Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3331-3342.doi: 10.12307/2026.162
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics screening and experimental verification of core genes in chronic myeloid leukemia and imatinib resistance
Zhou Man1, 2, Long Meiting1, 2, Xin Guoyan1, Huang Mengjun1, 2, Yao Zhenglian1, 2, Zhao Huajuan1, 2, Shen Linqiang1, 2, Wu Xijun3, Yang Xiaoyan1, 2
- 1Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Pediatric Hematology, 3Department of Scientific Research, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-08-30Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-25 -
Contact:ang Xiaoyan, MD, Chief physician, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Pediatric Hematology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Co-corresponding author: Wu Xijun, MD, Associate chief technician, Department of Scientific Research, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhou Man, Master candidate, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Pediatric Hematology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province, No. 2k[2023]366 (to YXY); Guizhou Province Overseas Talents Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project, No. (2022)10 (to YXY); Key Laboratory Construction Task of Guizhou Medical University, No. [2024]004 (to YXY); Guiyang Municipal Science and Technology Plan Project, No. [2021]43-26 (to WXJ); Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Fund Project for 2024, No. gzwkj2024-131 (to WXJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Man, Long Meiting, Xin Guoyan, Huang Mengjun, Yao Zhenglian, Zhao Huajuan, Shen Linqiang, Wu Xijun, Yang Xiaoyan. Bioinformatics screening and experimental verification of core genes in chronic myeloid leukemia and imatinib resistance[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3331-3342.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
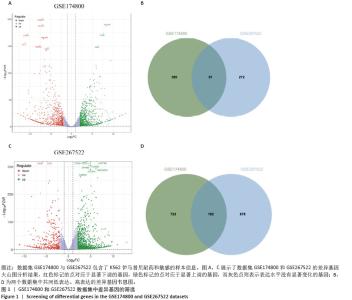
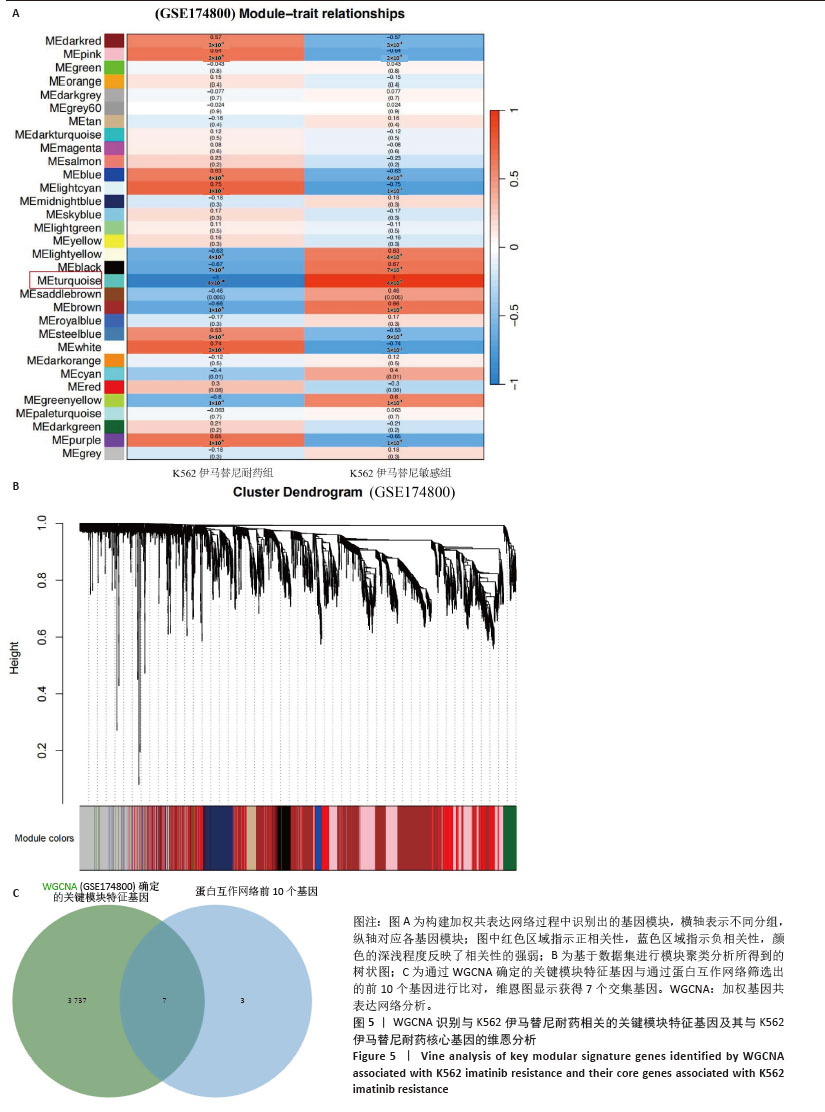
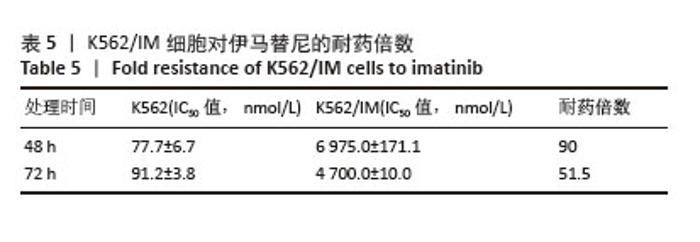
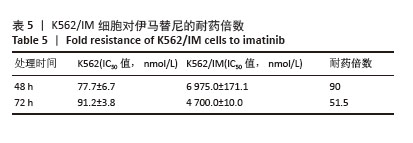
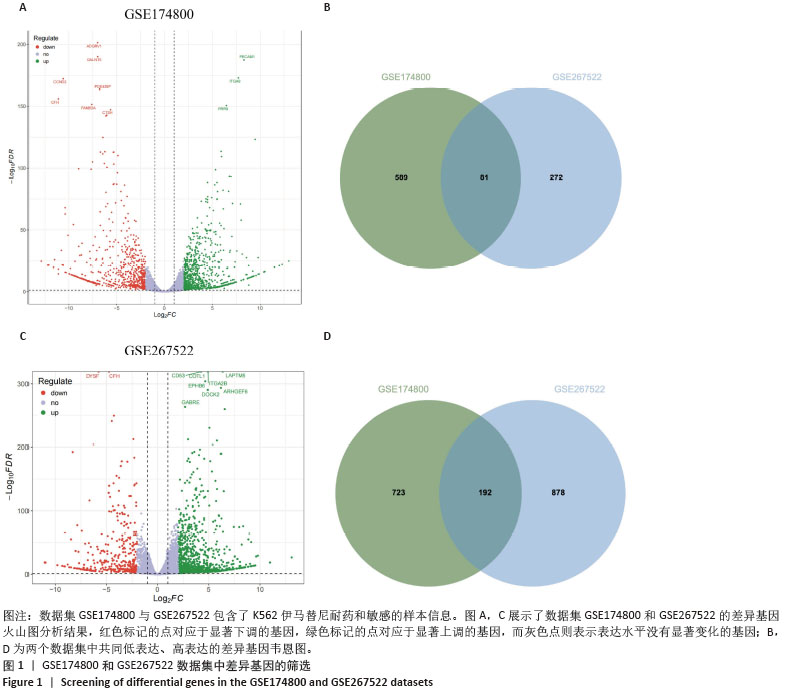
2.1 差异耐药基因的筛选 选取GSE267522和GSE174800基因表达数据集,两者各包含3例对伊马替尼耐药和3例对伊马替尼敏感的K562细胞样本。将伊马替尼敏感的K562细胞样本作为对照组,并依据校正后的P < 0.05且|log2FC|≥1的标准,从GSE174800数据集中鉴定出1 312个差异表达的基因,其中589个基因表达下调,723个基因表达上调。从GSE267522数据集中鉴定出1 150个差异表达的基因,其中272个基因表达下调,878个基因表达上调。然后,对两个数据集中低表达和高表达的基因进行维恩图分析,发现共有81个低表达基因和192个高表达基因,将这273个差异基因定义为伊马替尼耐药相关的基因(图1)。"
