Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3308-3320.doi: 10.12307/2026.153
Previous Articles Next Articles
Anti-inflammatory activity and mechanism of Lonicera japonica Thunb.-derived extracellular vesicle-like particles
Chen Yuanjun, Lin Sixing, Ji Lichun, Li Dongxiao, Liao Guangzhi, Lin Xingdong
- The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-09-22Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-25 -
Contact:Lin Xingdong, MS, Chief physician, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Yuanjun, MS, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:2022 Guangdong Provincial Colleges and Universities Key Field Special Project (Biomedicine and Health), No. 2022ZDZX2013 (to LXD); Major Scientific and Technological Project (Innovation Project) of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Guangzhou in 2025, No. 2025CX011 (to LXD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Yuanjun, Lin Sixing, Ji Lichun, Li Dongxiao, Liao Guangzhi, Lin Xingdong. Anti-inflammatory activity and mechanism of Lonicera japonica Thunb.-derived extracellular vesicle-like particles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3308-3320.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
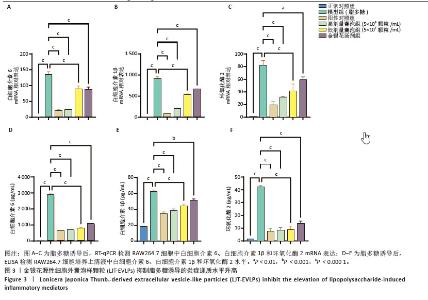
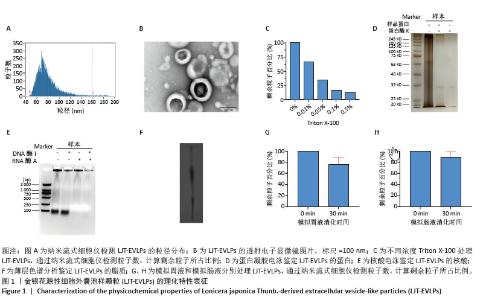
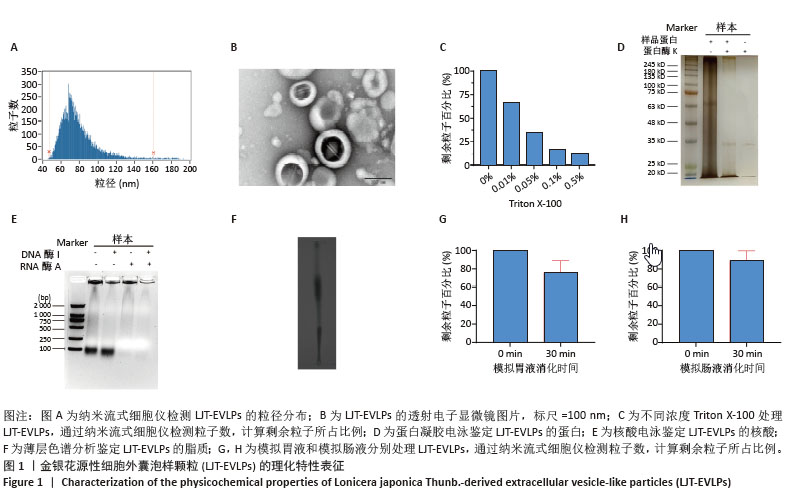
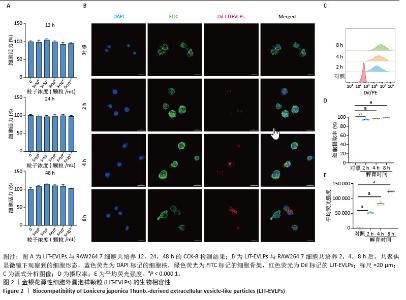
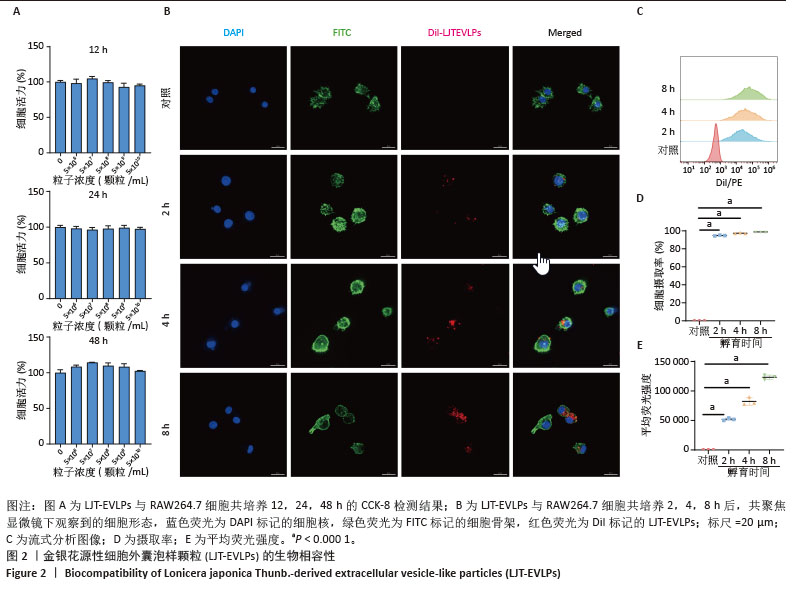
2.3 金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒的体外抗炎活性 RT-qPCR和ELISA分析显示,与正常对照组相比,模型组白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和环氧化酶2的mRNA表达和细胞上清中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和环氧化酶2水平显著升高(P < 0.000 1)。与模型组相比,金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒组白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和环氧化酶2的mRNA表达和细胞上清中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和环氧化酶2水平显著降低,且表现出浓度依赖性(P < 0.000 1)。 此外,阳性对照组和金银花汤剂组同样显著降低了这些炎症递质的表达,且阳性对照组优于金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒组,而金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒组优于金银花汤剂组。见图3。"
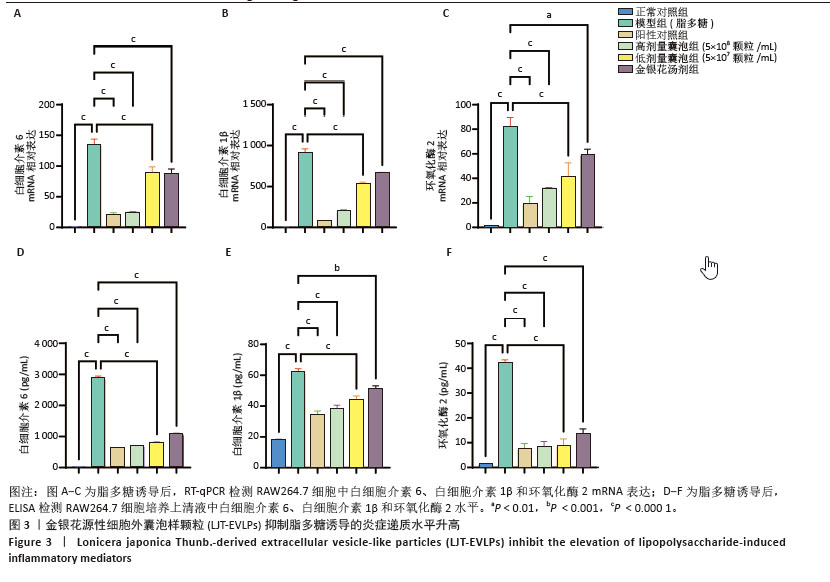
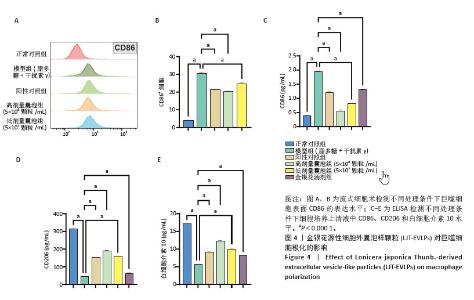
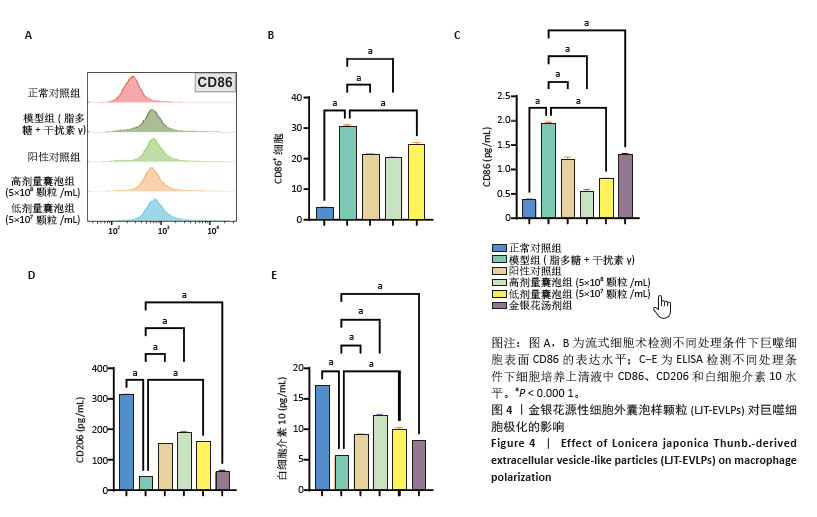
2.4 金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒对巨噬细胞极化的影响 流式细胞术结果显示,与正常对照组相比,脂多糖和干扰素γ诱导后,巨噬细胞CD86表达显著增强,表明细胞向M1型极化。与模型组相比,金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒和地塞米松均显著降低了CD86+细胞率(P < 0.000 1),且高浓度金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒的抑制效果与地塞米松相当。ELISA检测显示,与正常对照组相比,模型组CD86水平显著升高,而CD206和白细胞介素10水平显著降低(P < 0.000 1)。与模型组相比,不同浓度的金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒组、阳性对照组和金银花汤剂组均能显著抑制CD86的升高(P < 0.000 1),并显著提高CD206和白细胞介素10水平,其中高剂量金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒组优于其他两组。见图4。"
