Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4472-4486.doi: 10.12307/2026.183
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of ischemic preconditioning on sport performance: a systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis
Zhang Yilin1, Xu Kai2, Yin Mingyue2, Kong Hao1, Liu Chenghao1, Xie Yun1
- 1School of Sports Training, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China; 2School of Sports Performance, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China
-
Received:2025-06-06Accepted:2025-09-17Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-12-03 -
Contact:Xie Yun, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Sports Training, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China -
About author:Zhang Yilin, MS candidate, School of Sports Training, Tianjin University of Sport, Tianjin 301617, China Xu Kai, MS candidate, School of Sports Performance, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China Yin Mingyue, MS candidate, School of Sports Performance, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China Zhang Yilin, Xu Kai and Yin Mingyue contributed equally to this work.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yilin, Xu Kai, Yin Mingyue, Kong Hao, Liu Chenghao, Xie Yun. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on sport performance: a systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4472-4486.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
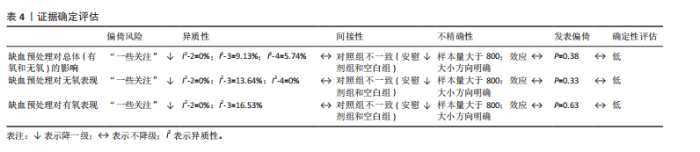
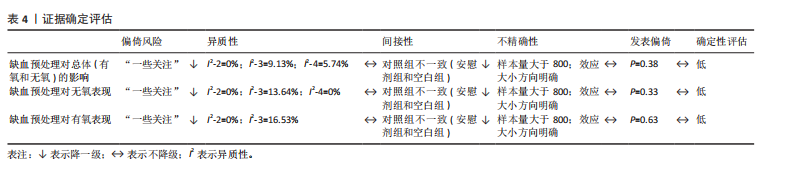
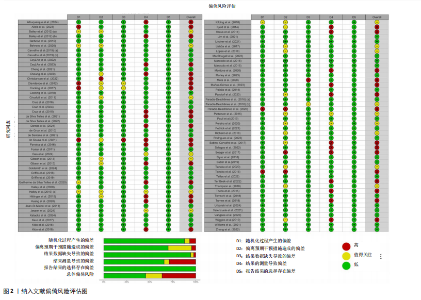
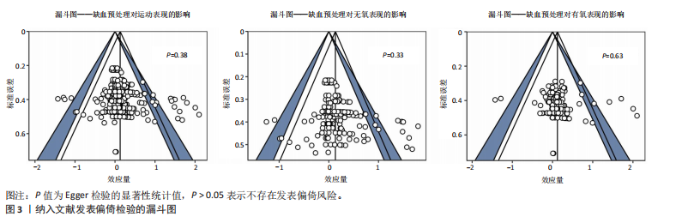
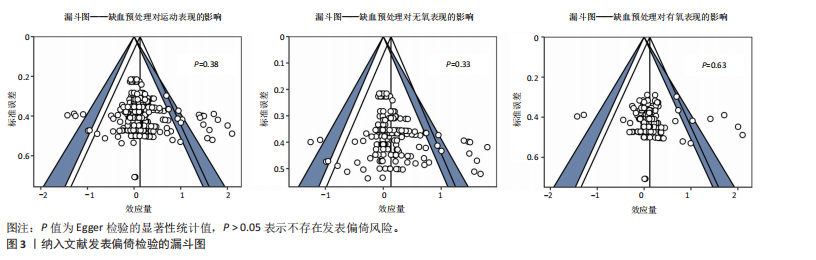
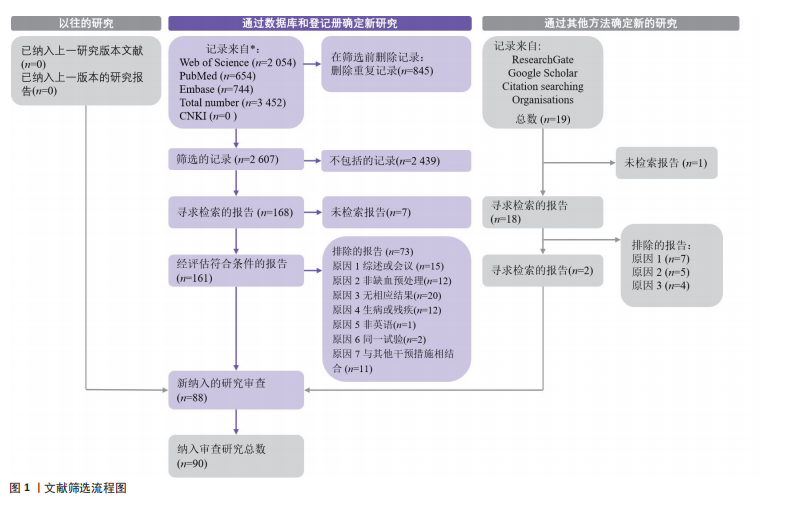
2.1 检索结果 通过制定的检索词共检索到3 452篇文献。去除重复文献后,剩余2 607篇文献。经过标题和摘要筛选以及纳入和排除标准筛选后,剩余88篇文献。此外,通过其他来源(如“ResearchGate”“Google Scholar”等)最终补充了2篇文献。因此,最终符合纳入标准的文献数量为90篇(图1)。 2.2 纳入研究特征 附表1-3提供了90篇纳入文献的详细研究特征列表[5,10-21,23-27,29-30,32-33,35-39,59,67-128],涵盖人口统计学因素和缺血预处理相关参数。90篇文献均为随机交叉试验或随机对照试验,共涉及1 439名参与者,其中包括1 033名男性和210名女性,另有196名参与者的性别在研究中未明确报告。根据运动持续时间75 s的标准[45-46],46篇文献被归类为无氧运动研究(附表1)[11-16,23-24,26-27,29-30,69-102],41篇文献被归类为有氧运动研究(附表2)[5,10,17-21,32-33,35-39,59,103-128],3篇文献同时报告了无氧和有氧运动的结果(附表3)[25,67-68]。 2.3 偏倚风险 所有纳入研究的总体偏倚风险被评估为“存在一些担忧”。根据RoB 2.0工具,主要原因是:①未报告参与者的基线特征;②受试者未完全参与,导致部分结果数据缺失(图2)。 2.4 发表偏倚与证据等级质量评估 漏斗图显示对称分布,且Egger检验结果不显著(图3),表明此研究不存"
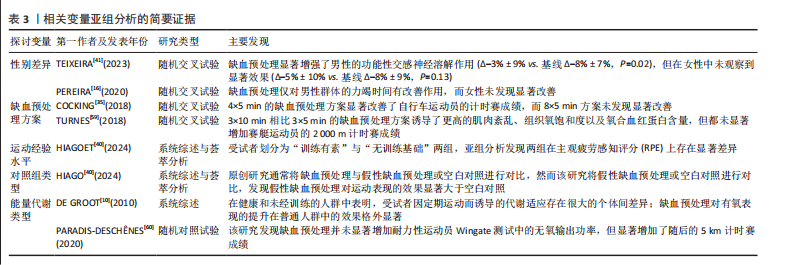
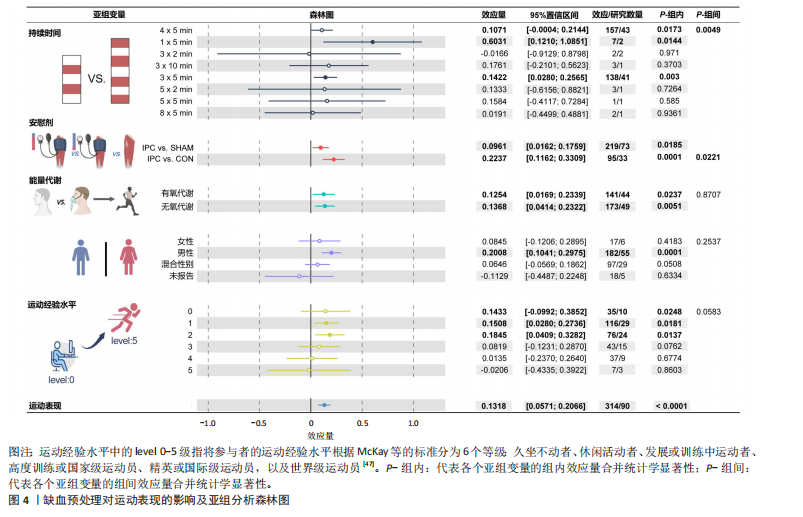
在发表偏倚风险。 鉴于不存在发表偏倚和较高异质性(图3),同时样本量为1 439(超过800),因此未进行降级。然而,偏倚风险被认为“存在一些担忧”,导致证据质量从高降至中。此外,观察到“间接性”不一致,参考组为假性缺血预处理和空白对照,因此进一步降级。最终,此研究的证据等级被降2级,最终评定为低(表4)。 2.5 缺血预处理对运动表现的效应量 纳入90篇文献(314项效应,1 439名受试者)荟萃分析发现(图4),缺血预处理结合运动能够显著提高运动表现但效果较小[ES=0.13,95%CI(0.06,0.21),P < 0.01,Q=427,I2-Level 2=0%,I2-Level 3=9.13%,I2-Level 4=5.74%,PI(-0.18,0.44)]。 2.6 亚组分析结果 2.6.1 能量代谢类型对缺血预处理的效果 不同能量代谢特点(无氧、有氧运动)不是缺血预处理的调节因素,组间差异在统计学上不显著(P=0.87)。组内分析无论是无氧运动[ES=0.14,95%CI(0.04,0.23),P < 0.01]还是有氧运动[ES=0.13,95%CI(0.02,0.23),P=0.01],缺血预处理都能显著提高运动表现。 2.6.2 对照组对缺血预处理效果的影响 研究发现,不同对照组(假性缺血预处理和空白对照)会显著影响缺血预处理的运动表现(P=0.02),缺血预处理相对于空白对照(ESCON=0.22,95%CI (0.12,0.33),P < 0.01)的效果提升显著大于假性缺血预处理[ESSHAM=0.10,95%CI (0.02,0.18),P < 0.01]。 2.6.3 缺血与再灌注持续时间对缺血预处理的影响 组间差异显示缺血与再灌注持续时间可能是影响缺血预处理的调节因素(P=0.049),其中1×5 min[ES=0.60,95%CI(0.12,1.09),P=0.01]的方案显著大于其余所有方案。组内分析发现,仅3×5 min [ES=0.14,95%CI (0.03,0.26),P < 0.01] 以及4×5 min[ES=0.11,95%CI(0.00,0.21),P=0.02]的方案在统计学上显著。"
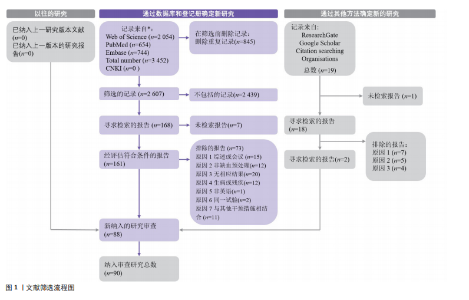
2.6.4 运动经验水平对缺血预处理的影响 组间差异显示运动经验水平不是缺血预处理的调节因素(P > 0.05)。组内分析显示,仅运动经验水平低(0-2级)受试者在统计学上显著,运动水平较高(3-5级)的受试者均不显著,其效果分别为:水平0[ES=0.14,95%CI (-0.10,0.39),P=0.03]、水平1[ES=0.15,95%CI(0.03,0.27),P=0.02]、水平2[ES=0.19,95%CI(0.04,0.33),P=0.01]。 2.6.5 性别对缺血预处理的影响 组间比较显示性别不是缺血预处理干预效果的显著调节因素(P=0.25)。组内分析表明,仅男性受试者在缺血预处理后表现提升达到统计显著性[ES=0.20,95%CI (0.10,0.30),P < 0.01],而女性组未表现出明显效应。 2.7 回归分析结果 年龄对缺血预处理提升运动表现、无氧表现以及有氧表现的影响较小,该影响在统计上均不显著(P > 0.05)。回归系数β分别为0.000 9、0.001 7和0.003 1。"
