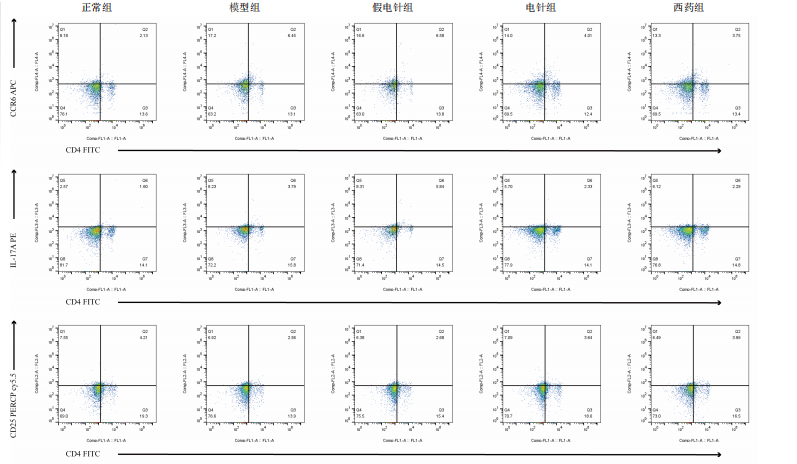
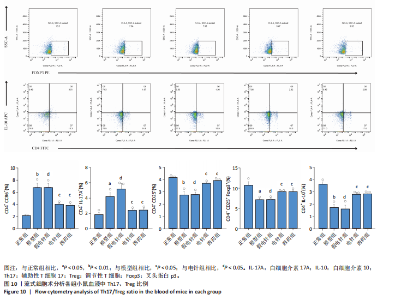
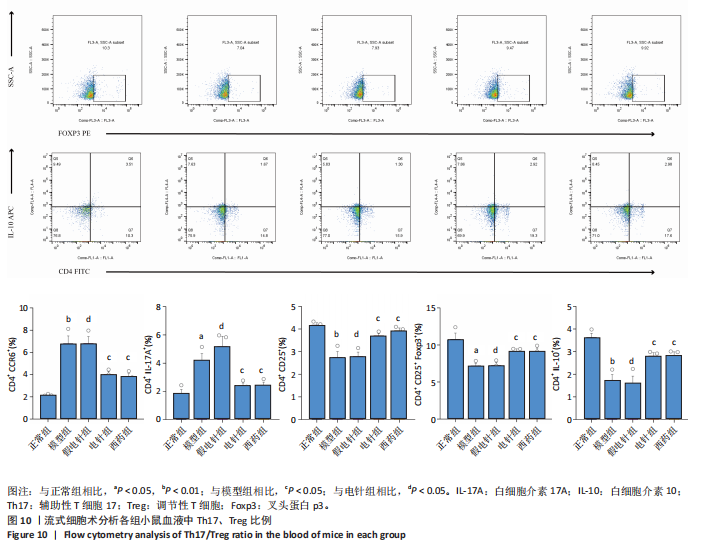
针组相比,电针组和西药组小鼠结肠组织中低氧诱导因子1α、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、CC趋化因子配体2免疫组化阳性表达降低(P < 0.01),见图6,7。 2.7 各组小鼠结肠组织中过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ、环氧化酶2表达 与正常组比较,模型组结肠组织中环氧化酶2免疫荧光染色的平均荧光强度升高(P < 0.01),过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的平均荧光强度降低(P < 0.01);与模型组及假电针组相比,电针组和西药组小鼠结肠组织中环氧化酶2的平均荧光强度降低(P < 0.01),过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的平均荧光强度升高(P < 0.01),见图8。 2.8 各组小鼠血液中相关基因表达 与正常组相比,模型组白细胞介素17、白细胞介素23、维甲酸相关孤儿受体γt mRNA表达显著升高(P < 0.01);与模型组和假电针组比较,电针组和西药组白细胞介素17、白细胞介素23、维甲酸相关孤儿受体γt mRNA表达降低(P < 0.01)。与模型组和假电针组比较,电针组和西药组转化生长因子β、白细胞介素10、叉头蛋白p3 mRNA表达升高(P < 0.01),见图9。 2.9 流式细胞术检测辅助性T细胞17/调节性T细胞免疫平衡 用CD4+、CCR6+、白细胞介素17A+标记辅助性T17细胞,圈出阳性表达的细胞群即为辅助性T细胞17群,用CD4+、CD25+、叉头蛋白p3+、白细胞介素10+标记调节性T细胞,圈出阳性表达的细胞群即为调节性T细胞群。与正常组相比,模型组辅助性T细胞17阳性细胞群比例升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),调节性T细胞阳性细胞群比例降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);与模型组和假电针组比较,电针组和西药组辅助性T细胞17阳性细胞群比例降低(P < 0.05),调节性T细胞阳性细胞群比例升高(P < 0.05),见图10。"
| [1] ZHANG J, JIANG B, YUN X, et al. Discovery of novel N-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-heterocyclic ketone analogs as potent anti-inflammatory agents against ulcerative colitis. Bioorg Chem. 2025; 161:108576. [2] YAO D, MA C, KE C, et al. Integrating transcriptomics, metabolomics, and microbiomics to explore the mechanism of action of bran-fried Atractylodes lancea rhizome polysaccharide in ameliorating the enhanced pharmacological effects of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025;349:119805. [3] LIU Y, CHEN N, HE H, et al. Sodium butyrate alleviates DSS-induced inflammatory bowel disease by inhibiting ferroptosis and modulating ERK/STAT3 signaling and intestinal flora. Ann Med. 2025;57(1):2470958. [4] LIU Z, ZHANG H, WANG J, et al. Clca1 deficiency exacerbates colitis susceptibility via impairment of mucus barrier integrity and gut microbiota homeostasis. Microbiol Res. 2025;297:128191. [5] 黄金科,张佳琪,王凤云,等.加味葛根芩连汤对溃疡性结肠炎模型小鼠肠黏液屏障和肠道干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].中医杂志, 2025,66(9):941-947. [6] 郜婕,唐成林,刘仁建,等.不同强度电针对肥胖大鼠细胞因子信号转导抑制蛋白-3及过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体-γ mRNA表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2013,38(1):31-34. [7] 郑丽红,王海强,丁晓明,等.愈肠栓对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠PPARγ/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2019,25(7):486-490. [8] 周睿璇,彭嘉颖,向晶,等.电针刺激上巨虚、天枢对溃疡性结肠炎模型大鼠Th17相关特异性因子及Treg的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2023,43(5):877-884. [9] DI Y, LI H, YANG J, et al. PPARγ/NF-κB axis contributes to cold-induced resolution of experimental colitis and preservation of intestinal barrier. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024;1870(7):167326. [10] QUAN X, MIAO Z, HAN R, et al. Proteomic analysis reveals that Acalypha australis L. mitigates chronic colitis by modulating the FABP4/PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025;345:119585. [11] LIU C, ZENG H, OUYANG J, et al. Eurotium-Cristatum fermented black tea alleviates ulcerative colitis through the PPARγ-NF-κB signaling axis. Food Res Int. 2025;200:115436. [12] DAI Y, LU Q, LI P, et al. Xianglian Pill attenuates ulcerative colitis through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;300:115690. [13] 鲁慧东,李艳梅.