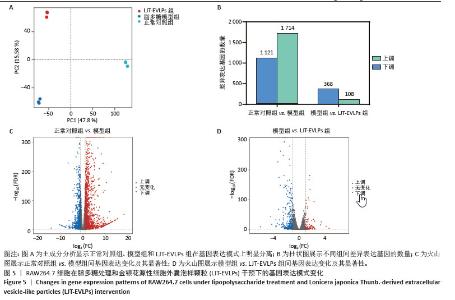
2.5 转录组学分析金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒的抗炎机制 转录组学分析揭示了金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒对脂多糖诱导炎症反应的调节机制。主成分分析结果显示,正常对照组、模型组和囊泡组在基因表达模式上明显分离。与正常对照组相比,模型组的RAW264.7细胞基因表达发生显著变化,共鉴定出2 835个差异基因,其中1 714个上调,1 121个下调。金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒干预后,囊泡组细胞基因表达出现逆转,与模型组相比,共鉴定出476个差异基因,其中108个上调,368个下调,表明金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒对脂多糖诱导的炎症反应具有显著的调节作用。差异火山图进一步展示了这些基因的表达变化。见图5。"
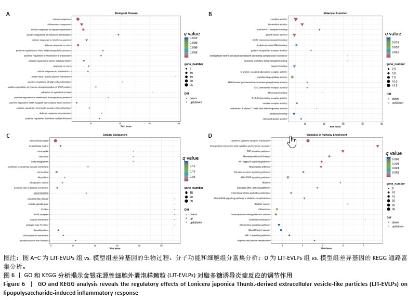
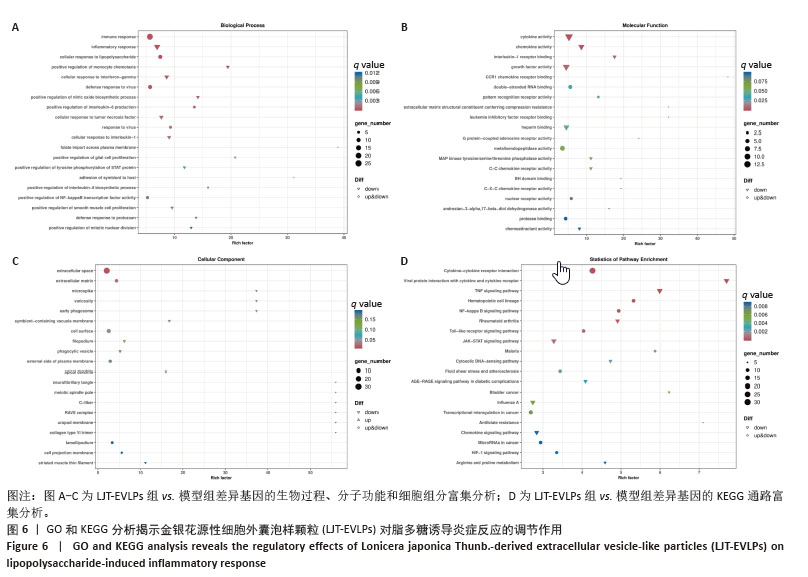
GO分析显示差异基因在免疫反应、炎症反应和对脂多糖的细胞反应等生物过程中富集,整体下调,提示金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒抑制脂多糖诱导的炎症反应。在分子功能层面,差异基因在细胞因子活性和趋化因子活性中富集,其下调表明金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒通过调节这些分子活性减轻炎症。此外,差异基因在丝状伪足和吞噬小泡中富集,可能与细胞运动性和吞噬作用有关。为了进一步探讨金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒的抗炎机制,采用KEGG分析差异基因显著富集的通路。结果显示,差异基因显著富集于肿瘤坏死因子、核因子κB和Toll样受体信号通路,这些通路在炎症反应中起关键作用,提示金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒可能通过调节这些通路减轻脂多糖诱导的炎症反应。见图6。"
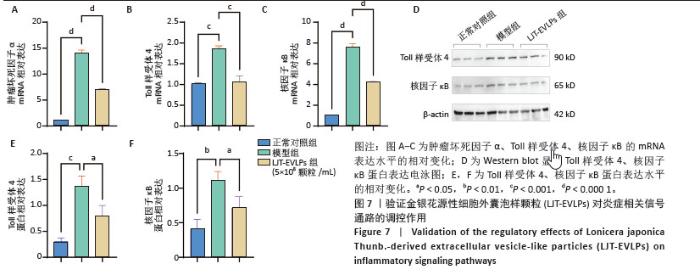
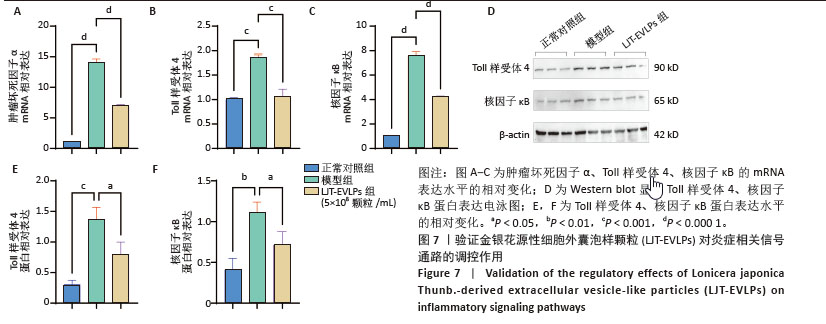
为了深入探究金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒对相关信号通路的调控作用,采用RT-qPCR和Western blot实验进行验证。结果显示,与正常对照组相比,模型组显著上调了肿瘤坏死因子α、Toll样受体4和核因子κB的mRNA表达水平(P < 0.000 1);与模型组相比,囊泡组显著抑制了这些因子的mRNA上调(P < 0.001)。Western blot实验进一步证实,与对照组相比,模型组中Toll样受体4和核因子κB蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.001和P < 0.01);而囊泡组相较模型组显著降低了这两种蛋白的表达(P < 0.05)。这些结果表明,金银花源性细胞外囊泡样颗粒可能通过下调核因子κB信号通路和Toll样受体信号通路相关蛋白的表达,进而有效减轻细胞内的炎症反应。见图7。"
| [1] SEMENZA GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and cardiovascular disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 2014;76:39-56. [2] LIN A, MIANO JM, FISHER EA, et al. Chronic inflammation and vascular cell plasticity in atherosclerosis. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024;3(12):1408-1423. [3] YAN Y, LI S, LIU Y, et al. Temporal relationship between inflammation and insulin resistance and their joint effect on hyperglycemia: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):109. [4] COHEN J, MATHEW A, DOURVETAKIS KD, et al. Recent Research Trends in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells. 2024;13(6):511. [5] HAJISHENGALLIS G, NETEA MG, CHAVAKIS T. Trained immunity in chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025; 