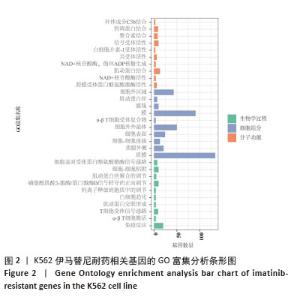
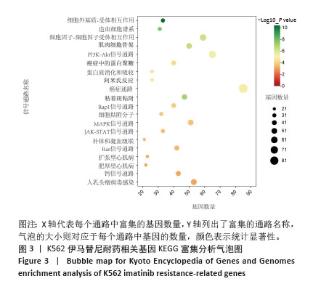
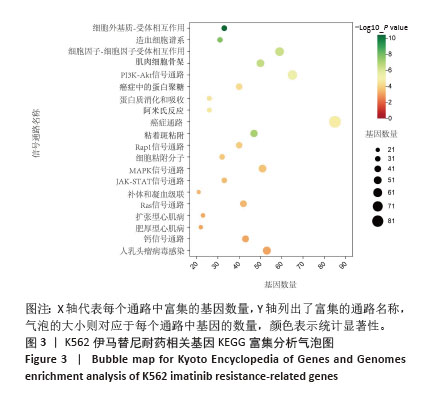
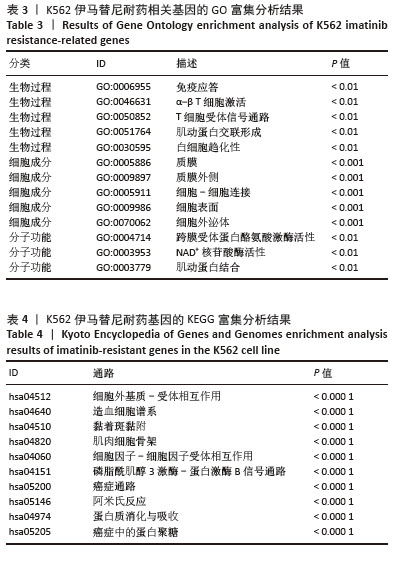
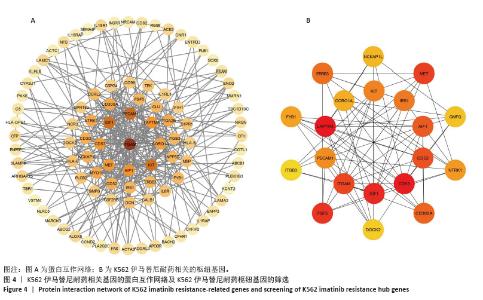
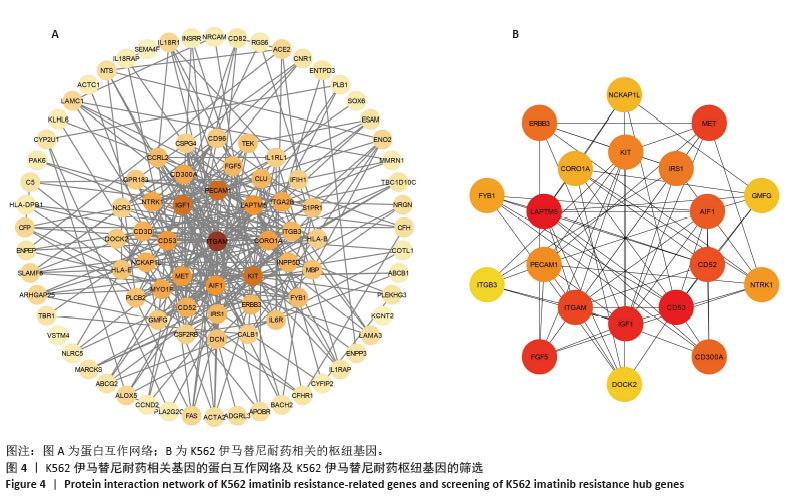
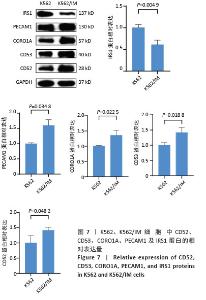
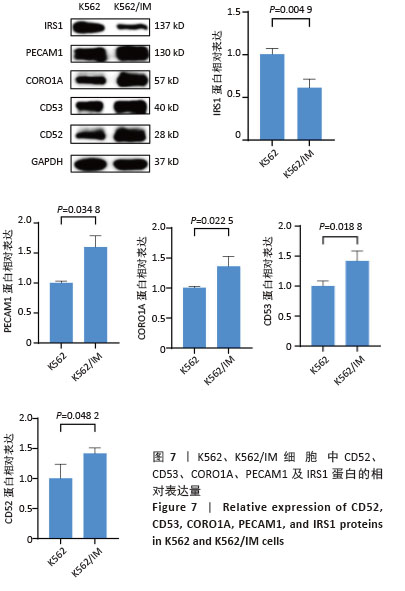
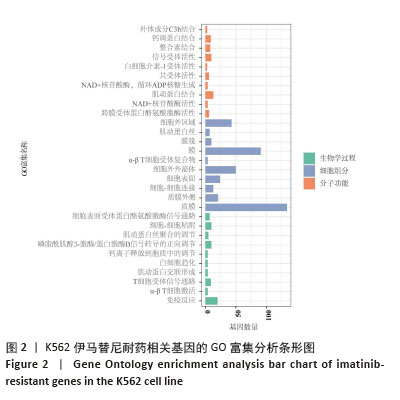
2.2 耐药相关基因的GO和KEGG功能富集分析 为了深入理解差异表达基因如何参与调节机体功能并影响信号通路,借助DAVID平台,对273个与伊马替尼耐药相关的差异基因开展功能富集分析,包括GO和KEGG分析。GO结果显示,K562伊马替尼耐药相关基因在生物学过程中主要参与细免疫反应、α-β T细胞激活、T细胞受体信号通路、肌动蛋白交联形成及白细胞趋化性等过程;细胞组分显示其主要存在于质膜、质膜外侧、细胞连接、细胞表面、细胞外泌体等;分子功能显示其在与跨膜受体蛋白,NAD+核苷酸酶活性、肌动蛋白结合中发挥作用(图2、表3)。 KEGG富集分析显示K562伊马替尼耐药相关基因在多个信号通路中显著富集,特别是细胞外基质-受体相互作用、造血细胞谱系、细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶-蛋白激酶B信号通路、癌症通路等(图3、表4)。"
| [1] CORTES J, PAVLOVSKY C, SAUßELE S. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2021;398(10314):1914-1926. [2] MINCIACCHI VR, KUMAR R, KRAUSE DS. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Model Disease of the Past, Present and Future. Cells. 2021;10(1):117. [3] L’ABBATE A, MORETTI V, PUNGOLINO E, et al. Occurrence of L1M Elements in Chromosomal Rearrangements Associated to Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Insights from Patient-Specific Breakpoints Characterization. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(7):1351. [4] BRAUN TP, EIDE CA, DRUKER BJ. Response and Resistance to BCR-ABL1-Targeted Therapies. Cancer Cell. 2020;37(4):530-542. [5] HADDAD FG, KANTARJIAN H. Navigating the Management of Chronic Phase CML in the Era of Generic BCR::ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2024;22(1):e237116. [6] DEREME J, SÉGOT A, FRIEDRICH N, et al. Recognizing and managing side effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Rev Med Suisse. 2023;19(850):2175-2181. [7] SRINIVASAN N, OLIVIER T, HASLAM A, et al. Imatinib remains the best frontline therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: Critical analysis of the ASC4FIRST trial. Am J Hematol. 2024;99(12):2392-2394. [8] LAGANÀ A, SCALZULLI E, BISEGNA ML, et al. Understanding and overcoming resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Expert Rev Hematol. 