| [1] GIRARD O, AMANN M, AUGHEY R, et al. Position statement--altitude training for improving team-sport players’ performance: current knowledge and unresolved issues. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i8-16. [2] CARU M, LEVESQUE A, LALONDE F, et al. An overview of ischemic preconditioning in exercise performance: A systematic review. J Sport Health Sci. 2019;8(4): 355-369. [3] DAVIDS CJ, ROBERTS LA, BJØRNSEN T, et al. Where Does Blood Flow Restriction Fit in the Toolbox of Athletic Development? A Narrative Review of the Proposed Mechanisms and Potential Applications. Sports Med. 2023;53(11):2077-2093. [4] BLAZEVICH AJ, BABAULT N. Post-activation Potentiation Versus Post-activation Performance Enhancement in Humans: Historical Perspective, Underlying Mechanisms, and Current Issues. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1359. [5] CRISAFULLI A, TANGIANU F, TOCCO F, et al. Ischemic preconditioning of the muscle improves maximal exercise performance but not maximal oxygen uptake in humans. J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(2):530-536. [6] MURRY CE, JENNINGS RB, REIMER KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74(5):1124-1136. [7] MURRY CE, RICHARD VJ, REIMER KA, et al. Ischemic preconditioning slows energy metabolism and delays ultrastructural damage during a sustained ischemic episode. Circ Res. 1990;66(4):913-931. [8] REIMER KA, MURRY CE, JENNINGS RB. Cardiac adaptation to ischemia. Ischemic preconditioning increases myocardial tolerance to subsequent ischemic episodes. Circulation. 1990;82(6):2266-2268. [9] REIMER KA, MURRY CE, YAMASAWA I, et al. Four brief periods of myocardial ischemia cause no cumulative ATP loss or necrosis. Am J Physiol. 1986;251(6 Pt 2):H1306-1315. [10] DE GROOT PC, THIJSSEN DH, SANCHEZ M, et al. Ischemic preconditioning improves maximal performance in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;108(1):141-146. [11] FERREIRA TN, SABINO-CARVALHO JL, LOPES TR, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning and Repeated Sprint Swimming: A Placebo and Nocebo Study. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016;48(10):1967-1975. [12] MAROCOLO M, DA MOTA GR, PELEGRINI V, et al. Are the Beneficial Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Performance Partly a Placebo Effect? Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(10):822-825. [13] CARVALHO L, BARROSO R. Ischemic Preconditioning Improves Strength Endurance Performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(12):3332-3337. [14] DA SILVA NOVAES J, DA SILVA TELLES LG, MONTEIRO ER, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Improves Resistance Training Session Performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2021;35(11):2993-2998. [15] PETHICK J, CASSELTON C, WINTER SL, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Blunts Loss of Knee Extensor Torque Complexity with Fatigue. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2021; 53(2):306-315. [16] PEREIRA HM, DE LIMA FF, SILVA BM, et al. Sex differences in fatigability after ischemic preconditioning of non-exercising limbs. Biol Sex Differ. 2020;11(1):59. [17] BAILEY TG, BIRK GK, CABLE NT, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning prevents reduction in brachial artery flow-mediated dilation after strenuous exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;303(5):H533-538. [18] BAILEY TG, JONES H, GREGSON W, et al. Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Lactate Accumulation and Running Performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012; 44(11):2084-2089. [19] CHEUNG CP, SLYSZ JT, BURR JF. Ischemic Preconditioning: Improved Cycling Performance Despite Nocebo Expectation. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2020;15(3): 354-360. [20] CRUZ RS, DE AGUIAR RA, TURNES T, et al. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on maximal constant-load cycling performance. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015;119(9):961-967. [21] PAULL EJ, VAN GUILDER GP. Remote ischemic preconditioning increases accumulated oxygen deficit in middle-distance runners. J Appl Physiol. 2019;126(5):1193-1203. [22] 苏玉莹,李卫.远程缺血预处理对运动表现的影响及其生理机制研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2024,60(10):31-39. [23] GIBSON N, WHITE J, NEISH M, et al. Effect of ischemic preconditioning on land-based sprinting in team-sport athletes. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2013;8(6):671-676. [24] JEAN-ST-MICHEL E, MANLHIOT C, LI J, et al. Remote preconditioning improves maximal performance in highly trained athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(7):1280-1286. [25] WILLIAMS N, RUSSELL M, COOK CJ, et al. Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Maximal Swimming Performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2021;35(1):221-226. [26] RICHARD P, BILLAUT F. Time-Trial Performance in Elite Speed Skaters After Remote Ischemic Preconditioning. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2018;13(10): 1308-1316. [27] LINDNER TD, SCHOLTEN SD, HALVERSON JM, et al. The Acute Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Power and Sprint Performance. S D Med. 2021;74(5):210-219. [28] NIESPODZINSKI B, MIESZKOWSKI J, KOCHANOWICZ M, et al. Effect of 10 consecutive days of remote ischemic preconditioning on local neuromuscular performance. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2021;60:102584. [29] DE SOUZA HLR, ARRIEL RA, MOTA GR, et al. Does ischemic preconditioning really improve performance or it is just a placebo effect? PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0250572. [30] VALENZUELA PL, MARTÍN-CANDILEJO R, SÁNCHEZ-MARTÍNEZ G, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning and Muscle Force Capabilities. J Strength Cond Res. 2021; 35(8):2187-2192. [31] SLYSZ JT, BURR JF. Impact of 8 weeks of repeated ischemic preconditioning on running performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019;119(6):1431-1437. [32] SEEGER JPH, TIMMERS S, PLOEGMAKERS DJM, et al. Is delayed ischemic preconditioning as effective on running performance during a 5km time trial as acute IPC? J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20(2):208-212. [33] PARADIS-DESCHÊNES P, LAPOINTE J, JOANISSE DR, et al. Similar Recovery of Maximal Cycling Performance after Ischemic Preconditioning, Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation or Active Recovery in Endurance Athletes. J Sports Sci Med. 2020;19(4):761-771. [34] MIESZKOWSKI J, STANKIEWICZ B, KOCHANOWICZ A, et al. Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Marathon-Induced Changes in Serum Exerkine Levels and Inflammation. Front Physiol. 2020;11: 571220. [35] COCKING S, WILSON MG, NICHOLS D, et al. Is There an Optimal Ischemic-Preconditioning Dose to Improve Cycling Performance? Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2018;13(3):274-282. [36] BEHRENS M, ZSCHORLICH V, MITTLMEIER T, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Did Not Affect Central and Peripheral Factors of Performance Fatigability After Submaximal Isometric Exercise. Front Physiol. 2020; 11:371. [37] CLEVIDENCE MW, MOWERY RE, KUSHNICK MR. The effects of ischemic preconditioning on aerobic and anaerobic variables associated with submaximal cycling performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(10):3649-3654. [38] GOLDSMITH M, SIEGLER J, GREEN S. Targeted effect of ischemic preconditioning on the gas exchange threshold in healthy males and females. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024;124(9):2697-2706. [39] KAUR G, BINGER M, EVANS C, et al. No influence of ischemic preconditioning on running economy. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(2):225-235. [40] SOUZA HLR, OLIVEIRA GT, MEIRELES A, et al. Does ischemic preconditioning enhance sports performance more than placebo or no intervention? A systematic review with meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci. 2024;14:101010. [41] TEIXEIRA AL, GANGAT A, BOMMARITO JC, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Acutely Improves Functional Sympatholysis during Handgrip Exercise in Healthy Males but not Females. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2023;55(7):1250-1257. [42] PAGE MJ, MCKENZIE JE, BOSSUYT PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71. [43] STERNE JAC, SAVOVIĆ J, PAGE MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019; 366:l4898. [44] CUMPSTON M, LI T, PAGE MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;2019(10):ED000142. [45] GASTIN PB. Energy system interaction and relative contribution during maximal exercise. Sports Med Auckl NZ. 2001;31(10):725-741. [46] INCOGNITO AV, BURR JF, MILLAR PJ. The Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Human Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 2016;46(4):531-544. [47] MCKAY AKA, STELLINGWERFF T, SMITH ES, et al. Defining Training and Performance Caliber: A Participant Classification Framework. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2021;17(2):317-331. [48] SLYSZ JT, PETRICK HL, MARROW JP, et al. An examination of individual responses to ischemic preconditioning and the effect of repeated ischemic preconditioning on cycling performance. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(5):633-640. [49] HEDGES LV, OLKIN I. Statistical methods for meta-analysis. Pittsburgh:Academic Press. 2014. [50] VAN DEN NOORTGATE W, LÓPEZ-LÓPEZ JA, MARÍN-MARTÍNEZ F, et al. Three-level meta-analysis of dependent effect sizes. Behav Res Methods. 2013;45(2):576-594. [51] HEDGES LV, TIPTON E, JOHNSON MC. Robust variance estimation in meta-regression with dependent effect size estimates. Res Synth Methods. 2010;1(1):39-65. [52] CHEUNG MW. A Guide to Conducting a Meta-Analysis with Non-Independent Effect Sizes. Neuropsychol Rev. 2019;29(4):387-396. [53] FERNÁNDEZ-CASTILLA B, ALOE AM, DECLERCQ L, et al. Estimating outcome-specific effects in meta-analyses of multiple outcomes: A simulation study. Behav Res Methods. 2021;53(2):702-717. [54] JUKIC I, CASTILLA AP, RAMOS AG, et al. The Acute and Chronic Effects of Implementing Velocity Loss Thresholds During Resistance Training: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Critical Evaluation of the Literature. Sports Med. 2023;53(1): 177-214. [55] VEMBYE MH, JAMES EP. Power approximations for overall average effects in meta-analysis with dependent effect sizes. J Educ Behav Stat. 2023;48(1):70-102. [56] TIPTON E, PUSTEJOVSKY JE. Small-Sample Adjustments for Tests of Moderators and Model Fit Using Robust Variance Estimation in Meta-Regression. J Educ Behav Stat. 2015;40(6):604-634. [57] VIECHTBAUER W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw. 2010;36:1-48. [58] PUSTEJOVSKY JE, TIPTON E. Meta-analysis with Robust Variance Estimation: Expanding the Range of Working Models. Prev Sci. 2022;23(3):425-438. [59] TURNES T, DE AGUIAR RA, DE OLIVEIRA CRUZ RS, et al. Impact of ischaemia-reperfusion cycles during ischaemic preconditioning on 2000-m rowing ergometer performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(8):1599-1607. [60] PARADIS-DESCHÊNES P, JOANISSE DR, MAURIÈGE P, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Enhances Aerobic Adaptations to Sprint-Interval Training in Athletes Without Altering Systemic Hypoxic Signaling and Immune Function. Front Sports Act Living. 2020;2:41. [61] RICO-GONZÁLEZ M, PINO-ORTEGA J, CLEMENTE FM, et al. Guidelines for performing systematic reviews in sports science. Biol Sport. 2022;39(2):463-471. [62] PETERS JL, SUTTON AJ, JONES DR, et al. Contour-enhanced meta-analysis funnel plots help distinguish publication bias from other causes of asymmetry. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(10):991-996. [63] EGGER M, DAVEY SMITH G, SCHNEIDER M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315(7109):629-634. [64] SCHÜNEMANN HJ, HIGGINS JPT, VIST GE, et al. Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence//HIGGINS JPT, THOMAS J, CHANDLER J, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2019:375-402. [65] GUYATT G, OXMAN AD, AKL EA, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(4):383-394. [66] SANTESSO N, CARRASCO-LABRA A, LANGENDAM M, et al. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 3: detailed guidance for explanatory footnotes supports creating and understanding GRADE certainty in the evidence judgments. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016;74:28-39. [67] ALBUQUERQUE MR, FLÔR CAG, RIBEIRO AIS, et al. Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Sport-Specific Performance in Highly Trained Taekwondo Athletes. Sports (Basel). 2024;12(7):179. [68] TELLES LGDS, BILLAUT F, CUNHA G, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Improves Handgrip Strength and Functional Capacity in Active Elderly Women. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(11):6628. [69] ALLOIS R, PAGLIARO P, ROATTA S. Ischemic Conditioning to Reduce Fatigue in Isometric Skeletal Muscle Contraction. Biology (Basel). 