25(7):497-514. [6] SONG H, XIA M, ZHAO P, et al. Overexpression of TGFBR3 Aggravates Cognitive Impairment and Neuroinflammation by Promoting Microglia M1 Polarization in the APP/PS1 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2025;62(6):7706-7722. [7] SALIS Z, SAINSBURY A. Association of long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with knee osteoarthritis: a prospective multi-cohort study over 4-to-5 years. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):6593. [8] CHO JH, SUH S. Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperglycemia: A Neglected Problem. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024;39(2):222-238. [9] CHI CC, WANG SH. Efficacy and cost-efficacy of biologic therapies for moderate to severe psoriasis: a meta-analysis and cost-efficacy analysis using the intention-to-treat principle. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:862851. [10] DAI C, LIU Y, LV F, et al. An alternative approach to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria: new insights into traditional Chinese medicine monomers combined with antibiotics. Adv Biotechnol (Singap). 2025; 3(1):6. [11] SHI Z, WANG Q, JIA F, et al. Pharmacological and toxicological effects of Jiangfangbaoxin and determination of its components in the blood of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):4934. [12] 宋亚玲,王红梅,倪付勇,等.金银花中酚酸类成分及其抗炎活性研究[J].中草药,2015,46(4):490-495. [13] 雷玲,李兴平,白筱璐,等.金银花抗内毒素、解热、抗炎作用研究[J].中药药理与临床,2012,28(1):115-117. [14] 李康宁,宋志领,贾利龙,等.金银花提取物对LPS诱导的急性前部葡萄膜炎小鼠的抗炎作用及其机制 [J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2021,47(4):978-983. [15] HUANG J, XIE M, HE L, et al. Chlorogenic acid: a review on its mechanisms of anti-inflammation, disease treatment, and related delivery systems. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1218015. [16] MUKKAVILLI R, YANG C, SINGH TANWAR R, et al. Absorption, Metabolic Stability, and Pharmacokinetics of Ginger Phytochemicals. Molecules. 2017;22(4):553. [17] 李坤艳.含绿原酸的清热解毒类中药注射剂不良反应及其机理探讨[J].中国卫生产业,2014,11(8):87-88. [18] ZHAO Q, WANG T, WANG H, et al. Consensus statement on research and application of Chinese herbal medicine derived extracellular vesicles-like particles (2023 edition). Chin Herb Med. 2023;16(1):3-12. [19] MU N, LI J, ZENG L, et al. Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18: 4987-5009. [20] WANG X, XIN C, ZHOU Y, et al. Plant-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles: The Next-Generation Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(5):588. [21] MENG Y, GAO J, HUANG X, et al. Molecular Trojan Based on Membrane-Mimicking Conjugated Electrolyte for Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release. Adv Mater. 