2025;18(1):65-79. [9] SUN J, HU R, HAN M, et al. Mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Biol Sci. 2024;20(1):175-181. [10] KAEHLER M, VON BUBNOFF N, CASCORBI I, et al. Molecular biomarkers of leukemia: convergence-based drug resistance mechanisms in chronic myeloid leukemia and myeloproliferative neoplasms. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1422565. [11] HASANOVA A, ASADOV C, SHIRINOVA A, et al. Role of genetic factors in imatinib resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia: P53, RB1, ASS1 gene deletions, and chromosome 8 hyperdiploidy. Pathol Res Pract. 2025;269:155943. [12] XU XL, CAO YJ, ZHANG W, et al. Research Status, Synthesis and Clinical Application of Recently Marketed and Clinical BCR-ABL Inhibitors. Curr Med Chem. 2022;29(17):3050-3078. [13] LAGANÀ A, SCALZULLI E, BISEGNA ML, et al. Treatment free remission (TFR) after second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (2G-TKIs) treatment in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): from feasibility to safety. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2024;23(8):969-979. [14] VELTMAAT L, CORTES J. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor for CML: all the same? Blood Adv. 2024;8(20):5339-5341. [15] LIPTON JH, CORTES JE. Bosutinib for the Treatment of CML-Using it Safely: a Podcast. Target Oncol. 2025;20(2):183-189. [16] GEORGE B, CHAN KH, RIOS A. Therapeutic options for chronic myeloid leukemia following the failure of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1446517. [17] YUDA J, DOKI N, MATSUOKA H, et al. Asciminib vs bosutinib in CML patients pretreated with ≥2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Results from the Japanese subgroup analysis of ASCEMBL study. Cancer Med. 2023;12(3):2990-2998. [18] JABBOUR E, KANTARJIAN H. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Review. JAMA. 2025;333(18):1618-1629. [19] MALKAN UY, HAZNEDAROGLU IC. Chronic myeloid leukemia, tyrosine kinase inhibitors and cardiovascular system. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023;27(12):5493-5506. [20] RÉA D. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for chronic myeloid leukemia. Rev Prat. 2023;73(10):1051-1055. [21] BAI J, FENG Z, CHEN Y, et al. Lycorine attenuated proliferation and induced apoptosis on imatinib-resistant K562 cell by inhibiting autophagy. Discov Oncol. 