2023;12(3):460. [70] BARBOSA TC, MACHADO AC, BRAZ ID, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning delays fatigue development during handgrip exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(3):356-364. [71] CARVALHO L, BARROSO R. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on the isometric test variables. Sci Sports. 2019;34(3): E225-E228. [72] CEYLAN B, FRANCHINI E. Ischemic preconditioning does not improve judo-specific performance but leads to better recovery in elite judo athletes. Sci Sports. 2022;37(4):322.e1-322.e7. [73] CEYLAN B, TAŞKIN HB, ŠIMENKO J. Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Acute Recovery in Elite Judo Athletes: A Randomized, Single-Blind, Crossover Trial. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2023;18(2):180-186. [74] CHENG CF, KUO YH, HSU WC, et al. Local and Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Improves Sprint Interval Exercise Performance in Team Sport Athletes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(20):10653. [75] CRUZ RS, DE AGUIAR RA, TURNES T, et al. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on short-duration cycling performance. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016;41(8):825-831. [76] CRUZ R, TRAMONTIN AF, OLIVEIRA AS, et al. Ischemic preconditioning increases spinal excitability and voluntary activation during maximal plantar flexion contractions in men. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2024;34(3):e14591. [77] DANTAS PAM, DA SILVA NOVAES J, PAZ CR, et al. Acute effect of Ischemic Preconditioning in different blood flow restriction compressions on the anaerobic performance of trained individuals. Nuevas Tend EN Educ Fis Deporte Recreacion. 2024;(54):721-727. [78] DE SANTANA VJ, DE OLIVEIRA DEANGELO CE, CURY SALEMI VM, et al. The Influence of Ischemic Preconditioning on Neuromuscular Performance. Rev Bras Med Esporte. 2021; 27(2):207-211. [79] GAO X, WANG A, FAN J, et al. The effect of ischemic preconditioning on repeated sprint cycling performance: a randomized crossover study. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2024;64(11):1147-1156. [80] GIBSON N, MAHONY B, TRACEY C, et al. Effect of ischemic preconditioning on repeated sprint ability in team sport athletes. J Sports Sci. 2015;33(11):1182-1188. [81] GRIFFIN PJ, HUGHES L, GISSANE C, et al. Effects of local versus remote ischemic preconditioning on repeated sprint running performance. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2019;59(2):187-194. [82] GUILHERME DA SILVA TELLES L, CRISTIANO CARELLI L, DUTRA BRÁZ I, et al. Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning as a Warm-Up on Leg Press and Bench Press Performance. J Hum Kinet. 2020;75:267-277. [83] HUANG BH, WANG TY, LU KH, et al. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on local hemodynamics and isokinetic muscular function. Isokinet Exerc Sci. 2020;28(1):73-81. [84] KATAOKA R, SONG JS, YAMADA Y, et al. The Impact of Different Ischemic Preconditioning Pressures on Pain Sensitivity and Resistance Exercise Performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2024;38(5):864-872. [85] KRAUS AS, PASHA EP, MACHIN DR, et al. Bilateral upper limb remote ischemic preconditioning improves peak anaerobic power. Open Sports Med J. 2015;9:1-6. [86] LIM AT, LIM J, GIRARD O, et al. Effect of ischemic preconditioning on badminton-specific endurance and subsequent changes in physical performance. Sci Sports. 2023; 38(1):102.e1-102.e7. [87] LISBÔA FD, TURNES T, CRUZ RS, et al. The time dependence of the effect of ischemic preconditioning on successive sprint swimming performance. J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20(5):507-511. [88] LOPES TR, SABINO-CARVALHO JL, FERREIRA THN, et al. Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on the Recovery of Cardiac Autonomic Control From Repeated Sprint Exercise. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1465. [89] MAROCOLO M, MAROCOLO IC, DA MOTA GR, et al. Beneficial Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning in Resistance Exercise Fade Over Time. Int J Sports Med. 2016; 37(10):819-824. [90] MAROCOLO M, WILLARDSON JM, MAROCOLO IC, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning and Placebo Intervention Improves Resistance Exercise Performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2016;30(5):1462-1469. [91] PAIXÃO RC, DA MOTA GR, MAROCOLO M. Acute effect of ischemic preconditioning is detrimental to anaerobic performance in cyclists. Int J Sports Med. 2014;35(11): 912-915. [92] PARADIS-DESCHÊNES P, JOANISSE DR, BILLAUT F. Ischemic preconditioning increases muscle perfusion, oxygen uptake, and force in strength-trained athletes. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016; 41(9):938-944. [93] PARADIS-DESCHÊNES P, JOANISSE DR, BILLAUT F. Sex-Specific Impact of Ischemic Preconditioning on Tissue Oxygenation and Maximal Concentric Force. Front Physiol. 2017;7:674. [94] PATTERSON SD, BEZODIS NE, GLAISTER M, et al. The Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Repeated Sprint Cycling Performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(8):1652-1658. [95] RODRIGUES AL, IDE BN, SASAKI JE, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Improves the Bench-Press Maximal Strength in Resistance-Trained Men. Int J Exerc Sci. 2023;16(4):217-229. [96] SALAGAS A, TSOUKOS A, TERZIS G, et al. Effectiveness of either short-duration ischemic pre-conditioning, single-set high-resistance exercise, or their combination in potentiating bench press exercise performance. Front Physiol. 2022;13: 1083299. [97] SLYSZ JT, BURR JF. Enhanced Metabolic Stress Augments Ischemic Preconditioning for Exercise Performance. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1621. [98] SUTTER EN, MATTLAGE AE, BLAND MD, et al. Remote Limb Ischemic Conditioning and Motor Learning: Evaluation of Factors Influencing Response in Older Adults. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(4):362-371. [99] TANAKA D, SUGA T, TANAKA T, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Enhances Muscle Endurance during Sustained Isometric Exercise. Int J Sports Med. 2016;37(8): 614-618. [100] TELLES LG, BILLAUT F, DE SOUZA RIBEIRO A, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning with High and Low Pressure Enhances Maximum Strength and Modulates Heart Rate Variability. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(13):7655. [101] THOMPSON KMA, WHINTON AK, FERTH S, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning: No Influence on Maximal Sprint Acceleration Performance. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2018;13(8):986-990. [102] VANGSOE MT, NIELSEN JK, PATON CD. A Comparison of Different Prerace Warm-Up Strategies on 1-km Cycling Time-Trial Performance. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2020;15(8):1109-1116. [103] CHRISTIANSEN D, OLSEN CBL, KEHLER F, et al. Active Relative to Passive Ischemic Preconditioning Enhances Intense Endurance Performance in Well-Trained Men. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2022; 17(6):979-990. [104] COCKING S, LANDMAN T, BENSON M, et al. The impact of remote ischemic preconditioning on cardiac biomarker and functional response to endurance exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017;27(10):1061-1069. [105] FOSTER GP, WESTERDAHL DE, FOSTER LA, et al. Ischemic preconditioning of the lower extremity attenuates the normal hypoxic increase in pulmonary artery systolic pressure. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011;179(2-3):248-253. [106] GRIFFIN PJ, FERGUSON RA, GISSANE C, et al. Ischemic preconditioning enhances critical power during a 3 minute all-out cycling test. J Sports Sci. 2018;36(9):1038-1043. [107] HALLEY SL, PEELING P, BROWN H, et al. Repeat Application of Ischemic Preconditioning Improves Maximal 1,000-m Kayak Ergometer Performance in a Simulated Competition Format. J Strength Cond Res. 2020. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003748. [108] HALLEY SL, MARSHALL P, SIEGLER JC. Effect of ischemic preconditioning and changing inspired O2 fractions on neuromuscular function during intense exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;127(6):1688-1697. [109] HITTINGER EA, MAHER JL, NASH MS, et al. Ischemic preconditioning does not improve peak exercise capacity at sea level or simulated high altitude in trained male cyclists. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2015;40(1):65-71. [110] JESSEN S, ZEUTHEN M, SOMMER JEPPESEN J, et al. Active ischemic pre-conditioning does not additively improve short-term high-intensity cycling performance when combined with caffeine ingestion in trained young men. Eur J Sport Sci. 2024;24(6):693-702. [111] KIDO K, SUGA T, TANAKA D, et al. Ischemic preconditioning accelerates muscle deoxygenation dynamics and enhances exercise endurance during the work-to-work test. Physiol Rep. 2015;3(5):e12395. [112] KIDO K, SUGA T, TANAKA D, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning accelerates systemic O2 dynamics and enhances endurance during work-to-work cycling exercise. Transl Sports Med. 2018;1(5):204-211. [113] KILDING AE, SEQUEIRA GM, WOOD MR. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on economy, VO2 kinetics and cycling performance in endurance athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(12):2541-2549. [114] KJELD T, RASMUSSEN MR, JATTU T, et al. Ischemic preconditioning of one forearm enhances static and dynamic apnea. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;46(1):151-155. [115] MACDOUGALL KB, MCCLEAN ZJ, MACINTOSH BR, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning, But Not Priming Exercise, Improves Exercise Performance in Trained Rock Climbers. J Strength Cond Res. 2023; 37(11):2149-2157. [116] MONTOYE AHK, MITCHINSON CJ, TOWNSEND OR, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Does Not Improve Time Trial Performance in Recreational Runners. Int J Exerc Sci. 2020;13(6):1402-1417. [117] MORLEY WN, MURRANT CL, BURR JF. Ergogenic effect of ischemic preconditioning is not directly conferred to isolated skeletal muscle via blood. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023; 123(8):1851-1861. [118] MOTA GR, RIGHTMIRE ZB, MARTIN JS, et al. Ischemic preconditioning has no effect on maximal arm cycling exercise in women. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020;120(2):369-380. [119] MUÑOZ-GÓMEZ E, MOLLÀ-CASANOVA S, SEMPERE-RUBIO N, et al. Potential Benefits of a Single Session of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning and Walking in Sedentary Older Adults: A Pilot Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(4):3515. [120] PANDORF Z, ERICKSON S, SCHOLTEN SD. Ischemic Preconditioning On Swimming Performance: An Exploration Into Practical Application. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2023; 55(9):377. [121] SABINO-CARVALHO JL, LOPES TR, OBEID-FREITAS T, et al. Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Endurance Performance Does Not Surpass Placebo. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017;49(1):124-132. [122] TANAKA D, SUGA T, KIDO K, et al. Acute remote ischemic preconditioning has no effect on quadriceps muscle endurance. Transl Sports Med. 2020;3(4):314-320. [123] TER BEEK F, JOKUMSEN PS, SLOTH BN, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Attenuates Rating of Perceived Exertion But Does Not Improve Maximal Oxygen Consumption or Maximal Power Output. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(9):2479-2485. [124] TOCCO F, MARONGIU E, GHIANI G, et al. Muscle ischemic preconditioning does not improve performance during self-paced exercise. Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(1):9-15. [125] TOMSCHI F, NIEMANN D, BLOCH W, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning Enhances Performance and Erythrocyte Deformability of Responders. Int J Sports Med. 2018; 39(8):596-603. [126] URBANSKI R, ASCHENBRENNER P, ZMIJEWSKI P, et al. Effect of Simultaneous Lower- and Upper-Body Ischemic Preconditioning on Lactate, Heart Rate, and Rowing Performance in Healthy Males and Females. Applied Sciences. 2024;14(9):3539. [127] WIGGINS CC, CONSTANTINI K, PARIS HL, et al. Ischemic Preconditioning, O2 Kinetics, and Performance in Normoxia and Hypoxia. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(5):900-911. [128] ZHONG Z, DONG H, WU Y, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning enhances aerobic performance by accelerating regional oxygenation and improving cardiac function during acute hypobaric hypoxia exposure. Front Physiol. 