羽扇豆醇调节PI3K/AKT/NF-κB信号通路对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠Th17/Treg免疫平衡的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2025, 41(5):1060-1065. [14] CHEN W, XU L, WANG L, et al. Qing-Re-Hua-Shi Decoction ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by modulating multiple signaling pathways and remodeling the gut microbiota and metabolite profile. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025;15:1541289. [15] ZHANG QW, YANG MJ, LIAO CY, et al. Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz polysaccharide ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by regulating the gut microbiota and tryptophan metabolism. Br J Pharmacol. 2025; 182(7):1508-1527. [16] NIU MM, LI Y, SU Q, et al. A mannose-rich exopolysaccharide-1 isolated from Bifidobacterium breve mitigates ovalbumin-induced intestinal damage in mice by modulation CD4 + T cell differentiation and inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;280(Pt 3): 135850. [17] CHANG L, WANG C, PENG J, et al. Rattan Pepper Polysaccharide Regulates DSS-Induced Intestinal Inflammation and Depressive Behavior through Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. J Agric Food Chem. 2024; 72(1):437-448. [18] HE H, CHEN Q, FAN H, et al. Extracellular vesicles produced by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing programmed death-ligand 1 ameliorate dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by regulating Th17/Treg cell balance through PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;37(12):2243-2254. [19] ZHANG Y, JI W, QIN H, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides alleviate DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by restoring SCFA production and regulating Th17/Treg cell homeostasis in a microbiota-dependent manner. Carbohydr Polym. 2025;349(Pt A):122829. [20] SHI G, KONG J, WANG Y, et al. Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through inhibiting of NF-κB signaling pathways and modulating intestinal microbiota. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;298:115640. [21] LI Z, LIN M, LI Y, et al. Total flavonoids of Sophora flavescens and kurarinone ameliorated ulcerative colitis by regulating Th17/Treg cell homeostasis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;297:115500. [22] XIE Q, LI H, MA R, et al. Effect of Coptis chinensis franch and Magnolia officinalis on intestinal flora and intestinal barrier in a TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis rats model. Phytomedicine. 2022;97:153927. [23] BANG B, LICHTENBERGER LM. Methods of Inducing Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice. Curr Protoc Pharmacol. 2016;72:5.58.1-5.58.42. [24] 实验动物常用穴位名称与定位第3部分:小鼠[J].针刺研究,2021, 46(5):445-446. [25] 王翊文,夏裔灵,刘尔乐,等.芍药汤通过调控糖代谢重编程影响Th17/Treg细胞平衡治疗溃疡性结肠炎[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025,31(13):78-85. [26] 刘力,卢云琼,曹姚佳妮,等.艾灸“天枢”穴对溃疡性结肠炎模型大鼠结肠组织铁死亡及氧化损伤的影响[J].中医杂志,2023 64(15):1576-1584. [27] 陈小梅,黄于婷,柯以晨,等.基于海马小胶质细胞α7烟碱乙酰胆碱受体途径探讨电针“足三里”改善系统性炎性反应小鼠认知障碍的作用机制[J].针刺研究,2025,50(3):251-259. [28] 王正文,陈碧玮,陈少宗,等.电针“足三里”配伍“天枢”对肠易激综合征大鼠结肠功能及自主神经平衡性的影响[J].针刺研究, 2023,48(2):165-171. [29] WU M, WANG Q, LI X, et al. Gut microbiota-derived 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid from pumpkin polysaccharides supplementation alleviates colitis via MAPKs-PPARγ/NF-κB inhibition. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;264(Pt 1):130385. [30] XU L, ZHAO B, CHENG H, et al. Bergapten enhances mitophagy to regulate intestinal barrier and Th17/Treg balance in mice with Crohn’s disease-like colitis via PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024;397(10):7589-7597. [31] ARAFA EA, MOHAMED WR, ZAHER DM, et al. Gliclazide attenuates acetic acid-induced colitis via the modulation of PPARγ, NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;391:114919. [32] ZHAO J, WU R, WEI P, et al. Ethanol extract of Piper wallichii ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice: Involvement of TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;308:116293. [33] MEI C, MENG F, WANG X, et al. CD30L is involved in the regulation of the inflammatory response through inducing homing and differentiation of monocytes via CCL2/CCR2 axis and NF-κB pathway in mice with colitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:108934. [34] LI YX, LIU J, LI F. Hinesol attenuates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis through the suppression of Src-mediated NF-κB and chemokine signaling pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024;82(3):2747-2757. [35] LIU X, ZHOU M, DAI Z, et al. Salidroside alleviates ulcerative colitis via inhibiting macrophage pyroptosis and repairing the dysbacteriosis-associated Th17/Treg imbalance. Phytother Res. 2023;37(2):367-382. [36] CHENG C, HU J, LI Y, et al. Qing-Chang-Hua-Shi granule ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by activating NLRP6 signaling and regulating Th17/Treg balance. Phytomedicine. 2022;107:154452. [37] ZHAO Y, LUAN H, JIANG H, et al. Gegen Qinlian decoction relieved DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice by modulating Th17/Treg cell homeostasis via suppressing IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Phytomedicine. 2021;84:153519. [38] ALEXANDER M, ANG QY, NAYAK RR, et al. Human gut bacterial metabolism drives Th17 activation and colitis. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30(1):17-30.e9. [39] WANG J, ZHAO X, WAN YY. Intricacies of TGF-β signaling in Treg and Th17 cell biology. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023;20(9):1002-1022. [40] WU X, PAN B, CHU C, et al. CXCL16/CXCR6/TGF-β Feedback Loop Between M-MDSCs and Treg Inhibits Anti-Bacterial Immunity During Biofilm Infection. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025;12(7):e2409537. [41] DENG G, SONG X, FUJIMOTO S, et al. Foxp3 Post-translational Modifications and Treg Suppressive Activity. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:2486. |
| [1] | Liu Tongyan, Li Yuan, Sun Wei, Yao Bing, Fang Shanshan, Zhou Lingyun. Current status and hotspot analysis of experimental research on electroacupuncture intervention for peripheral nerve regeneration: electroacupuncture parameters, acupuncture effects and molecular mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2608-2617. |
| [2] | Zheng Rongfa, Mo Weibin, Huang Peng, Chen Junji, Liang Ting, Zi Fangyu, Li Guofeng. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of metabolic enzymes and autophagy genes in gastrocnemius muscle tissues of exercising rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1127-1136. |