2024;15(1):217. [22] PETTINELLA F, MARIOTTI B, LATTANZI C, et al. Surface CD52, CD84, and PTGER2 mark mature PMN-MDSCs from cancer patients and G-CSF-treated donors. Cell Rep Med. 2024;5(2):101380. [23] KARNAN S, HANAMURA I, OTA A, et al. CD52 is a novel target for the treatment of FLT3-ITD-mutated myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):121. [24] AN N, BIAN K, LI C. Alemtuzumab for haematological malignancies. Ann Hematol. 2025;104(5):2593-2603. [25] FUHR V, HEIDENREICH S, SRIVASTAVA M, et al. CD52 and OXPHOS-potential targets in ibrutinib-treated mantle cell lymphoma. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):505. [26] OEHLER VG, WALTER RB, CUMMINGS C, et al. CD52 Expression In Leukemic Stem/Progenitor Cells. Blood. 2010;116(21):2743. [27] BALISE VD, SAITO-REIS CA, GILLETTE JM. Tetraspanin Scaffold Proteins Function as Key Regulators of Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:598. [28] DUNLOCK VE. Tetraspanin CD53: an overlooked regulator of immune cell function. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2020;209(4):545-552. [29] GREENBERG ZJ, PARACATU LC, MONLISH DA, et al. The tetraspanin CD53 protects stressed hematopoietic stem cells via promotion of DREAM complex-mediated quiescence. Blood. 2023;141(10):1180-1193. [30] DUNLOCK VE, ARP AB, SINGH SP, et al. Tetraspanin CD53 controls T cell immunity through regulation of CD45RO stability, mobility, and function. Cell Rep. 2022;39(13):111006. [31] KARABACZ N, CABEZAS-WALLSCHEID N. CD53 sends HSCs to sweet DREAMs. Blood. 2023;141(10):1100-1101. [32] HE Y, DING J, LIU L, et al. Investigation of TSRP reverses imatinib resistance through the PI3K / Akt pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2024;103(12):5285-5296. [33] QIU Q, SUN Y, YANG L, et al. TSPAN32 suppresses chronic myeloid leukemia pathogenesis and progression by stabilizing PTEN. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):90. [34] AFIFY SM, OO AKK, HASSAN G, et al. How can we turn the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway down? Insights into inhibition and treatment of cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2021;21(6):605-619. [35] FILIK Y, BAUER K, PETER B, et al. Deciphering the Mechanisms of Osteoblast-Induced Resistance of Leukemic Stem Cell (LSC) in Ph+ CML: Role of PI3-Kinase, BRD4 and MYC and Development of Strategies to Overcome Osteoblast-Induced Resistance. Blood. 