2022;13:950086. [129] 范紫菡,吴迎.缺血处理在运动训练中的应用:效果、机制及问题[J].中国运动医学杂志,2024,43(9):753-766. [130] CHEN Z, WU W, QIANG L, et al. The effect of ischemic preconditioning on physical fitness and performance: a meta-analysis in healthy adults. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2025;125(3):805-821. [131] 徐恺,殷明越,王然.中文体育类核心期刊元分析的选题和方法学问题[J].体育科学,2024,44(1):88-97. [132] PANG CY, YANG RZ, ZHONG A, et al. Acute ischaemic preconditioning protects against skeletal muscle infarction in the pig. Cardiovasc Res. 1995;29(6):782-788. [133] SCHULZ R, POST H, VAHLHAUS C, et al. Ischemic preconditioning in pigs: a graded phenomenon: its relation to adenosine and bradykinin. Circulation. 1998;98(10):1022-1029. [134] MAROCOLO M, HOHL R, ARRIEL RA, et al. Ischemic preconditioning and exercise performance: are the psychophysiological responses underestimated? Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023;123(4):683-693. [135] SANTOS CERQUEIRA M, KOVACS D, MARTINS DE FRANÇA I, et al. Effects of Individualized Ischemic Preconditioning on Protection Against Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sports Health. 2021; 13(6):554-564. [136] MARCORA SM, STAIANO W, MANNING V. Mental fatigue impairs physical performance in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009;106(3):857-864. [137] OKANO AH, FONTES EB, MONTENEGRO RA, et al. Brain stimulation modulates the autonomic nervous system, rating of perceived exertion and performance during maximal exercise. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(18):1213-1218. [138] MEIRELES A, SOUZA HLR, ARRIEL RA, et al. Attenuation of Neuromuscular Fatigue by Ischemic Preconditioning with Moderate Cuff Pressure is Not Related to Muscle Oxygen Saturation in Men. Int J Exerc Sci. 2023;16(2):1025-1037. [139] HERROD PJJ, LUND JN, PHILLIPS BE. Time-efficient physical activity interventions to reduce blood pressure in older adults: a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing. 2021;50(3):980-984. [140] ZHANG Y, KONG H, XU K, et al. Comment on “Does ischemic preconditioning enhance sports performance more than placebo or no intervention? A systematic review with meta-analysis”. J Sport Health Sci. 2025;14:101056. |
| [1] | Feng Qiang, Pi Yihua, Huang Huasheng, Huang Delun, Zhang Yan. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for myocardial infarction in rats: effects of acute and chronic exercises [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4868-4877. |
| [2] |
Fu Changxi, He Ruibo, Ma Gang, Zhu Zheng, Ma Wenchao.
Effect and mechanism of different training modes on skeletal muscle remodeling in rats with heart failure induced by myocardial infarction
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 221-230.
|
| [3] | Sun Yuma, Ma Wenchao, Fu Changxi. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor combined with high-intensity intermittent exercise preconditioning improved cardiac remodeling in rats with acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 4987-4994. |
| [4] | Xu Wenjie, Xie Xudong, He Ruibo, Ma Gang, Peng peng. Effect and mechanism of angiotensin (1-7) supplementation combined with exercise therapy on cardiac remodeling in rats with renal hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4137-4144. |
| [5] | Zhang Min, Lou Guo, Fu Changxi. Aerobic exercise preconditioning improves therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3988-3993. |
| [6] | Yang Mengxiao, Fu Changxi. Mechanism by which strength training improves bone injury in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3150-3156. |
| [7] | Liu Peng, Ma Gang, He Ruibo, Peng Peng. Effect of aerobic exercise on renal fibrosis in rats with chronic renal failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3209-3215. |
| [8] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [9] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [10] | Yuan Guoqiang, Qin Yongsheng, Peng Peng. High-intensity interval training for treating pathological cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3708-3715. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||