2025;37(12):e2415705. [22] 王若宁,张迎洁,王笑红,等.不同来源细胞外囊泡在中药组分高效递送领域中应用的研究进展[J].中草药,2023,54(14):4672-4681. [23] 吕品,李晓天.基于体外试验和网络药理学研究金银花抗炎抗菌活性及分子机制[J].中国现代应用药学,2021,38(14):1678-1685. [24] KUMAR P, GOEL A, DASH B, et al. Innovations in Drug Delivery Systems for Biologics: Enhancing Stability and Targeted Delivery for Next-Generation Therapeutics. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2025;41:e20250001. [25] MOHITE P, SULE S, PAWAR A, et al. Development and characterization of a self-nano emulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for Ornidazole to improve solubility and oral bioavailability of BCS class II drugs. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):27724. [26] PEINKOFER G, MAASS M, PFANNKUCHE K, et al. Persistence of intramyocardially transplanted murine induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes from different developmental stages. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):46. [27] HUNTER AC. Molecular hurdles in polyfectin design and mechanistic background to polycation induced cytotoxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58(14):1523-1531. [28] MOGHIMI SM, SYMONDS P, MURRAY JC, et al. A two-stage poly(ethylenimine)-mediated cytotoxicity: implications for gene transfer/therapy. Mol Ther. 2005;11(6):990-995. [29] WANG Y, WANG Z, XIE K, et al. High-Efficiency Cellular Reprogramming by Nanoscale Puncturing. Nano Lett. 2020;20(7):5473-5481. [30] BOKKA R, RAMOS AP, FIUME I, et al. Biomanufacturing of Tomato-Derived Nanovesicles. Foods. 2020;9(12):1852. [31] BRUNO SP, PAOLINI A, D’ORIA V, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Citrus sinensis Modulate Inflammatory Genes and Tight Junctions in a Human Model of Intestinal Epithelium. Front Nutr. 2021;8:778998. [32] POCSFALVI G, TURIÁK L, AMBROSONE A, et al. Protein biocargo of citrus fruit-derived vesicles reveals heterogeneous transport and extracellular vesicle populations. J Plant Physiol. 2018;229:111-121. [33] JU S, MU J, DOKLAND T, et al. Grape exosome-like nanoparticles induce intestinal stem cells and protect mice from DSS-induced colitis. Mol Ther. 2013;21(7):1345-1357. [34] XIAO Q, ZHAO W, WU C, et al. Lemon-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Nanodrugs Enable to Efficiently Overcome Cancer Multidrug Resistance by Endocytosis-Triggered Energy Dissipation and Energy Production Reduction. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(20):e2105274. [35] ZHANG Z, YU Y, ZHU G, et al. The Emerging Role of Plant-Derived Exosomes-Like Nanoparticles in Immune Regulation and Periodontitis Treatment. Front Immunol. 2022;13:896745. [36] CUI Y, GAO J, HE Y, et al. Plant extracellular vesicles. Protoplasma. 2020;257(1):3-12. [37] FENG J, XIU Q, HUANG Y, et al. Plant-Derived Vesicle-Like Nanoparticles as Promising Biotherapeutic Tools: Present and Future. Adv Mater. 2023;35(24):e2207826. [38] CONG M, TAN S, LI S, et al. Technology insight: Plant-derived vesicles-How far from the clinical biotherapeutics and therapeutic drug carriers? Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;182:114108. [39] DAD HA, GU TW, ZHU AQ, et al. Plant Exosome-like Nanovesicles: Emerging Therapeutics and Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms. Mol Ther. 2021;29(1):13-31. [40] PINEDO M, DE LA CANAL L, DE MARCOS LOUSA C. A call for Rigor and standardization in plant extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(6):e12048. [41] ZHANG M, VIENNOIS E, PRASAD M, et al. Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials. 2016;101:321-340. [42] ZHUANG X, DENG ZB, MU J, et al. Ginger-derived nanoparticles protect against alcohol-induced liver damage. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:28713. [43] LIU C, YAN X, ZHANG Y, et al. Oral administration of turmeric-derived exosome-like nanovesicles with anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving bioactions for murine colitis therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):206. [44] GAO C, ZHOU Y, CHEN Z, et al. Turmeric-derived nanovesicles as novel nanobiologics for targeted therapy of ulcerative colitis. Theranostics. 2022;12(12):5596-5614. [45] ZHENG S, LIU S, HOU A, et al. Systematic review of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos: A significant food and traditional Chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1013992. [46] MA P, YUAN L, JIA S, et al. Lonicerae Japonicae Flos with the homology of medicine and food: a review of active ingredients, anticancer mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, quality control, toxicity and applications. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1446328. [47] KWEON B, OH J, LIM Y, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Honeysuckle Leaf Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation on BV2 Microglia. Nutrients. 2024;16(22):3954. [48] CHAI M, GAO B, WANG S, et al. Leveraging plant-derived nanovesicles for advanced nucleic acid-based gene therapy. Theranostics. 2025; 15(1):324-339. [49] YOU JY, KANG SJ, RHEE WJ. Isolation of cabbage exosome-like nanovesicles and investigation of their biological activities in human cells. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4321-4332. [50] MAJUMDER J, TARATULA O, MINKO T. Nanocarrier-based systems for targeted and site specific therapeutic delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;144:57-77. |