2021; 138(Supplement 1):1481-1482. [36] GU WJ, LIU XX, SHEN YW, et al. TRIM4 enhances small-molecule-induced neddylated-degradation of CORO1A for triple negative breast cancer therapy. Theranostics. 2024;14(18):7023-7041. [37] KROS JM, ZENEYEDPOUR L, PEDROSA RMSM, et al. T cell induced expression of Coronin-1A facilitates blood-brain barrier transmigration of breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):31516. [38] STOCKER TJ, PIRCHER J, SKENDERI A, et al. The Actin Regulator Coronin-1A Modulates Platelet Shape Change and Consolidates Arterial Thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118(12):2098-2111. [39] SIEGMUND K, THUILLE N, POSCH N, et al. Novel protein kinase C θ: coronin 1A complex in T lymphocytes. Cell Commun Signal. 2015; 13:22. [40] GAUR P, SAINI S, RAY K, et al. Temporal transcriptome analysis suggest modulation of multiple pathways and gene network involved in cell-cell interaction during early phase of high altitude exposure. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0238117. [41] PAMUK GE, CHOW ECY, IONAN AC, et al. FDA Approval Summary: Asciminib for Ph+ CML in Chronic Phase Treated with Two or More Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and for the T315I Mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2024;30(19):4266-4271. [42] DWYER AR, TRUONG TH, KERKVLIET CP, et al. Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) mediates progesterone receptor-driven stemness and endocrine resistance in oestrogen receptor+ breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2021;124(1):217-227. [43] LEI Y, JAMAL M, ZENG X, et al. Insulin receptor substrate 1(IRS1) is related with lymph node metastases and prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gene. 2022;835:146651. [44] POUDEL G, TOLLAND MG, HUGHES TP, et al. Mechanisms of Resistance and Implications for Treatment Strategies in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(14):3300. [45] VOCKOVA P, MOLINSKY J, KLANOVA M, et al. CD31/PECAM-1 impacts engraftment, growth and spread of mantle cell lymphoma cells and positively correlates with extramedullary involvement. Leuk Lymphoma. 2021;62(4):861-867. [46] LERTKIATMONGKOL P, LIAO D, MEI H, et al. Endothelial functions of platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31). Curr Opin Hematol. 2016;23(3):253-259. [47] YAN Y, SUN D, HU J, et al. Multi-omic profiling highlights factors associated with resistance to immuno-chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet. 2025;57(1):126-139. |