| [3] | Zhang Zihan¹, Wang Jiaxin¹, Yang Wenyi², Zhu Lei¹. Regulatory mechanism of exercise promoting mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6499-6508. |
| [4] | Sun Rongyan, Xu Luchun, Jiang Guozheng, Song Jiawei, Ma Yukun, Fan Jiaojiao, Wang Guanlong, Yang Yongdong, Yu Xing. Du Meridian electroacupuncture inhibits ferroptosis and promotes neurorepair in rats with acute cervical spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6228-6238. |
| [5] | Gao Simiao, Han Xue, Wu Xiaoguang, Zheng Jinyu, Gao Fangwen, Li Kuihua, Peng Yong, Liu Lanxiang. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with low-frequency transcranial ultrasound stimulation on the electroencephalographic signals of rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 402-408. |
| [6] | Wu Haiyang, Duan Mian, Li Chenglong, Zhang Junyu, Ji Haisheng, Wang Haitao, Mao Wei, Wang Ying. Neuroprotective mechanism of electroacupuncture in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3811-3818. |
| [7] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [8] | Li Longyang, Zhang Songjiang, Zhao Xianmin, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Electroacupuncture intervention on the proliferation and differentiation of hippocampal neurons and oligodendrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1029-1035. |
| [9] | Wen Huaneng, Lin Run, Wang Yixiao, Wang Bingshui, Liu Lu, Liu Chuanyao, Cai Canxin, Cui Shaoyang, Xu Mingzhu. Effects of electroacupuncture with “Zhi San Zhen” on Notch signaling pathway and synaptic plasticity in 5xFAD mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5148-5153. |
| [10] | Jiao Ziyuan, Zhuo Yue, Liang Roujun, Ding Qiangsheng, Zeng Xuejiu, Xu Ming, Zhang Hong. Electroacupuncture improves morphological structure of the detrusor muscle and bladder function in rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4484-4490. |
| [11] | Luo Fu, Shu Xiangzhong, Liu Danni, Tan Jinqu, Peng Ting, Huang Xiarong, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Wang Jinling, Zhou Jun. Electroacupuncture reduces inflammatory factor expression by suppressing Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2186-2190. |
| [12] | Duan Zhaoyuan, Wu Mingli, Luo Meng, Liu Chengmei, Gao Jing, Li Ruiqing, Feng Xiaodong. Effect of electroacupuncture modulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway on CD133 protein expression in rat ventricular zone cells after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3858-3864. |
| [13] | Yao Haihua, Min Youjiang, Hong Dongying, Wang Li, Lu Xiuyun, Yang Yihua. Effects of Santong electroacupuncture on the activity of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 in rats with spinal cord injury via the Rho/Rho kinase and MEK/ERK signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3158-3166. |
| [14] | Ma Munan, Xie Jun, Sang Yuchao, Huang Lei, Zhang Guodong, Yang Xiaoli, Fu Songtao. Electroacupuncture combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 1-7. |
| [15] | LIU Danni, SUN Guanghua, ZHOU Guijuan, LIU Hongya, ZHOU Jun, TAN Jinqu, HUANG Xiarong, PENG Ting, FENG Wei-bin, LUO Fu. Effect of electroacupuncture on apoptosis of neurons in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury at "Shuigou" and "Baihui" points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||