| [1] | Cao Yong, Teng Hongliang, Tai Pengfei, Li Junda, Zhu Tengqi, Li Zhaojin. Interactions between cytokines and satellite cells in muscle regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [2] | Song Puzhen, Ma Hebin, Chen Hongguang, Zhang Yadong. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes combined with transforming growth factor beta 1 on macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1616-1623. |
| [3] | Cai Ziming, Yu Qinghe, Ma Pengfei, Zhang Xin, Zhou Longqian, Zhang Chongyang, Lin Wenping. Heme oxygenase-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1624-1631. |
| [4] | He Jiale, Huang Xi, Dong Hongfei, Chen Lang, Zhong Fangyu, Li Xianhui. Acellular dermal matrix combined with adipose-derived stem cell exosomes promotes burn wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1699-1710. |
| [5] | Xia Linfeng, Wang Lu, Long Qianfa, Tang Rongwu, Luo Haodong, Tang Yi, Zhong Jun, Liu Yang. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate blood-brain barrier damage in mice with septic encephalopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1711-1719. |
| [6] | Cui Lianxu, Li Haomin, Xu Junrong, Tan Baodong, Lu Dahong, Peng Siwei, Wang Jinhui. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium on tissue repair after traumatic craniocerebral injury in miniature pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1730-1735. |
| [7] | Hou Chaowen, Li Zhaojin, Kong Jianda, Zhang Shuli. Main physiological changes in skeletal muscle aging and the multimechanism regulatory role of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [8] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [9] | Zhang Di, Zhao Jun, Ma Guangyue, Sun Hui, Jiang Rong. Mechanism of depression-like behavior in chronic social defeat stress mice based on high-throughput sequencing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1139-1146. |
| [10] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [11] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [12] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [13] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [14] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [15] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||