| [1] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [2] | Lai Jiaming, , Song Yuling, Chen Zixi, Wei Jinghuan, Cai Hao, , Li Guoquan, . Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1450-1463. |
| [3] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [4] | Liu Kexin, , Hao Kaimin, Zhuang Wenyue, , Li Zhengyi. Autophagy-related gene expression in pulmonary fibrosis models: bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1129-1138. |
| [5] | Hu Xiaoyong, Song Qianhua, Yang Zhaoying, Tang Rui, Li Hongjian. Potential mechanism by which iroquois homeobox 3 regulates the browning of perivascular adipose tissue in vascular injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5671-5681. |
| [6] | Li Wenhui, Fan Weijing, Liu Guobin. Impact of Zi-Zhu ointment on the miRNA expression profile in mouse models of diabetic ulcers: a high-throughput sequencing analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4337-4346. |
| [7] | Lu Liwei, Huang Keqi, Chen Yueping, Zhuo Yinghong, Zhu Naihui, Wei Peng. Bioinformatics-based analysis of shared genes and associations in immune mechanisms between rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4253-4264. |
| [8] | Tian Minghao, Liao Yehui, Zhou Wenyang, He Baoqiang, Leng Yebo, Xu Shicai, Zhou Jiajun, Li Yang, Tang Chao, Tang Qiang, Zhong Dejun . Neuroprotective regulation of the IRF9 gene after spinal cord injury: bioinformatics analysis combined with experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2712-2726. |
| [9] | Qi Xiang, Cao Shan, Chen Jian, Zhang Yijia, Liu Keke, Xu Zifu, Liu Wang, Fu Xiaoxiao, Yin Xiaolei. Screening of genes related to mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis in atherosclerosis and target prediction of regulatory traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2641-2652. |
| [10] | Xue Hui, Li Dongnan, Zhao Yadi, Chen Chao, Xie Zongyuan. Relationship between BCR/ABL gene expression and recurrence before and after allogeneic transplantation in Ph chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 139-144. |
| [11] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [12] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [13] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [14] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||